Documenti di Didattica
Documenti di Professioni
Documenti di Cultura
Signs & Symptoms: Fluid and Electrolyte Imbalances
Caricato da
MerielLouiseAnneVillamil0 valutazioniIl 0% ha trovato utile questo documento (0 voti)
10 visualizzazioni3 pagineoral rev
Titolo originale
Chronic Renal Failure
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Formati disponibili
DOCX, PDF, TXT o leggi online da Scribd
Condividi questo documento
Condividi o incorpora il documento
Hai trovato utile questo documento?
Questo contenuto è inappropriato?
Segnala questo documentooral rev
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Formati disponibili
Scarica in formato DOCX, PDF, TXT o leggi online su Scribd
0 valutazioniIl 0% ha trovato utile questo documento (0 voti)
10 visualizzazioni3 pagineSigns & Symptoms: Fluid and Electrolyte Imbalances
Caricato da
MerielLouiseAnneVillamiloral rev
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Formati disponibili
Scarica in formato DOCX, PDF, TXT o leggi online su Scribd
Sei sulla pagina 1di 3
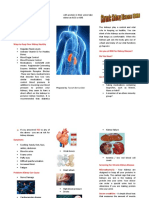
CHRONIC RENAL FAILURE A blood urea nitrogen (BUN) test measures how interference with the system of the
much nitrogen from the waste product urea is in renin-angiotensin-aldosterone system
Chronic kidney disease, also called chronic kidney your blood. BUN level rises when the kidneys (caused by renal dysfunction).
failure, describes the gradual loss of kidney function. aren't working well enough to remove urea from
the blood. 3 Investigate complaints of chest
Signs & Symptoms pain, note the location, radiation,
Nausea A fasting blood glucose test is done to measure severity (0-10 scale).
Vomiting R: HT and CRF can cause pain.
your blood sugar. High blood sugar
Loss of appetite levels damage blood vessels in the kidneys.
4 Assess activity level, response to
Fatigue and weakness
activity.
Sleep problems Blood tests measure levels of waste products R: Fatigue can also accompany
Changes in how much you urinate and electrolytes in your blood that should be CRF anemia.
Decreased mental sharpness removed by your kidneys. 2. Fluid and Electrolyte
Muscle twitches and cramps imbalances related
Swelling of feet and ankles Urinalysis (UA) and a urine test for micro to secondary edema (fluid volume
Persistent itching albumin, or other urine tests, can measure unbalanced because of the
Chest pain, if fluid builds up around the lining protein in your urine. Normally there is little or retention of Na and H2O).
no protein in urine Interventions:
of the heart
1 Assess fluid status with daily weigh,
Shortness of breath, if fluid builds up in the
balance input and output, skin turgor,
lungs Perform an ultrasound or CT scan to get a
vital signs.
High blood pressure (hypertension) that's picture of your kidneys and urinary tract.
difficult to control 2 Limit your fluid intake.
Etiology Perform a kidney biopsy, which is done in R: fluid restriction akn determine ideal
Type 1 or type 2 diabetes some cases to check for a specific type of body weight, urine output, and response
High blood pressure kidney disease, see how much kidney damage to therapy.
Glomerulonephritis an inflammation of the has occurred and help plan treatment
kidney's filtering units (glomeruli) Medications 3 Explain to the patient and family about
Interstitial nephritis an inflammation of the ACE inhibitors. high blood pressure the liquid restrictions.
kidney's tubules and surrounding structures Angiotensin II receptor blockers (ARBs). R: Understanding to increase cooperation
Polycystic kidney disease Beta-blockers. of patients and families in the fluid
Calcium channel blockers. restriction.
Prolonged obstruction of the urinary tract,
from conditions such as enlarged prostate, Direct renin inhibitors.
4. Instruct the patient / teach the patient to
kidney stones and some cancers Diuretics. For edema record the use of fluid intake and output
Vesicoureteral reflux, a condition that causes Vasodilators mainly.
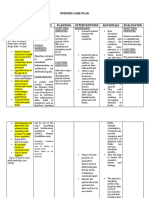
urine to back up into your kidneys Nursing Diagnosis R: To determine the balance of inputs and
Recurrent kidney infection, also called 1. Decreased Cardiac Output related outputs.
pyelonephritis to increased cardiac load.
Labs and diagnostic test Interventions: 3. Imbalanced Nutrition, Less Than
A blood creatinine test helps to estimate 1 Auscultation of heart and lung Body Requirements related to
the glomerular filtration rate (GFR) by sounds. anorexia, nausea, vomiting.
measuring the level of creatinine in your blood. R: The presence of tachycardia, Interventions
The doctor can use the GFR to regularly check irregular heart rate. 1 Monitor the consumption of foods /
how well the kidneys are working and liquids.
to stage your kidney disease. 2 Assess for hypertension. R: Identifying nutritional deficiencies.
R: Hypertension may occur due to
2 Notice of nausea and vomiting. presence of redness. medulla is triangular regions with a striped appearance,
R: Symptoms that accompany R: Indicates area of poor circulation
the medullary pyramids.
the accumulation of endogenous toxins or damage that may lead to the
that can alter or lower income and require formation of pressure sores /
intervention. infections. The broader base of each pyramid faces
toward the inner region of the kidney. The pyramids are
3 Give food a little but often. 2 Monitor fluid intake
R: The portion of a smaller can increase and hydration of the skin and mucous separated by extensions of cortex-like tissue, the renal
food intake. membranes. columns. Medial to the hilus is a flat, basinlike cavity,
R: Detecting the presence of
4 Increase visits by people nearby during dehydration or overhydration the renal pelvis. The pelvis is continuous with the
meals. affecting circulation and tissue ureter leaving the hilus. Extensions of the pelvis,
R: Provides transfer and improve the integrity.
social aspects. 3 Inspection of the area depends on calyces, form cup-shaped areas that enclose the tips of
edema the pyramid. The calyces collect urine, which
5. Provide frequent mouth care. R: Tissue edema is more likely to be
R: Lowering stomatitis oral discomfort damaged / torn. continuously drains from the tips of the pyramids into
and unwelcome taste in the mouth that 4 Change positions as often as the renal pelvis. Urine then flows from the pelvis into
can affect food intake. possible.
4. Ineffective Breathing R: Reduce pressure on edema, poorly te ureter, which transports it to the bladder.
Pattern related to perfused tissue to reduce ischemia.
hyperventilation secondary: Blood supply
compensation via respiratory 5. Give skin care.
alkalosis. R: Reduce drying, skin tears. The kidneys continuously cleanse the blood
Interventions
1 Auscultation of breath sounds, note the and adjust its composition, so it is not surprising that
presence of crakles. Anatomy and Physiology kidney have a very rich blood supply. Approximately
R: To declare the existence of the Kidneys
collection of secretions. one-quarter of the total blood supply of the body passes
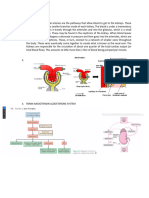
Kidneys are located in the lower back, this is through the kidneys each minute. The arterial supply of
2 Teach patient effective coughing and
deep breathing. not their location. Instead, these small, dark red organs each kidney is the renal artery. As the renal artery
R: Cleaning the airway and facilitate the with a kidney-bean shaped lie against the dorsal body approaches the hilus, it divides into segmental arteries.
flow O2.
wall in a retroperitoneal position in the superior lumbar Once inside the pelvis, the segmental artery break up
3 Adjust the position as comfortable as region. The kidneys extend from the T12 to L3 into lobar arteries, each of which gives off several
possible.
R: Preventing the occurrence of shortness veterbrae thus they receive some protection from the branches called interlobar arteries. At the medulla-
of breath. lower part of the rib cage. cortex junction, interlobar arteries give off the acuate
4 Limit to move. arteries, which curve over the medullary pyramids.
When a kidney is cut lengthwise, three distinct
R: Reduce workload and prevent
tightness or hypoxia. regions become apparent. The outer region which is Venous blood draining from the kidney flows
5. Impaired Skin Integrity related to light in color, is the renal cortex. Deep to the cortex is a through veins that trace the pathway of the arterial
pruritis
Interventions darker reddish-brown area, the renal medulla. The blood supply but in reverse direction interlobular
1. Inspection of the skin to change veins to arcuate veins to interlobar veins to the renal
color, turgor, vascular, note the
vein, which emerges from the kidney hilus.
Nephrons and Urine Formation The different tubules have specific names: Urine Formation
proximal convoluted tubule (PCT), loop of henle, and
Nephrons Urine formation is a result of three processes
the distal convoluted tubule (DCT)
filtration, reabsorption, and secretion.
Each kidney contains over a million tiny
Most nephrons are called cortical nephrons
structures called nephrons. Nephrons are the structural 1.) Glomerular filtration creates a plasmalike
because they are located almost entirely within the
and functional units of the kidneys and as such they are filtrate of the blood
cortex. In a few cases, the nephrons are called 2.) Tubular reabsorption removes useful solutes
responsible for forming the urine product. Each
juxtamedullary nephrons because they are situated from the filtrate, returns them to the blood
nephron consist of two main structures: a glomerulus,
close to the cortex-medulla junction. The collecting 3.) Tubular secretion removes additional wastes
which is a knot of capillaries, and a renal tubule.
ducts, each of which receives urine from many from the blood and adds them to the filtrate
Bowmans capsule a cup-shaped and completely 4.) Water conservation removes water from the
nephrons, run downward through the medullary
surrounds the glomerulus. The inner layer of the urine and returns it to the blood, concentrates
pyramids, delivering the final urine product into
capsule is made up of higly modified octopus like cells wastes
calyces and renal pelvis.
called podocytes. Podocytes have long branching
processes called pedicels that interwine with one The glomerulus is both fed and drained by
another and cling to the glomerulus. arterioles. The afferent arteriole, which arises from an
interlobular artery. The efferent arteriole receives blood
that has passed through the glomerulus.
Potrebbero piacerti anche
- NCP ProperDocumento9 pagineNCP Properstephanie eduarteNessuna valutazione finora
- Renal FailureDocumento19 pagineRenal FailuredianaNessuna valutazione finora
- By: Yzobelle RedondoDocumento4 pagineBy: Yzobelle RedondoArabelle GONessuna valutazione finora
- Kidney FailureDocumento4 pagineKidney FailureAslimah RakimNessuna valutazione finora
- A Computer Generated Number: Prepared By: Tawiah Bernice EbbiDocumento2 pagineA Computer Generated Number: Prepared By: Tawiah Bernice EbbiAfia Tawiah100% (1)
- AKI Developing Critical Thinking Through Understanding Pathophysiology-1-6Documento5 pagineAKI Developing Critical Thinking Through Understanding Pathophysiology-1-6Anonymous StudentNessuna valutazione finora
- Renal System: Diagnostic ExaminationsDocumento8 pagineRenal System: Diagnostic Examinationsjoan olanteNessuna valutazione finora
- Cystatin C A Comparison To Creatinine and Other Clearance MarkersDocumento5 pagineCystatin C A Comparison To Creatinine and Other Clearance MarkersRalphael CataloNessuna valutazione finora
- Renal Concept MapDocumento1 paginaRenal Concept MapShaira Ann CalambaNessuna valutazione finora
- NCP1 LimDocumento3 pagineNCP1 LimRica RegasaNessuna valutazione finora
- Assessment Diagnosis Planning Intervention-Rationale Evaluation Fluid Volume Excess Related ToDocumento3 pagineAssessment Diagnosis Planning Intervention-Rationale Evaluation Fluid Volume Excess Related ToJen BallesterosNessuna valutazione finora
- Chronic Renal Failure Nursing Care PlanDocumento6 pagineChronic Renal Failure Nursing Care PlanRuva Oscass JimmyNessuna valutazione finora
- Laboratory TestsDocumento5 pagineLaboratory TestsLouise Alysson OrtegaNessuna valutazione finora
- DialysisDocumento7 pagineDialysisAhmed SabryNessuna valutazione finora
- All About Chronic Kidney Disease (CKD) : Fact SheetDocumento4 pagineAll About Chronic Kidney Disease (CKD) : Fact SheetJar JarNessuna valutazione finora
- Ladja, Irish V. BSN 3-C Laboratory ResultsDocumento13 pagineLadja, Irish V. BSN 3-C Laboratory ResultsEzra LambarteNessuna valutazione finora
- GI Bleeding Team Work - 2nd EditionDocumento9 pagineGI Bleeding Team Work - 2nd EditionUsman Ali AkbarNessuna valutazione finora
- Arcipe Iccu Case 5Documento98 pagineArcipe Iccu Case 5Maria Charis Anne Indanan100% (1)
- Chronic Kidney Disease: Prepared by Zakia RogerDocumento27 pagineChronic Kidney Disease: Prepared by Zakia Rogerbene dugaNessuna valutazione finora
- "Kidney": Klinik Healthcare Dan SurgeriDocumento2 pagine"Kidney": Klinik Healthcare Dan SurgeriKlinikHealthcareMidvalleyNessuna valutazione finora
- A Guide To House Officers in Surgery Casualty ReceptionDocumento19 pagineA Guide To House Officers in Surgery Casualty ReceptionVinicio LabanoNessuna valutazione finora
- Difficulty Voiding: Symptom Flow ChartDocumento2 pagineDifficulty Voiding: Symptom Flow ChartJeff ZhouNessuna valutazione finora
- Dialysis Treatment - A Comprehensive DescriptionDocumento13 pagineDialysis Treatment - A Comprehensive Descriptionrmprskgwk5Nessuna valutazione finora
- Acute Renal Failure: Dr. Rebecca JacobDocumento6 pagineAcute Renal Failure: Dr. Rebecca JacobRevalitha PutriNessuna valutazione finora
- Aki NotesDocumento10 pagineAki NotesGennel Mae GarovilloNessuna valutazione finora
- Assessment Scientific Analysis Planning Intervention Rationale Evaluation Short Term GoalDocumento4 pagineAssessment Scientific Analysis Planning Intervention Rationale Evaluation Short Term GoalJayson OlileNessuna valutazione finora
- NCP Nausea and VomitingDocumento4 pagineNCP Nausea and VomitingKingJayson Pacman06Nessuna valutazione finora
- Drug Study of FurosemideDocumento5 pagineDrug Study of FurosemideAntonette Lei100% (1)
- Acute Renal FailureDocumento10 pagineAcute Renal FailureAlia PutriNessuna valutazione finora
- NCP Liver CirrhosisDocumento2 pagineNCP Liver Cirrhosismarlx5100% (3)
- SssDocumento2 pagineSsssagemontefalco01Nessuna valutazione finora
- Date Physician's Order RationaleDocumento4 pagineDate Physician's Order RationaleJerremy LuqueNessuna valutazione finora
- Final Doctors OrderDocumento4 pagineFinal Doctors OrderKaye Aligato ParaderoNessuna valutazione finora
- Kidney Function Tests 2Documento30 pagineKidney Function Tests 2kamalNessuna valutazione finora
- Nursing Care Plan Diarrhea Assessment Diagnosis Planning Interventions Rationale EvaluationDocumento8 pagineNursing Care Plan Diarrhea Assessment Diagnosis Planning Interventions Rationale EvaluationKrahNessuna valutazione finora
- Urinary System: - Ridho IslamieDocumento27 pagineUrinary System: - Ridho IslamieLaksmi DwiNessuna valutazione finora
- Acute Renal Failure Nursing Care PlanDocumento4 pagineAcute Renal Failure Nursing Care PlanKrisianne Mae Lorenzo Francisco80% (5)
- 313 - Disorders of Renal and Urinary SystemsDocumento8 pagine313 - Disorders of Renal and Urinary SystemsChrissy Mendoza100% (2)
- Perlis CRF Renal ReplacementDocumento65 paginePerlis CRF Renal ReplacementFikri SeptianNessuna valutazione finora
- Renal Function TestsDocumento38 pagineRenal Function TestsSupriya NayakNessuna valutazione finora
- Laboratory and Diagnostic ProceduresDocumento12 pagineLaboratory and Diagnostic ProceduresKrishcel Canlapan InsoNessuna valutazione finora
- Benign Prostatic Hyperplasia. NCM 109Documento16 pagineBenign Prostatic Hyperplasia. NCM 109Niña Jean Tormis AldabaNessuna valutazione finora
- SC Aspera, Hazel-Gin Lorenzo: History of Present IllnessDocumento4 pagineSC Aspera, Hazel-Gin Lorenzo: History of Present IllnessHazel AsperaNessuna valutazione finora
- CKD Case StudyDocumento27 pagineCKD Case StudyMary Rose Vito100% (1)
- Nursing Care Plan 1Documento1 paginaNursing Care Plan 1Janhabi BeheraNessuna valutazione finora
- NCP Excess Fluid VolumeDocumento4 pagineNCP Excess Fluid VolumeIngrid Nicolas100% (1)
- NCM 106: Self Directed Learning Activity Name and Section: John Michael O. Villanueva BSN 2 ADocumento4 pagineNCM 106: Self Directed Learning Activity Name and Section: John Michael O. Villanueva BSN 2 AKaye PatriarcaNessuna valutazione finora
- Case Pre NotesDocumento3 pagineCase Pre NotesErica FabrigasNessuna valutazione finora
- (KULIAH 1) Penyakit Ginjal 1Documento16 pagine(KULIAH 1) Penyakit Ginjal 1si errikaNessuna valutazione finora
- Global City Innovative CollegeDocumento3 pagineGlobal City Innovative CollegemadypadNessuna valutazione finora
- Acute Renal FailureDocumento3 pagineAcute Renal FailureJASTINE NICOLE SABORNIDONessuna valutazione finora
- Lesion Renal Aguda NursingDocumento6 pagineLesion Renal Aguda NursingYesica Katerine Novoa GarciaNessuna valutazione finora
- K9 Kidney DiseaseDocumento6 pagineK9 Kidney DiseaseKitch MallariNessuna valutazione finora
- Hepatic Dysfunction: Nursing Disease AnalysisDocumento74 pagineHepatic Dysfunction: Nursing Disease AnalysisAisha Valles MalintadNessuna valutazione finora
- NursingDocumento7 pagineNursingHannah Angelu CabadingNessuna valutazione finora
- Assessment Diagnosis Scientific Explanation Objectives Intervention Rationale EvaluationDocumento6 pagineAssessment Diagnosis Scientific Explanation Objectives Intervention Rationale EvaluationKRISTINE BULACANNessuna valutazione finora
- C370 Lecture 1 Lecture Notes Part 1Documento41 pagineC370 Lecture 1 Lecture Notes Part 1Yan Mui ChanNessuna valutazione finora
- Nursing Diagnosis Nursing Diagnosis: Nursing Diagnosis:: Kidney Biopsy - Diffuse Proliferative GlomerulonephritisDocumento1 paginaNursing Diagnosis Nursing Diagnosis: Nursing Diagnosis:: Kidney Biopsy - Diffuse Proliferative GlomerulonephritisRiza Angela BarazanNessuna valutazione finora
- Renal Nursing - HandoutDocumento16 pagineRenal Nursing - HandoutJoms Kim Mina100% (3)
- Ascites, A Simple Guide To The Condition, Treatment And Related ConditionsDa EverandAscites, A Simple Guide To The Condition, Treatment And Related ConditionsNessuna valutazione finora
- ScheduleDocumento1 paginaScheduleMerielLouiseAnneVillamilNessuna valutazione finora
- Evaluation Licensing ChecklistDocumento1 paginaEvaluation Licensing ChecklistMerielLouiseAnneVillamilNessuna valutazione finora
- Hiv AidsDocumento5 pagineHiv AidsMerielLouiseAnneVillamil100% (1)
- Acute Coronary SyndromeDocumento4 pagineAcute Coronary SyndromeMerielLouiseAnneVillamilNessuna valutazione finora
- Discharge PlanDocumento1 paginaDischarge PlanMerielLouiseAnneVillamilNessuna valutazione finora
- Lola A Lola A Lola A Lolo A: Patient RomeoDocumento2 pagineLola A Lola A Lola A Lolo A: Patient RomeoMerielLouiseAnneVillamilNessuna valutazione finora
- Martin Heidegger'S Phenomenology of Death: By: Manuel B. Dy, JRDocumento5 pagineMartin Heidegger'S Phenomenology of Death: By: Manuel B. Dy, JRMerielLouiseAnneVillamilNessuna valutazione finora
- Campus Clubs Organization: Monthly Financial ReportDocumento3 pagineCampus Clubs Organization: Monthly Financial ReportMerielLouiseAnneVillamilNessuna valutazione finora
- PrognosisDocumento2 paginePrognosisMerielLouiseAnneVillamilNessuna valutazione finora
- Nursing Student Executive Council: Budget Proposal For The Month of October 2016Documento2 pagineNursing Student Executive Council: Budget Proposal For The Month of October 2016MerielLouiseAnneVillamilNessuna valutazione finora
- Names (Long Bond Paper)Documento2 pagineNames (Long Bond Paper)MerielLouiseAnneVillamilNessuna valutazione finora
- Aras & FNCPDocumento10 pagineAras & FNCPMerielLouiseAnneVillamilNessuna valutazione finora
- Appendix A Letter To The Barangay CaptainDocumento4 pagineAppendix A Letter To The Barangay CaptainMerielLouiseAnneVillamilNessuna valutazione finora
- AbortionDocumento39 pagineAbortionMerielLouiseAnneVillamilNessuna valutazione finora
- Capsule For GuyabanoDocumento1 paginaCapsule For GuyabanoMerielLouiseAnneVillamilNessuna valutazione finora
- Maternity Signs and FormulaDocumento2 pagineMaternity Signs and FormulaMerielLouiseAnneVillamilNessuna valutazione finora
- Surgical AsepsisDocumento1 paginaSurgical AsepsisMerielLouiseAnneVillamilNessuna valutazione finora
- Sampling MethodsDocumento3 pagineSampling MethodsMerielLouiseAnneVillamilNessuna valutazione finora
- Drug Study (Decocon A)Documento4 pagineDrug Study (Decocon A)MerielLouiseAnneVillamilNessuna valutazione finora
- HPWJ Medical Alert Card SampleDocumento2 pagineHPWJ Medical Alert Card SampleSameer Kumar JubailNessuna valutazione finora
- Essential DrugsDocumento10 pagineEssential DrugsZarish IftikharNessuna valutazione finora
- Pandu Anaemia An Ayurvedic Literature ReviewDocumento7 paginePandu Anaemia An Ayurvedic Literature ReviewAmith G R AnajiNessuna valutazione finora
- Psychiatric TriageDocumento30 paginePsychiatric TriageastroirmaNessuna valutazione finora
- Sujok Global MagazineDocumento52 pagineSujok Global MagazineNidhi ShahNessuna valutazione finora
- OligohydramniosDocumento4 pagineOligohydramniossalamredNessuna valutazione finora
- Nursing Exam Questions 2023 Part 4Documento5 pagineNursing Exam Questions 2023 Part 4Lejo SunnyNessuna valutazione finora
- Anal AbscessDocumento5 pagineAnal AbscessFernia StevaniNessuna valutazione finora
- Overt Diabetes in PregnancyDocumento12 pagineOvert Diabetes in PregnancyGestne AureNessuna valutazione finora
- Koch PostulatesDocumento1 paginaKoch PostulatescdumenyoNessuna valutazione finora
- Insan Anatomisi Atlasi Mcminn 1515167549Documento18 pagineInsan Anatomisi Atlasi Mcminn 1515167549Müslüm ŞahinNessuna valutazione finora
- FDA Marijuana Negative Monograph RejectionDocumento7 pagineFDA Marijuana Negative Monograph RejectionMarijuana MomentNessuna valutazione finora
- Ca BladderDocumento11 pagineCa Bladdersalsabil aurellNessuna valutazione finora
- Anti Dumping DietDocumento3 pagineAnti Dumping DietFelixDrummaruNessuna valutazione finora
- KE153 - Social WorkerDocumento2 pagineKE153 - Social Workerbosco kiuriaNessuna valutazione finora
- Hypertension Pathophysiology and TreatmentDocumento8 pagineHypertension Pathophysiology and TreatmentrizkaNessuna valutazione finora
- Spastic Diplegic Cerebral PalsyDocumento43 pagineSpastic Diplegic Cerebral PalsyRachel GardnerNessuna valutazione finora
- Sme Product Brochure PDFDocumento37 pagineSme Product Brochure PDFNoor Azman YaacobNessuna valutazione finora
- Journal Pediatric IndiaDocumento5 pagineJournal Pediatric IndiaHhhNessuna valutazione finora
- Moh Cimu April 2020Documento9 pagineMoh Cimu April 2020ABC News GhanaNessuna valutazione finora
- Analytical EpidemiologyDocumento64 pagineAnalytical EpidemiologyQueency Dangilan100% (1)
- Office of The Information and Privacy Commissioner of Alberta - Public Inquiry 005994, University of Alberta Freedom of Information RequestDocumento60 pagineOffice of The Information and Privacy Commissioner of Alberta - Public Inquiry 005994, University of Alberta Freedom of Information RequestWilliam Makis100% (3)
- Nursing Care For HipopituitarismeDocumento10 pagineNursing Care For Hipopituitarismevita marta100% (1)
- Potassium Chloride GuidelinesDocumento25 paginePotassium Chloride GuidelinesYasser Gebril86% (7)
- Alemnesh MandeshDocumento94 pagineAlemnesh MandeshDNessuna valutazione finora
- SgotsgptDocumento23 pagineSgotsgptUmi MazidahNessuna valutazione finora
- AcuteExpertSystem PDFDocumento3 pagineAcuteExpertSystem PDFMMHMOONNessuna valutazione finora
- Sales and Distribution Management PDFDocumento30 pagineSales and Distribution Management PDFNalin SenthilNessuna valutazione finora
- Atracurium BesylateDocumento3 pagineAtracurium BesylateAP TOROBXNessuna valutazione finora
- Telepharmacy ResearchDocumento8 pagineTelepharmacy Researchugwuja marcyNessuna valutazione finora