Documenti di Didattica
Documenti di Professioni
Documenti di Cultura
K Ecology-1
Caricato da
luciferDescrizione originale:
Titolo originale
Copyright
Formati disponibili
Condividi questo documento
Condividi o incorpora il documento
Hai trovato utile questo documento?
Questo contenuto è inappropriato?
Segnala questo documentoCopyright:
Formati disponibili
K Ecology-1
Caricato da
luciferCopyright:
Formati disponibili
Cambridge AS level Biology
[SECTION: K ECOLOGY]
MCQs
1. The diagram shows part of the nitrogen cycle.
Which kind of bacteria are involved in steps 1, 2 and 3?
2. What name is given to all the organisms in an area and their interactions with their environment?
A community
B ecosystem
C niche
D population
3. Which statement explains why two species cannot permanently occupy the same ecological niche?
A The two species could not interbreed.
B The two species may be part of separate food webs.
C The two species would compete for the same resources.
D The two species would have different nutritional requirements.
4. How does denitrification occur in the soil?
A active uptake of nitrate ions by plant roots
B bacterial reduction of nitrate ions to nitrogen gas
C drainage of manured fields
D leaching of nitrate ions
5. What name is given to all the organisms of the same species living in an area?
A community
B ecosystem
C niche
D population
Waleed Ahmad Khan
(ECP 2013 2015)
Phone: 0347 4443879 |
Cambridge AS level Biology
[SECTION: K ECOLOGY]
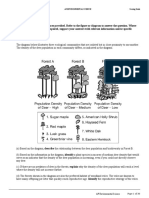
6. The diagram shows the energy flow model for all the species in a forest. The width of the arrows is
proportional to the amount of energy transferred. Which circle represents the decomposers?
7. Which group could be a single population?
A all the animals and plants on an isolated island
B all the birds counted in one day in a garden
C all the bacteria in a colony of Bacillus subtilis
D all the insects occupying three hectares of farmland
8. What is the role of decomposers in the nitrogen cycle?
A They convert proteins to ammonium compounds.
B They fix atmospheric nitrogen.
C They oxidise ammonium compounds to nitrites.
D They oxidise nitrites to nitrates.
9. Within an ecosystem, the top consumers in a food chain are few in number.
Which statement explains this?
A Energy losses occur at each trophic level.
B Energy losses occur within the consumers digestive systems.
C Top consumers have a low reproductive rate.
D Top consumers are large in size.
10. A square metre of grassland receives about 1 047 000 kJ of solar light energy each year.
The table shows what happens to this energy.
How much energy is used by the grass in photosynthesis?
A 2000 kJ
B 19 500 kJ
C 21 500 kJ
Waleed Ahmad Khan
(ECP 2013 2015)
D 23 500 kJ
Phone: 0347 4443879 |
Cambridge AS level Biology
[SECTION: K ECOLOGY]
11. Why does the application of nitrate fertilisers cause an increase in crop production?
A Green plants manufacture more protein.
B More nitrogen is fixed in leguminous plants.
C The fertiliser adds energy to the ecosystem.
D The number of denitrifying bacteria decreases.
12. What name is given to all the organisms of different species living in an area?
A community
B ecosystem
C niche
D population
13. Which agricultural practice will not provide an alternative to the use of ammonium nitrate as a
fertiliser to increase the productivity of wheat?
A growing wheat and another cereal crop in the same field in alternate years
B growing wheat and beans in the same field in alternate years
C ploughing animal waste such as dung into the soil
D using synthetic urea as a fertilizer
14. Which stage in the nitrogen cycle is linked to its bacteria?
15. What is the ecological definition of the term community?
A all the food webs in an ecosystem
B all the individuals of one species in an area
C all the organisms in an area
D the living organisms and their non-living environment
16. Which stage of energy transfer has the lowest efficiency?
A sunlight producer
B producer primary consumer
C primary consumer secondary consumer
D secondary consumer tertiary consumer
17. Leguminous plants have root nodules containing bacteria. The diagram shows a transverse section
through part of the root and root nodule of a leguminous plant.
Waleed Ahmad Khan
(ECP 2013 2015)
Phone: 0347 4443879 |
Cambridge AS level Biology
[SECTION: K ECOLOGY]
What is indicated by the labels 1, 2, 3 and 4?
18. A tree carries out photosynthesis and provides organic compounds for other organisms in a forest. It
takes carbon dioxide from and returns oxygen to the atmosphere. It takes water from the soil into
its roots and its leaves lose water to the atmosphere. Many other organisms live in the tree. Which
of these terms applies to the description of the tree?
A community
B ecosystem
C habitat
D niche
19. Which box contains only the parts of an ecosystem which are classed as a food web?
20. Which process does not make nitrogen-containing compounds available to plants?
A ammonification by decomposers
B denitrification by denitrifying bacteria
C nitrogen fixation in plant root nodules
D nitrogen fixation by soil bacteria
Waleed Ahmad Khan
(ECP 2013 2015)
Phone: 0347 4443879 |
Cambridge AS level Biology
[SECTION: K ECOLOGY]
21. The diagram shows a food web.
How many trophic levels are represented in the food web?
A3
B4
C5
D6
22. The diagram represents loss of energy from a food chain to decomposers, transfer of energy to the
next trophic level and energy loss through respiration. All figures are in kJ m2y1.
What is illustrated by this diagram?
A Carnivores lose more energy than herbivores.
B Energy loss to decomposers is higher than respiratory loss.
C Energy transfer between trophic levels is about 10 %.
D The energy of the final trophic level is not used.
23. The diagram represents part of the nitrogen cycle.
Which process is carried out by nitrifying bacteria?
Waleed Ahmad Khan
(ECP 2013 2015)
Phone: 0347 4443879 |
Cambridge AS level Biology
[SECTION: K ECOLOGY]
24. What limits the number of trophic levels in a food chain?
A biomass of the autotrophs
B efficiency of energy conversion between levels
C net productivity of the ecosystem
D species diversity in the ecosystem
25. The following are definitions of three ecological terms.
1 all of the organisms and their environment
2 group of individuals of one species living in an area
3 all of the organisms living in a habitat
What are the correct definitions of a community and a population?
26. The diagram shows the circulation of nitrogen in nature.
What is correct?
Waleed Ahmad Khan
(ECP 2013 2015)
Phone: 0347 4443879 |
Cambridge AS level Biology
[SECTION: K ECOLOGY]
27. Which statement explains why two species cannot permanently occupy the same ecological niche?
A The two species could not interbreed.
B The two species may be part of separate food webs.
C The two species would compete for the same resources.
D The two species would have different nutritional requirements.
28. Following an environmental disaster of a major volcanic eruption, the atmosphere contains greatly
increased amounts of dust. How does this affect the following organisms?
29. The diagram shows the flow of energy through an ecosystem. Photosynthesis is the gross
productivity. Producers lose some energy in respiration and the energy left is the net productivity.
This can also be expressed as an equation:
Net Productivity (NP) = Gross Productivity (GP) Respiration (R)
Some of the net productivity passes to herbivores.
Waleed Ahmad Khan
(ECP 2013 2015)
Phone: 0347 4443879 |
Cambridge AS level Biology
[SECTION: K ECOLOGY]
Which calculation gives the proportion of net productivity passing to herbivores?
30. The diagram shows some chemical conversions during the nitrogen cycle.
Which conversions involve microorganisms?
31. What is the correct match of example to ecological term?
32. The diagram shows a simplified nitrogen cycle. During which stage does nitrification take place?
Waleed Ahmad Khan
(ECP 2013 2015)
Phone: 0347 4443879 |
Cambridge AS level Biology
[SECTION: K ECOLOGY]
33. Grasshoppers eat only the leaves of grass. Grasshoppers are eaten by carnivorous beetles.
What does this description of grasshoppers give us sufficient information to define?
1 habitat
2 niche
3 trophic level
A 2 only
B 3 only
C 2 and 3 only
D 1, 2 and 3
34. Of the prey consumed by the lion, into which box does the largest amount of energy go?
Waleed Ahmad Khan
(ECP 2013 2015)
Phone: 0347 4443879 |
Cambridge AS level Biology
[SECTION: K ECOLOGY]
KEY:
1.
2.
3.
4.
5.
6.
7.
8.
9.
10.
11.
12.
13.
14.
15.
16.
17.
18.
19.
20.
21.
22.
23.
24.
25.
26.
27.
28.
29.
30.
31.
32.
33.
34.
B
B
C
B
D
B
C
A
A
D
A
A
A
B
C
A
A
D
B
B
C
C
C
B
D
D
C
B
C
B
A
C
B
C
For Any Error in typing, contact:
Waleed Ahmad Khan
0347 4443879
Waleed Ahmad Khan
(ECP 2013 2015)
Phone: 0347 4443879 |
10
Cambridge AS level Biology
[SECTION: K ECOLOGY]
Theory
1. Fig. 2.1 shows the flow of energy through an ecosystem. All the figures are in kJ m2 year1.
(a) Calculate how much energy is available to the primary consumers in this ecosystem.
......................................................................................................................................[1]
Waleed Ahmad Khan
(ECP 2013 2015)
Phone: 0347 4443879 |
11
Cambridge AS level Biology
[SECTION: K ECOLOGY]
(b) The efficiency of energy transfer between trophic levels is calculated by comparing the energy
available to a trophic level with the energy available to the next trophic level. Between secondary and
tertiary consumers, this is calculated as follows.
Use the formula above to calculate the efficiency of energy transfer between the secondary consumers
and the tertiary consumers in this ecosystem.
.............................................................................................................................................
..........................................................................................................................................
......................................................................................................................................[1]
(c) In some food webs, individual consumer species feed at different trophic levels. With reference to
Fig. 2.1, explain an advantage of this for these consumer species.
..........................................................................................................................................
..........................................................................................................................................
........................................................................................................................................[2]
(d) Explain the role of decomposers in the cycling of carbon and nitrogen in ecosystems.
..........................................................................................................................................
.............................................................................................................................................
.............................................................................................................................................
..........................................................................................................................................
.......................................................................................................................................
........................................................................................................................................[4]
Waleed Ahmad Khan
(ECP 2013 2015)
Phone: 0347 4443879 |
12
Cambridge AS level Biology
[SECTION: K ECOLOGY]
2. Food webs in hot deserts are much simpler than those of other areas, such as temperate woodlands
or coral reefs. The physical conditions in deserts are so extreme that few organisms can survive.
However, there are plants and animals that have special adaptations to withstand big changes in
temperature and lack of rainfall. Desert plants provide shade and food for herbivorous animals, such
as insects, lizards and rodents. Snakes, scorpions and spiders feed on the herbivores. Animals such
as the fennec fox and hawks feed as top carnivores.
(a) State the term that best describes each of the following.
(i) Organisms, such as desert plants, that form the first trophic level in a food web.
term ......................................................................................................................[1]
(ii) All the fennec foxes living in one area at the same time.
term ......................................................................................................................[1]
(iii) All the different species that inhabit a desert at the same time.
term ......................................................................................................................[1]
(iv) A natural unit, such as a desert, consisting of all the living organisms and the physical
environment interacting together to give a stable system.
term ......................................................................................................................[1]
(v) Herbivorous animals, such as lizards and rodents, which are prey for carnivores.
term ......................................................................................................................[1]
(b) Using information from the passage, explain the term habitat.
........................................................................................................................................................................
........................................................................................................................................................................
........................................................................................................................................................................
...................................................................................................................................................................[2]
(c) Explain how the leaves of desert plants may be adapted for survival in areas with little rainfall.
..........................................................................................................................................
..........................................................................................................................................
..........................................................................................................................................
..........................................................................................................................................
....................................................................................................................................... [3]
Waleed Ahmad Khan
(ECP 2013 2015)
Phone: 0347 4443879 |
13
Cambridge AS level Biology
[SECTION: K ECOLOGY]
3. Complete the table below by describing one role in living organisms for each of the ions listed.
4. (a) An ecosystem may be as small as a pond or as large as a forest. Some scientists consider that the
whole biosphere is an ecosystem. Give a detailed definition of the term ecosystem. You may use
another example in your answer.
........................................................................................................................................................................
........................................................................................................................................................................
........................................................................................................................................................................
........................................................................................................................................................................
....................................................................................................................................................................[3]
(b) In 1978, the American ecologist Paul Colinvaux published a book of essays with the title Why Big
Fierce Animals are Rare. Explain why big, fierce animals are rare in ecosystems.
........................................................................................................................................................................
........................................................................................................................................................................
........................................................................................................................................................................
........................................................................................................................................................................
....................................................................................................................................................................[3]
Waleed Ahmad Khan
(ECP 2013 2015)
Phone: 0347 4443879 |
14
Cambridge AS level Biology
[SECTION: K ECOLOGY]
(c) Many tropical islands have nitrogen-deficient soils. Leguminous trees, such as Royal Poinciana,
Delonix regia, grow well in such conditions. Explain why leguminous plants grow well in these
conditions.
........................................................................................................................................................................
........................................................................................................................................................................
........................................................................................................................................................................
........................................................................................................................................................................
....................................................................................................................................................................[3]
5. The element nitrogen is present in many biological molecules, such as amino acids, proteins and
nucleotides. Fig. 6.1 shows part of the nitrogen cycle.
Waleed Ahmad Khan
(ECP 2013 2015)
Phone: 0347 4443879 |
15
Cambridge AS level Biology
Waleed Ahmad Khan
[SECTION: K ECOLOGY]
(ECP 2013 2015)
Phone: 0347 4443879 |
16
Potrebbero piacerti anche
- Aquatic Ecosystems Biomes Ws Manuel TzulDocumento2 pagineAquatic Ecosystems Biomes Ws Manuel Tzulapi-32383118280% (5)
- Biodiversity Biological Population FRQ AnswerDocumento30 pagineBiodiversity Biological Population FRQ AnswerAllan YUNessuna valutazione finora
- Chapter 3 The Biosphere Test ADocumento7 pagineChapter 3 The Biosphere Test ATUTORKIMNessuna valutazione finora
- Artificial Intelligence Report MS WordDocumento11 pagineArtificial Intelligence Report MS Wordlucifer75% (4)
- Korean Drama QuotesDocumento19 pagineKorean Drama Quoteslucifer0% (1)
- Energy and Ecosystem Paper 1 (Multiple Choices)Documento9 pagineEnergy and Ecosystem Paper 1 (Multiple Choices)Tia wkwkNessuna valutazione finora
- Unit 7. The Dynamics of Ecosystems.Documento12 pagineUnit 7. The Dynamics of Ecosystems.nimolesaNessuna valutazione finora
- Chapter 4 - Ecology: MarkschemeDocumento33 pagineChapter 4 - Ecology: MarkschemeSebastian Enriquez EstradaNessuna valutazione finora
- Biology SL 2025 Interaction & Interdependence - Transfers of Energy & MatterDocumento52 pagineBiology SL 2025 Interaction & Interdependence - Transfers of Energy & MatterAlyasin FrougaNessuna valutazione finora
- Ecology by Prof. Galvez No AnswerDocumento12 pagineEcology by Prof. Galvez No AnswerREB2020Nessuna valutazione finora
- Ecology TestDocumento6 pagineEcology TestaldemairaNessuna valutazione finora
- Practice Questions 1 Ecology ClickersDocumento17 paginePractice Questions 1 Ecology ClickersGiri Raj SinghNessuna valutazione finora
- Our Environment PRevious YEar QuestionsDocumento11 pagineOur Environment PRevious YEar QuestionsZhugzhuang ZuryNessuna valutazione finora
- Hkcee Biology - 2.2 Ecosystem - P.1Documento22 pagineHkcee Biology - 2.2 Ecosystem - P.1Kathy WongNessuna valutazione finora
- Te-Our Environment Final Revisor (2022-23)Documento86 pagineTe-Our Environment Final Revisor (2022-23)Gautam SharrmaNessuna valutazione finora
- Ecology Revision SheetDocumento4 pagineEcology Revision SheetkaylatheunicornytNessuna valutazione finora
- The Living World Ecosystem Unit 1 TestDocumento11 pagineThe Living World Ecosystem Unit 1 Testprince darkoNessuna valutazione finora
- SL Paper1Documento18 pagineSL Paper1Yoshua Yanottama100% (1)
- HS 1 Ecology Practice ReviewerDocumento5 pagineHS 1 Ecology Practice ReviewerRamon GasgasNessuna valutazione finora
- TERM 3 Chapter 15Documento90 pagineTERM 3 Chapter 15IRESHA TAN KALEESVARAN MoeNessuna valutazione finora
- Biology - Freeman 3E - Ecology Chapter 54 QuizDocumento14 pagineBiology - Freeman 3E - Ecology Chapter 54 QuizEtoileCamelliaNessuna valutazione finora
- Ecologyreviewsheet2 Answer KeyDocumento6 pagineEcologyreviewsheet2 Answer Keyapi-235160519Nessuna valutazione finora
- Ecosystem (Quiz)Documento3 pagineEcosystem (Quiz)Karol MelendezNessuna valutazione finora
- Chapter-15 Our Environment: DefineDocumento7 pagineChapter-15 Our Environment: DefineAkisaturo XunNessuna valutazione finora
- Class - 10 - LN - 15 - Class Test-1Documento2 pagineClass - 10 - LN - 15 - Class Test-1Srivatsan BalajiNessuna valutazione finora
- Markscheme SL Paper1Documento27 pagineMarkscheme SL Paper1Yoshua YanottamaNessuna valutazione finora
- Biology 1 Post-Test: DIRECTIONS: Select The Best Answer To Each of TheDocumento3 pagineBiology 1 Post-Test: DIRECTIONS: Select The Best Answer To Each of TheGette AcupanNessuna valutazione finora
- SFG 2022 Level 1 Test 38 Solutions EnglishDocumento28 pagineSFG 2022 Level 1 Test 38 Solutions EnglishAatish AlokNessuna valutazione finora
- GE6351-Environmental Science and EngineeringDocumento22 pagineGE6351-Environmental Science and EngineeringChennaiSuperkingsNessuna valutazione finora
- CHP 24 & 25 ObjectivesDocumento9 pagineCHP 24 & 25 ObjectivesTay Joo FangNessuna valutazione finora
- CH 3Documento6 pagineCH 32020 78 Aditya patilNessuna valutazione finora
- Env Questions PDFDocumento33 pagineEnv Questions PDFDeepti KulkarniNessuna valutazione finora
- BIOL 203 Spring 2015 Mock FinalDocumento6 pagineBIOL 203 Spring 2015 Mock FinalMASNessuna valutazione finora
- GE6351 - Environmental Science and EngineeringDocumento16 pagineGE6351 - Environmental Science and EngineeringBala AndersonNessuna valutazione finora
- G9 Summative TestDocumento4 pagineG9 Summative Testmarisa canoNessuna valutazione finora
- Ge15 Practice Set AnswersDocumento11 pagineGe15 Practice Set AnswersSilentNessuna valutazione finora
- HL Paper1Documento13 pagineHL Paper1Jane ChangNessuna valutazione finora
- EcosystemDocumento1 paginaEcosystemsouvikNessuna valutazione finora
- Evs Ans Key 2018Documento10 pagineEvs Ans Key 2018Abinash BoruahNessuna valutazione finora
- Introducing Physical Geography 5Th Edition Strahler Test Bank Full Chapter PDFDocumento55 pagineIntroducing Physical Geography 5Th Edition Strahler Test Bank Full Chapter PDFstevenwhitextsngyadmk100% (11)
- Introducing Physical Geography 5th Edition Strahler Test BankDocumento34 pagineIntroducing Physical Geography 5th Edition Strahler Test Bankadelaidelatifahjq8w5100% (30)
- Test Bank For Ecology The Economy of Nature 8th Edition Rick Relyea Robert e RicklefsDocumento13 pagineTest Bank For Ecology The Economy of Nature 8th Edition Rick Relyea Robert e RicklefsJohn Rigby100% (32)
- Evs Notes 21civ57Documento10 pagineEvs Notes 21civ57Akshay VivekanadaNessuna valutazione finora
- EcosystemDocumento10 pagineEcosystemKrish BagNessuna valutazione finora
- 18CIV59 Practice QPDocumento33 pagine18CIV59 Practice QPRakesh PatilNessuna valutazione finora
- 4THQ Sci8 ExaminationDocumento4 pagine4THQ Sci8 ExaminationJonathan donanNessuna valutazione finora
- Science 20-Unit D TestDocumento6 pagineScience 20-Unit D Testapi-697899968Nessuna valutazione finora
- Georgia Biology Eoct Mini Sample Test With Answer SheetDocumento5 pagineGeorgia Biology Eoct Mini Sample Test With Answer SheetTiffany GallinaNessuna valutazione finora
- Lecture8 Homework BIO1401 Sp23Documento7 pagineLecture8 Homework BIO1401 Sp23wafae moutanaNessuna valutazione finora
- Science CFA - Energy TransferDocumento6 pagineScience CFA - Energy TransferHelina AmbayeNessuna valutazione finora
- Nutrient Cycles PogilDocumento8 pagineNutrient Cycles Pogiljvalenzuela4909Nessuna valutazione finora
- (Shrija Mandilwar) 2023-24 MYP5 Biology U4 SADocumento13 pagine(Shrija Mandilwar) 2023-24 MYP5 Biology U4 SAshrija nooporNessuna valutazione finora
- QB 1 10civ28Documento14 pagineQB 1 10civ28Mithesh KumarNessuna valutazione finora
- NCERT Exemplar Solution Class 10 Science Chapter 15Documento14 pagineNCERT Exemplar Solution Class 10 Science Chapter 15Priyanshu BhardwajNessuna valutazione finora
- All Important Question/Answer: Aso PublicationsdjkfcDocumento5 pagineAll Important Question/Answer: Aso PublicationsdjkfcAMIT KUMAR SINGHNessuna valutazione finora
- Biology Grade 10thDocumento13 pagineBiology Grade 10thXavier MehrezNessuna valutazione finora
- Gr.10 Weekend Worksheet Bio - 09.09.23Documento2 pagineGr.10 Weekend Worksheet Bio - 09.09.23Hema LathaNessuna valutazione finora
- Essential Biology 05 - Ecology, Evolution & ConservationDocumento31 pagineEssential Biology 05 - Ecology, Evolution & ConservationManuel TorresNessuna valutazione finora
- Class 5-6Documento31 pagineClass 5-6Krupali ChothaniNessuna valutazione finora
- Ecology Study Guide 4 - EcosystemsDocumento6 pagineEcology Study Guide 4 - EcosystemsJoeNessuna valutazione finora
- Nutrient Cycles and Energy Pyramids ActivityDocumento5 pagineNutrient Cycles and Energy Pyramids ActivityCamden J. LienNessuna valutazione finora
- A) Environ: 18CIV59: Environmental Studies Module 1-QB Set 1 and 2Documento14 pagineA) Environ: 18CIV59: Environmental Studies Module 1-QB Set 1 and 2Sourabh HalagekarNessuna valutazione finora
- Microbial Engineering: First International Symposium on Advances in Microbial EngineeringDa EverandMicrobial Engineering: First International Symposium on Advances in Microbial EngineeringNessuna valutazione finora
- 36 Hours in SeoulDocumento7 pagine36 Hours in SeoulluciferNessuna valutazione finora
- A Kushan-Period Sculpture: From The Reign of Jaya Varma-, A.D. 184/185 K NDocumento7 pagineA Kushan-Period Sculpture: From The Reign of Jaya Varma-, A.D. 184/185 K NluciferNessuna valutazione finora
- Depiction of Victorian Era in The Novel Great Expectations by Charles DickensDocumento6 pagineDepiction of Victorian Era in The Novel Great Expectations by Charles DickensluciferNessuna valutazione finora
- Summary of The Wolfman Study 1Documento1 paginaSummary of The Wolfman Study 1luciferNessuna valutazione finora
- Jivan Kandola Completed Poster UrssDocumento1 paginaJivan Kandola Completed Poster UrssluciferNessuna valutazione finora
- Event Date Week: Academic Calendar SPRING - 2021Documento2 pagineEvent Date Week: Academic Calendar SPRING - 2021luciferNessuna valutazione finora
- Chapter 2Documento40 pagineChapter 2luciferNessuna valutazione finora
- Lecture 14 & 15Documento16 pagineLecture 14 & 15luciferNessuna valutazione finora
- Thermal StabilityDocumento1 paginaThermal StabilityluciferNessuna valutazione finora
- Presentation On Social MediaDocumento5 paginePresentation On Social MedialuciferNessuna valutazione finora
- Main Features of Romantic Poetry2393832108542687685Documento3 pagineMain Features of Romantic Poetry2393832108542687685luciferNessuna valutazione finora
- Just A Housewife by Arti ChopraDocumento1 paginaJust A Housewife by Arti ChopraluciferNessuna valutazione finora
- 5 Chemical EnergeticsDocumento21 pagine5 Chemical EnergeticsluciferNessuna valutazione finora
- C EnzymesDocumento18 pagineC Enzymeslucifer100% (1)
- G Transport (Plants I)Documento18 pagineG Transport (Plants I)luciferNessuna valutazione finora
- 9A - Gas Exchange and SmokingDocumento79 pagine9A - Gas Exchange and SmokingluciferNessuna valutazione finora
- The Chaparral Group 4Documento8 pagineThe Chaparral Group 4Princess Sophia BillonesNessuna valutazione finora
- EARTHLIFE SCIENCE Q2 Week 8 Edited 1 11.pdf Version 1Documento11 pagineEARTHLIFE SCIENCE Q2 Week 8 Edited 1 11.pdf Version 1Princess Nicole ManoguidNessuna valutazione finora
- HATE March 28Documento4 pagineHATE March 28Diva PrestiaNessuna valutazione finora
- Ecology QuestionsDocumento4 pagineEcology QuestionsMrGilmartinNessuna valutazione finora
- Ecology PracticeTest 1Documento3 pagineEcology PracticeTest 1h8alfredNessuna valutazione finora
- Republic Act No. 11038Documento15 pagineRepublic Act No. 11038Yao ConaNessuna valutazione finora
- (Demetrio Boltovskoy) South Atlantic ZooplanktonDocumento1.491 pagine(Demetrio Boltovskoy) South Atlantic ZooplanktonMitzi BernalNessuna valutazione finora
- Create A Food Web ActivityDocumento2 pagineCreate A Food Web ActivityJohn Carlo VillenaNessuna valutazione finora
- Biome ClimatogramsDocumento2 pagineBiome ClimatogramsMjunaidiNessuna valutazione finora
- Terrestrial Ecosystem HomeworkDocumento2 pagineTerrestrial Ecosystem HomeworkNash LopezNessuna valutazione finora
- Earth and Life Science: Quarter 2 - Module 30: Interaction and InterdependenceDocumento20 pagineEarth and Life Science: Quarter 2 - Module 30: Interaction and Interdependencemaria matsuokaNessuna valutazione finora
- Ecology EntomologyDocumento112 pagineEcology EntomologyShimul DasNessuna valutazione finora
- Biology ProjectDocumento19 pagineBiology ProjectShriti Sikta Panda100% (1)
- An Assessment of Floristic Diversity of Daroji Sloth Bear Sanctuary, Hospet, Bellary District, Karnataka, IndiaDocumento12 pagineAn Assessment of Floristic Diversity of Daroji Sloth Bear Sanctuary, Hospet, Bellary District, Karnataka, IndiaresearchinbiologyNessuna valutazione finora
- CAPE Env. Science 2012 U1 P2Documento9 pagineCAPE Env. Science 2012 U1 P2Christina FrancisNessuna valutazione finora
- Biodiversity MCQDocumento5 pagineBiodiversity MCQKUMAR RISHAV100% (1)
- Exploring Biomes ReadingDocumento3 pagineExploring Biomes Readingapi-254428474Nessuna valutazione finora
- Ecological BalanceDocumento2 pagineEcological BalanceDiana Jane Gare100% (1)
- Sci 8 4TH Quarter Module 5Documento11 pagineSci 8 4TH Quarter Module 5Diosa BakingNessuna valutazione finora
- 3 EcosystemDocumento21 pagine3 EcosystemKishore KNessuna valutazione finora
- Fungal Flora in The Philippines: Values and Conservation: Anjela J. LageraDocumento19 pagineFungal Flora in The Philippines: Values and Conservation: Anjela J. LageraGerald GamboaNessuna valutazione finora
- Role of An Architect For Wetland RestorationDocumento7 pagineRole of An Architect For Wetland RestorationSyamantakNessuna valutazione finora
- Ecosystem Recovery by Genotypic DiversityDocumento1 paginaEcosystem Recovery by Genotypic DiversityHamada Elsayed AliNessuna valutazione finora
- Ecology Unit Study Guide AP BiologyDocumento3 pagineEcology Unit Study Guide AP Biologytanu96tpNessuna valutazione finora
- Ecology WorksheetDocumento7 pagineEcology WorksheetLaya ShrbagiNessuna valutazione finora
- Human Impact EssayDocumento2 pagineHuman Impact Essayapi-271877096Nessuna valutazione finora
- Levels of BiodiversityDocumento4 pagineLevels of BiodiversitySachin ShrivastavNessuna valutazione finora
- Estes Et Al (2011) - Trophic Downgrading of Planet EarthDocumento7 pagineEstes Et Al (2011) - Trophic Downgrading of Planet EarthMatthias MacéNessuna valutazione finora