Documenti di Didattica
Documenti di Professioni
Documenti di Cultura
Note Chapter 2
Caricato da
Mandy VoonCopyright
Formati disponibili
Condividi questo documento
Condividi o incorpora il documento
Hai trovato utile questo documento?
Questo contenuto è inappropriato?
Segnala questo documentoCopyright:
Formati disponibili
Note Chapter 2
Caricato da
Mandy VoonCopyright:
Formati disponibili
CHAPTER TWO:
Blood Circulation and Transport
2.1 Transport System in Humans
2.2 Human Blood
2.3 Transport System in Plants
Mandy Voon
Science PT3
2015/2016
CHAPTER TWO
Blood Circulation and Transport
2.1 Transport System in Humans
-Human transport system is called circulatory system.
-It consists of heart and blood vessels (arteries, veins and capillaries)
Figure 2.1 The human blood circulatory system
Figure 2.2 The capillary
2.1.1 Structure and function of the human heart
-Characteristic of heart:
a) Heart is situated inside the thoracic cavity, behind the breastbone and between
the left and the right lung.
b) Cone-shaped and muscular organ.
c) Made up of cardiac muscle. These cells required food and oxygen to carry out
activities
-Function of heart:
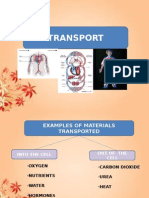
a) To pump blood to all parts of the body
b) Transport nutrient and oxygen to body cell
c) Transport carbon dioxide, urea and water from the body cell
CHAPTER TWO
Blood Circulation and Transport
Figure2.3 The Structure of human heart
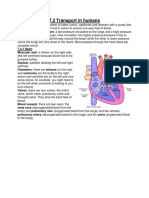
-Heart is made up of four chambers.
a) two chamber at the top are the left and right atrium
b) two chamber at the below the left and right ventricles
- Right atrium and right ventricle carry deoxygenated blood
-Left atrium and left carry the oxygenated blood
- The left and right chambers are separated by the muscular known as septum to
avoid the deoxygenated blood combine with oxygenated blood.
- Characteristic of the atrium and ventricle:
a) Ventricle has larger space and volume
b) Ventricle has thicker wall
c) Left ventricle is thicker and more muscular than right ventricle because this
chamber pumps blood under high pressure to entire body.
2
CHAPTER TWO
Blood Circulation and Transport
-Each chamber linked to big blood vessels:
a) Right atrium link to vena cava
b) Right ventricle link to Pulmonary artery
c) Left atrium link to Pulmonary vein
d) Left ventricle is link Aorta
-Three type of valves inside the heart:
a) Tricuspid valve between right atrium and right ventricle
b) Bicuspid valve between left atrium and left ventricle
c) Semilunar valve- beginning of aorta and pulmonary artery
-The valves are to ensure the blood flow in one direction to prevent flow back of
blood
-Pumping action of heart:
a) Deoxygenated blood flow from body to right atrium through vena cave.
b) Oxygenated blood from the lungs flow into the left atrium through pulmonary vein
c) Both atria (singular: atrium) contract and push the blood through the valves into
the ventricles
d) Both ventricles contract and force the deoxygenated blood in to pulmonary artery
and oxygenated blood to aorta. The semilunar valves close to prevent the blood from
flowing back into the atria
e) The pulmonary artery carry deoxygenated blood to lungs and aorta carries the
oxygenated blood to whole body.
2.1.2 Blood vessels and their functions
- Three types of blood vessels: arteries, veins and capillaries.
3
CHAPTER TWO
Blood Circulation and Transport
-human circulation system is a closed system because blood flow in blood vessels
that are connected
Figure 2.5 Type of Blood vessels
Vein
Artery
CHAPTER TWO
Blood Circulation and Transport
Big lumen
Small Lumen
Small L
Thin wall
Thick Wall to withstand high pressure
Very th
exchan
nutrien
With valve
Without valve
Withou
Carry deoxygenated blood except
pulmonary vein
Carry oxygenated blood except pulmonary
artery
Carry o
except
Blood flows from all parts of body to the
heart
Blood flow away from heart to all parts of
body
Blood f
oxygen
and bo
Slow and low pressure
Fast and high pressure
Very sl
CHAPTER TWO
Blood Circulation and Transport
2.1.3 Path of blood flow in circulatory system
-Human circulatory system is double circulatory system because he blood in the
body is pumped twice through heart.
- The human circulatory system is divided into two parts:
a) Pulmonary circulation- Pulmonary artery carries deoxygenated blood from heart to
lungs while pulmonary vein carries oxygenated blood from lungs back to the heart.
b) Systemic circulation- Aorta carries oxygenated blood from heart to others bodys
cell while vena cave carries the deoxygenated blood from the bodys cell back to the
heart.
- RS: Deoxygenated blood flow from body parts to the heart then up to the lung
Figure 2.5 Flow of human circulatory system
- Important to maintain a healthy heart to prevent heart diseases and maintain the
continuous supply of oxygen to the body cells.
- Exercise keeps the heart healthy by
a) Strengthen the heart muscles
b) Control the blood pressure.
- A narrow blood vessel will cause heart attack, hypertension and stoke.
- The healthy blood vessels can pump a greater amount of blood at faster rate while
arrowed blood vessel can pump less amount of blood at slower rate.
-Patient with narrow blood vessel are advised to
6
CHAPTER TWO
Blood Circulation and Transport
a) Avoid taking saturated fat (lead to high blood cholesterol level and heart diseases)
b) Eat plenty fruits and vegetables
c) Take a balanced diet
d) Lunch menu: rice, steamed fish / chicken, vegetable, salad / fruit and water
2.2 Human Blood
- Composition of blood:
a) Plasma- 55% of volume of blood
- a pale of yellowish liquid made up of 90% water and 10 % soluble
substances such as glucose , amino acids and mineral
b) Cellular components
i) Red blood cells- produce in bone marrow
- Biconcave disc
- No nuclei
- Each red blood cell contain a pigment call haemoglobin
i) White blood cells- produce in bone marrow and lymph nodes
- Irregular shape and can change
- Protect against diseases and infection
- Lymphocytes produce antibodies to kill germs
-Phagocytes carry out phagocytosis by surrounding the bacteria,
swallow and digest it thus kill it
iii) Platelets- small fragment of cells from larger cell in the bone marrow.
- Help in clotting blood to stop the bleeding
2.2.1 Functions of blood
- Functions of blood:
a) As transport medium- carries dissolved gases like oxygen, carbon dioxide, food
substances, hormones and waste from one part of body to another. Red blood cell
carries oxygen and plasma carries other substances.
b) White blood cells protect against disease.
c) Plasma distribute heat from liver to other parts of body to maintain body
temperature at 370C
2.2.2 Blood group and compatibility
- Human blood is divided into four main groups A, B, AB, and O
7
CHAPTER TWO
Blood Circulation and Transport
- Universal donor group O
- Universal recipients group AB
- Blood transfusion- transfer blood from donor to recipient
- Not compatible blood transfusion causing agglutination or coagulation in blood
vessels
2.3 Transport System in Plants
- Plants like human being need a transport system to transport food and water.
- Transport system of plants made up of xylem and phloem tissues.
- There are found in the roots, stems and leaves.
2.3.1 Transport tissues in plant
-Phloem transport food (glucose) produced through photosynthesis from leaves to
other parts of the plant
-Xylem transport water and dissolved mineral from root up to the stem and leave
during transpiration. Xylem also gives support to the plant.
- The cambium separates the xylem and the phloem. It also builds new xylem and
phloem cells.
Figure 2.6 Distribution of tissues in the root, stem and leaf of a plant
Figure 2.6 Investigate transports of synthesised food substances via the phloem
CHAPTER TWO
Blood Circulation and Transport
Plant B function as a control experiment.
Hypothesis: Phloem transports food.
Variables
Manipulated : ringed or unringed
Constant : type of plant
Responding: condition of the bark.
Conclusion : Phloem transport food from the leaves down to the roots.
Inferences:
i. The swelling is due to the accumulation of food substances that is unable to be
transported downwards as the phloem has been removed.
ii. The ringed area is wiped with paraffin to prevent the area from being dried up.
iii. After two weeks, the lower part of the plant dies first because the lower part of the
plant does not receive food substances.
2.3.2 Transpiration and function of stoma
-Transpiration defines as loss of water in the form of water vapour.
-Water vapour is evaporates through stoma, tiny pore on surface of leaf
- Stoma is tiny pore in between two bean shaped cells called guard
-Guard contain chloroplast to carry out photosynthesis and control the close and
opening of stoma.
- Stoma is open during the day to allow exchange of oxygen and carbon dioxide
during photosynthesis and allow evaporation of water vapour.
- A plant wilts when it loses more water to surrounding than it absorbs from soil.
2.3.3 Factors affect the rate of transpiration
-Rate of transpiration influence by:
a) Light density
b) Temperature
c) Humidity
d) Air movement
CHAPTER TWO
Blood Circulation and Transport
Rate of transpiration can be measured using weight potometer and bubble
potometer.
2.3.4 Role of transpiration in transport system
-Transpiration is import because
a) Help to transport water and dissolved minerals from roots to leaves.
b) Help root to absorb water .Keep cell turgid to support the plant
c) Evaporation of water vapour from leaves keep the plant cool in hot weather.
10
Potrebbero piacerti anche
- Chapter 2 Blood Circulation & TransportDocumento37 pagineChapter 2 Blood Circulation & TransportYanhyNessuna valutazione finora
- Chapter 2 Blood Circulation Doc2Documento10 pagineChapter 2 Blood Circulation Doc2Kazariyah KasaNessuna valutazione finora
- Circulatory System and Parts 1Documento38 pagineCirculatory System and Parts 1Atasha Ivory RagragioNessuna valutazione finora
- PT3 Science Chapter 19 Blood Circulation and TransportDocumento8 paginePT3 Science Chapter 19 Blood Circulation and TransportSpike ChingyenNessuna valutazione finora
- CHP 5 Form 5 InheritanceDocumento10 pagineCHP 5 Form 5 InheritancepuvanesvaranNessuna valutazione finora
- CHP 05 (Blood and Circulation) DrRiyadAhmed PC 3Documento69 pagineCHP 05 (Blood and Circulation) DrRiyadAhmed PC 3Kamrun NaherNessuna valutazione finora
- Science Form 3 Chapter 2Documento31 pagineScience Form 3 Chapter 2rosya100% (5)
- Transport System in HumanDocumento7 pagineTransport System in HumanMSMohanaNessuna valutazione finora
- 11S HSB Notes The Circulatory SystemDocumento4 pagine11S HSB Notes The Circulatory SystemTenika RodriguezNessuna valutazione finora
- Lesson 6 Life Processes Part IIDocumento9 pagineLesson 6 Life Processes Part IIjokerbladed19Nessuna valutazione finora
- Science F3 Chap 2 Blood Circulation and TransportDocumento44 pagineScience F3 Chap 2 Blood Circulation and TransportCt SarahNessuna valutazione finora
- Transportation in Animals and PlantsDocumento3 pagineTransportation in Animals and Plantsravilulla100% (1)
- Circulation in AnimalsDocumento38 pagineCirculation in Animalsvuminhtut66Nessuna valutazione finora
- Biology Notes On Transport of Materials in AnimalsDocumento13 pagineBiology Notes On Transport of Materials in Animalsbukenya MosesNessuna valutazione finora
- Life Process Part 2 2Documento32 pagineLife Process Part 2 2Anin BertNessuna valutazione finora
- Chapter 10 (Transport System)Documento207 pagineChapter 10 (Transport System)Norizan Darawi0% (1)
- Life Processes - Transport of Food and Minerals in Animals and PlantsDocumento5 pagineLife Processes - Transport of Food and Minerals in Animals and PlantsmasaminathanNessuna valutazione finora
- Blood Circulation Chapter 2Documento37 pagineBlood Circulation Chapter 2Raja InaNessuna valutazione finora
- Circulation Notes I To VIDocumento8 pagineCirculation Notes I To VIStacey KwiatkowskiNessuna valutazione finora
- Gist Class 10 Transport 1 & 2Documento2 pagineGist Class 10 Transport 1 & 2Binode SarkarNessuna valutazione finora
- Summary Unit 4 3esoDocumento9 pagineSummary Unit 4 3esoMeneses Oriano SaraNessuna valutazione finora
- The Cardiovascular SystemDocumento5 pagineThe Cardiovascular Systemjuly3ciaNessuna valutazione finora
- CH 2 ScineceDocumento4 pagineCH 2 Scinece07carbonmanNessuna valutazione finora
- UntitledDocumento51 pagineUntitledMuhammad FadhilNessuna valutazione finora
- Life Processes - Transportation QB 2019-20 PDFDocumento5 pagineLife Processes - Transportation QB 2019-20 PDFRatheesh HrishikeshNessuna valutazione finora
- Blood Circulation and AnswersDocumento2 pagineBlood Circulation and AnswersAyush SinghNessuna valutazione finora
- BiologyDocumento28 pagineBiologyrdgaefaNessuna valutazione finora
- Core CH 8 Transport in HumansDocumento10 pagineCore CH 8 Transport in Humansommp100% (1)
- Biology Form 5 Notes Chapter 1Documento39 pagineBiology Form 5 Notes Chapter 1Mayghen SelvanayagamNessuna valutazione finora
- 07 Human Transport Biology Notes IGCSE 2014 PDFDocumento27 pagine07 Human Transport Biology Notes IGCSE 2014 PDFJohn DeHans100% (2)
- Alwadi International School Grade 9 Biology 9. Transport in Animals NotesDocumento62 pagineAlwadi International School Grade 9 Biology 9. Transport in Animals NotesMohammed HelmyNessuna valutazione finora
- Science Form 3: Chapter 2 Blood Circulation and TransportDocumento39 pagineScience Form 3: Chapter 2 Blood Circulation and TransportNadzirah RedzuanNessuna valutazione finora
- Bal Bharati Public School, Pitampura, Delhi-110034Documento4 pagineBal Bharati Public School, Pitampura, Delhi-110034Tapas BanerjeeNessuna valutazione finora
- Bio ReviewDocumento7 pagineBio ReviewLim MonyratanakNessuna valutazione finora
- 007 - Comparing Transport in Mammals and PlantsDocumento2 pagine007 - Comparing Transport in Mammals and PlantsCoran St Nicholi Beckford INessuna valutazione finora
- Chapter 08 - Transport in HumansDocumento84 pagineChapter 08 - Transport in Humanshussaini polackNessuna valutazione finora
- The Circulatory SystemDocumento50 pagineThe Circulatory Systemfan dingNessuna valutazione finora
- The Circulatory SystemDocumento50 pagineThe Circulatory SystemIshan Jacob PiadocheNessuna valutazione finora
- The Circulatory SystemDocumento50 pagineThe Circulatory SystemGay For anime girlzNessuna valutazione finora
- Cardiovascular SystemDocumento5 pagineCardiovascular SystemWayneNessuna valutazione finora
- Transport in HumansDocumento8 pagineTransport in HumansRaima QaiserNessuna valutazione finora
- TransportationDocumento5 pagineTransportationdeveshigiricontactNessuna valutazione finora
- TransportationDocumento10 pagineTransportationSarika SinhaNessuna valutazione finora
- AcknowledgementDocumento9 pagineAcknowledgementJovin AshickNessuna valutazione finora
- Notes - Life Processes - Transportation - C-X - PART-IIIDocumento4 pagineNotes - Life Processes - Transportation - C-X - PART-IIIApoorv ChauhanNessuna valutazione finora
- Animal TransportDocumento20 pagineAnimal TransportFeranmi AkinboboyeNessuna valutazione finora
- TransportDocumento26 pagineTransportBhaskar MajumdarNessuna valutazione finora
- Circulatory SystemDocumento4 pagineCirculatory SystemGennelle GabrielNessuna valutazione finora
- Chapter 6 - 2Documento7 pagineChapter 6 - 2Prit mistryNessuna valutazione finora
- Transportation in Plants and Animals Ncert and Extra QuestionsDocumento6 pagineTransportation in Plants and Animals Ncert and Extra QuestionsNaitik MeenaNessuna valutazione finora
- Cardiovascular System - Kd13Documento63 pagineCardiovascular System - Kd13Alyssa Curry BroderickNessuna valutazione finora
- Biology Chapter 10Documento9 pagineBiology Chapter 10wongchengen2006Nessuna valutazione finora
- Chidrawi M1 Ch02 PDFDocumento36 pagineChidrawi M1 Ch02 PDFZA AustraliaNessuna valutazione finora
- Chapter 2: Blood Circulation and Transport 2.1 Transport System in HumansDocumento4 pagineChapter 2: Blood Circulation and Transport 2.1 Transport System in HumansSiti NorhayatiNessuna valutazione finora
- Blood Circulation and TransportDocumento23 pagineBlood Circulation and TransportcikzafirahNessuna valutazione finora
- The Water Prescription: For Health, Vitality, and RejuvenationDa EverandThe Water Prescription: For Health, Vitality, and RejuvenationValutazione: 5 su 5 stelle5/5 (2)
- Human Body Book | Introduction to the Vascular System | Children's Anatomy & Physiology EditionDa EverandHuman Body Book | Introduction to the Vascular System | Children's Anatomy & Physiology EditionNessuna valutazione finora
- Note Chapter 4Documento9 pagineNote Chapter 4Mandy VoonNessuna valutazione finora
- Note Chapter 2 - StudentDocumento11 pagineNote Chapter 2 - StudentMandy VoonNessuna valutazione finora
- Huawei FusionServer Pro V5Documento22 pagineHuawei FusionServer Pro V5Mandy VoonNessuna valutazione finora
- Note Chapter 3Documento5 pagineNote Chapter 3Mandy VoonNessuna valutazione finora
- Note Chapter 3Documento5 pagineNote Chapter 3Mandy VoonNessuna valutazione finora
- Note Chapter 2Documento12 pagineNote Chapter 2Mandy VoonNessuna valutazione finora
- Simple Machines: Chapter TenDocumento4 pagineSimple Machines: Chapter TenMandy VoonNessuna valutazione finora
- Note Chapter 1Documento18 pagineNote Chapter 1Mandy VoonNessuna valutazione finora
- Presentation On Wireless Technology v3Documento25 paginePresentation On Wireless Technology v3Mandy VoonNessuna valutazione finora
- Wireless TestingDocumento37 pagineWireless TestingMandy VoonNessuna valutazione finora
- WirelessDocumento2 pagineWirelessMandy VoonNessuna valutazione finora
- Management Process Ii. Organizing: Dr. Hanan A. Ezzat DDocumento32 pagineManagement Process Ii. Organizing: Dr. Hanan A. Ezzat DMandy VoonNessuna valutazione finora
- Ruckus Indoor-AP User-Guide 100.2.0Documento193 pagineRuckus Indoor-AP User-Guide 100.2.0Anonymous GPw8phMiKtNessuna valutazione finora
- Aruba 3D Outdoor PlannerDocumento52 pagineAruba 3D Outdoor PlannerMandy VoonNessuna valutazione finora
- Management Process Ii. Organizing: Dr. Hanan A. Ezzat DDocumento32 pagineManagement Process Ii. Organizing: Dr. Hanan A. Ezzat DMandy VoonNessuna valutazione finora
- HaematologyReport PDFDocumento78 pagineHaematologyReport PDFhamody662002Nessuna valutazione finora
- 043 Eco Star Oxy BriteDocumento2 pagine043 Eco Star Oxy Briteeng20072007Nessuna valutazione finora
- 3.Applied-A Study On Properties of Cissus Quadrangularis-Ms.G.manimekalaiDocumento4 pagine3.Applied-A Study On Properties of Cissus Quadrangularis-Ms.G.manimekalaiImpact JournalsNessuna valutazione finora
- 3 Perubahan Fisiologis Pada LansiaDocumento5 pagine3 Perubahan Fisiologis Pada Lansiaalbert fernandoNessuna valutazione finora
- Practice Midterm Animal PhysDocumento12 paginePractice Midterm Animal Physrk0% (3)
- General Abbreviations For Medical RecordsDocumento9 pagineGeneral Abbreviations For Medical Recordsjainy12Nessuna valutazione finora
- Aims of The Subjective AssessmentDocumento2 pagineAims of The Subjective AssessmentAnonymous PQ4NOe2Nessuna valutazione finora
- 1 The Basics 1Documento19 pagine1 The Basics 11202blackNessuna valutazione finora
- Homeo MedicinesDocumento31 pagineHomeo MedicinesSaleem RazaNessuna valutazione finora
- Autism EnglishDocumento129 pagineAutism EnglishRaí Caetano de JesusNessuna valutazione finora
- TetrabenazinaDocumento23 pagineTetrabenazinanieve2010Nessuna valutazione finora
- School of Nursing Science and Research (Sharda University) : Assignment ON Alternative Modalities of CareDocumento13 pagineSchool of Nursing Science and Research (Sharda University) : Assignment ON Alternative Modalities of CareSamjhana Neupane100% (1)
- EuthanasiaDocumento16 pagineEuthanasiaTheresa BreadNessuna valutazione finora
- 6 DOH Sample FormsDocumento136 pagine6 DOH Sample FormsSir Cris CapiliNessuna valutazione finora
- Physical ExaminationDocumento7 paginePhysical ExaminationCha CulveraNessuna valutazione finora
- Push Up Fact SheetDocumento1 paginaPush Up Fact SheetNor AmalinaNessuna valutazione finora
- Bender Visual Motor Gestalt TestDocumento39 pagineBender Visual Motor Gestalt TestKent100% (1)
- A Know LodgementDocumento1 paginaA Know LodgementMahmmoud EltaweelNessuna valutazione finora
- Femas Adetya Laudry - 22323052 - Tugas Bahasa Inggris Week 10Documento8 pagineFemas Adetya Laudry - 22323052 - Tugas Bahasa Inggris Week 10asfem9935Nessuna valutazione finora
- AyaskritiDocumento2 pagineAyaskritidrbhaveshpNessuna valutazione finora
- Of Thyroid and Antithyroid Drugs - Part IIDocumento16 pagineOf Thyroid and Antithyroid Drugs - Part IIVikas Viki100% (1)
- CDSMP PresentationDocumento16 pagineCDSMP Presentationapi-314835119Nessuna valutazione finora
- Extravasations DiagramDocumento1 paginaExtravasations DiagramJohnNessuna valutazione finora
- Badianus Manuscript An Aztec HerbalDocumento12 pagineBadianus Manuscript An Aztec HerbalIgnacio Pamplona100% (1)
- Acute PainDocumento3 pagineAcute PainGerardeanne ReposarNessuna valutazione finora
- Leggett Announces County Suit Against 14 Opioid CompaniesDocumento163 pagineLeggett Announces County Suit Against 14 Opioid CompaniesPublic Information OfficeNessuna valutazione finora
- Emergency NursingDocumento16 pagineEmergency NursingMandy Jamero100% (1)
- Goljan Step 1 QuestionsDocumento3 pagineGoljan Step 1 QuestionsMary0% (1)
- Bac - A Healthy Dose of LaughterDocumento3 pagineBac - A Healthy Dose of LaughterBen Hussa100% (2)