Documenti di Didattica
Documenti di Professioni
Documenti di Cultura
9702 PHYSICS: MARK SCHEME For The October/November 2014 Series
Caricato da
SzeYee OonTitolo originale
Copyright
Formati disponibili
Condividi questo documento
Condividi o incorpora il documento
Hai trovato utile questo documento?
Questo contenuto è inappropriato?
Segnala questo documentoCopyright:
Formati disponibili
9702 PHYSICS: MARK SCHEME For The October/November 2014 Series
Caricato da
SzeYee OonCopyright:
Formati disponibili
CAMBRIDGE INTERNATIONAL EXAMINATIONS
Cambridge International Advanced Subsidiary and Advanced Level
MARK SCHEME for the October/November 2014 series
9702 PHYSICS
9702/23 Paper 2 (AS Structured Questions), maximum raw mark 60
This mark scheme is published as an aid to teachers and candidates, to indicate the requirements of
the examination. It shows the basis on which Examiners were instructed to award marks. It does not
indicate the details of the discussions that took place at an Examiners meeting before marking began,
which would have considered the acceptability of alternative answers.
Mark schemes should be read in conjunction with the question paper and the Principal Examiner
Report for Teachers.
Cambridge will not enter into discussions about these mark schemes.
Cambridge is publishing the mark schemes for the October/November 2014 series for
most Cambridge IGCSE, Cambridge International A and AS Level components and some
Cambridge O Level components.
IGCSE is the registered trademark of Cambridge International Examinations.
Page 2 Mark Scheme Syllabus Paper
Cambridge International AS/A Level October/November 2014 9702 23
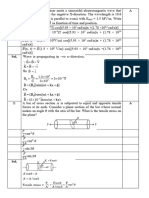
1 (a) ampere B1
kelvin B1 [2]
(allow mole and candela)
(b) (i) stress: N m2 C1
kg m s2 / m2 = kg m1 s2 A1 [2]
(ii) Young modulus = stress / strain and strain has no units
hence units: kg m1 s2 B1 [1]
2 (a) (i) amplitude scale reading 2.2 (cm) C1
amplitude = 2.2 2.5 = 5.5 mV A1 [2]
(ii) time period scale reading = 3.8 (cm) C1
time period = 3.8 0.5 103 = 0.0019 (s) C1
frequency f = 1 / 0.0019 = 530 (526) Hz A1 [3]
(iii) uncertainty in reading = 0.2 in 3.8 (cm) or 5.3% or 0.2 in 7.6 (cm)
or 2.6% [allow other variations of the distance on the x-axis] M1
actual uncertainty = 5.3% of 526 = 27.7 or 28 Hz
or 2.6% of 526 = 13 or 14 A1 [2]
(b) frequency = 530 30 Hz or 530 10 Hz A1 [1]
3 (a) displacement / velocity / acceleration / momentum / etc.
three correct (none wrong) 2, two correct (none or one wrong) 1 A2 [2]
(b) (i) Y = 70 N [allow 71 N as + small square on graph] A1 [1]
(ii) = 90 M1
(for equilibrium) the direction of Y must be opposite to Z
or using Y sin = Z, hence sin = 70 / 70 = 1, = 90 A1 [2]
(iii) 1. Y cos = 160 and Y sin = 70 C1
tan = 70 / 160 hence = 23.6 (24) A1 [2]
2. Y = 160 / cos 23.6 or 70 / sin 23.6 C1
= 174.6 or 175 or 170 N A1 [2]
or:
1602 + 702 = Y2 (C1)
Y = 174.6 or 175 or 170 N (A1)
Cambridge International Examinations 2014
Page 3 Mark Scheme Syllabus Paper
Cambridge International AS/A Level October/November 2014 9702 23
(c) (equilibrium not possible as) there is no vertical component from Y to balance Z B1 [1]
4 (a) for a system (of interacting bodies) the total momentum remains constant M1
provided there is no resultant force acting (on the system) A1 [2]
(b) (i) total momentum = m1v1 + m2v2 C1
= 0.4 0.65 + 0.6 0.45 C1
= 0.26 + 0.27 = 0.53 N s A1 [3]
(ii) 0.53 = 0.4 0.41 + 0.6 v C1
v = 0.366 / 0.6 = 0.61 m s1 A1 [2]
(iii) KE = mv2 C1
total initial KE = 0.4 (0.65)2 + 0.6 (0.45)2 C1
= 0.0845 + 0.06075 = 0.15 (0.145) J A1 [3]
(c) check relative speed of approach equals relative speed of separation
or:
total final kinetic energy equals the total initial kinetic energy B1 [1]
(d) the forces on the two bodies (or on X and Y) are equal and opposite B1
time same for both forces and force is change in momentum / time B1 [2]
5 evaporation: molecules escape from the surface B1
at all temperatures B1
boiling: takes place throughout / in the liquid B1
at the boiling point / at specific temperatures B1 [4]
6 (a) R = l / A C1
A = [ (0.38 103)2] / 4 (= 0.113 106 m2) C1
R = (4.5 107 1.00) / ( [ (0.38 103)2] / 4 ) = 4.0 (3.97) M1 [3]
(b) (i) = V / R C1
= 2.0 / 5.0 = 0.4(0) A A1 [2]
(ii) p.d. across BD = 4 0.4 = 1.6 V A1 [1]
(iii) p.d. across BC (l) = 1.5 (V) C1
BC (l) = (1.5 / 1.6) 100 = 94 (93.75) cm A1 [2]
Cambridge International Examinations 2014
Page 4 Mark Scheme Syllabus Paper
Cambridge International AS/A Level October/November 2014 9702 23
(c) p.d. across wire not balancing e.m.f. of cell OR cell Y has current B1
energy lost or lost volts due to internal resistance B1 [2]
7 (a) (i) progressive: energy is moved / transferred / propagated from one place to
another (without the bulk movement of the medium) B1
transverse: (particles) oscillate / vibrate at right angles to the direction of
travel of the energy / wavefront B1 [2]
(ii) number of oscillations per unit time / number of wavefronts passing a point
per unit time B1 [1]
(b) (i) P and T B1 [1]
(ii) P and S or Q and T B1 [1]
(c) = 1.2 102 (m) C1
v = f
= 15 1.2 102 C1
= 0.18 m s1 A1 [3]
(d) ratio = (1.4)2 / (2.1)2 C1
= 0.44 A1 [2]
Cambridge International Examinations 2014
Potrebbero piacerti anche
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryDa EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryValutazione: 3.5 su 5 stelle3.5/5 (231)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Da EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Valutazione: 4.5 su 5 stelle4.5/5 (121)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceDa EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceValutazione: 4 su 5 stelle4/5 (588)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItDa EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItValutazione: 4.5 su 5 stelle4.5/5 (838)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingDa EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingValutazione: 3.5 su 5 stelle3.5/5 (400)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaDa EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaValutazione: 4.5 su 5 stelle4.5/5 (266)
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeDa EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeValutazione: 4 su 5 stelle4/5 (5795)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesDa EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesValutazione: 4 su 5 stelle4/5 (821)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreDa EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreValutazione: 4 su 5 stelle4/5 (1090)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyDa EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyValutazione: 3.5 su 5 stelle3.5/5 (2259)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersDa EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersValutazione: 4.5 su 5 stelle4.5/5 (345)
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeDa EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeValutazione: 4.5 su 5 stelle4.5/5 (537)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerDa EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerValutazione: 4.5 su 5 stelle4.5/5 (271)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnDa EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnValutazione: 4.5 su 5 stelle4.5/5 (234)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceDa EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceValutazione: 4 su 5 stelle4/5 (895)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureDa EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureValutazione: 4.5 su 5 stelle4.5/5 (474)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealDa EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealValutazione: 4 su 5 stelle4/5 (74)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Da EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Valutazione: 4 su 5 stelle4/5 (98)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaDa EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaValutazione: 4 su 5 stelle4/5 (45)
- More Projectile Motion Practice Problems and SolutionsDocumento3 pagineMore Projectile Motion Practice Problems and SolutionsJocelyn Yemyem Mantilla Veloso100% (1)
- QRD Diffusers - Technical OverviewDocumento30 pagineQRD Diffusers - Technical Overviewnathan_hw100% (1)
- PHYSICS Review Guide 2D Motion: M - L B NDocumento4 paginePHYSICS Review Guide 2D Motion: M - L B Npotatoman51325Nessuna valutazione finora
- 9702 s08 QP 2 PDFDocumento20 pagine9702 s08 QP 2 PDFSzeYee OonNessuna valutazione finora
- University of Cambridge International Examinations General Certificate of Education Advanced Subsidiary Level and Advanced LevelDocumento24 pagineUniversity of Cambridge International Examinations General Certificate of Education Advanced Subsidiary Level and Advanced LevelSzeYee OonNessuna valutazione finora
- University of Cambridge International Examinations General Certificate of Education Advanced Subsidiary Level and Advanced LevelDocumento20 pagineUniversity of Cambridge International Examinations General Certificate of Education Advanced Subsidiary Level and Advanced LevelSzeYee OonNessuna valutazione finora
- Cambridge International Advanced Subsidiary and Advanced LevelDocumento16 pagineCambridge International Advanced Subsidiary and Advanced LevelSzeYee OonNessuna valutazione finora
- Cambridge International Advanced Subsidiary and Advanced LevelDocumento4 pagineCambridge International Advanced Subsidiary and Advanced LevelSzeYee OonNessuna valutazione finora
- Cambridge International Advanced Subsidiary and Advanced LevelDocumento4 pagineCambridge International Advanced Subsidiary and Advanced LevelSzeYee OonNessuna valutazione finora
- Computing and Engineering: Date: May 2017 Time Allowed: 2 Hours Instructions To CandidatesDocumento9 pagineComputing and Engineering: Date: May 2017 Time Allowed: 2 Hours Instructions To CandidatesJulian TomlinsonNessuna valutazione finora
- WavesDocumento4 pagineWavesDuran_Go_Adfel_6305Nessuna valutazione finora
- Namma Kalvi 12th Physics Important Questions em 216618Documento10 pagineNamma Kalvi 12th Physics Important Questions em 216618rameshjeya971Nessuna valutazione finora
- Sri Vidya College of Engineering and Technology, Virudhunagar Course Material (Question Bank)Documento4 pagineSri Vidya College of Engineering and Technology, Virudhunagar Course Material (Question Bank)Ajinkya RajeNessuna valutazione finora
- MRTS-3 (Paper With Solution)Documento35 pagineMRTS-3 (Paper With Solution)semofederationNessuna valutazione finora
- Bi 207 PDFDocumento1 paginaBi 207 PDFEstudante de CiênciasNessuna valutazione finora
- Background Radiation Adapted WorksheetDocumento1 paginaBackground Radiation Adapted WorksheetKHA HarrisonNessuna valutazione finora
- Conduction Alond Simple BarDocumento5 pagineConduction Alond Simple BarMohamad MousaNessuna valutazione finora
- Reaction PaperDocumento2 pagineReaction PaperChicha WatersNessuna valutazione finora
- 01 Largescale HandoutDocumento39 pagine01 Largescale HandoutMona SinghNessuna valutazione finora
- Chemical Engineering Graduate Transport - HW 3Documento3 pagineChemical Engineering Graduate Transport - HW 3Luthfir RahmanNessuna valutazione finora
- Tugas Pembuktian Hukum PembiasanDocumento4 pagineTugas Pembuktian Hukum PembiasanNatifatul latifahNessuna valutazione finora
- Make Your MEP Design Better Using Autodesk CFD Simulation: Dr. Munirajulu. MDocumento78 pagineMake Your MEP Design Better Using Autodesk CFD Simulation: Dr. Munirajulu. MArun CherianNessuna valutazione finora
- Y12 Oscilloscope QuestionsDocumento25 pagineY12 Oscilloscope QuestionsHarry StuarttitchenerNessuna valutazione finora
- Numerical Modeling of Antenna Radiation PatternsDocumento2 pagineNumerical Modeling of Antenna Radiation PatternsRAJKUMARSCRIBD_123Nessuna valutazione finora
- Lecture 19Documento14 pagineLecture 19rakshithbt2359gowdaNessuna valutazione finora
- 40 Meter AddOn Kit Hexbeam EnglishDocumento7 pagine40 Meter AddOn Kit Hexbeam EnglishCPC PHCNessuna valutazione finora
- Glass and Thermal InsulationDocumento9 pagineGlass and Thermal InsulationSónia AraújoNessuna valutazione finora
- Optical MCQDocumento9 pagineOptical MCQkavitha saravananNessuna valutazione finora
- Temperature Distribution in Long Porous Fins in Natural Convection ConditionDocumento6 pagineTemperature Distribution in Long Porous Fins in Natural Convection ConditionPrakash InturiNessuna valutazione finora
- Stars: Dr. Simone ScaringiDocumento374 pagineStars: Dr. Simone ScaringiCorreos WebNessuna valutazione finora
- CLL-251 Heat Transfer (Free Convection) : Dr. Manojkumar C. RamtekeDocumento11 pagineCLL-251 Heat Transfer (Free Convection) : Dr. Manojkumar C. RamtekeHriday GoelNessuna valutazione finora
- HeisenbergDocumento16 pagineHeisenbergkethavarapuramjiNessuna valutazione finora
- Edit Theory 9702 - m20 - QP - 22Documento15 pagineEdit Theory 9702 - m20 - QP - 22anitajohnson.prakriyaNessuna valutazione finora
- Ideal FlowDocumento30 pagineIdeal FlowCollano M. Noel RogieNessuna valutazione finora
- Kinematics and DynamicsDocumento16 pagineKinematics and DynamicsmartinNessuna valutazione finora