Documenti di Didattica
Documenti di Professioni
Documenti di Cultura
Cross Aldol Condensation
Caricato da
yash0 valutazioniIl 0% ha trovato utile questo documento (0 voti)
34 visualizzazioni1 paginaCross Aldol Condensation
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Formati disponibili
PDF, TXT o leggi online da Scribd
Condividi questo documento
Condividi o incorpora il documento
Hai trovato utile questo documento?
Questo contenuto è inappropriato?
Segnala questo documentoCross Aldol Condensation
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Formati disponibili
Scarica in formato PDF, TXT o leggi online su Scribd
0 valutazioniIl 0% ha trovato utile questo documento (0 voti)
34 visualizzazioni1 paginaCross Aldol Condensation
Caricato da
yashCross Aldol Condensation
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Formati disponibili
Scarica in formato PDF, TXT o leggi online su Scribd
Sei sulla pagina 1di 1
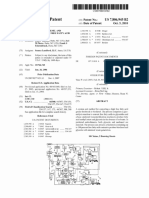
Mechanism of Cross Aldol Condensation
Crossed Aldol Reactions
In a crossed aldol reaction, two different carbonyl compounds are applied. If both carbonyl
compounds contain an hydrogen atom, both may act as electrophilic carbonyl compound, as
well as nucleophilic enol or enolate. In addition, each enol may nucleophilically attack the two
different carbonyl compounds. As a result, such a crossed aldol reaction yields four different
products. Therefore, crossed aldol reactions of this kind are synthetically less valuable. The
starting products depicted in the illustration are symmetric ketones. If this were not the case
additional products would be possible, due to the problem of regioselectivity.
If a starting product does not contain any hydrogen atom, the variety of possible products is
reduced to two, as this starting product can only act as an electrophilic carbonyl compound,
though it cannot act as a nucleophilic enolate. Benzaldehyde, which contains no hydrogen
atoms, is such an aldehyde.
CHEMISTRY tUTORIALS III A 41 Nehru Nagar, Ghaziabad. U.P. Pin 201001
www.chemistrytutorial.in email:- chtgzb@gmail.com ,
Mobile:-7042090378,7579218698
Potrebbero piacerti anche
- Claisen CondensationDocumento1 paginaClaisen CondensationyashNessuna valutazione finora
- Carbylamine ReactionDocumento1 paginaCarbylamine ReactionyashNessuna valutazione finora
- Balz Schiemann Reaction PDFDocumento1 paginaBalz Schiemann Reaction PDFyashNessuna valutazione finora
- Dmr's Physics Notes - Oersted's ExperimentDocumento4 pagineDmr's Physics Notes - Oersted's ExperimentyashNessuna valutazione finora
- DMR's PHYSICS NOTES - Introduction - Magnetic FieldDocumento4 pagineDMR's PHYSICS NOTES - Introduction - Magnetic FieldyashNessuna valutazione finora
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeDa EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeValutazione: 4.5 su 5 stelle4.5/5 (537)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Da EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Valutazione: 4 su 5 stelle4/5 (98)
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeDa EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeValutazione: 4 su 5 stelle4/5 (5794)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingDa EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingValutazione: 3.5 su 5 stelle3.5/5 (400)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceDa EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceValutazione: 4 su 5 stelle4/5 (588)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureDa EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureValutazione: 4.5 su 5 stelle4.5/5 (474)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryDa EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryValutazione: 3.5 su 5 stelle3.5/5 (231)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceDa EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceValutazione: 4 su 5 stelle4/5 (895)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnDa EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnValutazione: 4.5 su 5 stelle4.5/5 (234)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItDa EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItValutazione: 4.5 su 5 stelle4.5/5 (838)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerDa EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerValutazione: 4.5 su 5 stelle4.5/5 (271)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaDa EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaValutazione: 4.5 su 5 stelle4.5/5 (266)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealDa EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealValutazione: 4 su 5 stelle4/5 (74)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaDa EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaValutazione: 4 su 5 stelle4/5 (45)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersDa EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersValutazione: 4.5 su 5 stelle4.5/5 (345)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyDa EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyValutazione: 3.5 su 5 stelle3.5/5 (2259)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreDa EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreValutazione: 4 su 5 stelle4/5 (1090)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Da EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Valutazione: 4.5 su 5 stelle4.5/5 (121)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesDa EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesValutazione: 4 su 5 stelle4/5 (821)
- Chapter 3 Hydraulic SystemDocumento88 pagineChapter 3 Hydraulic SystemAhmad Anas100% (1)
- Heterogeneous Azeotropic Distillation Column DesignDocumento67 pagineHeterogeneous Azeotropic Distillation Column Designvenkatesh801100% (1)
- 715 1Documento155 pagine715 1Aniculaesi MirceaNessuna valutazione finora
- Tallentex Class 10 # 2022-23Documento20 pagineTallentex Class 10 # 2022-23Sreeja SujithNessuna valutazione finora
- Paracetamol e Ibuprofeno Como Contaminantes EmergentesDocumento27 pagineParacetamol e Ibuprofeno Como Contaminantes EmergentesElmer VargasNessuna valutazione finora
- Coir PitDocumento110 pagineCoir Pittest1100% (2)
- K02 Mechanical Seal Leak - RCA DocumentDocumento8 pagineK02 Mechanical Seal Leak - RCA DocumentMidha NeerNessuna valutazione finora
- Yellow Passion Fruits Headspace Werkhoff1998Documento18 pagineYellow Passion Fruits Headspace Werkhoff1998mapollo2000Nessuna valutazione finora
- United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 7,806,945 B2: The To In... TDocumento21 pagineUnited States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 7,806,945 B2: The To In... TesiNessuna valutazione finora
- New List of GLP Approved LabsDocumento15 pagineNew List of GLP Approved LabsMulayam Singh YadavNessuna valutazione finora
- Advantages and Disadvantages of Hydraulic SystemsDocumento3 pagineAdvantages and Disadvantages of Hydraulic SystemsTina MilovanovićNessuna valutazione finora
- Refractories IP PDFDocumento52 pagineRefractories IP PDFJarlys ZaniNessuna valutazione finora
- Pcac - Ucm486146Documento429 paginePcac - Ucm486146leoncioNessuna valutazione finora
- Musk AmbretteDocumento19 pagineMusk AmbretteSachin KausadikarNessuna valutazione finora
- Phenguard™ 935: Product Data SheetDocumento6 paginePhenguard™ 935: Product Data SheetMuthuKumarNessuna valutazione finora
- Applications Assignment 2Documento7 pagineApplications Assignment 2Chrystal BrownNessuna valutazione finora
- Poster Concrete (SMY1B) 270612FINALDocumento1 paginaPoster Concrete (SMY1B) 270612FINALIsalfi JahroNessuna valutazione finora
- Overview of The ProcessDocumento10 pagineOverview of The ProcessChaitanya PottiNessuna valutazione finora
- 20 eDocumento57 pagine20 eakanksha vermaNessuna valutazione finora
- Spark Sensor FM 1-8 - EngDocumento86 pagineSpark Sensor FM 1-8 - EngBarosz0% (1)
- Catalogo Rieles PDFDocumento133 pagineCatalogo Rieles PDFWilliam AguilarNessuna valutazione finora
- Product Data Sheet Metco 9MBM / 9MBH Plasma Spray GunDocumento4 pagineProduct Data Sheet Metco 9MBM / 9MBH Plasma Spray GunMuhammad ZulfaqarNessuna valutazione finora
- NAAMM NOMMA Finishes Manual PDFDocumento116 pagineNAAMM NOMMA Finishes Manual PDFMichaelTorresNessuna valutazione finora
- Safety and Health Topics - Hydrogen Sulfide - Evaluating and Controlling ExposureDocumento3 pagineSafety and Health Topics - Hydrogen Sulfide - Evaluating and Controlling ExposurehazopmanNessuna valutazione finora
- Catalogue Product M-Plus FilterDocumento40 pagineCatalogue Product M-Plus FilterAdrian Samuel ThenochNessuna valutazione finora
- AHMSW 8 Fiche de PhaseDocumento12 pagineAHMSW 8 Fiche de PhaseBOUBAKER LOGBINessuna valutazione finora
- Biogas From HuskDocumento10 pagineBiogas From HuskRaghavendra Raghav0% (1)
- Gerflor Catalog SPM 2019 348 EnrichDocumento152 pagineGerflor Catalog SPM 2019 348 EnrichsuhaamuhammadNessuna valutazione finora
- Lecture02 - Hubert - Melting and Fining ProcessesDocumento71 pagineLecture02 - Hubert - Melting and Fining ProcessesasitchawlaNessuna valutazione finora
- Additives in Australian FoodsDocumento11 pagineAdditives in Australian FoodsSarah AnnesleyNessuna valutazione finora