Documenti di Didattica
Documenti di Professioni
Documenti di Cultura
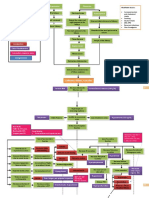
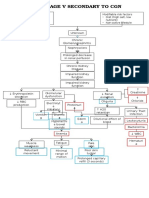
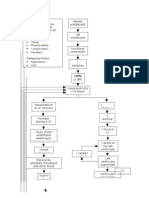
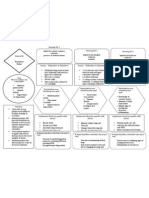
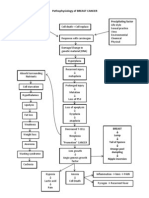
Age Greater Than 60 Y/o Hereditary Precipitating Factors: Hypertension Increase Protein and Fat Intake
Caricato da
nursing concept mapsTitolo originale
Copyright
Formati disponibili
Condividi questo documento
Condividi o incorpora il documento
Hai trovato utile questo documento?
Questo contenuto è inappropriato?
Segnala questo documentoCopyright:
Formati disponibili
Age Greater Than 60 Y/o Hereditary Precipitating Factors: Hypertension Increase Protein and Fat Intake
Caricato da
nursing concept mapsCopyright:
Formati disponibili
Predisposing Factors: Precipitating factors:
Age greater than Hypertension
60 y/o Increase protein
Hereditary and fat intake
Decreased renal blood Extracorporeal
flow Shock Wave
Diabetes mellitus
Lithotripsy (ESWL)
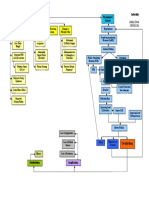
Urine outflow
Increase Increase serum
Decreased
BUN glomerular creatinine
filtration
Hypertrophy of
polyuria Loss of sodium in
remaining
urine
nephrons
dehydration Inability to concentrate Hyponatremia
urine
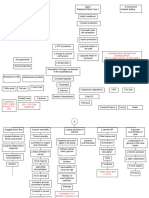
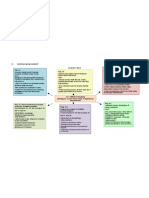
Anxiety related to change in health
Further loss of nephrons
status, relationships, role function
function
and threat of death.
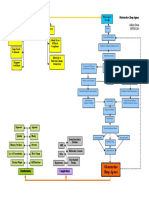
Loss of non-excretory renal Insertion of Intrajugular Loss of excretory renal
Failure to Failure to Impaired vein cather Increase Immune Disturbances
convert produce insulin Production of disturban in
inactive Impaired skin integrity
eryhtropoieti related to
action lipids Risk for infection
ces related to invasive reproduction
forms of insertion n
of permanent IJ catheter procedures (Insertion of permanent IJ
HEMODIALY
secondary to hemodialysis. Cath. And hemodialysis).
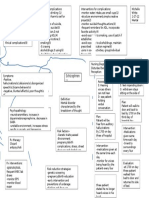
Anemia Erratic blood Advanced
Decrease Pallor atheroscle Delayed Infection Decreas Infertility
Calcium glucose
levels rosis wound e Libido
absorption healing
Vitamin
Hypocalcemia K
Moriamin
Fatigue related to disease states,
altered metabolic energy production
and anemia.
Kalium
Phosphatidyl
Durule
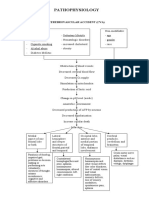
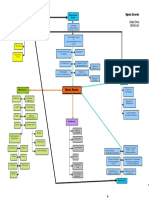
Excretion of Decreased Decreased Decreased Decreased
nitrogenous sodium potassium phosphate hydrogen
waste reabsorption in excretion excretion
tubule excretion
Uremia
Hyperkalemia Hyperphosphatemia Metabolic acidosis
BUN, Water Retention
Excess fluid volume related to
accumulation of fluid in the peritoneal
Creatinine cavity secondary to ascites.
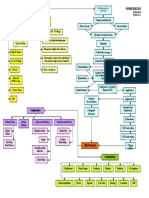
Decreased
Increased
Decreased
calcium
potassium
Hypocalcemia
potassium excretion
absorption
Hyperparathyroidism
Proteniuria
Excess fluid volume related to sodium,
Hypertension
chloride and water retention secondary
Peripheral Heart Failure to chronic kidney failure.
nerve changes
Edema
Acites
Pericarditis Amlodipi Risk for imbalance nutrition: Less than
body requirements related to inability
to ingest or digest food or absorption
CNS changes
nutrients as a result of physiologic
Decreased cardiac output related to
factors
altered myocardial contractility
Pruritus
secondary to chronic kidney failure.
Altered Taste LEGEND:
SIGNS AND SYMPTOMS
Bleeding
Tendencies
NURSING DIAGNOSIS
TREATMENTS and
MEDICATIONS
Potrebbero piacerti anche
- Hypertension Obstruction: Chronic Renal FailureDocumento3 pagineHypertension Obstruction: Chronic Renal FailureDiane-Richie PezLo100% (1)
- End Stage Renal Disease: A. Pathophysiology A. Schematic DiagramDocumento2 pagineEnd Stage Renal Disease: A. Pathophysiology A. Schematic DiagramSharmaine Camille de LeonNessuna valutazione finora
- Precipitating Factors Predisposing Factors Chronic Kidney DiseaseDocumento3 paginePrecipitating Factors Predisposing Factors Chronic Kidney DiseaseGrace Jane DionaldoNessuna valutazione finora
- Path o PhysiologyDocumento9 paginePath o PhysiologyKyle Ü D. CunanersNessuna valutazione finora
- Chronic Kidney Disease: A. Pathophysiology A. Schematic DiagramDocumento3 pagineChronic Kidney Disease: A. Pathophysiology A. Schematic DiagramDaniel GeduquioNessuna valutazione finora
- Pathophysiology of Acute Kidney InjuryDocumento4 paginePathophysiology of Acute Kidney InjuryJane Arian Berzabal0% (1)
- Pathophysio CRF RevisedDocumento2 paginePathophysio CRF Revisedroseanne18Nessuna valutazione finora
- "Acute Coronary Syndrome Non ST Elevation Myocardial Infarction, Hypertensive Cardiovascular Disease, Diabetes Mellitus Type 2, and Community Acquired Pneumonia" Client Centered PathophysiologyDocumento3 pagine"Acute Coronary Syndrome Non ST Elevation Myocardial Infarction, Hypertensive Cardiovascular Disease, Diabetes Mellitus Type 2, and Community Acquired Pneumonia" Client Centered PathophysiologyCarl Elexer Cuyugan Ano50% (2)
- Diabetes Mellitus Type 2 Hospital CaseDocumento3 pagineDiabetes Mellitus Type 2 Hospital CaseAngel FiloteoNessuna valutazione finora
- Pathophysiology of ESRD: Organ Dysfunctions & Associated AbnormalitiesDocumento5 paginePathophysiology of ESRD: Organ Dysfunctions & Associated AbnormalitiesCarl JardelezaNessuna valutazione finora
- CeVD, MI, HCVD & Atrial Fibrillation PathophysiologyDocumento3 pagineCeVD, MI, HCVD & Atrial Fibrillation PathophysiologyJjessmar Bolivar FamaNessuna valutazione finora
- Pathophysiology of Chronic Renal Failure: By: Jonnel Montoya Musngi BSN 4-BDocumento1 paginaPathophysiology of Chronic Renal Failure: By: Jonnel Montoya Musngi BSN 4-BKenrick Randell IbanaNessuna valutazione finora
- Pathophysiology of Liver CirrhosisDocumento2 paginePathophysiology of Liver CirrhosisAprille Rose UrbanoNessuna valutazione finora
- Chronic Renal FailureDocumento3 pagineChronic Renal FailureAura Salve Ildefonso AllasNessuna valutazione finora
- Hypertension Pathophysiology and Treatment PDFDocumento6 pagineHypertension Pathophysiology and Treatment PDFBella TogasNessuna valutazione finora
- PatofkuDocumento3 paginePatofkunisaaa88Nessuna valutazione finora
- CKD - For Concept MappingDocumento7 pagineCKD - For Concept MappingKennette Lim0% (1)
- Pathophysiology of ESRDDocumento3 paginePathophysiology of ESRDjake90210100% (1)
- Pathophysiology of StrokeDocumento4 paginePathophysiology of StrokeACe JAyNessuna valutazione finora
- PathophysiologyDocumento1 paginaPathophysiologynitlihpNessuna valutazione finora
- NCP AgnDocumento2 pagineNCP Agnj3nann3Nessuna valutazione finora
- Osteoarthritis 1583-170210113823Documento34 pagineOsteoarthritis 1583-170210113823Angelic khanNessuna valutazione finora
- Assaz Predisposing Factors: Advanced Age Gender Ileal Resection/Disease RaceDocumento3 pagineAssaz Predisposing Factors: Advanced Age Gender Ileal Resection/Disease RaceryanNessuna valutazione finora
- Addison'sDocumento4 pagineAddison'sKoRnflakesNessuna valutazione finora
- HCVDDocumento5 pagineHCVDkhrizaleehNessuna valutazione finora
- Pathophysio Chronic GlomerulonephritisDocumento1 paginaPathophysio Chronic GlomerulonephritisRan Ma100% (1)
- Gouty Arthritissss PathophyDocumento2 pagineGouty Arthritissss Pathophybilliam123Nessuna valutazione finora
- Bladder Cancer Types, Symptoms, Tests & TreatmentDocumento1 paginaBladder Cancer Types, Symptoms, Tests & TreatmentCarmina AguilarNessuna valutazione finora
- Pathophysiology ESRDDocumento9 paginePathophysiology ESRDJaye DangoNessuna valutazione finora
- Pa Tho Physiology of PIHDocumento2 paginePa Tho Physiology of PIHCarren_Louise__8090Nessuna valutazione finora
- Pathophysiology CKD Secondary To CGNDocumento1 paginaPathophysiology CKD Secondary To CGNNathan Vince CruzNessuna valutazione finora
- Qtsoi Concept MapDocumento5 pagineQtsoi Concept MapGenella BabantoNessuna valutazione finora
- Schematic Diagram of CKD Sec. To DM Nephropathy, DM Type 2, DM FootDocumento8 pagineSchematic Diagram of CKD Sec. To DM Nephropathy, DM Type 2, DM Footbeuwolfagate50% (2)
- Pathophysiology HPN CvaDocumento1 paginaPathophysiology HPN Cvatresdos09Nessuna valutazione finora
- Pathophysiology of Hypertension, Diabetes, Ubm, BPHDocumento3 paginePathophysiology of Hypertension, Diabetes, Ubm, BPHCarly Beth Caparida LangerasNessuna valutazione finora
- Individual Case Study Acute GlomerulonephritisDocumento26 pagineIndividual Case Study Acute GlomerulonephritisBatrisyia HalimsNessuna valutazione finora
- Chronic Kidney Disease Case PresDocumento32 pagineChronic Kidney Disease Case Presnnaesor_1091Nessuna valutazione finora
- Pathophysio CRF2 - RevisedDocumento1 paginaPathophysio CRF2 - Reviseddeborah malnegroNessuna valutazione finora
- XAVIER UNIVERSITY – ATENEO DE CAGAYAN COLLEGE OF NURSING CONCEPT MAP: HYPONATREMIADocumento9 pagineXAVIER UNIVERSITY – ATENEO DE CAGAYAN COLLEGE OF NURSING CONCEPT MAP: HYPONATREMIAElleNessuna valutazione finora
- Nephrotic Syndrome PathophysiologyDocumento1 paginaNephrotic Syndrome PathophysiologyKrisianne Mae Lorenzo FranciscoNessuna valutazione finora
- Pathophysiology of Urinary Tract ObstructionDocumento50 paginePathophysiology of Urinary Tract ObstructionPryo UtamaNessuna valutazione finora
- Impaired Tissue Perfusion Related To The Weakening / Decreased Blood Flow To The Area of Gangrene Due To Obstruction of Blood VesselsDocumento3 pagineImpaired Tissue Perfusion Related To The Weakening / Decreased Blood Flow To The Area of Gangrene Due To Obstruction of Blood VesselsKat AlaNessuna valutazione finora
- Pathophysiology Diagram of Congestive Heart FailureDocumento3 paginePathophysiology Diagram of Congestive Heart FailureLeng Royo BrionesNessuna valutazione finora
- Patof DMDocumento1 paginaPatof DMxerwaneNessuna valutazione finora
- DIabetes Mellitus ! Patho (Complete)Documento8 pagineDIabetes Mellitus ! Patho (Complete)freyaNessuna valutazione finora
- Schistosomiasis (From Anatomy To Pathophysiology)Documento10 pagineSchistosomiasis (From Anatomy To Pathophysiology)Tiger Knee100% (1)
- CHRONIC KIDNEY DISEASE Secondary To Chronic GlomerulonephritisDocumento31 pagineCHRONIC KIDNEY DISEASE Secondary To Chronic GlomerulonephritisJerwin Jade Bolor33% (3)
- Causes and Effects of Uremia in Chronic Kidney DiseaseDocumento17 pagineCauses and Effects of Uremia in Chronic Kidney DiseaseSong Hành Vạn KiếpNessuna valutazione finora
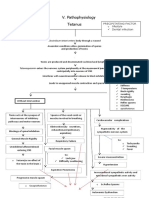
- Pathophysiology of TetanusDocumento2 paginePathophysiology of TetanusAnitha SuprionoNessuna valutazione finora
- Relationship Between CKD Stage and Pulmonary Edema on Chest X-RayDocumento6 pagineRelationship Between CKD Stage and Pulmonary Edema on Chest X-RayAnnisa RabbaniNessuna valutazione finora
- Anemia Unspecified FinalDocumento47 pagineAnemia Unspecified FinalMaria Paula BungayNessuna valutazione finora
- Pathophysiology in Liver CirrhosisDocumento4 paginePathophysiology in Liver CirrhosisCyrus Ortalla RobinNessuna valutazione finora
- CVA PathophysiologyDocumento3 pagineCVA Pathophysiologyshmily_0810Nessuna valutazione finora
- Pathophysiology of Hyperthyroidism and Thyroid StormDocumento3 paginePathophysiology of Hyperthyroidism and Thyroid StormPen MontanteNessuna valutazione finora
- Hypertension PathophysiologyDocumento1 paginaHypertension PathophysiologyZaida Eunice EstabayaNessuna valutazione finora
- Chronic Kidney Disease: A. Pathophysiology A. Schematic DiagramDocumento3 pagineChronic Kidney Disease: A. Pathophysiology A. Schematic DiagramJet Ray-Ann GaringanNessuna valutazione finora
- Pathophysiology of Kidney DiseaseDocumento3 paginePathophysiology of Kidney DiseaseSTEPHANIE JOSUE100% (1)
- Chronic Kidney Disease Pathophysiology Schematic DiagramDocumento3 pagineChronic Kidney Disease Pathophysiology Schematic Diagramnursing concept maps100% (5)
- Asuhan Keperawatan Pada Pasien Dengan Chronic Kidney DiseasesDocumento24 pagineAsuhan Keperawatan Pada Pasien Dengan Chronic Kidney DiseasestidaktahudiriNessuna valutazione finora
- Pathophy DMDocumento1 paginaPathophy DMCarmella CaritosNessuna valutazione finora
- Emphysema Pathophysiology ExplainedDocumento1 paginaEmphysema Pathophysiology ExplainedGil AswiguiNessuna valutazione finora
- Concept Map TemplateDocumento1 paginaConcept Map Templatenursing concept mapsNessuna valutazione finora
- Concept Map BlankDocumento2 pagineConcept Map Blanknursing concept mapsNessuna valutazione finora
- Bipolar Concept MapDocumento3 pagineBipolar Concept Mapnursing concept maps100% (2)
- Bronchial Asthma in Acute Exacerbation BAIAE Pathophysiology Schematic DiagramDocumento3 pagineBronchial Asthma in Acute Exacerbation BAIAE Pathophysiology Schematic DiagramVictor Angelo VeraNessuna valutazione finora
- Patent Ductus Arteriosus PathophsyiologyDocumento3 paginePatent Ductus Arteriosus Pathophsyiologynursing concept mapsNessuna valutazione finora
- Physiological ChangesDocumento1 paginaPhysiological ChangesJilian McGuganNessuna valutazione finora
- Hip FractureDocumento3 pagineHip Fracturenursing concept mapsNessuna valutazione finora
- PATHODocumento2 paginePATHOmycoclitNessuna valutazione finora
- Diagnostics: Disorder & Basic Patho/Etiology: Clinical ManifestationsDocumento1 paginaDiagnostics: Disorder & Basic Patho/Etiology: Clinical Manifestationsnursing concept mapsNessuna valutazione finora
- Diabetes Mellitus Type 2 Schematic DiagramDocumento1 paginaDiabetes Mellitus Type 2 Schematic DiagramJhe Lyn82% (11)
- Mental Health Concept MapDocumento2 pagineMental Health Concept Mapnursing concept mapsNessuna valutazione finora
- PathoPhysiology of Renal Failure OverviewDocumento7 paginePathoPhysiology of Renal Failure Overviewnursing concept maps100% (1)
- Critical Care Concept MapDocumento1 paginaCritical Care Concept Mapkonniep69100% (1)
- ESRD PathophysiologyDocumento2 pagineESRD Pathophysiologynursing concept mapsNessuna valutazione finora
- Pathophysiology of Burn InjuryDocumento1 paginaPathophysiology of Burn InjuryAnonymous XvwKtnSrMR100% (1)
- Infertility Concept MapDocumento1 paginaInfertility Concept Mapnursing concept maps50% (2)
- Sleep Apnea Concept MapDocumento1 paginaSleep Apnea Concept Mapashleydean100% (2)
- Bipolar Disorder Concept MapDocumento1 paginaBipolar Disorder Concept Mapnursing concept maps100% (1)
- Pathophysio CRF2 - RevisedDocumento1 paginaPathophysio CRF2 - Reviseddeborah malnegroNessuna valutazione finora
- Schizophrenia MapDocumento1 paginaSchizophrenia Mapnursing concept mapsNessuna valutazione finora
- Degenerative Disc Disease Concept MapDocumento1 paginaDegenerative Disc Disease Concept Mapnursing concept mapsNessuna valutazione finora
- Osteoarthritis Concept MapDocumento1 paginaOsteoarthritis Concept Mapnursing concept maps0% (1)
- Pituitary Adenoma Concept MapDocumento1 paginaPituitary Adenoma Concept Mapnursing concept mapsNessuna valutazione finora
- Pathophysiology of BREAST CANCERDocumento1 paginaPathophysiology of BREAST CANCERAlinor Abubacar100% (6)
- Nursing Management Concept MapDocumento1 paginaNursing Management Concept MapXy-Za Roy Marie100% (1)
- ARF PathophysiologyDocumento2 pagineARF Pathophysiologykathy100% (9)
- Concept MapDocumento1 paginaConcept Mapnursing concept mapsNessuna valutazione finora
- Hypertension Concept MapDocumento1 paginaHypertension Concept Mapashleydean100% (7)
- CALE Formulas 83 BestDocumento119 pagineCALE Formulas 83 BestAyanna CobbNessuna valutazione finora
- Hallucinations: Soundarya. A - N Roll No.: 112Documento17 pagineHallucinations: Soundarya. A - N Roll No.: 112Jayashree goveraNessuna valutazione finora
- DR Jay Davidson How Invisible Radiation Exposure Robs Your EnergyDocumento6 pagineDR Jay Davidson How Invisible Radiation Exposure Robs Your EnergySkyla ReadNessuna valutazione finora
- February Case StudyDocumento6 pagineFebruary Case Studyapi-210258673Nessuna valutazione finora
- Pain BrochureDocumento24 paginePain Brochurelordhavok33Nessuna valutazione finora
- Fall Risk AssessmentDocumento14 pagineFall Risk AssessmentLa navida Mv100% (1)
- Dementia AssignmentDocumento19 pagineDementia AssignmentVandna Vikram Novlani50% (2)
- Hypospadias Explained: Birth Defect GuideDocumento5 pagineHypospadias Explained: Birth Defect GuideAnonymous MWd5UOUuiyNessuna valutazione finora
- La Consolacion College Manila School of Nursing Course SyllabusDocumento4 pagineLa Consolacion College Manila School of Nursing Course SyllabusJayson Magdael SalvadorNessuna valutazione finora
- 1 +Theresia+Jamini+1-9Documento9 pagine1 +Theresia+Jamini+1-9Florentina yohana ngeluNessuna valutazione finora
- Review of Mirizzi Syndrome Classification and PresentationDocumento5 pagineReview of Mirizzi Syndrome Classification and PresentationNovi WiarniNessuna valutazione finora
- Doctors NoteDocumento3 pagineDoctors NotenanaikungaNessuna valutazione finora
- Entamoeba histolytica (True PathogenDocumento112 pagineEntamoeba histolytica (True PathogenMiaQuiambaoNessuna valutazione finora
- Grading ScaleDocumento2 pagineGrading ScaleFelipe SanchezNessuna valutazione finora
- APPENDICITISDocumento2 pagineAPPENDICITISRichie Marie BajaNessuna valutazione finora
- Case Study 1: Rhinitis AllergyDocumento18 pagineCase Study 1: Rhinitis AllergyAsfiksia NeonatorumNessuna valutazione finora
- Unit Two The Health Benefits of Physical ActivityDocumento10 pagineUnit Two The Health Benefits of Physical ActivityYoseph DefaruNessuna valutazione finora
- AMC MCQ Recalls 2017Documento2 pagineAMC MCQ Recalls 2017prepengo90% (10)
- Cancer Medicine - 2019 - Xiang - Traditional Chinese Medicine As A Cancer Treatment Modern Perspectives of Ancient ButDocumento18 pagineCancer Medicine - 2019 - Xiang - Traditional Chinese Medicine As A Cancer Treatment Modern Perspectives of Ancient ButIstyNessuna valutazione finora
- TURP Procedure Guide for Prostate RemovalDocumento4 pagineTURP Procedure Guide for Prostate RemovalJylme Keziah Manzano DoronioNessuna valutazione finora
- Optimizing Fluid Therapy in Shock.10Documento6 pagineOptimizing Fluid Therapy in Shock.10Paulo Victor100% (1)
- NeuroendosDocumento25 pagineNeuroendosBabu Ramakrishnan100% (1)
- Pathology Course Audit-3Documento26 paginePathology Course Audit-3Joana Marie PalatanNessuna valutazione finora
- Checklist Mgu Sabtu 2016Documento3 pagineChecklist Mgu Sabtu 2016dudi herlambangNessuna valutazione finora
- Abdminal Compartment SyndromeDocumento9 pagineAbdminal Compartment SyndromeRafael BagusNessuna valutazione finora
- Complete Revision Notes by Vincent Helyar and Aidan Shaw 2018Documento645 pagineComplete Revision Notes by Vincent Helyar and Aidan Shaw 2018Zubair Lone100% (4)
- Gastritis Erosif PatofisiologiDocumento3 pagineGastritis Erosif PatofisiologiLargactil CpzNessuna valutazione finora
- PREVENT EXTRAVASATION OF CONTRAST MEDIADocumento4 paginePREVENT EXTRAVASATION OF CONTRAST MEDIAmanishbabuNessuna valutazione finora
- Warwick Boulevard, Newport News, VA 23606-3401 Phone: 757-591-4646Documento2 pagineWarwick Boulevard, Newport News, VA 23606-3401 Phone: 757-591-4646Rosaline JordanNessuna valutazione finora
- Spinal TumorsDocumento59 pagineSpinal TumorsAl-Banji MohammadNessuna valutazione finora