Documenti di Didattica
Documenti di Professioni
Documenti di Cultura
2015 Wall Chart STD Guideline
Caricato da
Aum ThanchanokCopyright
Formati disponibili
Condividi questo documento
Condividi o incorpora il documento
Hai trovato utile questo documento?
Questo contenuto è inappropriato?
Segnala questo documentoCopyright:
Formati disponibili
2015 Wall Chart STD Guideline
Caricato da
Aum ThanchanokCopyright:
Formati disponibili
CDC
Sexually Transmitted Diseases
Summary of
2015
CDC Treatment Guidelines
National Center for HIV/AIDS, Viral Hepatitis, STD, and TB Prevention
Division of STD Prevention
Sexually Transmitted Diseases: Summary of 2015 CDC Treatment Guidelines
These summary guidelines reflect the 2015 CDC Guidelines for the Treatment of Sexually Transmitted Diseases. They are intended as a source of clinical guidance. An important component of STD treatment is partner management. Providers can arrange
for the evaluation and treatment of sex partners either directly or with assistance from state and local health departments. Complete guidelines can be ordered online at www.cdc.gov/std/treatment or by calling 1 (800) CDC-INFO (1-800-232-4636).
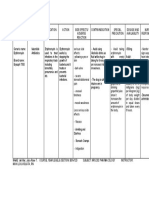
DISEASE RECOMMENDED Rx DOSE/ROUTE ALTERNATIVES
Bacterial Vaginosis metronidazole oral1
metronidazole gel 0.75%1
OR
OR
500 mg orally 2x/day for 7 days
One 5 g applicator intravaginally 1x/day for 5 days
tinidazole 2 g orally 1x/day for 2 days
tinidazole 1 g orally 1x/day for 5 days
OR
OR
clindamycin cream 2%1,2 One 5 g applicator intravaginally at bedtime for 7 days clindamycin 300 mg orally 2x/day for 7 days OR
clindamycin ovules 100 mg intravaginally at bedtime for 3 days
Treatment is recommended for all symptomatic pregnant women.
Cervicitis azithromycin
doxycycline3
OR 1 g orally in a single dose
100 mg orally 2x/day for 7 days
Consider concurrent treatment for gonococcal infection if at risk of gonorrhea or lives in a community where the prevalence of
gonorrhea is high. Presumptive treatment with antimicrobials for C. trachomatis and N. gonorrhoeae should be provided for women at
increased risk (e.g., those aged <25 years and those with a new sex partner, a sex partner with concurrent partners, or a sex partner who
has a sexually transmitted infection), especially if follow-up cannot be ensured or if NAAT testing is not possible.
Chlamydial Infections azithromycin
doxycycline3
OR 1 g orally in a single dose
100 mg orally 2x/day for 7 days
erythromycin base4 500 mg orally 4x/day for 7 days
erythromycin ethylsuccinate5 800 mg orally 4x/day for 7 days
OR
OR
Adults and adolescents
levofloxacin6 500 mg 1x/day orally for 7 days OR
ofloxacin6 300 mg orally 2x/day for 7 days
Pregnancy3 azithromycin7 1 g orally in a single dose amoxicillin 500 mg orally 3x/day for 7 days OR
erythromycin base4,8 500 mg orally 4x/day for 7 days OR
erythromycin base 250 mg orally 4x/day for 14 days OR
erythromycin ethylsuccinate 800 mg orally 4x/day for 7 days OR
erythromycin ethylsuccinate 400 mg orally 4x/day for 14 days
Infants and Children (<45 kg): urogenital, rectal erythromycin base9 OR 50 mg/kg/day orally (4 divided doses) daily for 14 days Data are limited on the effectiveness and optimal dose of azithromycin
ethylsuccinate for chlamydial infection in infants and children < 45 kg
Neonates: opthalmia neonatorum, pneumonia erythromycin base9 ethylsuccinate OR 50 mg/kg/day orally (4 divided doses) daily for 14 days azithromycin 20 mg/kg/day orally, 1 dose daily for 3 days
Epididymitis 10,11
For acute epididymitis most likely caused by ceftriaxone PLUS 250 mg IM in a single dose
sexually transmitted CT and GC doxycycline 100 mg orally 2x/day for 10 days
For acute epididymitis most likely caused by ceftriaxone
PLUS 250 mg IM in a single dose
sexually-transmitted chlamydia and gonorrhea levofloxacin
OR 500 mg orally 1x/day for 10 days
and enteric organisms (men who practice insertive ofloxacin
300 mg orally 2x/day for 10 days
anal sex)
For acute epididymitis most likely caused by enteric levofloxacin OR 500 mg orally 1x/day for 10 days
organisms ofloxacin 300 mg orally 2x/day for 10 days
Genital Herpes Simplex acyclovir OR 400 mg orally 3x/day for 7-10 days13
First clinical episode of genital herpes acyclovir OR 200 mg orally 5x/day for 7-10 days13
valacyclovir12 OR 1 g orally 2x/day for 7-10 days13
famciclovir12 250 mg orally 3x/day for 7-10 days13
Episodic therapy for recurrent genital herpes acyclovir OR 400 mg orally 3x/day for 5 days
acyclovir OR 800 mg orally 2x/day for 5 days
acyclovir OR 800 mg orally 3x/day for 2 days
valacyclovir12 OR 500 mg orally 2x/day for 3 days
valacyclovir12 OR 1 g orally 1x/day for 5 days
famciclovir12 OR 125 mg orally 2x/day for 5 days
famciclovir12 OR 1000 mg orally 2x/day for 1 day13
famciclovir12 500 mg orally once, followed by 250 mg 2x/day for 2 days
Suppressive therapy14 for recurrent genital herpes acyclovir OR 400 mg orally 2x/day
valacyclovir12 OR 500 mg orally 1x/day
valacyclovir12 OR 1 g orally once a day
famciclovir12 250 mg orally 2x/day
Recommended regimens for episodic infection in acyclovir OR 400 mg orally 3x/day for 5-10 days
persons with HIV infection valacyclovir12 OR 1 g orally 2x/day for 5-10 days
famciclovir12 500 mg orally 2x/day for 5-10 days
Recommended regimens for daily suppressive acyclovir OR 400-800 mg orally 2-3x/day
therapy in persons with HIV infection valacyclovir12 OR 500 mg orally 2x/day
famciclovir12 500 mg orally 2x/day
Genital Warts15 Patient Applied
imiquimod 3.75% or 5%12 cream OR See complete CDC guidelines.
(Human Papillomavirus)
podofilox 0.5%15 solution or gel OR
External genital and perianal warts
sinecatechins 15% ointment2,12
Provider Administered Apply small amount, dry, apply weekly if necessary podophyllin resin 10%25% in compound tincture of benzoin may be
OR
Cryotherapy OR considered for provider-administered treatment if strict adherence to the
trichloroacetic acid or bichloroacetic acid 80%-90% OR recommendations for application.
surgical removal intralesional interferon
OR
photodynamic therapy
OR
topical cidofovir
Gonococcal Infections16 ceftriaxone PLUS 250 mg IM in a single dose If ceftriaxone is not available:
Adults, adolescents, and cefixime17 400 mg orally in a single dose PLUS
children >45 kg: uncomplicated gonococcal azithromycin7 1 g orally in a single dose azithromycin7 1 g orally in a single dose
infections of the cervix, urethra, and rectum
If cephalosporin allergy:
gemifloxacin 320 mg orally in a single dose PLUS
azithromycin 2 g orally in a single dose OR
gentamicin 240 mg IM single dose PLUS
azithromycin 2 g orally in a single dose
Pharyngeal18 ceftriaxone PLUS 250 mg IM in a single dose
azithromycin7 1 g orally in a single dose
Pregnancy See complete CDC guidelines.
Adults and adolescents: ceftriaxone PLUS 1 g IM in a single dose
conjunctivitis azithromycin7 1 g orally in a single dose
Children (45 kg): urogenital, rectal, pharyngeal ceftriaxone19 25-50 mg/kg IV or IM, not to exceed 125 mg IM in a single dose
Lymphogranuloma venereum doxycycline3 100 mg orally 2x/day for 21 days erythromycin base 500 mg orally 4x/day for 21 days
Nongonococcal Urethritis (NGU) azithromycin7
doxycycline3
OR 1 g orally in a single dose
100 mg orally 2x/day for 7 days
erythromycin base4 500 mg orally 4x/day for 7 days
erythromycin ethylsuccinate5 800 mg orally 4x/day for 7 days
OR
OR
levofloxacin 500 mg 1x/day for 7 days OR
ofloxacin 300 mg 2x/day for 7 days
Persistent and recurrent NGU3,20,21 Men initially treated with doxycycline :
azithromycin 1 g orally in a single dose
Men who fail a regimen of azithromycin:
moxifloxacin 400 mg orally 1x/day for 7 days
Heterosexual men who live in areas where T. vaginalis is
highly prevalent:
metronidazole22 OR 2 g orally in a single dose
tinidazole 2 g orally in a single dose
Pediculosis Pubis permethrin 1% cream rinse
pyrethrins with piperonyl butoxide
OR Apply to affected area, wash off after 10 minutes
Apply to affected area, wash off after 10 minutes
malathion 0.5% lotion, applied 8-12 hrs then washed off
ivermectin 250 g/kg, orally repeated in 2 weeks
OR
Pelvic Inflammatory Parenteral Regimens
Cefotetan PLUS 2 g IV every 12 hours
Parenteral Regimen
Ampicillin/Sulbactam 3 g IV every 6 hours PLUS
Disease10 Doxycycline OR 100 mg orally or IV every 12 hours
Doxycycline 100 mg orally or IV every 12 hours
Cefoxitin PLUS 2 g IV every 6 hours
Doxycycline 100 mg orally or IV every 12 hours
Recommended Intramuscular/Oral Regimens
Ceftriaxone PLUS 250 mg IM in a single dose
Doxycycline WITH or 100 mg orally twice a day for 14 days
Metronidazole WITHOUT 500 mg orally twice a day for 14 days
OR
Cefoxitin PLUS 2 g IM in a single dose
Probenecid, PLUS 1 g orally administered concurrently in a single dose The complete list of recommended regimens can be found in
Doxycycline WITH or 100 mg orally twice a day for 14 days CDCs 2015 STD Treatment Guidelines.
Metronidazole WITHOUT 500 mg orally twice a day for 14 days
Scabies permethrin 5% cream
ivermectin
OR Apply to all areas of body from neck down, wash off after 8-14 hours
200 g/kg orally, repeated in 2 weeks
lindane 1%23,24 1 oz. of lotion or 30 g of cream, applied thinly to all
areas of the body from the neck down, wash off after 8 hours
Syphilis benzathine penicillin G 2.4 million units IM in a single dose doxycycline3,25 100 mg 2x/day for 14 days
tetracycline3,25 500 mg orally 4x/day for 14 days
OR
Primary, secondary, or early latent <1 year
Latent >1 year, latent of unknown duration benzathine penicillin G 2.4 million units IM in 3 doses each at 1 week intervals doxycycline3,25 100 mg 2x/day for 28 days OR
(7.2 million units total) tetracycline3,25 500 mg orally 4x/day for 28 days
Pregnancy See complete CDC guidelines.
Neurosyphilis aqueous crystalline penicillin G 1824 million units per day, administered as 34 million units IV procaine penicillin G 2.4 MU IM 1x daily PLUS
every 4 hours or continuous infusion, for 1014 days probenecid 500 mg orally 4x/day, both for 10-14 days.
Congenital syphilis See complete CDC guidelines. See CDC STD Treatment guidelines for discussion of alternative therapy in
patients with penicillin allergy.
Children: Primary, secondary, or early latent <1 year benzathine penicillin G 50,000 units/kg IM in a single dose (maximum 2.4 million units)
Children: Latent >1 year, latent of unknown duration benzathine penicillin G 50,000 units/kg IM for 3 doses at 1 week intervals
(maximum total 7.2 million units)
Trichomoniasis metronidazole22
tinidazole26
OR 2 g orally in a single dose
2 g orally in a single dose
metronidazole22 500 mg 2x/day for 7 days
metronidazole 500mg orally 2x/day for 7 days
Persistent or recurrent trichomoniasis
If this regimen fails:
metronidazole OR 2g orally for 7 days
tinidazole 2g orally for 7 days
If this regimen fails, susceptibility testing is recommended.
CS253348
1.
2.
3.
4.
5.
6.
7.
8.
9.
10.
11.
12.
13.
14.
15.
The recommended regimens are equally efcacious.
These creams are oil-based and may weaken latex condoms and diaphragms. Refer to product labeling for
further information.
Should not be administered during pregnancy, lactation, or to children <8 years of age.
If patient cannot tolerate high-dose erythromycin base schedules, change to 250 mg 4x/day for 14 days.
If patient cannot tolerate high-dose erythromycin ethylsuccinate schedules, change to 400 mg orally 4 times a
day for 14 days.
Contraindicated for pregnant or lactating women.
Clinical experience and published studies suggest that azithromycin is safe and effective.
Erythromycin estolate is contraindicated during pregnancy.
Effectiveness of erythromycin treatment is approximately 80%; a second course of therapy may be
required.
Patients who do not respond to therapy (within 72 hours) should be re-evaluated.
For patients with suspected sexually transmitted epididymitis, close follow-up is essential.
No denitive information available on prenatal exposure.
Treatment may be extended if healing is incomplete after 10 days of therapy.
Consider discontinuation of treatment after one year to assess frequency of recurrence.
Vaginal, cervical, urethral meatal, and anal warts may require referral to an appropriate specialist.
16. CDC recommends that treatment for uncomplicated gonococcal infections of the cervix, urethra, and/or
rectum should include dual therapy, i.e., both a cephalosporin (e.g., ceftriaxone) plus azithromycin.
17. CDC recommends that cexime in combination with azithromycin or doxycycline be used as an alternative
when ceftriaxone is not available.
18. Only ceftriaxone is recommended for the treatment of pharyngeal infection. Providers should inquire
about oral sexual exposure
19. Use with caution in hyperbilirubinemic infants, especially those born prematurely.
20. MSM are unlikely to benet from the addition of nitroimidazoles.
21. Moxifloxacin 400mg orally 1x/day for 7 days is effective against Mycoplasma genitalium.
22. Pregnant patients can be treated with 2 g single dose.
23. Contraindicated for pregnant or lactating women, or children <2 years of age.
24. Do not use after a bath; should not be used by persons who have extensive dermatitis.
25. Pregnant patients allergic to penicillin should be treated with penicillin after desensitization.
26. Randomized controlled trials comparing single 2 g doses of metronidazole and tinidazole suggest
that tinidazole is equivalent to, or superior to, metronidazole in achieving parasitologic cure and
resolution of symptoms.
Indicates update from the 2010 CDC Guidelines for the Treatment of Sexually Transmitted Diseases.
Reviewed by the CDC 6/2015
C
Potrebbero piacerti anche
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Da EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Valutazione: 4.5 su 5 stelle4.5/5 (119)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaDa EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaValutazione: 4.5 su 5 stelle4.5/5 (265)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingDa EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingValutazione: 3.5 su 5 stelle3.5/5 (399)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryDa EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryValutazione: 3.5 su 5 stelle3.5/5 (231)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceDa EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceValutazione: 4 su 5 stelle4/5 (587)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItDa EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItValutazione: 4.5 su 5 stelle4.5/5 (838)
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeDa EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeValutazione: 4 su 5 stelle4/5 (5794)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnDa EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnValutazione: 4.5 su 5 stelle4.5/5 (234)
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeDa EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeValutazione: 4.5 su 5 stelle4.5/5 (537)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyDa EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyValutazione: 3.5 su 5 stelle3.5/5 (2219)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerDa EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerValutazione: 4.5 su 5 stelle4.5/5 (271)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreDa EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreValutazione: 4 su 5 stelle4/5 (1090)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersDa EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersValutazione: 4.5 su 5 stelle4.5/5 (344)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesDa EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesValutazione: 4 su 5 stelle4/5 (821)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceDa EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceValutazione: 4 su 5 stelle4/5 (894)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureDa EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureValutazione: 4.5 su 5 stelle4.5/5 (474)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaDa EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaValutazione: 4 su 5 stelle4/5 (45)
- Vaccine Adverse Events Separating Myth From RealityDocumento9 pagineVaccine Adverse Events Separating Myth From RealityPaul MuñozNessuna valutazione finora
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Da EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Valutazione: 4 su 5 stelle4/5 (98)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealDa EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealValutazione: 4 su 5 stelle4/5 (73)
- Documentation Pharmaceutical IndustryDocumento102 pagineDocumentation Pharmaceutical IndustryRagulNessuna valutazione finora
- PK/PD Changes in Critically Ill PatientsDocumento31 paginePK/PD Changes in Critically Ill Patientshuong LNessuna valutazione finora
- Drug Prescription in DentistryDocumento59 pagineDrug Prescription in DentistryIyad Abou-Rabii100% (1)
- Forensic Toxicology Drug TestingDocumento53 pagineForensic Toxicology Drug TestingNarciso Ana Jenecel100% (1)
- Drugs of Abuse: Evelyn B. Yumiaco M.D. Department of Pharmacology School of Medicine Angeles University FoundationDocumento92 pagineDrugs of Abuse: Evelyn B. Yumiaco M.D. Department of Pharmacology School of Medicine Angeles University FoundationBenjamin PrabhuNessuna valutazione finora
- PATIENT SAFETYDocumento9 paginePATIENT SAFETYKok Hui DiongNessuna valutazione finora
- Botanical Drug Development Quality StandardsDocumento23 pagineBotanical Drug Development Quality Standards刘朝阳Nessuna valutazione finora
- # CLINICAL PHARMA FINALS MCQs 2021-1-30Documento30 pagine# CLINICAL PHARMA FINALS MCQs 2021-1-30Pavan chowdaryNessuna valutazione finora
- Usp40 Redesign List OnlineDocumento146 pagineUsp40 Redesign List OnlineTyoNessuna valutazione finora
- Quality Attributes Chewable TabletsDocumento16 pagineQuality Attributes Chewable TabletsSreekanth ChNessuna valutazione finora
- GFTR 9Documento52 pagineGFTR 9vishal vishalNessuna valutazione finora
- Panduan Penanggulangan TBDocumento132 paginePanduan Penanggulangan TBice mayasopaNessuna valutazione finora
- Piis0885392404002155 PDFDocumento36 paginePiis0885392404002155 PDFRohit ParasharNessuna valutazione finora
- Far MacoDocumento28 pagineFar MacoChristian Jara100% (1)
- BCS 1 1 PDFDocumento38 pagineBCS 1 1 PDFHely PatelNessuna valutazione finora
- Chemotherapy and Renal Andhepatic Insufficiency 2008Documento24 pagineChemotherapy and Renal Andhepatic Insufficiency 2008Vika RatuNessuna valutazione finora
- 1 Min To Introduce The Topic Flash Cards ListeningDocumento18 pagine1 Min To Introduce The Topic Flash Cards ListeningkrishnasreeNessuna valutazione finora
- VISANNE - Obat Untuk EndometriosisDocumento39 pagineVISANNE - Obat Untuk EndometriosisroykelumendekNessuna valutazione finora
- Pemakaian Obat RS Tahun 2020Documento20 paginePemakaian Obat RS Tahun 2020ENDAH SANDIAHNessuna valutazione finora
- Pharmacologictreatment Fortemporomandibular Andtemporomandibularjoint DisordersDocumento11 paginePharmacologictreatment Fortemporomandibular Andtemporomandibularjoint DisordersDušanNessuna valutazione finora
- Drug Study AssignmentDocumento1 paginaDrug Study AssignmentDaniela Claire FranciscoNessuna valutazione finora
- Clive G. Wilson Massoud Bakhshaee Howard N. E. Stevens Alan C. Perkins Malcolm Frier Elaine P. Blackshaw Julie S. Binns Drug Delivery, 1521-0464, Volume 4, Issue 3, 1997, Pages 201 - 206Documento45 pagineClive G. Wilson Massoud Bakhshaee Howard N. E. Stevens Alan C. Perkins Malcolm Frier Elaine P. Blackshaw Julie S. Binns Drug Delivery, 1521-0464, Volume 4, Issue 3, 1997, Pages 201 - 206Damodar GautamNessuna valutazione finora
- Analgesia New DrugsDocumento40 pagineAnalgesia New DrugsZulkarnainBustamamNessuna valutazione finora
- Immune System Drugs - FinalDocumento56 pagineImmune System Drugs - FinalSarte Rachelle AnneNessuna valutazione finora
- RF FVDB-19 Veterinary Drug and Product Declaration FormDocumento2 pagineRF FVDB-19 Veterinary Drug and Product Declaration FormLeogarda NudoNessuna valutazione finora
- Pediatric Code SheetDocumento2 paginePediatric Code SheetDerick RanaNessuna valutazione finora
- Neuromuscular Blocking Agents: Suxamethonium (Succinylcholine)Documento5 pagineNeuromuscular Blocking Agents: Suxamethonium (Succinylcholine)Montaser BadranNessuna valutazione finora
- Corrective Action and Preventive Action PlanDocumento3 pagineCorrective Action and Preventive Action Planbrocs relucioNessuna valutazione finora
- Management of Antithrombotic Therapy After Bleeding in Patients With Coronary Artery Disease And/or Atrial FibrillationDocumento20 pagineManagement of Antithrombotic Therapy After Bleeding in Patients With Coronary Artery Disease And/or Atrial Fibrillationdeni2razmoskiNessuna valutazione finora