Documenti di Didattica
Documenti di Professioni
Documenti di Cultura
Pneumonia
Caricato da
nursing concept mapsTitolo originale
Copyright
Formati disponibili
Condividi questo documento
Condividi o incorpora il documento
Hai trovato utile questo documento?
Questo contenuto è inappropriato?
Segnala questo documentoCopyright:
Formati disponibili
Pneumonia
Caricato da
nursing concept mapsCopyright:
Formati disponibili
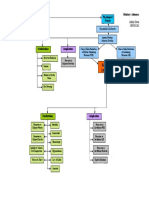
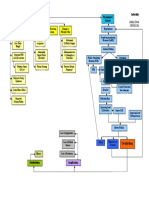
CONCEPT MAP Saucier, Hali SNPLU 2/25/08
encourage pt to take deeper breaths. Do pt teaching to explain Collaborate with physician to administer antibiotics to resolve infection Medical Diagnosis Patients Story
importance of lung expansion with pneumonia. administer supplemental O2 as needed to maintain adequate oxygenation
sit pt up in bed (high fowlers) to decrease pressure on chest and allow for help the client cough and deep breath at least q2hrs to clear airways and
adequate lung expansion. expand the lungs at the bases Pathophysiology Diagnostic Workup
Obtain an incentive spirometer for the pt to encourage deep breathing. administer prescribed nebulizer breathing treatments to open airways
Pt teaching on the importance of weight loss
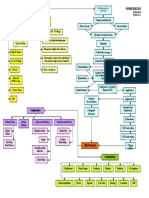
Clinical Manifestation Nursing Diagnosis
Etiology & Risk Factors Expected Outcome
Pt. will achieve adequate ventilation Pt will experience improved oxygenation
Secondary Diagnosis Nursing Interventions
Ineffective breathing pattern r/t obesity and Impaired gas exchange r/t ed functional lung tissue Patients Medications: (2).
fatigue, AEB SOB, RR, depth of breathing, and pt (4) AEB dyspnea, tachycardia, ed RR, and O2 of less than For pneumonia:
reports difficulty taking deep breaths (4). 92% on RA. - Levofloxacin (Levaquin): anti-infective
- Cefalosporin): anti-infective, 3rd
generation.
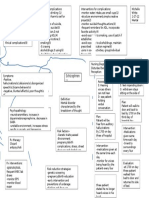
My patient was a female in her 60s who - Albuterol: adrenergic bronchodilator
lives in an assisted living rehab facility. She - Ipratropium (Atrovent): anticholinergic
came to the hospital with chest pain, SOB, Chest X-ray shows white shadows bronchodilator
(parenchymal infiltrates (3). Other Medications:
fever, and productive cough. She also had
cellulitis in her lower extremities that was
Pneumonia Culture and sensitivity. Gram-stain of - Viramune: antiviral (plus one other
getting worse. She was admitted for 5 days to sputum to differentiate bacterial from antiviral that I forgot the name)
Incidence: Health-care Associated Pneumonia - Insulin coverage for diabetes
receive IV antibiotics. I cared for her on the occurs in about 5-15 cases out of every 1000 viral causes and gram + vs. -.
5th day, so she had few s/s of pneumonia. - Nystatin (candida)
hospital admissions. HAP is the 2nd most WBC elevation (greater than 15,000/l
- Heparin sc (DVT prevention)
common nosocomial infection after UTIs (1.) (3).) - Warfarin (DVT prevention
anticoagulant)
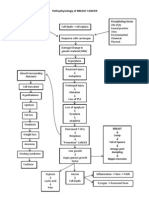
Pneumonia is an inflammation in the alveoli and the - Furosemide (Lasix): edema
interstitium of the lung, usually caused by an infection - Acetaminophen (for pain)
(3). There are several different types, including sudden onset of fever/chills
SOB, increased RR
community acquired, hospital acquired, aspiration, Productive cough (bacterial) - breast cancer Discharge Planning:
fungal, and opportunistic (1). This particular patient had Pleuritic chest pain - communicate with LCT facility to
HIV
what is called health-care associated pneumonia, Confusion or stupor (due to hypoxia)
update on pt discharge status
Crackles, fremitus, bronchial breath (both of the above are 2 diagnoses that could
because she had been living in an assisted living - ensure pt has adequate
sounds have contributed to the development of
facility. However, I think it could also be considered ventilation/oxygenation before d/c.
pneumonia due to compromised immunity from
opportunistic because of her compromised immune Arrange for portable O2 if needed.
HIV and from chemotherapy.)
status. In pneumonia, the infective agent enters the lung - Pt teaching on pneumonia prevention
Diabetes
(pseudomonas in this case), multiplies, and triggers
Risk factors: Lymphedema and Cellulitis in lower extremities References:
inflammation. The alveoli fill with exudative fluid 1. Lewis S.L., Heitkemper M.M., Dirkesen S.R., OBrien
chronic illness Hx of MRSA, Hep C, CHF, MI, A-fib
which impairs gas exchange. Exudate can consolidate P.G., & Bucher L. (2007). Medical surgical
immobility
and become difficult to cough up (3). Bacterial immunosuppression
nursing: Assessment and management of clinical
pneumonia is usually associated with a productive problems (7th ed.). St. Louis: Mosby Elsevier.
post-surgery/anesthesia 2. Deglin J.H., & Vallerand A.H. (2007). Daviss drug guide
cough, whereas viral is not (1). for nurses (10th ed.). Philadelphia: F.A. Davis
Company
3. Copstead L.C., & Banasik J.L. (2005). Pathophysiology (3rd
ed.). St. Louis: Elsevier Saunders.
4. Ackley B.J. & Ladwig G.B. (2006). Nursing diagnosis
handbook: A guide to planning care (7th ed.). St.
Potrebbero piacerti anche
- Pneumonia ConceptDocumento1 paginaPneumonia ConceptRevie Iglesias100% (1)
- Chronic Renal Failure: PathophysiologyDocumento1 paginaChronic Renal Failure: PathophysiologyCindy Mae Dela Torre100% (2)
- Pneumonia Concept MapDocumento11 paginePneumonia Concept Mapiz11100% (3)
- Concept Map PTBDocumento1 paginaConcept Map PTBJoan Abardo100% (2)
- Concept Map COPDDocumento2 pagineConcept Map COPDJilian McGugan88% (40)
- Concept Map SeizuresDocumento1 paginaConcept Map SeizuresMary GiuntiniNessuna valutazione finora
- ACUTE RESPIRATORY DISTRESSDocumento1 paginaACUTE RESPIRATORY DISTRESSchristine louise bernardo100% (1)
- Small Bowel Obstruction Concept MapDocumento1 paginaSmall Bowel Obstruction Concept MapTessa Claire JaranowskiNessuna valutazione finora
- ARDS MANAGEMENT GUIDEDocumento2 pagineARDS MANAGEMENT GUIDETisha CarretteNessuna valutazione finora
- Hypertension Concept MapDocumento1 paginaHypertension Concept Mapgfhbgfhgf71% (7)
- COPD PathoDocumento1 paginaCOPD PathoLeah May AnchetaNessuna valutazione finora
- Pneumonia Care PlanDocumento1 paginaPneumonia Care Plantcumurphish67% (3)
- Medical Surgical: Nervous SystemDocumento90 pagineMedical Surgical: Nervous SystemCatherine G. Borras100% (1)
- Nursing Care Plan 4 Gas Exchange, ImpairedDocumento9 pagineNursing Care Plan 4 Gas Exchange, Impaireddbryant0101100% (6)
- Monitor for signs of respiratory distress and failureDocumento3 pagineMonitor for signs of respiratory distress and failureChie Hyun-AeNessuna valutazione finora
- Pathophysiology EmphysemaDocumento1 paginaPathophysiology Emphysemanursing concept mapsNessuna valutazione finora
- Copd PathoDocumento2 pagineCopd PathoAlvin RamirezNessuna valutazione finora
- Pharmacology Drug ClassificationDocumento4 paginePharmacology Drug ClassificationjetdoctrzNessuna valutazione finora
- Concept Map Pleural EffusionDocumento1 paginaConcept Map Pleural Effusionapi-341263362Nessuna valutazione finora
- PP - Community-Acquired PneumoniaDocumento1 paginaPP - Community-Acquired Pneumonialpetallo100% (2)
- Nursing Care PlanDocumento53 pagineNursing Care Planztvill88% (26)
- Concept Map of Nasal ObstructionDocumento2 pagineConcept Map of Nasal ObstructionChad Viajar100% (1)
- Nursing Care Plan 2Documento6 pagineNursing Care Plan 2KM TopacioNessuna valutazione finora
- DM Case StudyDocumento4 pagineDM Case Studyapi-273276737100% (3)
- Copd PathDocumento2 pagineCopd Pathnursing concept maps100% (2)
- Nursing Management For Acute Respiratory FailureDocumento7 pagineNursing Management For Acute Respiratory FailureEvolynNessuna valutazione finora
- Concept Map HypertensionDocumento1 paginaConcept Map Hypertensiongeorge pearson0% (1)
- COPD PathoDocumento1 paginaCOPD PathoGlenn_Ancheta_2074100% (1)
- Assessment and Management of Patients With Hearing and Balance Disorders WebDocumento36 pagineAssessment and Management of Patients With Hearing and Balance Disorders WebStephKirstin Velasco Malapit100% (2)
- Asthma Pathophysiology and TreatmentDocumento3 pagineAsthma Pathophysiology and TreatmentKaren HutchinsonNessuna valutazione finora
- Copd Pathophysiology DiagramDocumento2 pagineCopd Pathophysiology DiagramVHyneh Basher100% (1)
- COPD Risk Factors, Signs, Treatments & Nursing CareDocumento2 pagineCOPD Risk Factors, Signs, Treatments & Nursing CareJilian McGugan100% (9)
- Teaching Plan PneumoniaDocumento4 pagineTeaching Plan PneumoniadeannesemonNessuna valutazione finora
- NCP Ineffective Airway Clearance Related To The Accumulation of Secretions As Evidence by Decrease in Respiratory Rate and NGT and ET Tube Attached and Crackles at The Left Base of The LungsDocumento3 pagineNCP Ineffective Airway Clearance Related To The Accumulation of Secretions As Evidence by Decrease in Respiratory Rate and NGT and ET Tube Attached and Crackles at The Left Base of The LungsSarah Ann Jamilla FaciolanNessuna valutazione finora
- Congestive Heart Failure and Pulmonary Edema Concept MapDocumento1 paginaCongestive Heart Failure and Pulmonary Edema Concept MapAndrew Godwin100% (5)
- IV Solution Cheat SheetDocumento13 pagineIV Solution Cheat Sheetisapatrick8126100% (4)
- CHF Cardiomegaly Volume OverloadDocumento1 paginaCHF Cardiomegaly Volume Overloadnursing concept mapsNessuna valutazione finora
- Nursing Care Plan For PneumoniaDocumento2 pagineNursing Care Plan For PneumoniaJonas Galeos100% (2)
- Concept Map of Copd: Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary DiseaseDocumento1 paginaConcept Map of Copd: Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary DiseaseWayne Calderon75% (4)
- Nursing Intervention For Chest PainDocumento2 pagineNursing Intervention For Chest Painjhaden100% (3)
- 1 Ineffective Breathing PatternDocumento8 pagine1 Ineffective Breathing PatternNoel MontemayorNessuna valutazione finora
- Drug Study in PneumoniaDocumento17 pagineDrug Study in PneumoniaKara Kathrina FuentesNessuna valutazione finora
- Iloilo Doctors' College Nursing Care Plan for Anaphylactic ShockDocumento7 pagineIloilo Doctors' College Nursing Care Plan for Anaphylactic ShockAbie Jean BalbontinNessuna valutazione finora
- Concept Map 2Documento1 paginaConcept Map 2lanrevoiceNessuna valutazione finora
- ARDS Concept MapDocumento1 paginaARDS Concept Mapadro100% (2)
- Pathophysiology of PneumoniaDocumento1 paginaPathophysiology of Pneumoniaoxidalaj97% (31)
- PATHOPHYSIOLOGY UrtiDocumento2 paginePATHOPHYSIOLOGY UrtiCris Soland88% (8)
- Name of DrugDocumento6 pagineName of Drug私 シャーロット100% (1)
- Ards Cmap FinalDocumento4 pagineArds Cmap FinalPam Araune67% (3)
- Pathophysiology of Tuberculosis: Group 5 Latosa, Selene Lee, Guk Lim, Johanna Magalona, Stephen Mendoza, ColeenDocumento22 paginePathophysiology of Tuberculosis: Group 5 Latosa, Selene Lee, Guk Lim, Johanna Magalona, Stephen Mendoza, ColeenAlexander Santiago ParelNessuna valutazione finora
- Pathophysiology of Bronchial AsthmaDocumento2 paginePathophysiology of Bronchial AsthmaFirenze Fil100% (21)
- Sample Nursing Care PlanDocumento3 pagineSample Nursing Care Planhyunbin18100% (4)
- Covid - 19 NCPDocumento4 pagineCovid - 19 NCPKrisianne Mae Lorenzo FranciscoNessuna valutazione finora
- Case Presentation ManingasDocumento7 pagineCase Presentation ManingasestimojervsNessuna valutazione finora
- Nursing Care Plan For InflammationDocumento2 pagineNursing Care Plan For InflammationJobelle AcenaNessuna valutazione finora
- Santillaruby NCPDocumento3 pagineSantillaruby NCPRuby SantillanNessuna valutazione finora
- NCP - PneumoniaDocumento3 pagineNCP - PneumoniaNikiNessuna valutazione finora
- Drug StudyDocumento5 pagineDrug Studyboxed juiceNessuna valutazione finora
- Pneumonia Couse in The WardDocumento2 paginePneumonia Couse in The Wardyssasarmiento09Nessuna valutazione finora
- Cues Nursing Diagnosis Inference Planning Nursing Intervention Rationale EvaluationDocumento3 pagineCues Nursing Diagnosis Inference Planning Nursing Intervention Rationale EvaluationNichol John MalabananNessuna valutazione finora
- Emphysema Pathophysiology ExplainedDocumento1 paginaEmphysema Pathophysiology ExplainedGil AswiguiNessuna valutazione finora
- Concept Map TemplateDocumento1 paginaConcept Map Templatenursing concept mapsNessuna valutazione finora
- Concept Map BlankDocumento2 pagineConcept Map Blanknursing concept mapsNessuna valutazione finora
- Bronchial Asthma in Acute Exacerbation BAIAE Pathophysiology Schematic DiagramDocumento3 pagineBronchial Asthma in Acute Exacerbation BAIAE Pathophysiology Schematic DiagramVictor Angelo VeraNessuna valutazione finora
- PathoPhysiology of Renal Failure OverviewDocumento7 paginePathoPhysiology of Renal Failure Overviewnursing concept maps100% (1)
- Physiological ChangesDocumento1 paginaPhysiological ChangesJilian McGuganNessuna valutazione finora
- Patent Ductus Arteriosus PathophsyiologyDocumento3 paginePatent Ductus Arteriosus Pathophsyiologynursing concept mapsNessuna valutazione finora
- Bipolar Concept MapDocumento3 pagineBipolar Concept Mapnursing concept maps100% (2)
- Diagnostics: Disorder & Basic Patho/Etiology: Clinical ManifestationsDocumento1 paginaDiagnostics: Disorder & Basic Patho/Etiology: Clinical Manifestationsnursing concept mapsNessuna valutazione finora
- Diabetes Mellitus Type 2 Schematic DiagramDocumento1 paginaDiabetes Mellitus Type 2 Schematic DiagramJhe Lyn82% (11)
- Sleep Apnea Concept MapDocumento1 paginaSleep Apnea Concept Mapashleydean100% (2)
- ESRD PathophysiologyDocumento2 pagineESRD Pathophysiologynursing concept mapsNessuna valutazione finora
- Mental Health Concept MapDocumento2 pagineMental Health Concept Mapnursing concept mapsNessuna valutazione finora
- PATHODocumento2 paginePATHOmycoclitNessuna valutazione finora
- Hip FractureDocumento3 pagineHip Fracturenursing concept mapsNessuna valutazione finora
- Pathophysiology of Burn InjuryDocumento1 paginaPathophysiology of Burn InjuryAnonymous XvwKtnSrMR100% (1)
- Bipolar Disorder Concept MapDocumento1 paginaBipolar Disorder Concept Mapnursing concept maps100% (1)
- Critical Care Concept MapDocumento1 paginaCritical Care Concept Mapkonniep69100% (1)
- Pituitary Adenoma Concept MapDocumento1 paginaPituitary Adenoma Concept Mapnursing concept mapsNessuna valutazione finora
- ARF PathophysiologyDocumento2 pagineARF Pathophysiologykathy100% (9)
- Pathophysiology of BREAST CANCERDocumento1 paginaPathophysiology of BREAST CANCERAlinor Abubacar100% (6)
- Schizophrenia MapDocumento1 paginaSchizophrenia Mapnursing concept mapsNessuna valutazione finora
- Age Greater Than 60 Y/o Hereditary Precipitating Factors: Hypertension Increase Protein and Fat IntakeDocumento3 pagineAge Greater Than 60 Y/o Hereditary Precipitating Factors: Hypertension Increase Protein and Fat Intakenursing concept mapsNessuna valutazione finora
- Pathophysio CRF2 - RevisedDocumento1 paginaPathophysio CRF2 - Reviseddeborah malnegroNessuna valutazione finora
- Hypertension Concept MapDocumento1 paginaHypertension Concept Mapashleydean100% (7)
- Infertility Concept MapDocumento1 paginaInfertility Concept Mapnursing concept maps50% (2)
- Degenerative Disc Disease Concept MapDocumento1 paginaDegenerative Disc Disease Concept Mapnursing concept mapsNessuna valutazione finora
- Nursing Management Concept MapDocumento1 paginaNursing Management Concept MapXy-Za Roy Marie100% (1)
- Concept MapDocumento1 paginaConcept Mapnursing concept mapsNessuna valutazione finora
- Osteoarthritis Concept MapDocumento1 paginaOsteoarthritis Concept Mapnursing concept maps0% (1)
- Radical NephrectomyDocumento3 pagineRadical NephrectomyBiggs JuntillaNessuna valutazione finora
- The Feldenkrais Method - Application, Practice and PrinciplesDocumento8 pagineThe Feldenkrais Method - Application, Practice and PrinciplesPaul Asturbiaris100% (1)
- Special Stains in Histotechnology:: DR CN Srinivas Director-Dept of Lab Medicine MIOT International ChennaiDocumento28 pagineSpecial Stains in Histotechnology:: DR CN Srinivas Director-Dept of Lab Medicine MIOT International ChennaiMalliga SundareshanNessuna valutazione finora
- IMSS Nursing Knowledge ExamDocumento11 pagineIMSS Nursing Knowledge ExamScribdTranslationsNessuna valutazione finora
- 2009 Mar Consumer NewsletterDocumento7 pagine2009 Mar Consumer NewsletterWileyProtocolNessuna valutazione finora
- English-Khmer Biology DictionaryDocumento579 pagineEnglish-Khmer Biology DictionaryCarlosAmadorFonseca89% (9)
- Evolve Resources For Goulds Pathophysiology For The Health Professions 6Th Edition Hubert Test Bank Full Chapter PDFDocumento30 pagineEvolve Resources For Goulds Pathophysiology For The Health Professions 6Th Edition Hubert Test Bank Full Chapter PDFRyanFernandezqxzkc100% (8)
- 38 - HypofibrinogenaemiaDocumento8 pagine38 - Hypofibrinogenaemiadr_asalehNessuna valutazione finora
- Acute Poisoning and Its AntidoteDocumento10 pagineAcute Poisoning and Its AntidoteRachman UsmanNessuna valutazione finora
- Posthumanism Cyborgs and Interconnected Bodies by Jon BaileyDocumento59 paginePosthumanism Cyborgs and Interconnected Bodies by Jon BaileyDavid García MonteroNessuna valutazione finora
- Lecture 8 Testing of BiomaterialsDocumento23 pagineLecture 8 Testing of BiomaterialsTayyab AhsanNessuna valutazione finora
- Identified Nursing Diagnoses and PrioritizationDocumento4 pagineIdentified Nursing Diagnoses and Prioritizationrheinz-marlon-m-carlos-7771Nessuna valutazione finora
- MRI ProtocolsDocumento11 pagineMRI ProtocolsDaniel Mella TreumunNessuna valutazione finora
- Cardiogenic ShockDocumento2 pagineCardiogenic ShockChristine QuironaNessuna valutazione finora
- Relation Between Blood Pressure, Renin, Aldosterone and Urinary ElectrolytesDocumento5 pagineRelation Between Blood Pressure, Renin, Aldosterone and Urinary ElectrolytesAndrea ForcinitiNessuna valutazione finora
- NFM Cia 3Documento11 pagineNFM Cia 3RNessuna valutazione finora
- Tutorials in Surgery For 4th Medical StudentsDocumento180 pagineTutorials in Surgery For 4th Medical StudentsAnonymous jSTkQVC27bNessuna valutazione finora
- Child As A Spiritual EmbryoDocumento6 pagineChild As A Spiritual EmbryoSa100% (1)
- MRCGP Exam CSA Case Course Courses Chest PainDocumento6 pagineMRCGP Exam CSA Case Course Courses Chest PainMRCGP CSA Prep Courses / CSA courseNessuna valutazione finora
- Axilla Boundaries and ContentDocumento47 pagineAxilla Boundaries and Contentchzaheer72Nessuna valutazione finora
- Final CreamDocumento22 pagineFinal CreamCyrus VizonNessuna valutazione finora
- Fluids&LytesDocumento33 pagineFluids&LytesMateen ShukriNessuna valutazione finora
- Physical Education Class 12 Short Answers Chapter 3Documento7 paginePhysical Education Class 12 Short Answers Chapter 3Anushka TomarNessuna valutazione finora
- Year 10 Biology - Plant Processes: Lesson 5 - Transpiration & TranslocationDocumento4 pagineYear 10 Biology - Plant Processes: Lesson 5 - Transpiration & TranslocationJake OsbornNessuna valutazione finora
- Guidelines Angina FTDocumento63 pagineGuidelines Angina FTMikhwanul JumarNessuna valutazione finora
- Cardiac, Diabetic and General Range Drug ListDocumento6 pagineCardiac, Diabetic and General Range Drug ListLisa PutriNessuna valutazione finora
- 1 - Natural History of Periodontal DiseaseDocumento42 pagine1 - Natural History of Periodontal DiseasejazzNessuna valutazione finora
- CNS PathologyDocumento10 pagineCNS Pathologysarguss1483% (6)
- A&p - All Files in One PDFDocumento201 pagineA&p - All Files in One PDFandreeaNessuna valutazione finora
- 2nd Anatomy QuizDocumento2 pagine2nd Anatomy QuizbevorsiNessuna valutazione finora