Documenti di Didattica
Documenti di Professioni
Documenti di Cultura
Utkast Grona Boken 2
Caricato da
maria lukCopyright
Formati disponibili
Condividi questo documento
Condividi o incorpora il documento
Hai trovato utile questo documento?
Questo contenuto è inappropriato?
Segnala questo documentoCopyright:
Formati disponibili
Utkast Grona Boken 2
Caricato da
maria lukCopyright:
Formati disponibili
T
C
A
R
T
Fetal surveillance and assessment of fetal reactions
The Green Book of Neoventa Part II
X
K G Rosn
Annika Mrtendal
IFD Increased variability Alarm reaction
T
A 24 year old G1 P0. Gestation age 39+5. Normal pregnancy.
PROGRESS OF LABOUR
Admitted to hospital with contractions. SROM at 21.00.
22:40 VE: Cx fully effaced, dilated 5 cm, vx-1. Clear liquor draining. IUPC inserted, FSE
C
applied due to uncomplicated variable decelerations, noted on external CTG.
23:30 Epidural sited.
01:00 VE: Cx fully dilated, vx at the spines, clear liquor.
01:13 An attempt to start pushing. Fig. 3 Very marked FHR variations in connection with decelerations and pushing.
01:29 Pushing stopped, allowing the presenting part to descend. Oxytocin infusion is started.
02:50 VE: Cx fully dilated, vx +2. Active pushing started.
03:52 Normal vaginal delivery.
A
NEONATAL OUTCOME
Baby girl. BW 3910 g. Apgar scores 9 10.
Cord Artery pH 7.11 pCO2 9.1 kPa BDecf 6.8 mmol/l.
Cord Vein pH 7.23 pCO2 6.8 kPa BDecf 5.3 mmol/l.
Normal outcome.
R
Fig. 4 Last hour of labour identifying a continuation of the increased reactivity/FHRV with
ASSESSMENT OF RECORDING ST-episodes of increase in T/QRS.
Recording of high quality starting
at 22:45 and finishing at 03:50,
COMMENTS
2 minutes prior to delivery.
An example of a stress response by a fetus in full control of the strain of labour characteri-
sed by the following:
Fig. 1 Stable baseline and marked
T
FHR reactivity at start. Stable T/QRS
1. Maximal reactivity at onset of the recording as seen by a saltatory pattern where the
immediate FHR variations exceed 25 bpm.
2. Prolonged arousal reaction by a further increased FHRV in response to pushing.
showing a decrease during the initial 3. Final episode in 2nd stage where the arousal becomes an alarm as the increase in reacti-
15 minutes.
vity is combined with an ST rise. This episode occurs within 20 minutes of delivery and we
would not expect any acidemia.
Why would we see these extraordinary FHR changes? The initial, more regular pattern may
X
be regarded as a strong reaction to a stimulus (contractions, skin puncture from FSE app-
lication?). Later on when pushing starts, hypoxia due to intermittent blockade of cord vein
blood flow seems to be a probable explanation. Although hypoxic episodes are short lasting,
they became frequent enough to initiate an ST rise.
MESSAGE
A saltatory FHR + ST Event = an alarm and intervention is required.
Fig. 2 The first hour.
54
Potrebbero piacerti anche
- Cardiac Assessment ScenariosDocumento11 pagineCardiac Assessment ScenariosShaneNessuna valutazione finora
- Nursing Care Plans (NCP) of Abruptio PlacentaDocumento13 pagineNursing Care Plans (NCP) of Abruptio PlacentaKath76% (21)
- EFMDocumento15 pagineEFMslcNessuna valutazione finora
- Aesthetic and Reconstructive Breast Surgery - Solving Complications and Avoiding Unfavorable Results PDFDocumento222 pagineAesthetic and Reconstructive Breast Surgery - Solving Complications and Avoiding Unfavorable Results PDFAhmed Attia100% (1)
- The Medical City Clark List of Doctors May 2019Documento13 pagineThe Medical City Clark List of Doctors May 2019Paopao BacalingNessuna valutazione finora
- A Case of Electrical BurnDocumento34 pagineA Case of Electrical BurnryanyganaNessuna valutazione finora
- About: MOA Not Known, But Induction of Bilateral Generalised Seizures Required For Effects. An inDocumento1 paginaAbout: MOA Not Known, But Induction of Bilateral Generalised Seizures Required For Effects. An inmeilunlyNessuna valutazione finora
- Non Stress Test 1Documento8 pagineNon Stress Test 1Ala'a Emerald AguamNessuna valutazione finora
- Labour Pain & ReliefDocumento67 pagineLabour Pain & ReliefAslam RizviNessuna valutazione finora
- MODULE2Documento12 pagineMODULE2Macasieb Renz Jian BalcitaNessuna valutazione finora
- Fetal Heart Rate MonitoringDocumento11 pagineFetal Heart Rate Monitoringanon_32140107Nessuna valutazione finora
- Pearson Assesment: Admission Day Day 1 Day 2 Day 3, Day 1 Post-OpDocumento12 paginePearson Assesment: Admission Day Day 1 Day 2 Day 3, Day 1 Post-OpMelodia Turqueza GandezaNessuna valutazione finora
- Ketamine Drug SummaryDocumento3 pagineKetamine Drug SummarySydney JenningsNessuna valutazione finora
- H MoleDocumento3 pagineH Molemark OrpillaNessuna valutazione finora
- Residents Notes GuatloDocumento2 pagineResidents Notes GuatloRizielle MendozaNessuna valutazione finora
- Antoons, 2002 - Mechanisms Underlying The Frequency Dependence of Contraction and Ca Transients in Mouse Ventricular MyocytesDocumento10 pagineAntoons, 2002 - Mechanisms Underlying The Frequency Dependence of Contraction and Ca Transients in Mouse Ventricular MyocytesAlessio LissoniNessuna valutazione finora
- 02-03-21 - Impending Thyroid Storm PerioperativeDocumento4 pagine02-03-21 - Impending Thyroid Storm PerioperativeWilujeng AnggrainiNessuna valutazione finora
- Pulse Controlled Laser Acupuncture - The RAC / VASDocumento12 paginePulse Controlled Laser Acupuncture - The RAC / VASbob marleyNessuna valutazione finora
- JObstetAnaesthCritCare22113-8106512 223105Documento2 pagineJObstetAnaesthCritCare22113-8106512 223105AuliaNessuna valutazione finora
- The Journal of Neuroscience, July 1992, 12 (7) : 2516-2522Documento7 pagineThe Journal of Neuroscience, July 1992, 12 (7) : 2516-2522Carrie PartchNessuna valutazione finora
- Cough Dyspnoea Asthma Bronchiale: A 33-Year-Old Female With and MimickingDocumento4 pagineCough Dyspnoea Asthma Bronchiale: A 33-Year-Old Female With and Mimickingfiji drNessuna valutazione finora
- Comprehensive Life Support Tutorial Case 1: Question/Action Information Note/Reference TipsDocumento3 pagineComprehensive Life Support Tutorial Case 1: Question/Action Information Note/Reference Tipshyukkie minnieNessuna valutazione finora
- Azzi, R., Fix, D. S. R., Keller, F. S., & Rocha e Silva, M. I. (1964) - Exteroceptive Control of Response Under Delayed Reinforcement. Journal of The Experimental Analysis of Behavior, 7, 159-162.Documento4 pagineAzzi, R., Fix, D. S. R., Keller, F. S., & Rocha e Silva, M. I. (1964) - Exteroceptive Control of Response Under Delayed Reinforcement. Journal of The Experimental Analysis of Behavior, 7, 159-162.Isaac CaballeroNessuna valutazione finora
- General Medical PrinciplesDocumento5 pagineGeneral Medical PrinciplesNisha DNessuna valutazione finora
- Jared Step 3 TQsDocumento5 pagineJared Step 3 TQsJamieNessuna valutazione finora
- Baseline Vital Signs Learner's Actions: Maria Centennia A. Ortega BSN IvDocumento2 pagineBaseline Vital Signs Learner's Actions: Maria Centennia A. Ortega BSN IvMacen OrtegaNessuna valutazione finora
- Complete Atrioventricular Block Under Epidural Ropivacaine Infusion in A Patient With First-Degree Atrioventricular Block and Myasthenia GravisDocumento4 pagineComplete Atrioventricular Block Under Epidural Ropivacaine Infusion in A Patient With First-Degree Atrioventricular Block and Myasthenia GravisMSNessuna valutazione finora
- Intrapartum AssessmentDocumento8 pagineIntrapartum Assessmentangela mamauagNessuna valutazione finora
- OxytocinDocumento2 pagineOxytocinshefawNessuna valutazione finora
- Supplementary Material 1a Acute AsthmaDocumento3 pagineSupplementary Material 1a Acute AsthmaJanela Chriselle B. TICARNessuna valutazione finora
- Avoidance Conditioning With Brief Shock and No Exteroceptive Warning SignalDocumento2 pagineAvoidance Conditioning With Brief Shock and No Exteroceptive Warning SignalVíctor FuentesNessuna valutazione finora
- Fdar Lp6 MontemayorDocumento5 pagineFdar Lp6 MontemayorEden Marie MangaserNessuna valutazione finora
- V.A. Penning, D.J. Connolly, I. Gajanayake, L.A. Mcmahon, V. Luis Fuentes, K.E. Chandler, and H.A. VolkDocumento6 pagineV.A. Penning, D.J. Connolly, I. Gajanayake, L.A. Mcmahon, V. Luis Fuentes, K.E. Chandler, and H.A. VolkYushika DharmasuriyaNessuna valutazione finora
- Antiseizure Drugs H.O. Dental Pharm 2012Documento10 pagineAntiseizure Drugs H.O. Dental Pharm 2012profdrgenNessuna valutazione finora
- Thyroid Storm Prior To Induction of Anaesthesia: CasereportDocumento3 pagineThyroid Storm Prior To Induction of Anaesthesia: CasereportRizaru RinarudeNessuna valutazione finora
- Scenario Title: Community Acquired Pneumonia Learning Outcomes: 1. Assessment and Recognition of The Signs and Symptoms of PneumoniaDocumento6 pagineScenario Title: Community Acquired Pneumonia Learning Outcomes: 1. Assessment and Recognition of The Signs and Symptoms of PneumoniaDud AccNessuna valutazione finora
- Case Report: Hemodynamic Effects of Acute Tension PneumothoraxDocumento5 pagineCase Report: Hemodynamic Effects of Acute Tension PneumothoraxDinda Anita SeptianaNessuna valutazione finora
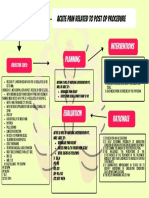
- Acute Pain Related To Post Op Procedure: Planning InterventionsDocumento1 paginaAcute Pain Related To Post Op Procedure: Planning InterventionsYamete KudasaiNessuna valutazione finora
- Case Study PresentationDocumento24 pagineCase Study Presentationapi-733590799Nessuna valutazione finora
- Barbiturates Drug SummaryDocumento5 pagineBarbiturates Drug SummarySydney JenningsNessuna valutazione finora
- Audit Ahad DepanDocumento16 pagineAudit Ahad DepanNorfaizah FxNessuna valutazione finora
- Ineffective Clearance NCP Peds 2Documento3 pagineIneffective Clearance NCP Peds 2api-394876374Nessuna valutazione finora
- Case Presentation: Ajitpal Singh J. BrarDocumento32 pagineCase Presentation: Ajitpal Singh J. BrarMa. Karina de LeonNessuna valutazione finora
- Test/Treatment What Is It? Complications To Monitor For Nursing Care NotesDocumento5 pagineTest/Treatment What Is It? Complications To Monitor For Nursing Care NotesNieka WNessuna valutazione finora
- OB Finals PptsDocumento537 pagineOB Finals PptsMorita TakaNessuna valutazione finora
- Supersticion en La Paloma SKINNER Estracto de Su ObraDocumento6 pagineSupersticion en La Paloma SKINNER Estracto de Su ObraGAEL IBRAHIM UDAVE ERIVESNessuna valutazione finora
- Electronic Fetal MonitoringDocumento25 pagineElectronic Fetal MonitoringMorita TakaNessuna valutazione finora
- JG 1075611Documento9 pagineJG 1075611aydinmemmedov9009Nessuna valutazione finora
- Clinical Short Form-PcuDocumento5 pagineClinical Short Form-Pcuapi-655558844Nessuna valutazione finora
- Residents Notes SegubreDocumento2 pagineResidents Notes SegubreRizielle MendozaNessuna valutazione finora
- Status Epileptico EmergencyDocumento13 pagineStatus Epileptico Emergencywys2dnqrj4Nessuna valutazione finora
- OB Care Map L&DDocumento3 pagineOB Care Map L&DYasmin Santibañez100% (1)
- Fetal Malposition UpdatedDocumento3 pagineFetal Malposition UpdatedJozarine Chelsea LopezNessuna valutazione finora
- Lp2 Drug Study FormsDocumento3 pagineLp2 Drug Study FormsJed Kachel BugayongNessuna valutazione finora
- QT Prolongation Due To Organophosphate Poisoning: AYC Siu, LCH Tsoi, WCB Lo, CCH ChungDocumento2 pagineQT Prolongation Due To Organophosphate Poisoning: AYC Siu, LCH Tsoi, WCB Lo, CCH ChunghlNessuna valutazione finora
- Drug StudyDocumento10 pagineDrug StudyFrancis BelotindosNessuna valutazione finora
- DHMVol484 57 59Documento3 pagineDHMVol484 57 59herliantyrukmanaNessuna valutazione finora
- Maternal: Stage of LaborDocumento5 pagineMaternal: Stage of LaborTree NahNessuna valutazione finora
- EMD2 - K9 - Status EpilepticusDocumento37 pagineEMD2 - K9 - Status EpilepticusJessica WijayaNessuna valutazione finora
- Nursing Care Plan: Obstetrics and Gynecology Nursing RotationDocumento8 pagineNursing Care Plan: Obstetrics and Gynecology Nursing RotationMary Justine Nuyad-AfricaNessuna valutazione finora
- ChartingDocumento41 pagineChartingArlene Saint AnthonieNessuna valutazione finora
- Asthma: Physiology, Immunopharmacology, and TreatmentDa EverandAsthma: Physiology, Immunopharmacology, and TreatmentValutazione: 5 su 5 stelle5/5 (1)
- Diccionario Medico Ingles EspañolDocumento191 pagineDiccionario Medico Ingles EspañolBrussel LasVegas100% (1)
- Diccionario Medico Ingles EspañolDocumento191 pagineDiccionario Medico Ingles EspañolBrussel LasVegas100% (1)
- Algorithm May 2014Documento1 paginaAlgorithm May 2014maria lukNessuna valutazione finora
- Intrapartum Fetal Surveillance: Clinical Guideline - Third Edition 2014Documento1 paginaIntrapartum Fetal Surveillance: Clinical Guideline - Third Edition 2014maria lukNessuna valutazione finora
- Yemisi Chapter ThreeDocumento10 pagineYemisi Chapter ThreeAbimbola OyarinuNessuna valutazione finora
- Assessing The Apical Pulse by AuscultationDocumento1 paginaAssessing The Apical Pulse by AuscultationydtrgnNessuna valutazione finora
- Ain ShamsJAnaesthesiol10184 2808197 074801 HYPOXAEMIADocumento7 pagineAin ShamsJAnaesthesiol10184 2808197 074801 HYPOXAEMIAOYEBOLA ADEKOLANessuna valutazione finora
- Women's Health Physiotherapy (Pelvic Health)Documento24 pagineWomen's Health Physiotherapy (Pelvic Health)syed imran100% (1)
- Clinical Guidelines Vol I FINALDocumento172 pagineClinical Guidelines Vol I FINALjohn mwangiNessuna valutazione finora
- 2016-Brochure Umbilical CatheterDocumento4 pagine2016-Brochure Umbilical CatheterSuman MondalNessuna valutazione finora
- USMLE Step 2 CK Lecture Notes 2018 MPPS Book Set (PDFDrive) - 657-662Documento6 pagineUSMLE Step 2 CK Lecture Notes 2018 MPPS Book Set (PDFDrive) - 657-662antonela alarcon loayzaNessuna valutazione finora
- SEM ProjectDocumento73 pagineSEM ProjectRahulKrishnan100% (1)
- Celecoxib Drug StudyDocumento2 pagineCelecoxib Drug Studymilkv100% (2)
- Solitaire Company ProfileDocumento71 pagineSolitaire Company ProfilesolitairepharmaciaNessuna valutazione finora
- Gastrointestinal Oncology Principles and PracticesDocumento794 pagineGastrointestinal Oncology Principles and Practicesjohny3333Nessuna valutazione finora
- Perioperative Nursing 101Documento2 paginePerioperative Nursing 101Anthony Dema-ala0% (1)
- Management of Pediatric Femoral Neck FractureDocumento21 pagineManagement of Pediatric Femoral Neck FracturevikidwirandaNessuna valutazione finora
- Biometry by Suryakant Jha and Wangchuk Doma PDFDocumento5 pagineBiometry by Suryakant Jha and Wangchuk Doma PDFJavier Andrés Pinochet SantoroNessuna valutazione finora
- Which OCP Is Best HandoutDocumento4 pagineWhich OCP Is Best HandoutMarianna LeeNessuna valutazione finora
- Cardiovascular Disease Certification Examination Electrocardiograms and Imaging Studies - AbimDocumento33 pagineCardiovascular Disease Certification Examination Electrocardiograms and Imaging Studies - AbimabimorgNessuna valutazione finora
- Drug Abuse in PregnancyDocumento91 pagineDrug Abuse in PregnancyCrystal Gayle Nario Sabado100% (1)
- PPIUDDocumento16 paginePPIUDmusicwizardNessuna valutazione finora
- Tamil Nadu Dental Council: Affix Your Recent P.P Size PhotoDocumento3 pagineTamil Nadu Dental Council: Affix Your Recent P.P Size PhotokerminkNessuna valutazione finora
- Ophthalmology: World Journal ofDocumento5 pagineOphthalmology: World Journal ofRohamonangan TheresiaNessuna valutazione finora
- Giovanni Maciocia Menorrhagia NotesDocumento22 pagineGiovanni Maciocia Menorrhagia Noteshihi12100% (5)
- Nursing Care of The Child Undergoing A TonsillectomyDocumento2 pagineNursing Care of The Child Undergoing A Tonsillectomykelsey0% (1)
- Ultrasound Basics and Artifacts Quiz - 123 Sonography Sakte PDFDocumento7 pagineUltrasound Basics and Artifacts Quiz - 123 Sonography Sakte PDFRexhailNessuna valutazione finora
- Pathologist List of Doctors PuneDocumento163 paginePathologist List of Doctors PuneSunnyraj Joshi100% (1)
- Management of Pregnancy in Women With Rheumatoid Arthritis: Clinical Focus Clinical FocusDocumento3 pagineManagement of Pregnancy in Women With Rheumatoid Arthritis: Clinical Focus Clinical FocusLatifa Tistanty Permadi AlchairidNessuna valutazione finora
- Theft of Womanhood - Polycystic Ovarian Syndrome: Role of HomeopathyDocumento11 pagineTheft of Womanhood - Polycystic Ovarian Syndrome: Role of HomeopathyMadhukar KNessuna valutazione finora
- TG 43Documento9 pagineTG 43qftgaugeNessuna valutazione finora
- Pharmacology Iii PracticalDocumento16 paginePharmacology Iii Practicaldoremon nobitaNessuna valutazione finora