Documenti di Didattica
Documenti di Professioni
Documenti di Cultura
The Chemistry of Coffee v2 PDF
Caricato da
Janifer JohnTitolo originale
Copyright
Formati disponibili
Condividi questo documento
Condividi o incorpora il documento
Hai trovato utile questo documento?
Questo contenuto è inappropriato?
Segnala questo documentoCopyright:
Formati disponibili
The Chemistry of Coffee v2 PDF
Caricato da
Janifer JohnCopyright:
Formati disponibili
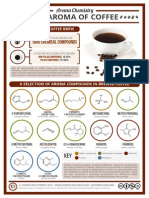
THE CHEMISTRY OF COFFEE
WHY IS COFFEE BITTER?
5-CAFFEOYLQUINIC ACID
OH
HO
O
HO OH
O
OH
O
HO
Chlorogenic acids account for up to 8% of the
composition of unroasted coffee beans. More than
40 different varieties have been identified in green
coffee beans, with 5-caffeoylquinic acid the most
prevalent. T H E C A F F E I N E CO N T E N T O F CO F F E E
The caffeine content of coffee is
Chlorogenic acid content decreases when
coffee beans are roasted, as they react to form O CH3 variable but is approximately 100mg
quinolactones, phenylindanes & melanoidins. in a cup.
These contribute to flavour and bitterness. H3C N
3-CAFFEOYLQUINIC-1,5-LACTONE O
N Caffeine works by blocking the action
of a group of brain chemicals called
O adenosines, which work to naturally
HO
O
O N N trigger tiredness.
O OH
The amount of caffeine in your
OH
CH3 bloodstream peaks 15 to 45 minutes
HO after ingestion.
C COMPOUND INTEREST 2014 - WWW.COMPOUNDCHEM.COM | Twitter: @compoundchem | Facebook: www.facebook.com/compoundchem
This graphic is shared under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-NoDerivatives Licence. BY NC ND
Potrebbero piacerti anche
- Overall Operation ManualDocumento207 pagineOverall Operation ManualCharith GomesNessuna valutazione finora
- Tannin ChemistryDocumento116 pagineTannin ChemistryExaudi EbennezerNessuna valutazione finora
- The Art of Brewing and The Biology of Lager Yeast: Tom Pugh Miller Brewing CompanyDocumento49 pagineThe Art of Brewing and The Biology of Lager Yeast: Tom Pugh Miller Brewing CompanyElly SufriadiNessuna valutazione finora
- Nita Mehta's Lebanese CookingDocumento52 pagineNita Mehta's Lebanese CookingZeina SalehNessuna valutazione finora
- Morebeer! Beer Making Instructions: Morebeer! Personal Brewery Starter SystemDocumento2 pagineMorebeer! Beer Making Instructions: Morebeer! Personal Brewery Starter SystemTeddy Riaño AlarconNessuna valutazione finora
- Lautering Back To BasicsDocumento3 pagineLautering Back To BasicsVohinh NgoNessuna valutazione finora
- Beverages and ConfectionaryDocumento146 pagineBeverages and ConfectionaryThanh Tam Tran100% (1)
- 101 HealthTipsDocumento29 pagine101 HealthTipsAnupam BhardwajNessuna valutazione finora
- Bavarian Weizen All GrainDocumento7 pagineBavarian Weizen All GrainDavide NicolisNessuna valutazione finora
- Ethanol RectificationDocumento10 pagineEthanol RectificationAnatolij Pamiatnikh100% (1)
- Tequila ProjectDocumento82 pagineTequila ProjectDeepak JettaNessuna valutazione finora
- Eighty Years of Rapid Maturation Studies - Distiller MagazineDocumento18 pagineEighty Years of Rapid Maturation Studies - Distiller Magazineamul ghimireNessuna valutazione finora
- Chen 382 FinalDocumento9 pagineChen 382 Finalapi-240464495Nessuna valutazione finora
- Beer Spoilage Bacteria and Hop Resistance PDFDocumento20 pagineBeer Spoilage Bacteria and Hop Resistance PDFkelamahimNessuna valutazione finora
- Beer and Hop ChemistryDocumento40 pagineBeer and Hop ChemistrydulongNessuna valutazione finora
- NR 23 Strictly Anaerobic Beer Spoilage Bacteria With Special Emphasis On New and Emerging Species Riikka JuvonenDocumento37 pagineNR 23 Strictly Anaerobic Beer Spoilage Bacteria With Special Emphasis On New and Emerging Species Riikka JuvonenIvana NikolicNessuna valutazione finora
- Almaguer Et Al-2014-Journal of The Institute of BrewingDocumento26 pagineAlmaguer Et Al-2014-Journal of The Institute of BrewingAngelo OliveiraNessuna valutazione finora
- Orsang Camp PackageDocumento3 pagineOrsang Camp PackageVishal Solanki50% (2)
- Conversation StartersDocumento7 pagineConversation StartersJuan ChavezNessuna valutazione finora
- Chemistry of Beer AgingDocumento25 pagineChemistry of Beer AgingAntonio Imperi100% (1)
- Factors Influencing PDFDocumento9 pagineFactors Influencing PDFMarceta BrankicaNessuna valutazione finora
- Review Beer AgeingDocumento25 pagineReview Beer AgeingTimothy WestNessuna valutazione finora
- Kombucha Flavor RecipesDocumento1 paginaKombucha Flavor RecipesAnonymous g7Tb3IOfNessuna valutazione finora
- Saccharomyces Yeasts Contribute On Innovative Brewing Fermentations - Innovacion en CervezasDocumento9 pagineSaccharomyces Yeasts Contribute On Innovative Brewing Fermentations - Innovacion en CervezasemannuellyNessuna valutazione finora
- Brettanomyces Bruxellensis, EssentialDocumento12 pagineBrettanomyces Bruxellensis, EssentialGabriela ChapchapNessuna valutazione finora
- 2014 MBAA Chris White Yeast ManagementDocumento30 pagine2014 MBAA Chris White Yeast ManagementAdrián LampazziNessuna valutazione finora
- TN 109 Beer Hop ExtractionDocumento4 pagineTN 109 Beer Hop ExtractionMaxPostvanderBurgNessuna valutazione finora
- Beer Aging Wiley Ibd ChemistryDocumento25 pagineBeer Aging Wiley Ibd Chemistryfakeyfake-2Nessuna valutazione finora
- A History of The World in 6 GlassesDocumento9 pagineA History of The World in 6 Glassesapi-276956064Nessuna valutazione finora
- Roast MarApr08 ScienceofBrowningDocumento5 pagineRoast MarApr08 ScienceofBrowningmadbakingNessuna valutazione finora
- Xanthan GumDocumento6 pagineXanthan GumFelipe AliNessuna valutazione finora
- Chapter 3 Brewing ProcessDocumento16 pagineChapter 3 Brewing ProcessmaniiiiiiiiNessuna valutazione finora
- Cocowater FaoDocumento48 pagineCocowater FaoPitz Bonilla100% (1)
- Sour BeersDocumento3 pagineSour Beersmauricio0327Nessuna valutazione finora
- Zero FreesampleDocumento10 pagineZero Freesampleroberfg99Nessuna valutazione finora
- Group 1 Soy Sauce Present 14 - 12 - 2022Documento58 pagineGroup 1 Soy Sauce Present 14 - 12 - 2022Phương ThảoNessuna valutazione finora
- First Wort Hopping SummaryDocumento5 pagineFirst Wort Hopping SummaryRodrigo Jacy Monteiro MartinsNessuna valutazione finora
- Tea Manufacturing & Process For Non-Orthodox TeaDocumento43 pagineTea Manufacturing & Process For Non-Orthodox TeaVũ HằngNessuna valutazione finora
- Polyols Confectionery Application Fact SheetDocumento2 paginePolyols Confectionery Application Fact SheetIngredion Knowledge BankNessuna valutazione finora
- National Coopers Journal Vol 41 1925 PDFDocumento198 pagineNational Coopers Journal Vol 41 1925 PDFCatalin ZestranNessuna valutazione finora
- TMP GCDL NDDocumento2.989 pagineTMP GCDL NDLe HuyNessuna valutazione finora
- The History of TequilaDocumento6 pagineThe History of TequilaAmanda RossNessuna valutazione finora
- Aroma Chemistry CoffeeDocumento1 paginaAroma Chemistry Coffeemariamtk100% (2)
- Prepare Salads and DressingDocumento54 paginePrepare Salads and DressingAngelica Lloveras88% (16)
- A Practical Treatise On The Raw Materials and The Distillatio Brannt-1885Documento5 pagineA Practical Treatise On The Raw Materials and The Distillatio Brannt-1885Eduardo CordovaNessuna valutazione finora
- HPP and BeerDocumento12 pagineHPP and BeerrafaelNessuna valutazione finora
- The Raise of Brettanomyces Yeast Species For Beer ProductionDocumento6 pagineThe Raise of Brettanomyces Yeast Species For Beer ProductionJuan Antonio DiazNessuna valutazione finora
- Physico-Chemical and Quality Characteristics of Fish Sauce Produced From Tuna Processing WastesDocumento14 paginePhysico-Chemical and Quality Characteristics of Fish Sauce Produced From Tuna Processing WastesMuhammad RafiqNessuna valutazione finora
- 32005mashing Unmalted 109Documento15 pagine32005mashing Unmalted 109Pulbere NeagraNessuna valutazione finora
- Parkin, Shellhammer - 2017 - Toward Understanding The Bitterness of Dry-Hopped BeerDocumento6 pagineParkin, Shellhammer - 2017 - Toward Understanding The Bitterness of Dry-Hopped BeerPablo Perez DonosoNessuna valutazione finora
- Response of Brewing Yeast To Acid Washing, WhiteLabsDocumento8 pagineResponse of Brewing Yeast To Acid Washing, WhiteLabsCRISTIAN ALEXIS CAZA PULUPANessuna valutazione finora
- Quantification of Selected Volatile Constituents and Anions in Mexican Agave Spirits (Tequila, Mezcal, Sotol, Bacanora)Documento5 pagineQuantification of Selected Volatile Constituents and Anions in Mexican Agave Spirits (Tequila, Mezcal, Sotol, Bacanora)René MartínezNessuna valutazione finora
- Cocoa Pulp by MCBDocumento2 pagineCocoa Pulp by MCBvkumaranNessuna valutazione finora
- Enzyme InformationDocumento7 pagineEnzyme InformationLong ThuậnNessuna valutazione finora
- The Journey From Cacao Pod To ChocolateDocumento9 pagineThe Journey From Cacao Pod To Chocolateronalit malintadNessuna valutazione finora
- Beer Fermentation Monitoring of Process Parameters by FTNIR and Multivariate Data AnalysisDocumento8 pagineBeer Fermentation Monitoring of Process Parameters by FTNIR and Multivariate Data AnalysisGuilherme BernardiNessuna valutazione finora
- Pear BrandyDocumento14 paginePear BrandyRachelHechanovaNessuna valutazione finora
- Humulus Lupulus - Hops: EtymologyDocumento15 pagineHumulus Lupulus - Hops: EtymologyKirk SantzNessuna valutazione finora
- Beer Brewing Fact SheetDocumento4 pagineBeer Brewing Fact SheetAsh88640% (1)
- The Changing Face of Beverage ProcessingDocumento4 pagineThe Changing Face of Beverage Processingthanhtl_hugolataNessuna valutazione finora
- Example of Fermentation ProcessDocumento34 pagineExample of Fermentation ProcessRedzuan Hussin100% (2)
- Soy AllergyDocumento4 pagineSoy Allergymelissascheichl416Nessuna valutazione finora
- Cocoa Butter CrystallisationDocumento8 pagineCocoa Butter Crystallisationmarica56100% (1)
- The Beer Geek Handbook - Living A Life Ruled by Beer (2016)Documento58 pagineThe Beer Geek Handbook - Living A Life Ruled by Beer (2016)zaratustra21Nessuna valutazione finora
- Zinc and FermentationDocumento6 pagineZinc and FermentationVictor AnibalNessuna valutazione finora
- Biochemistry Applied to the Brewing Processes - Mashing, Boiling, CoolingDa EverandBiochemistry Applied to the Brewing Processes - Mashing, Boiling, CoolingNessuna valutazione finora
- ErythritolDocumento3 pagineErythritolyuni fadilahNessuna valutazione finora
- Evaluating Beer PDFDocumento2 pagineEvaluating Beer PDFNicoleNessuna valutazione finora
- The Analysis and Control of Less Desirable Flavors in Foods and BeveragesDa EverandThe Analysis and Control of Less Desirable Flavors in Foods and BeveragesNessuna valutazione finora
- Brewing Root BeerDocumento3 pagineBrewing Root BeersanjosewhoreNessuna valutazione finora
- ObjectivesDocumento1 paginaObjectivesJanifer JohnNessuna valutazione finora
- S A Coffee FarmerDocumento3 pagineS A Coffee FarmerJanifer JohnNessuna valutazione finora
- Coffee - Chemistry in Every Cup - tcm18-201245 PDFDocumento4 pagineCoffee - Chemistry in Every Cup - tcm18-201245 PDFJanifer JohnNessuna valutazione finora
- Technical PresentationDocumento11 pagineTechnical PresentationJanifer JohnNessuna valutazione finora
- Application of Shell and Tube Heat ExchangerDocumento2 pagineApplication of Shell and Tube Heat ExchangerJanifer JohnNessuna valutazione finora
- PCS TP Outline-1Documento3 paginePCS TP Outline-1Janifer JohnNessuna valutazione finora
- Lesson Plan f4 2010Documento23 pagineLesson Plan f4 2010Nazatul Firdaus ZainonNessuna valutazione finora
- Baking FundamentalsDocumento67 pagineBaking FundamentalsjfargnoliNessuna valutazione finora
- Kpit Cummins Placement PapersDocumento8 pagineKpit Cummins Placement PapersAsitkumar Prusty100% (1)
- Moist Chocolate Cake RecipeDocumento9 pagineMoist Chocolate Cake RecipeRosalie Tilos OritoNessuna valutazione finora
- BatanesDocumento2 pagineBatanesFrancis Joseph Del Espiritu SantoNessuna valutazione finora
- Soft Drink ProjectDocumento4 pagineSoft Drink Projectvivek badhanNessuna valutazione finora
- Coca Cola Case Study - BeDocumento10 pagineCoca Cola Case Study - BeSomdipta MaityNessuna valutazione finora
- M973 37 PDFDocumento2 pagineM973 37 PDFdanzan1Nessuna valutazione finora
- Reduce The Following A) B) : Revision of FractionsDocumento5 pagineReduce The Following A) B) : Revision of FractionsDaniel DubeNessuna valutazione finora
- Vangibath Powder Recipe - Homemade Vangi Bath Masala Recipe - Cook With SmileDocumento7 pagineVangibath Powder Recipe - Homemade Vangi Bath Masala Recipe - Cook With Smilecastingforge4875Nessuna valutazione finora
- MLCC Code and Rules 343265 7Documento291 pagineMLCC Code and Rules 343265 7remybartonNessuna valutazione finora
- Brand PotencyDocumento50 pagineBrand Potencynikhilnu3878Nessuna valutazione finora
- PreservativeDocumento4 paginePreservativeHayyyNakuNeilNessuna valutazione finora
- Maths BookDocumento24 pagineMaths BookSaishaNessuna valutazione finora
- Pera Pera Penguin 66Documento1 paginaPera Pera Penguin 66brentk112Nessuna valutazione finora
- "We Proudly Serve" Digital Usage Guidelines: Starbucks Coffee Company Winter 2014Documento7 pagine"We Proudly Serve" Digital Usage Guidelines: Starbucks Coffee Company Winter 2014Jason LeeNessuna valutazione finora
- Future Simple Fun Activities Games GrammarDocumento1 paginaFuture Simple Fun Activities Games Grammarliceth hernandezNessuna valutazione finora
- TEA NotesDocumento14 pagineTEA NotesNikhil KulkarniNessuna valutazione finora
- Bihar, Liquor Ban and The Economy: Prof. Ashutosh Yadav Department of Commerce Hansraj College University of DelhiDocumento8 pagineBihar, Liquor Ban and The Economy: Prof. Ashutosh Yadav Department of Commerce Hansraj College University of DelhiAditya DiwakarNessuna valutazione finora
- Reducing Portion Size Reduces Food Intake and Plate Waste: Marjorie R. Freedman and Carolina BrochadoDocumento3 pagineReducing Portion Size Reduces Food Intake and Plate Waste: Marjorie R. Freedman and Carolina BrochadoAmaliah Chairul NusuNessuna valutazione finora
- Starter & Soup: All Prices Are in Malaysia RinggitDocumento3 pagineStarter & Soup: All Prices Are in Malaysia RinggitTemet NoscheNessuna valutazione finora
- Miscible Blend & ImMisible BlendDocumento18 pagineMiscible Blend & ImMisible BlendHamzahSardarNessuna valutazione finora