Documenti di Didattica
Documenti di Professioni
Documenti di Cultura
Questions While Teaching in The Class Discussion: A Higher Level Activity
Caricato da
sokkanlingamDescrizione originale:
Titolo originale
Copyright
Formati disponibili
Condividi questo documento
Condividi o incorpora il documento
Hai trovato utile questo documento?
Questo contenuto è inappropriato?
Segnala questo documentoCopyright:
Formati disponibili
Questions While Teaching in The Class Discussion: A Higher Level Activity
Caricato da
sokkanlingamCopyright:
Formati disponibili
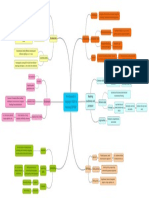
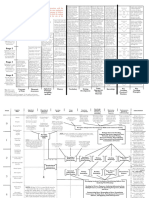
oral
Questions while teaching in the class
written 1. Questions
Discussion
oral-written
Eg: is it clear?
during teaching
do you get it?
2. Teaching Questions/ Testing questions
in examination, assignment, test....
Mental process
look for information in the texts "COGNITION"
"FACTS" 1. Factual involved in any kind of learning
A higher level activity
directly available when we look at the skills, especially Reading
inferring from the context "Read between the lines" 2. Inferential
basically cognitive in nature
personal feelings Evaluation
Three types of Q All skills
choices
bring
knowledge
journal - ELIJ
Reading research quarterly
experience
"Read beyond the lines" 3. Evaluative
deduce
ELTJ
deduct context - not available directly in the text-
TESOL
assume
Journal for reading skills Language learning
Every question should have very clear OBJECTIVES
JEFL
introducing theme
Looks at the END product of reading
interest
How much, how well are on understand
purpose 1. Product view
Comprehension or 1. (+) comprehension Complete comprehension
need to do something
WHAT happens at the RESULT of the reading no comprehension
2. (+, -) comprehension partial comprehension
identification
Motivation 1. pre-reading stage
3. (-) comprehension Nill (Zero) comprehension
curiosity
HOW does one read?
activates thinking
Questions
Two views of reading HOW to manage to comprehension?
provokes related framework
information in the text is already available in our cognition and
meaning captured
no pat of the text is new or unknown, unfamiliar
complete,
Stages
guessing approximation 1. TOP-DOWN PROCESS total comprehension
information flows from the cognition, storage and
checks with the text and finds that the text is already familiar
2. reading stage 2. Process view
some parts of the text are known
3. post reading stage partial unsuccessful,
2. INTERACTIVE PROCESS partial successful comprehension
while reading, we can GUESS "MEANING" of the unknown
4. teaching reading class room
Reading skills (RG) some parts of the text are new with the help of contextual clues.
no part of the text is known and everything is new
Comprehension starts form the text and
Detailed text
3. BOTTOM-UP PROCESS moves towards the cognition storage
unless, the words, expression, concepts, etc given in the text,
to teach vocabulary, grammar, reading, writing become known and familiar, comprehension will not take place
1. Intensive Reading
to give a close knowledge of the details
teaching everything slow + comprehension How do we understand reading?
two types
non-detailed text What is reading?
for reading, for pleasure, enjoyment How does one read and understand?
2. Extensive Reading
Eg: newspaper, page How does one fail to read and understand?
for general information SKIMMING
learn how to guess meaning Who is a good Reader?
fast + comprehension, rapid reading
Eg: film, theater, time for specific information SCANNING Who is an average of poor reader?
in general 1. Global comprehension Why, how some one become a poor, average and good reader,
Reading Comprehension what are the factors affect reading?
Questions
in specific 2. Local comprehension
Reading (types) Can one improve reading skills?
Reading silently
Can one become better reader, how?
skill
all adult reading is silent reading,
+ speed comprehension, not disturb reading aloud Why can't become better reader?
Reading activity
sub-vocalization Is reading skill essential? useful activity?
Mechanics
index finger Will there be problems, if I do not reading?
natural group chunks of information LSRW - are interlinked?
EYE-SPAN
Meaningful chunks
involves a number of activities
a complex process
who has words, syntax, meanings Inter-related process (Cyclical process)
previous knowledge 1. Every Reader uses his/her own cognition in reading What is comprehension?
Social knowledge How does comprehension take place?
Readers 1. Location of a piece of information
A set of ideas from experience "COMPREHENSION"
SCHEMA 2. A reader brings "A Lot of Information" into his reading
produce "SCHEMATA" 2. Recognition
3. Reading
The result of several "PROCESS" 4. Re-organization
5. Integration
6. Evaluation
7. Relocate Information
Potrebbero piacerti anche
- Reading Comprehension Mysteries, Grade 3Da EverandReading Comprehension Mysteries, Grade 3Nessuna valutazione finora
- Learning PlanDocumento7 pagineLearning PlanGenevieve HerreraNessuna valutazione finora
- Okay, We'll Do Madam! Use Metrimeter To Answer To The How You Study and Review Your Lessons?Documento1 paginaOkay, We'll Do Madam! Use Metrimeter To Answer To The How You Study and Review Your Lessons?Kyle TansiongcoNessuna valutazione finora
- Lesson Plan 12 - Ela Small GroupsDocumento2 pagineLesson Plan 12 - Ela Small Groupsapi-451776993Nessuna valutazione finora
- Sistema UNO Scope and Sequence 1st GradeDocumento2 pagineSistema UNO Scope and Sequence 1st GradeBryan CastañedaNessuna valutazione finora
- Navotas NAtional High Schoool Eng Dept. HandbookDocumento4 pagineNavotas NAtional High Schoool Eng Dept. Handbookmarco_meduranda100% (1)
- A Walk Through The Unit: LessonsDocumento1 paginaA Walk Through The Unit: LessonsMaría AvendañoNessuna valutazione finora
- Rewritable Semantic MapDocumento1 paginaRewritable Semantic Mapapi-574003540Nessuna valutazione finora
- P. Ed. 607 - DEVELOPMENTAL READING 1Documento9 pagineP. Ed. 607 - DEVELOPMENTAL READING 1Edlyn SarmientoNessuna valutazione finora
- Reading Intervention Plan CATCH UP FRIDAY READING 1Documento4 pagineReading Intervention Plan CATCH UP FRIDAY READING 1Katreen FelipeNessuna valutazione finora
- Development of Language Skills in Teaching ESPDocumento1 paginaDevelopment of Language Skills in Teaching ESPLUIS IVAN LLUMIQUINGA GUAMANNessuna valutazione finora
- Individual Learning Monitoring PlanDocumento2 pagineIndividual Learning Monitoring PlanOLIVE RAMOSNessuna valutazione finora
- Special Education Contemporary Perspectives For School Professionals 5th Edition Ebook PDFDocumento62 pagineSpecial Education Contemporary Perspectives For School Professionals 5th Edition Ebook PDFzelma.bennett12897% (37)
- Silabus: Jurusan Pendidikan Bahasa InggrisDocumento3 pagineSilabus: Jurusan Pendidikan Bahasa InggrisRusdin SurflakeyNessuna valutazione finora
- Plan 2ap 30 Ene - 04 Feb JRZ MontemayorDocumento10 paginePlan 2ap 30 Ene - 04 Feb JRZ MontemayorCLAUDIA ALEJANDRA FRANCONessuna valutazione finora
- RW - Dll-Week 15Documento5 pagineRW - Dll-Week 15Cherilyn M NimerNessuna valutazione finora
- WednesdayDocumento2 pagineWednesdayWan FirdauzNessuna valutazione finora
- Lesson Plan G8Documento8 pagineLesson Plan G8Keannu EstoconingNessuna valutazione finora
- Plan 3ap 30 Ene - 04 Feb JRZ MontemayorDocumento10 paginePlan 3ap 30 Ene - 04 Feb JRZ MontemayorCLAUDIA ALEJANDRA FRANCONessuna valutazione finora
- SMK SyllabusDocumento44 pagineSMK SyllabusRafika NuraidaNessuna valutazione finora
- 2021-2022 P3 Upper-Int Student Course OutlineDocumento10 pagine2021-2022 P3 Upper-Int Student Course OutlineEyNessuna valutazione finora
- SC Te1Documento5 pagineSC Te1AHMED AL-ZUMAIRNessuna valutazione finora
- Increasing Parenting Skills and Parenting E Cacy: Parent-Training Program Based Seamless Learning To Promoting Assessment Child DevelopmentDocumento1 paginaIncreasing Parenting Skills and Parenting E Cacy: Parent-Training Program Based Seamless Learning To Promoting Assessment Child Developmentkerja malamNessuna valutazione finora
- 08.06.2018 - Lesson Plan - Inter - Habits of Successful People - Trinhntt4Documento8 pagine08.06.2018 - Lesson Plan - Inter - Habits of Successful People - Trinhntt4Tihomir BozicicNessuna valutazione finora
- Toaz - Info Eapp Curriculum Map PRDocumento5 pagineToaz - Info Eapp Curriculum Map PRRonelle San buenaventuraNessuna valutazione finora
- Individual Learning Monitoring Plan GuronewsDocumento2 pagineIndividual Learning Monitoring Plan GuronewsManilyn VillareyNessuna valutazione finora
- WLP English 10Documento6 pagineWLP English 10Mary Joy IgnacioNessuna valutazione finora
- This Course Develops Critical Thinking and Problem-Solving Skills Through Qualitative ResearchDocumento5 pagineThis Course Develops Critical Thinking and Problem-Solving Skills Through Qualitative ResearchAdrian Reyes Capalar100% (3)
- Planifikimi Tremujorit Te Pare First Period Planning September-December FIELD: Languages and Communication Subject: English V First Period - 39 HoursDocumento13 paginePlanifikimi Tremujorit Te Pare First Period Planning September-December FIELD: Languages and Communication Subject: English V First Period - 39 HoursFatjona Cibuku HysolliNessuna valutazione finora
- Grade 1: Monday Tuesday Wednesday Thursday FridayDocumento5 pagineGrade 1: Monday Tuesday Wednesday Thursday FridayEvan Maagad LutchaNessuna valutazione finora
- 11.º Ano ContinuaçãoDocumento6 pagine11.º Ano ContinuaçãoRafael BorgesNessuna valutazione finora
- Reflecting On The Teaching and Learning CycleDocumento1 paginaReflecting On The Teaching and Learning CycleLeslie TorresNessuna valutazione finora
- Literature and PhilosophyDocumento11 pagineLiterature and PhilosophyLarbi NadiaNessuna valutazione finora
- Siti Nur Vadilah - 20237470018 - MATRIX OF REFERENCES OF GROUP 9Documento12 pagineSiti Nur Vadilah - 20237470018 - MATRIX OF REFERENCES OF GROUP 9vadilahNessuna valutazione finora
- Daily Lesson Plan - Form 1Documento1 paginaDaily Lesson Plan - Form 1Rozita KadirNessuna valutazione finora
- Observation ListeningDocumento4 pagineObservation ListeningЮлия КонашNessuna valutazione finora
- The Arts and Creativity: Personal Lifelong Learning PlanDocumento5 pagineThe Arts and Creativity: Personal Lifelong Learning PlanJahariah CernaNessuna valutazione finora
- Chapter 1 ActivitiesDocumento5 pagineChapter 1 ActivitiesCherry Ann Marcial NabascaNessuna valutazione finora
- Assessment Assignment 1Documento6 pagineAssessment Assignment 1api-285082666Nessuna valutazione finora
- 1° Ingles Student Book PDFDocumento19 pagine1° Ingles Student Book PDFYoshi DávilaNessuna valutazione finora
- English For Academic and Professional PurposesDocumento6 pagineEnglish For Academic and Professional PurposesOniuqa Santos MJ100% (1)
- 4.educational Perspectives and Readers Reading LiteratureDocumento1 pagina4.educational Perspectives and Readers Reading LiteraturefentipratamaNessuna valutazione finora
- PA00ZXQWDocumento27 paginePA00ZXQWJuasadf IesafNessuna valutazione finora
- American Family and Friends 2e Level 4 Teachers BookDocumento169 pagineAmerican Family and Friends 2e Level 4 Teachers BookSan Htiet OoNessuna valutazione finora
- Grade 11 Reading Intervention PlanDocumento5 pagineGrade 11 Reading Intervention PlanReimberto AlfaroNessuna valutazione finora
- Fidp Eapp 2021 2022Documento12 pagineFidp Eapp 2021 2022Mikkaella RimandoNessuna valutazione finora
- Eng.107 MidtermDocumento5 pagineEng.107 MidtermJeezreel AgadNessuna valutazione finora
- 5° Ingles Student BookDocumento19 pagine5° Ingles Student BookDaniel JarquinNessuna valutazione finora
- 6 Annual Planner FinalDocumento22 pagine6 Annual Planner FinalRavi DharawadkarNessuna valutazione finora
- Year 3 Lesson 63Documento3 pagineYear 3 Lesson 63TEE LENessuna valutazione finora
- ARW1 Correlation Online Resources and LGOOsDocumento6 pagineARW1 Correlation Online Resources and LGOOsFabian RuizNessuna valutazione finora
- Carolina ADocumento1 paginaCarolina Aapi-512818325Nessuna valutazione finora
- Didactics of English Mind MapDocumento2 pagineDidactics of English Mind MapIVONNE GARCIANessuna valutazione finora
- Things I Do Y3Documento16 pagineThings I Do Y3aidaatozNessuna valutazione finora
- Mouse and Me Plus Brochure - EnglishDocumento12 pagineMouse and Me Plus Brochure - EnglishAhmedSamehNessuna valutazione finora
- Teaching Guide 21st CenturyDocumento34 pagineTeaching Guide 21st CenturyRoi Skiyon BrownNessuna valutazione finora
- fs4 (Episode 4)Documento11 paginefs4 (Episode 4)Ces Reyes50% (2)
- Stages of Literacy ChartsDocumento3 pagineStages of Literacy Chartsbyunbacooon456Nessuna valutazione finora
- Reading Rubric Grade5 2013Documento3 pagineReading Rubric Grade5 2013Ivan IC100% (1)
- Term Month Unit Topic Standard S Competencie S Skills Assessment Strategies Activities Resources Institutional Core ValueDocumento5 pagineTerm Month Unit Topic Standard S Competencie S Skills Assessment Strategies Activities Resources Institutional Core ValueRoss OsorabNessuna valutazione finora
- Ideas: The Correlation Between Vocabulary Achievement and Reading ComprehensionDocumento17 pagineIdeas: The Correlation Between Vocabulary Achievement and Reading ComprehensionsokkanlingamNessuna valutazione finora
- Implementation of Mind Mapping Technique To Improve Students' Reading Comprehension in Descriptive TextDocumento7 pagineImplementation of Mind Mapping Technique To Improve Students' Reading Comprehension in Descriptive TextsokkanlingamNessuna valutazione finora
- Unit-I: Epistemological Bases of EducationDocumento14 pagineUnit-I: Epistemological Bases of EducationsokkanlingamNessuna valutazione finora
- Module 1 - British Literature For UGC NET - JRF English LiteratureDocumento12 pagineModule 1 - British Literature For UGC NET - JRF English Literaturesokkanlingam0% (1)
- Advt. Assistant ProfessorDocumento16 pagineAdvt. Assistant ProfessorsokkanlingamNessuna valutazione finora
- Evolution and Revolution in Artificial Intelligence in EducationDocumento18 pagineEvolution and Revolution in Artificial Intelligence in EducationsokkanlingamNessuna valutazione finora
- Interpersonal Skills List and ExamplesDocumento10 pagineInterpersonal Skills List and ExamplessokkanlingamNessuna valutazione finora
- Order of Adjectives - Language Quiz (Answers)Documento3 pagineOrder of Adjectives - Language Quiz (Answers)sokkanlingamNessuna valutazione finora
- Shortcut Keys For MS OfficeDocumento5 pagineShortcut Keys For MS OfficesokkanlingamNessuna valutazione finora
- Main Theme: Classroom Management Sub-Themes:: Call For PapersDocumento2 pagineMain Theme: Classroom Management Sub-Themes:: Call For PaperssokkanlingamNessuna valutazione finora
- Home Computers Laptops Lenovo Laptops: Lenovo G50-80 (80E5021XIN) G Series G50-80 80E50..Documento7 pagineHome Computers Laptops Lenovo Laptops: Lenovo G50-80 (80E5021XIN) G Series G50-80 80E50..sokkanlingamNessuna valutazione finora
- Second and Foreign Language Teaching Methods - MoraModulesDocumento26 pagineSecond and Foreign Language Teaching Methods - MoraModulessokkanlingam100% (1)
- Gavin Dudeney - Digital Literacy PrimerDocumento5 pagineGavin Dudeney - Digital Literacy Primersokkanlingam100% (1)
- Psychology TheoriesDocumento35 paginePsychology TheoriessokkanlingamNessuna valutazione finora
- 994 - Future Oriented 07062012Documento85 pagine994 - Future Oriented 07062012sokkanlingamNessuna valutazione finora
- Joshua Hakimian Cover LetterDocumento1 paginaJoshua Hakimian Cover Letterapi-290965174Nessuna valutazione finora
- Muet Speaking Exe (210519)Documento5 pagineMuet Speaking Exe (210519)Ida Ikhwan 이다 잌환Nessuna valutazione finora
- Mentoring TemplateDocumento13 pagineMentoring TemplateshalinaNessuna valutazione finora
- The Conjunction Analysis in David Beckham Speech: Vicky Rahmat Tanjung, SudiyonoDocumento7 pagineThe Conjunction Analysis in David Beckham Speech: Vicky Rahmat Tanjung, Sudiyonofirdaus adrNessuna valutazione finora
- Windows Phone Taxi Client: Software Requirements SpecificationDocumento19 pagineWindows Phone Taxi Client: Software Requirements SpecificationMihai ȘvețNessuna valutazione finora
- Reading. Forbes. 9 Differences Between Being A Leader and A ManagerDocumento5 pagineReading. Forbes. 9 Differences Between Being A Leader and A ManagerHiNessuna valutazione finora
- Telecommunication Numbering PlanDocumento25 pagineTelecommunication Numbering PlanphelomenaNessuna valutazione finora
- Professional Education QuestionsDocumento3 pagineProfessional Education QuestionsGie Marie Francisco Umali100% (1)
- Mawada Mohammed-CvDocumento3 pagineMawada Mohammed-Cvapi-380948601Nessuna valutazione finora
- Nitin Rawat: June 19 - PresentDocumento2 pagineNitin Rawat: June 19 - PresentBharat SaraswatNessuna valutazione finora
- Blending LearningDocumento4 pagineBlending Learningafeesha charlesNessuna valutazione finora
- Rich Learning Program: It'S Effectiveness On Btvted Students Different Learning Styles Amidst Covid 19 PandemicDocumento2 pagineRich Learning Program: It'S Effectiveness On Btvted Students Different Learning Styles Amidst Covid 19 PandemicAngelo RamiloNessuna valutazione finora
- Module in Purposive Com - Unit 2Documento12 pagineModule in Purposive Com - Unit 2Clarissa JuvidaNessuna valutazione finora
- PROPOSAL For Provision of Lang Lab-PAPPDocumento6 paginePROPOSAL For Provision of Lang Lab-PAPPDeddy Jait100% (1)
- Special Topics Case 1 & 2Documento3 pagineSpecial Topics Case 1 & 2elai loyNessuna valutazione finora
- United States Patent: (10) Patent No .: US 10,492,021 B2Documento20 pagineUnited States Patent: (10) Patent No .: US 10,492,021 B2Diogo CorreaNessuna valutazione finora
- PED 11 Portfolio ABELLA - 072041Documento72 paginePED 11 Portfolio ABELLA - 072041RAYGELLE MAE ALQUIZANessuna valutazione finora
- Impact of Culture On MarketingDocumento21 pagineImpact of Culture On MarketingmahalaxmiiNessuna valutazione finora
- Edl 201Documento14 pagineEdl 201Mina Flor RiofloridoNessuna valutazione finora
- Elaboracion de Una Escala de Actitudes Hacia La Educacion MulticulturalDocumento502 pagineElaboracion de Una Escala de Actitudes Hacia La Educacion MulticulturalJovi Griego100% (2)
- School Counseling Core Curriculum Action Plan (Academic)Documento2 pagineSchool Counseling Core Curriculum Action Plan (Academic)Cristina Vasquez50% (2)
- Unit of WorkDocumento3 pagineUnit of Workapi-359681874Nessuna valutazione finora
- Quality Management - Differing Perspectives On QualityDocumento13 pagineQuality Management - Differing Perspectives On QualitypandaNessuna valutazione finora
- BBA BRW 2024 Course HandoutDocumento3 pagineBBA BRW 2024 Course HandoutSahithiNessuna valutazione finora
- Department of Education: Individual Workweek Accomplishment ReportDocumento5 pagineDepartment of Education: Individual Workweek Accomplishment ReportARMANDO RESQUIRNessuna valutazione finora
- Lorem Ipsum PDFDocumento1 paginaLorem Ipsum PDFo livro infantil100% (1)
- Full Download Essentials of Business Communication 10th Edition Guffey Test BankDocumento35 pagineFull Download Essentials of Business Communication 10th Edition Guffey Test Bankblackinghemmeldsu0100% (32)
- The Power of Words Cloze TestDocumento4 pagineThe Power of Words Cloze TestAngel Angeleri-priftis.Nessuna valutazione finora
- Sample AE2 Writing - Essay THUDocumento3 pagineSample AE2 Writing - Essay THUThu Thu100% (1)
- Instructional Leadership: Becoming An Exemplary Instructional LeaderDocumento15 pagineInstructional Leadership: Becoming An Exemplary Instructional LeaderRyan Inopia86% (7)