Documenti di Didattica
Documenti di Professioni
Documenti di Cultura
Fetal Circulation in The Womb
Caricato da
ChristineAlaTitolo originale
Copyright
Formati disponibili
Condividi questo documento
Condividi o incorpora il documento
Hai trovato utile questo documento?
Questo contenuto è inappropriato?
Segnala questo documentoCopyright:
Formati disponibili
Fetal Circulation in The Womb
Caricato da
ChristineAlaCopyright:
Formati disponibili
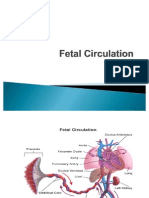
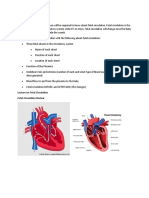
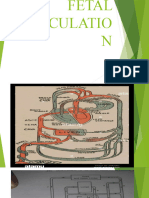
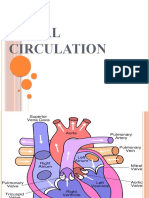
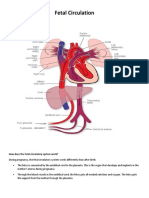
FETAL CIRCULATION IN THE WOMB
Because the fetus does not breathe or metabolize substances in the liver, several alterations of the
post birth circulatory route are needed. Three shunts ductus venosus, foramen ovale, And ductus
arterioles divert most of circulating blood away from the lungs and liver.
Oxygenated blood from the placenta enters the fetal body through the umbilical vein. About half
of the oxygenated venous blood goes through the liver during early pregnancy and the rest bypasses the
liver and enters the inferior vena cave through the first shunt, the ductus venosus. The blood then enters
the right atrium. Most of the blood passes directly into the left atrium through the second shunt, the
foramen ovale, where it mixes with the small amount of blood returning from the lungs. Blood is pumped
from the left ventricle into the aorta to nourish the body. A small amount of blood from the right ventricle
is circulated to the lungs to nourish the lung tissue. The rest of the blood from the right ventricle joins
oxygenated blood in the aorta through the third shut, ductus arteriosus.
CHANGES IN BLOOD CIRCULATION AFTER BIRTH
Fetal circulatory shunts are not needed after birth because the infant oxygenates blood in the
lungs, metabolizes substances in the liver, and stops circulating blood to the placenta. As the infant
breathes, blood flow to the lung increases, pressure in the right heart falls, and the foramen ovale closes.
Pressure in the aorta rises as pressure in the pulmonary artery falls, causing the direction of blood flow
through the ductus arteriosus to reverse, from the aorta into the pulmonary artery. The ductus arteriosus
constricts as the arterial oxygen levels rises. The ductus venosus constricts when blood flow from the
umbilical cord stops. The foramen ovale and ductus venosus permanently close as tissue proliferates in
these structures. The ductus venosus and ductus arteriosus become ligaments, as do the umbilical veins
and arteries.
DUCTUS ARTERIOSUS
Functional closure- 10-15 hours after
birth
(reversible
in
hypoxemia
and
hypovolemia)
Permanent closure 2-3 weeks
Remnant ligamentum arteriosum
FORAMEN OVALE
Increased pulmonary blood flow &
left atrial distention cause closure
Functional closure- at birth ,
anatomical closure by 1 year
maneuvers increase PVR increases
RA & RV pressure
Right to left atrial shunt may occur
in newborns & young infants
Potrebbero piacerti anche
- Fetal CirculationDocumento2 pagineFetal CirculationCJ PorrasNessuna valutazione finora
- Fetal CirculationDocumento62 pagineFetal CirculationRed Williams100% (4)
- Fetal CirculationDocumento5 pagineFetal CirculationJaime PorscheNessuna valutazione finora
- Fetal Circulation Anatomy and Physiology of Fetal Circulation Umbilical CordDocumento3 pagineFetal Circulation Anatomy and Physiology of Fetal Circulation Umbilical CordbobtagubaNessuna valutazione finora
- Fetal CirculationDocumento2 pagineFetal CirculationEric Gato100% (3)
- Update Fetal Circulation - MDM AmyDocumento10 pagineUpdate Fetal Circulation - MDM AmyNana Yunus100% (1)
- FetalcirculationDocumento32 pagineFetalcirculationannu panchalNessuna valutazione finora
- Fetal Circulation: Dr. Khush BakhtDocumento29 pagineFetal Circulation: Dr. Khush BakhtKhush BakhtNessuna valutazione finora
- Fetal CirculationDocumento8 pagineFetal CirculationKrestel Saligumba Palanog100% (1)
- 1 Fetal CirculationDocumento23 pagine1 Fetal Circulationmohanad11Nessuna valutazione finora
- Fetal Circulation-1Documento2 pagineFetal Circulation-1fxbukenyaNessuna valutazione finora
- Lecture 3 NCM 107Documento7 pagineLecture 3 NCM 107Anna YepisNessuna valutazione finora
- Fetal CirculationDocumento2 pagineFetal CirculationTracy88% (8)
- Congenital Heart DIseasesDocumento3 pagineCongenital Heart DIseasesAshan BopitiyaNessuna valutazione finora
- Fetal CirculationDocumento18 pagineFetal CirculationDr_ibk100% (1)
- Foetal CirculationDocumento39 pagineFoetal CirculationDr. Haricharan ANessuna valutazione finora
- FETALDocumento9 pagineFETALGunaNessuna valutazione finora
- Fetal CirculationDocumento20 pagineFetal CirculationMuhyeeSalaIdjadNessuna valutazione finora
- Unit 5Documento31 pagineUnit 5Bharat ThapaNessuna valutazione finora
- Embryonic Development of The HeartDocumento11 pagineEmbryonic Development of The HeartMatthew RyanNessuna valutazione finora
- Fetal CirculationDocumento3 pagineFetal Circulationyusrinastiti100% (1)
- Fetal CirculationDocumento8 pagineFetal Circulationfrimpong ChristopherNessuna valutazione finora
- Fetal CirculationDocumento3 pagineFetal CirculationDean MutemaNessuna valutazione finora
- Fetus Circulation LectureDocumento28 pagineFetus Circulation LecturecandrastefannNessuna valutazione finora
- Unit 6Documento32 pagineUnit 6Bharat ThapaNessuna valutazione finora
- Fetal CirculationDocumento5 pagineFetal Circulationbluemandrake2185Nessuna valutazione finora
- Fetal CirculatiDocumento1 paginaFetal CirculatiJonah MerabNessuna valutazione finora
- Dr. Nia-Fisiologi Sirkulasi Fetus, Bayi, DewasaDocumento21 pagineDr. Nia-Fisiologi Sirkulasi Fetus, Bayi, DewasaYuliasminde SofyanaNessuna valutazione finora
- Fetal Circulation FinalDocumento21 pagineFetal Circulation FinalpriyaNessuna valutazione finora
- Fetal CirculationDocumento26 pagineFetal CirculationMuskan TiwariNessuna valutazione finora
- Recitation AnatomyDocumento7 pagineRecitation AnatomyKent JuguilonNessuna valutazione finora
- Fetal CirculationDocumento16 pagineFetal CirculationArunashree ajayNessuna valutazione finora
- Fetal CirculationDocumento16 pagineFetal CirculationArunashree ajayNessuna valutazione finora
- Fetal To Neonatal TransitionDocumento6 pagineFetal To Neonatal TransitionGirma MitikuNessuna valutazione finora
- Submitted By: S.M. Tajuddin Group:245Documento18 pagineSubmitted By: S.M. Tajuddin Group:245KhurshidbuyamayumNessuna valutazione finora
- Adaption of Infants To Extra-Uterine LifeDocumento10 pagineAdaption of Infants To Extra-Uterine LifeJulienne QuintaoNessuna valutazione finora
- In The Fetal CirculationDocumento1 paginaIn The Fetal CirculationJesena SalveNessuna valutazione finora
- Fetal CirculationDocumento39 pagineFetal CirculationjerlinNessuna valutazione finora
- Murphy Essay - Give An Account of The Fetal Circulation and The Changes Which Take Place at Birth. What Clinical Problems Can Arise Here. EssayDocumento3 pagineMurphy Essay - Give An Account of The Fetal Circulation and The Changes Which Take Place at Birth. What Clinical Problems Can Arise Here. EssayscholifyNessuna valutazione finora
- RJI - Fetal CirculationDocumento10 pagineRJI - Fetal CirculationgalaetiNessuna valutazione finora
- Fetal CirculationDocumento19 pagineFetal CirculationAlozie PrestigeNessuna valutazione finora
- Fetalcirculation 181202080431 1Documento27 pagineFetalcirculation 181202080431 1mukiza FestusNessuna valutazione finora
- Fetal Circulation 4Documento24 pagineFetal Circulation 4UmarNessuna valutazione finora
- Fetal Circulation Fetal Circulation Begins in TheDocumento1 paginaFetal Circulation Fetal Circulation Begins in TheAkinfemi PreciousNessuna valutazione finora
- 1 Fetal CirculationDocumento21 pagine1 Fetal Circulationdr_mohanad100% (1)
- Fetal CirculationDocumento17 pagineFetal Circulationjibson2354Nessuna valutazione finora
- Fetal CirculationDocumento19 pagineFetal Circulation3sshhhNessuna valutazione finora
- Fetal CirculationDocumento27 pagineFetal CirculationSureshChevagoniNessuna valutazione finora
- Fetal CirculationDocumento2 pagineFetal Circulationanon_414797925Nessuna valutazione finora
- Fetal CirculationDocumento14 pagineFetal Circulationjoel david knda mj100% (3)
- Fetal Circulation...Documento2 pagineFetal Circulation...Ezra Dizon Manzano100% (1)
- Fetal Circulation and Adult CirculationDocumento2 pagineFetal Circulation and Adult Circulationchenglibag0% (1)
- Fetal CirculationDocumento1 paginaFetal CirculationnvhnygNessuna valutazione finora
- Fetal, Transition and Neonatal Circulation: Divya Mishra Dept of PediatricsDocumento37 pagineFetal, Transition and Neonatal Circulation: Divya Mishra Dept of PediatricsMathan KarthikNessuna valutazione finora
- Peñaso, J. - Ass. 2Documento5 paginePeñaso, J. - Ass. 2Jessica PeñasoNessuna valutazione finora
- Fetal CirculationDocumento4 pagineFetal CirculationTina Tin100% (1)
- Circulatory System: A Tutorial Study GuideDa EverandCirculatory System: A Tutorial Study GuideValutazione: 5 su 5 stelle5/5 (3)
- Human Body Book | Introduction to the Vascular System | Children's Anatomy & Physiology EditionDa EverandHuman Body Book | Introduction to the Vascular System | Children's Anatomy & Physiology EditionNessuna valutazione finora
- Ineffective Airway ClearanceDocumento1 paginaIneffective Airway ClearanceChristineAlaNessuna valutazione finora
- Nursing Care Plan - CancerDocumento3 pagineNursing Care Plan - CancerChristineAla0% (1)
- NCP PainDocumento2 pagineNCP PainChristineAlaNessuna valutazione finora
- Women With Many Sexual Partners Are at Greater Risk For Sexually Transmitted Diseases (STDS) and PidDocumento4 pagineWomen With Many Sexual Partners Are at Greater Risk For Sexually Transmitted Diseases (STDS) and PidChristineAla50% (2)
- NCP PainDocumento2 pagineNCP PainChristineAlaNessuna valutazione finora
- Items Quantity Price Per Unit TotalDocumento1 paginaItems Quantity Price Per Unit TotalChristineAlaNessuna valutazione finora
- Anatomy of Female PelvisDocumento16 pagineAnatomy of Female PelvisChristineAlaNessuna valutazione finora
- CHD CaseDocumento5 pagineCHD CaseChristineAlaNessuna valutazione finora
- Agree Needs ImprovementDocumento2 pagineAgree Needs ImprovementChristineAlaNessuna valutazione finora
- Emergency Nursing Journal, 217-222Documento2 pagineEmergency Nursing Journal, 217-222ChristineAlaNessuna valutazione finora
- Sensorimotor Stage: Approx. Age Piaget: Cognitive DevelopmentDocumento2 pagineSensorimotor Stage: Approx. Age Piaget: Cognitive DevelopmentChristineAlaNessuna valutazione finora
- Erik Erikson Stage of DevelopmentDocumento2 pagineErik Erikson Stage of DevelopmentChristineAlaNessuna valutazione finora
- Urine Analysis Lab ConDocumento13 pagineUrine Analysis Lab ConChristineAla63% (8)
- Patient'S Health HistoryDocumento2 paginePatient'S Health HistoryChristineAlaNessuna valutazione finora
- Nursing Responsibilities: By: Christine Joy A. AlaDocumento6 pagineNursing Responsibilities: By: Christine Joy A. AlaChristineAlaNessuna valutazione finora