Documenti di Didattica
Documenti di Professioni
Documenti di Cultura
Common Trigonometric Angle Measurements
Caricato da
ahmed mahamedCopyright
Formati disponibili
Condividi questo documento
Condividi o incorpora il documento
Hai trovato utile questo documento?
Questo contenuto è inappropriato?
Segnala questo documentoCopyright:
Formati disponibili
Common Trigonometric Angle Measurements
Caricato da
ahmed mahamedCopyright:
Formati disponibili
Common Trigonometric Angle Measurements
sin = cos = tan = csc = sec = cot =
Hypotenuse =
Angle in Degrees 0 30 45 60 90 120 135 150 180 210 225 240 270 300 315 330 360
Angle in Radians 0 2 3 5 7 5 4 3 5 7 11 2
6 4 3 2 3 4 6 6 4 3 2 3 4 6
SIN 0 1 2 3 1 3 2 1 0 -1 -2 -3 -1 -3 -2 -1 0
2 2 2 2 2 2 2 2 2 2 2 2
COS 1 3 2 1 0 -1 -2 -3 -1 -3 -2 -1 0 1 2 3 1
2 2 2 2 2 2 2 2 2 2 2 2
TAN 0 3 1 3 ND -3 -1 -3 0 3 1 3 ND -3 -1 -3 0
3 3 3 3
CSC ND 2 2 23 1 23 2 2 ND -2 -2 -23 -1 -23 -2 -2 ND
3 3 3 3
SEC 1 23 2 2 ND -2 -2 -23 -1 -23 -2 -2 ND 2 2 23 1
3 3 3 3
COT ND 3 1 3 0 -3 -1 -3 ND 3 1 3 0 -3 -1 -3 ND
3 3 3 3
Common Trigonometric Angle Measurements
Provided by Tutoring Services 1 Reviewed July 2008
Angles Q1 Q2 Q3 Q4 Reference Angles
sin and csc + + - -
If.. 0 90 then.. =
tan and cot + - + -
90 < 180 = 180 -
cos and sec + - - + 180 < 270 = - 180
270 < 360 = 360 -
To convert from Radians to
Degrees When using the unit circle:
Multiply by
Start at 0 and then.
To convert from Degrees to
Radians. Positive angles move
counter clockwise.
Multiply by
Negative angles move
clockwise.
Provided by Tutoring Services 2 Common Trigonometric Angle Measurements
Fundamental Identities
tan = cot = csc = sec = cot =
sin2 + cos2 = 1 1 + tan2 = sec2 1 + cot2 = csc2
Sum and Difference Identities
cos ( ) = cos cos + sin sin tan ( ) =
cos ( + ) = cos cos sin sin
sin ( ) = sin cos cos sin tan ( + ) =
sin ( + ) = sin cos + cos sin
Double-Angle Identities
sin 2 = 2 sin cos tan 2 =
cos 2 = cos2 sin2 = 1 2sin2 = 2cos2 1
Half-Angle Identities
sin = cos = tan = = =
Provided by Tutoring Services 3 Common Trigonometric Angle Measurements
Even and Odd Identities
sin (-) = - sin cos (-) = cos tan (-) = - tan csc (-) = - csc sec (-) = sec cot (-) = - cot
Power-Reducing Identities
sin2 = cos2 = tan2 =
Product-to-Sum Identities
Sum-to-Product Identities
For sums of the form a sin x + b cos x ..
Where , , and
Provided by Tutoring Services 4 Common Trigonometric Angle Measurements
Arc Length Formula Linear Speed ()
s=r or = radians = s = distance traveled
t = time
s = length of the arc
r = radius of the circle
= non-negative radian measure of the central angle Angular Speed ()
= = measure of angle in radians
Converting from Degrees to Minutes to Seconds t = time
1 (degree) = 60 (minutes)
Linear Speed Angular Speed Relationship
1 (minute) = 60 (seconds)
= r = linear speed
1 (degree) = 3,600 (seconds) r = radius
= angular speed
Provided by Tutoring Services 5 Common Trigonometric Angle Measurements
Law of Sines: used to solve triangles when two angles and a side are given or when two sides and an opposite angle are given.
Law of Cosines: used to solve triangles when two sides and the included angle or three sides of the triangle are given.
Area (K) Area (K) using Herons Formula
Provided by Tutoring Services 6 Common Trigonometric Angle Measurements
Potrebbero piacerti anche
- Quadratic Inequalities: Lesson 3.4Documento9 pagineQuadratic Inequalities: Lesson 3.4ahmed mahamedNessuna valutazione finora
- Android MySQL Tutorial To Perform Basic CRUD Operation2Documento54 pagineAndroid MySQL Tutorial To Perform Basic CRUD Operation2ahmed mahamedNessuna valutazione finora
- 7 2 PDFDocumento22 pagine7 2 PDFahmed mahamedNessuna valutazione finora
- Microsoft PowerPoint - IntroDocumento46 pagineMicrosoft PowerPoint - Introahmed mahamedNessuna valutazione finora
- Top Down ParsingDocumento13 pagineTop Down Parsingahmed mahamedNessuna valutazione finora
- 4.2mirrors 000Documento6 pagine4.2mirrors 000ahmed mahamedNessuna valutazione finora
- Thin LensesDocumento21 pagineThin Lensesahmed mahamedNessuna valutazione finora
- WA1 Sols PDFDocumento3 pagineWA1 Sols PDFahmed mahamedNessuna valutazione finora
- Progress Dialog Deprecated, Alternative Is SpotsDialog ExampleDocumento3 pagineProgress Dialog Deprecated, Alternative Is SpotsDialog Exampleahmed mahamed50% (2)
- LoginDocumento1 paginaLoginahmed mahamedNessuna valutazione finora
- Learning Directions PDFDocumento1 paginaLearning Directions PDFahmed mahamedNessuna valutazione finora
- Home Dashboard Design in Android Studio - AwsRhDocumento14 pagineHome Dashboard Design in Android Studio - AwsRhahmed mahamed100% (1)
- Answer Chapter 4 Fas Ed 3Documento19 pagineAnswer Chapter 4 Fas Ed 3ahmed mahamedNessuna valutazione finora
- Chap 3Documento54 pagineChap 3ahmed mahamedNessuna valutazione finora
- 16 Capacitor Energy, Connections, RC Transients PDFDocumento19 pagine16 Capacitor Energy, Connections, RC Transients PDFahmed mahamedNessuna valutazione finora
- Research Compiler DesignDocumento2 pagineResearch Compiler Designahmed mahamedNessuna valutazione finora
- JDBC Connection Code To Connect Servlet With Oracle.Documento7 pagineJDBC Connection Code To Connect Servlet With Oracle.ahmed mahamedNessuna valutazione finora
- First, Follow SetsDocumento24 pagineFirst, Follow Setsahmed mahamedNessuna valutazione finora
- CapacitorsDocumento14 pagineCapacitorsahmed mahamedNessuna valutazione finora
- INSERT, UPDATE, and DELETE Operations Using JDBC - Using Java Database Connectivity (JDBC) With Oracle - InformITDocumento5 pagineINSERT, UPDATE, and DELETE Operations Using JDBC - Using Java Database Connectivity (JDBC) With Oracle - InformITahmed mahamedNessuna valutazione finora
- Physics Past Papers To DoDocumento2 paginePhysics Past Papers To Doshania lewisNessuna valutazione finora
- Maths PracticeDocumento16 pagineMaths Practicesamisoma2011Nessuna valutazione finora
- Answers For Multiplication of MatricesDocumento1 paginaAnswers For Multiplication of Matricesahmed mahamedNessuna valutazione finora
- 24 Fluid PressureDocumento6 pagine24 Fluid Pressureahmed mahamedNessuna valutazione finora
- Pascal's Principle Formula - Definition and ExamplesDocumento4 paginePascal's Principle Formula - Definition and Examplesahmed mahamedNessuna valutazione finora
- BrightnessDocumento15 pagineBrightnessahmed mahamedNessuna valutazione finora
- 17 TheoryLL1 PDFDocumento4 pagine17 TheoryLL1 PDFahmed mahamedNessuna valutazione finora
- What Is Hyper-Threading - (Technology Explained)Documento8 pagineWhat Is Hyper-Threading - (Technology Explained)ahmed mahamedNessuna valutazione finora
- ProgramDocumento1 paginaProgramahmed mahamedNessuna valutazione finora
- Measurement and ConversionDocumento13 pagineMeasurement and Conversionahmed mahamedNessuna valutazione finora
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Da EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Valutazione: 4 su 5 stelle4/5 (98)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceDa EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceValutazione: 4 su 5 stelle4/5 (895)
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeDa EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeValutazione: 4 su 5 stelle4/5 (5794)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingDa EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingValutazione: 3.5 su 5 stelle3.5/5 (400)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaDa EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaValutazione: 4.5 su 5 stelle4.5/5 (266)
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeDa EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeValutazione: 4.5 su 5 stelle4.5/5 (537)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureDa EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureValutazione: 4.5 su 5 stelle4.5/5 (474)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItDa EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItValutazione: 4.5 su 5 stelle4.5/5 (838)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceDa EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceValutazione: 4 su 5 stelle4/5 (588)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryDa EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryValutazione: 3.5 su 5 stelle3.5/5 (231)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerDa EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerValutazione: 4.5 su 5 stelle4.5/5 (271)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyDa EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyValutazione: 3.5 su 5 stelle3.5/5 (2259)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealDa EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealValutazione: 4 su 5 stelle4/5 (73)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersDa EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersValutazione: 4.5 su 5 stelle4.5/5 (344)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnDa EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnValutazione: 4.5 su 5 stelle4.5/5 (234)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaDa EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaValutazione: 4 su 5 stelle4/5 (45)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreDa EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreValutazione: 4 su 5 stelle4/5 (1090)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Da EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Valutazione: 4.5 su 5 stelle4.5/5 (121)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesDa EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesValutazione: 4 su 5 stelle4/5 (821)
- Solutions of Triangle - 9Documento8 pagineSolutions of Triangle - 9rebel rocksNessuna valutazione finora
- Evaluation ExamDocumento3 pagineEvaluation ExamEmileandro Perito QuindiaganNessuna valutazione finora
- Inversion 5Documento3 pagineInversion 5Mohammed ImranNessuna valutazione finora
- 8M03 Understanding Quadrilaterals (v1)Documento3 pagine8M03 Understanding Quadrilaterals (v1)neomatrix70Nessuna valutazione finora
- Activity - Inscribed Angles and Intercepted ArcsDocumento7 pagineActivity - Inscribed Angles and Intercepted ArcsReygie FabrigaNessuna valutazione finora
- Latitude, Longitude, and Great Circle DistancesDocumento4 pagineLatitude, Longitude, and Great Circle DistancesTaz NazNessuna valutazione finora
- Trigonometry (Exercise For Cintya)Documento6 pagineTrigonometry (Exercise For Cintya)ybandik adicahyonoNessuna valutazione finora
- Math 112 Review Sheets - ANSWERSDocumento5 pagineMath 112 Review Sheets - ANSWERSGarryNessuna valutazione finora
- WWW Careerbless Com Aptitude Qa Area Imp PHP BackupDocumento12 pagineWWW Careerbless Com Aptitude Qa Area Imp PHP BackupRajiv SivalingamNessuna valutazione finora
- TrigonometryDocumento35 pagineTrigonometryAvi HafNessuna valutazione finora
- Circle 2Documento64 pagineCircle 2Rokaya fouadNessuna valutazione finora
- Extra Problems For Jacobs Using GSPDocumento21 pagineExtra Problems For Jacobs Using GSPpeter_ash_4Nessuna valutazione finora
- Review Material in Plane & Spherical TrigonometryDocumento9 pagineReview Material in Plane & Spherical TrigonometryVICTORIA OMEGA JARAMILLANessuna valutazione finora
- Similar Triangles TheoremDocumento29 pagineSimilar Triangles TheoremDarlyn Pimentel GalangNessuna valutazione finora
- PrimingDocumento3 paginePrimingLoranel EspirituNessuna valutazione finora
- Math12-1 Lesson 1 Angle MeasureDocumento8 pagineMath12-1 Lesson 1 Angle MeasureCharmane Lizette TarcenaNessuna valutazione finora
- Circle, Chord, Diameter PDFDocumento20 pagineCircle, Chord, Diameter PDFYzza Olaivar OliverosNessuna valutazione finora
- Adventitious AnglesDocumento10 pagineAdventitious Angles卢剑辉Nessuna valutazione finora
- SohcahtoaDocumento19 pagineSohcahtoaLoganTupperNessuna valutazione finora
- HSSLiVE-XI-Maths - CH-3 - TRIGONOMETRYDocumento11 pagineHSSLiVE-XI-Maths - CH-3 - TRIGONOMETRYsingh vijayNessuna valutazione finora
- Chapter 2 - Inverse Trigonometric FunctionsDocumento38 pagineChapter 2 - Inverse Trigonometric FunctionsmukunthaNessuna valutazione finora
- Vector AlgebraDocumento6 pagineVector AlgebrasudersanaviswanathanNessuna valutazione finora
- Fun With Angles and Polygons: A Unit For Learning About GeometryDocumento44 pagineFun With Angles and Polygons: A Unit For Learning About GeometryHazel Clemente CarreonNessuna valutazione finora
- MATH-Q3-Summative Test No. 1 (Nov. 15)Documento4 pagineMATH-Q3-Summative Test No. 1 (Nov. 15)Florecita CabañogNessuna valutazione finora
- 10th - Coordinate Geometry PDFDocumento5 pagine10th - Coordinate Geometry PDFhaloNessuna valutazione finora
- Circle Theorem Booklet PDFDocumento16 pagineCircle Theorem Booklet PDFPerry Sin100% (1)
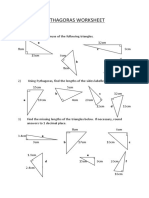
- Pythagoras WorksheetDocumento4 paginePythagoras Worksheetdelta charlieNessuna valutazione finora
- Angles in Parallel LinesDocumento27 pagineAngles in Parallel LinesNathaniel WhyteNessuna valutazione finora
- Chapter 5 SolutionsDocumento77 pagineChapter 5 SolutionsDhawal PanchalNessuna valutazione finora
- 5-1 Bisectors of TrianglesDocumento7 pagine5-1 Bisectors of Trianglesabc123asdNessuna valutazione finora