Documenti di Didattica
Documenti di Professioni
Documenti di Cultura
Heat Loss Insulated Pipe
Caricato da
Katie BensonCopyright
Formati disponibili
Condividi questo documento
Condividi o incorpora il documento
Hai trovato utile questo documento?
Questo contenuto è inappropriato?
Segnala questo documentoCopyright:
Formati disponibili
Heat Loss Insulated Pipe
Caricato da
Katie BensonCopyright:
Formati disponibili
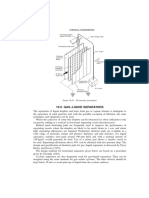
Heat Loss From An Insulated Pipe
Parameters
Pipe Outside Diameter 0.1 m Do Created By: Nauman
Fluid Temperature 84.188 C Tf
Ambient Temperature 18 C Ta
Insulation Thickness 0.01 m
Insulation Thermal Conductivit 0.06 W m-1 K-1 k
Surface Temperature Estimate 40 C TsEst
Heat Transfer Calculations
Outside Diameter 0.12 m Ds
Temp Difference at Surface 22 C T
Surface Heat Transfer Coefficie11.016 W m-2 K-1 hs
Heat Loss 91.368 W m-1 q
Surface Temperature Check 40 C Ts
Temperature Check 0 C
Temperature Check needs to be 0 for balanced heat transfer
Use Goal Seek to change any parameter so that
Temperature Check is 0
These equations are used in the spreadsheet to define the heat transfer process.
q is the heat flowrate through the pipe and insulation (W m-1)
Tsis the temperature at the surface of the insulation (K)
Tais the ambient air temperature (K)
Tfis the fluid temperature inside the pipe (K)
DOis the pipe diameter (m)
DSis the outside diameter of the insulated pipe (i.e. the pipe diameter plus two times the
insulation thickness) (m)
k is the insulation thermal conductivity (W m-1K-1)
T is the temperature difference between the insulation surface and ambient airT s-Ta(K)
hsis the insulation-to-air heat surface heat transfer coefficient (W m 2K-1)
The equation for the surface heat transferh scoefficient is a correlation; any other valid
relationship can besubstituted.
The equations are implicit - the heat transfer coefficient is a function of the surface
temperatureTs, but the surface temperature is a function oftheheat transfer coefficient.
Hence the equations need to be solved iteratively with Goal Seek in Excel.Simply
break the loop by estimating a value ofT s,
use this to calculate all other properties (including the heat transfer rate)
use the heat transfer rate to backcalculateT s
use Goal Seek to make the two values ofT sequal by varying the estimated value ofTs(or any
other parameter
You can easily modify the heat transfer equations to include more complex effects, such
aseffect of fouling on the pipe surface, multiple layers of different insulation, radiative losses,
thick large pipe walls (which act as a heat sink) etc
Potrebbero piacerti anche
- Heat Transfer. Heat Loss From A Pipe in An Indoor LocationDocumento29 pagineHeat Transfer. Heat Loss From A Pipe in An Indoor LocationselisenNessuna valutazione finora
- Pumps Calculation 2Documento2 paginePumps Calculation 2Alchemy EngNessuna valutazione finora
- Sizing Calculation Spreadsheet PSVDocumento1 paginaSizing Calculation Spreadsheet PSVkenoly123Nessuna valutazione finora
- STEAM TABLE FORMULATION AND VERIFICATIONDocumento8 pagineSTEAM TABLE FORMULATION AND VERIFICATIONcemal gümrükçüoğluNessuna valutazione finora
- Sizing and Rating BLOWDOWN - ExerciseDocumento19 pagineSizing and Rating BLOWDOWN - Exercisepolaris44Nessuna valutazione finora
- Line Sizing Design Basis - General Specification PDFDocumento11 pagineLine Sizing Design Basis - General Specification PDFSaiKumarNessuna valutazione finora
- Orifice Sizing Guidelines and Thumb RulesDocumento11 pagineOrifice Sizing Guidelines and Thumb RulesBsd FareedNessuna valutazione finora
- Compressor Stage Pressure - Design & OptimizationDocumento4 pagineCompressor Stage Pressure - Design & OptimizationAshwin ChandaranaNessuna valutazione finora
- Tube Side Velocity CalculationDocumento20 pagineTube Side Velocity CalculationNitin KurupNessuna valutazione finora
- Restriction OrificeDocumento8 pagineRestriction OrificekarthickNessuna valutazione finora
- TG Temperature GaugeDocumento2 pagineTG Temperature GaugeAr RahmanNessuna valutazione finora
- Gas Properties, Flowrate and Conditions: Reciprocating Compressor Calculation SheetDocumento5 pagineGas Properties, Flowrate and Conditions: Reciprocating Compressor Calculation SheetNaqqash Sajid0% (2)
- Calculation of Pipe Line Heat LossDocumento9 pagineCalculation of Pipe Line Heat LossradanpetricaNessuna valutazione finora
- Fire Relief Dynamic StudyDocumento2 pagineFire Relief Dynamic StudylguardiaNessuna valutazione finora
- Small Bore Orifice For Gas Flow PDFDocumento4 pagineSmall Bore Orifice For Gas Flow PDFManufacturer VerifyNessuna valutazione finora
- Steam Properties Paper2Documento9 pagineSteam Properties Paper2Gary JonesNessuna valutazione finora
- Orifice Flow Calculator For Gases, Steam, and VaporsDocumento2 pagineOrifice Flow Calculator For Gases, Steam, and Vaporsbakhtyar21Nessuna valutazione finora
- Pressure Drop in BendDocumento5 paginePressure Drop in BendfitratulqadriNessuna valutazione finora
- Steam Control Valve Sizing for Tag PV123Documento2 pagineSteam Control Valve Sizing for Tag PV123dilip matalNessuna valutazione finora
- Control Valve DPDocumento8 pagineControl Valve DPAmit SawantNessuna valutazione finora
- Consequence AnalyserDocumento23 pagineConsequence AnalyserGlacier RamkissoonNessuna valutazione finora
- API 12j SizingDocumento1 paginaAPI 12j SizingAdewunmi OlufemiNessuna valutazione finora
- Section 7 - Separation EquipmentDocumento9 pagineSection 7 - Separation Equipmentlulis171Nessuna valutazione finora
- Demister DatasheetDocumento1 paginaDemister Datasheetdeion29Nessuna valutazione finora
- Pump CalcDocumento1 paginaPump CalcMoch WildanNessuna valutazione finora
- Recip Compressor Calculations For GCP-3Documento4 pagineRecip Compressor Calculations For GCP-3Greg GolushkoNessuna valutazione finora
- Thermal Relief Rate Calculation for Jet A1 in 20Documento1 paginaThermal Relief Rate Calculation for Jet A1 in 20Ascend032100% (1)
- PG Pressure GaugeDocumento2 paginePG Pressure GaugeAr RahmanNessuna valutazione finora
- Tube Rupture Relief CalculationDocumento1 paginaTube Rupture Relief CalculationAmin RoisNessuna valutazione finora
- Weymouth Gas Flow CalculationsDocumento44 pagineWeymouth Gas Flow CalculationsPierre GermaineNessuna valutazione finora
- PSV Thermal SizingDocumento16 paginePSV Thermal Sizingahmad santoso0% (1)
- Gas Line Sizing by API 14E Method Revision #: ??: Pressure Drop (Fittings Etc) Elbows, Tees Elbows, Tees Elbows, TeesDocumento4 pagineGas Line Sizing by API 14E Method Revision #: ??: Pressure Drop (Fittings Etc) Elbows, Tees Elbows, Tees Elbows, Teesusaid saifullahNessuna valutazione finora
- Radiation and Convection Heat TransferDocumento5 pagineRadiation and Convection Heat TransfergsdaundhNessuna valutazione finora
- Fgas Refrigerant CalculatorDocumento10 pagineFgas Refrigerant CalculatorKumar sssssNessuna valutazione finora
- Circulation Heater SelectionDocumento3 pagineCirculation Heater SelectionWaqasNessuna valutazione finora
- Line Sizing (SI) Gas PhaseDocumento10 pagineLine Sizing (SI) Gas PhaseRian Intan SaputraNessuna valutazione finora
- Centrif Pumps1 SpreadsheetDocumento2 pagineCentrif Pumps1 SpreadsheetCast Ed Iv0% (1)
- PSV Calcs PDFDocumento8 paginePSV Calcs PDFatulNessuna valutazione finora
- Sizing of Restriction OrificesDocumento4 pagineSizing of Restriction OrificesYakubuNessuna valutazione finora
- Calculating Gas Properties with Mixing Rule SpreadsheetDocumento2 pagineCalculating Gas Properties with Mixing Rule Spreadsheetvictor javier nuñezNessuna valutazione finora
- ORIFICEDocumento1 paginaORIFICEhardavNessuna valutazione finora
- Instrumentation GPSA HandbookDocumento6 pagineInstrumentation GPSA HandbookmusaveerNessuna valutazione finora
- 10.9. Gas Liquid Separators: Chemical EngineeringDocumento6 pagine10.9. Gas Liquid Separators: Chemical EngineeringsterlingNessuna valutazione finora
- Tank Vent Calculation SpreadsheetDocumento3 pagineTank Vent Calculation SpreadsheetJack SonNessuna valutazione finora
- Relief Load CalculationDocumento8 pagineRelief Load CalculationMuthuKumar ArunachalamNessuna valutazione finora
- TSV CalculationDocumento3 pagineTSV CalculationAymen KhlifiNessuna valutazione finora
- Section 17 - Fluid Flow and PipingDocumento11 pagineSection 17 - Fluid Flow and PipingCHANADASNessuna valutazione finora
- Thermosyphon Reboiler (Horizontal) GPSADocumento6 pagineThermosyphon Reboiler (Horizontal) GPSAsyamsudin2006Nessuna valutazione finora
- Net Positive Suction Head (NPSH) and CavitationDocumento14 pagineNet Positive Suction Head (NPSH) and CavitationSri GaneshNessuna valutazione finora
- Wet Air Properties Calculation Sheet: at Low PressureDocumento2 pagineWet Air Properties Calculation Sheet: at Low Pressurezsmith0% (1)
- FTDocumento1 paginaFTmanodipNessuna valutazione finora
- Process Engineer - PSV SizingDocumento3 pagineProcess Engineer - PSV SizingLaorenciaNessuna valutazione finora
- Ogpe OGPE Oil Fields: Calculation SheetDocumento4 pagineOgpe OGPE Oil Fields: Calculation SheetFaber TrujilloNessuna valutazione finora
- Ognition PSV Sizing Calculation SpreadsheetDocumento2 pagineOgnition PSV Sizing Calculation Spreadsheetrisqi ilham zulfahmiNessuna valutazione finora
- Tutorial PipeFLoDocumento1 paginaTutorial PipeFLohel hel100% (1)
- SFW - FV Flash Steam and Flash Vessel CalculationDocumento2 pagineSFW - FV Flash Steam and Flash Vessel CalculationjnmanivannanNessuna valutazione finora
- Chevron Line Sizing GuidelinesDocumento6 pagineChevron Line Sizing GuidelinesWayne Monnery0% (1)
- Quick estimation compressor settle out conditionsDocumento1 paginaQuick estimation compressor settle out conditionsAhmed GattoufiNessuna valutazione finora
- Grey Water Discharge Line FEDocumento4 pagineGrey Water Discharge Line FEBayu AjiNessuna valutazione finora
- Handbook of Thermal Conductivity, Volume 2: Organic Compounds C5 to C7Da EverandHandbook of Thermal Conductivity, Volume 2: Organic Compounds C5 to C7Nessuna valutazione finora
- Target Energy Heat Loss From A Pipe CalculatorDocumento3 pagineTarget Energy Heat Loss From A Pipe CalculatorKatie BensonNessuna valutazione finora
- Heat Transfer Excel Calculations 1Documento39 pagineHeat Transfer Excel Calculations 1Sharon LambertNessuna valutazione finora
- Pipeline Daily Construction ReportDocumento2 paginePipeline Daily Construction ReportKatie Benson83% (6)
- Excel-Template Natural-Convection Sphere Si UnitsDocumento2 pagineExcel-Template Natural-Convection Sphere Si UnitsKatie BensonNessuna valutazione finora
- 01 - Fluid FlowDocumento76 pagine01 - Fluid FlowMubarak AhmadNessuna valutazione finora
- Pipe Insulation (Version 1)Documento3 paginePipe Insulation (Version 1)Katie BensonNessuna valutazione finora
- Heat Conduction Pipe InsulationDocumento1 paginaHeat Conduction Pipe InsulationJonson CaoNessuna valutazione finora
- Data Transfer - Primavera To MSprojectDocumento14 pagineData Transfer - Primavera To MSprojectaavijay100% (1)
- ARM7 Features and BenefitsDocumento19 pagineARM7 Features and BenefitsKatie BensonNessuna valutazione finora
- Create Excel File from SSIS with EPPlusDocumento49 pagineCreate Excel File from SSIS with EPPlusKatie BensonNessuna valutazione finora
- Excel 2007 Data Loader To SQL 2008 ServerDocumento3 pagineExcel 2007 Data Loader To SQL 2008 ServerKatie BensonNessuna valutazione finora
- ARM User Guide for Risk Identification and ManagementDocumento44 pagineARM User Guide for Risk Identification and ManagementKatie BensonNessuna valutazione finora
- Ensure That You Change The Text in Red To Suit Your Location of The TH FileDocumento2 pagineEnsure That You Change The Text in Red To Suit Your Location of The TH FileKatie BensonNessuna valutazione finora
- Add An Assembly To The GACDocumento3 pagineAdd An Assembly To The GACKatie BensonNessuna valutazione finora
- Response Spectra: Frequency (HZ)Documento1 paginaResponse Spectra: Frequency (HZ)Katie BensonNessuna valutazione finora
- 1 801 Primavera p6 Fundamentals r8Documento1 pagina1 801 Primavera p6 Fundamentals r8Katie BensonNessuna valutazione finora
- ARM User Guide for Risk Identification and ManagementDocumento44 pagineARM User Guide for Risk Identification and ManagementKatie BensonNessuna valutazione finora
- Project Management Systems: Supporting The TransformationDocumento16 pagineProject Management Systems: Supporting The TransformationKatie BensonNessuna valutazione finora
- September 2012copying Activities Between ProjectsDocumento6 pagineSeptember 2012copying Activities Between ProjectsKatie BensonNessuna valutazione finora
- Installation of Primavera Unifier v15Documento63 pagineInstallation of Primavera Unifier v15Katie Benson100% (1)
- SAP IDES ERP 6.0 EHP4 NetWeaver 7.01 Installation Guide On Windows 2003 64-BitDocumento25 pagineSAP IDES ERP 6.0 EHP4 NetWeaver 7.01 Installation Guide On Windows 2003 64-BitVijay NikamNessuna valutazione finora
- Adding WBS Id Next To Activity IDDocumento4 pagineAdding WBS Id Next To Activity IDKatie BensonNessuna valutazione finora
- SAPGUI Install StudentDocumento6 pagineSAPGUI Install StudentKatie BensonNessuna valutazione finora
- 106a-Administration in Primavera P6 and P6 Web AccessDocumento1 pagina106a-Administration in Primavera P6 and P6 Web AccessKatie BensonNessuna valutazione finora
- Ansys Parametric Design Language GuideDocumento106 pagineAnsys Parametric Design Language GuidewhocarNessuna valutazione finora
- Masonry Heaters InstallationDocumento37 pagineMasonry Heaters InstallationKatie BensonNessuna valutazione finora
- GAO Cost Estimating and Assessment Guide GAO-09-3SPDocumento440 pagineGAO Cost Estimating and Assessment Guide GAO-09-3SPalphajulietNessuna valutazione finora
- Cost - Code Data Date PR.01 PR.02 27-Jan-12 SC.01 27-Jan-12 SC.02 27-Jan-12 SC.03 27-Jan-12Documento18 pagineCost - Code Data Date PR.01 PR.02 27-Jan-12 SC.01 27-Jan-12 SC.02 27-Jan-12 SC.03 27-Jan-12Zitheeq UmarNessuna valutazione finora