Documenti di Didattica
Documenti di Professioni
Documenti di Cultura
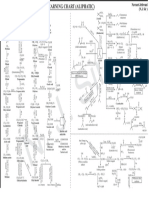
Carboxylic Acid Revision Slide
Caricato da
john nashCopyright
Formati disponibili
Condividi questo documento
Condividi o incorpora il documento
Hai trovato utile questo documento?
Questo contenuto è inappropriato?
Segnala questo documentoCopyright:
Formati disponibili
Carboxylic Acid Revision Slide
Caricato da
john nashCopyright:
Formati disponibili
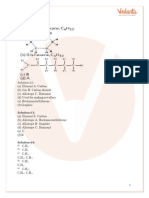
Carboxylic Acid & ITS
Derivatives
www.etoosindia.com
01. Carboxylic acid group can be detected by
(1) Sodium bisulphite test
(2) Fehlings solution test
(3) Tollens reagent
(4) With NaHCO3
02. Acetic acid exists as dimer in C6H6 due to
(1) Condensation reaction
(2) Hydrogen bonding
(3) Presence of a carboxyl group
(4) Presence of hydrogen at -carbon
03. Phenol is a weaker acid than acetic acid because
(1) Phenoxide ion is better stabilized by resonance
than acetate ion
(2) Acetate ion is better stabilized by resonance
than phenoxide ion
(3) Phenol is less soluble in water than acetic acid
(4) Both phenoxide ion and acetate ion are equally
stable
04. Which of the following is the weakest acid?
(1) Cl3CCOOH
(2) Cl2CHCOOH
(3) ClCH2COOH
(4) CH3COOH
05. Formic acid is a stronger acid than acetic acid.
This is due to the fact that ?
(1) Formic acid is a reducing agent
(2) Formic acid molecule is of smaller size
(3) There is no alkyl group on -carbon in formic
acid
(4) Formic acid does not undergo association
06. The Hell-Volhard Zelinsky reaction is used for
preparing a/an
(1) -Haloacid
(2) -Haloacid
(3) Acid halide
(4) -Haloacid
07. Identify Z in the following reaction sequence
(1) CH3COOH
(2) CH3MgI
(3) CH3COCl
(4) ClCH2COOH
08. Kolbes electrolysis of aqueous potassium ethanoate
leads to the formation of (1) Ethene
(2) Methane
(3) Ethane
(4) Ethyne
09. Which of the following lacks chirality
(1) 2-Hydroxy propanoic acid
(2) 2-Aminopropanoic acid
(3) 2, 3-Butene-dioic acid
(4) 2, 3-Dihydroxy butanoic acid
10. (CH3)2C=CHCOCH3 can be oxidised to
(CH3)2C=CHCOOH by
(1) Chromic acid
(2) I2 + NaOH or NaOI
(3) Cu at 300C
(4) KMnO4
11. The acid formed when propyl magnesium bromide
is treated with CO2 is
(1) CH3CH2COOH
(2) C3H7COOH
(3) CH3CH2CH2CH2COOH
(4) None
12.
What is not true for A and B
(1) A is hydrocarbon of general fromula CnH2n+2
while B belongs to alkanol
(2) A can be obtained by reducing CH3CH2Cl while
B by its hydrolysis
(3) A is alkene while B is alkanal
(4) A and B both belongs to different homologous
series
13. The product A, B, C and D in the reaction
are given by the set
(1) CO, H2O, CO2, H2
(2) CO2, H2O, CO, H2
(3) CO2, H2, CO, H2O
(4) CO, H2, CO2, H2O
14. Dry distillation of calcium acetate gives
(1) Acetaldehyde
(2) Acetone
(3) Ethane
(4) Propanal
15. Hydrolysis of 1,1, 1-trichloro derivate (A) of alkane
gives a molecule (B) on alkaline hydrolysis which
produces red coloration with aqueous FeCl3. The
compound (A) is
(1) CH3CH2CCl3
(2) CH3CCl3
(3) CHCl3
(4) None
16. Which of the following is the best representation of
the structure of the carboxylate ion
17. Which one of the following on oxidation will not
give a carboxylic acid with the same number of
carbon atoms
(1) CH3COCH3
(2) CCl3. CH2CHO
(3) CH3CH2CH2OH
(4) CH3CH2CHO
18. Identify Z in the sequence
(1) CH3CH2CONH2
(2) CH3CN
(3) CH3COOH
(4) (CH3CO)2O
19. A halogen compound A on hydrolysis with dilute
alkali followed by acidification gives acetic acid.
The compound A is
(1) ClCH2CH2Cl
(2) CH3CHCl2
(3) ClCH2CHCl2
(4) CH3CCl3
20. Acetic acid is obtained when
(1) Methyl alcohol is oxidised with potassium
permangnate
(2) Formaldehyde is oxidised with potassium
dichromate and sulphuric acid
(3) Acetonitrile is hydrolysed with a dilute mineral
acid
(4) Glycerol is heated with sulphuric acid
21.
The product of the above reaction is
(1) -Dibromo acid
(2) , - Dibromo acid
(3) , , -Tribromo acid
(4) No reaction takes place
22. The rate of esterfication of HCOOH (I),
CH3COOH (II), (CH3)2CHCOOH (III) and
(CH3)3CCOOH (IV)
with ethanol follows in the order
(1) IV > III > II > I
(2) I > II > III > IV
(3) II > I > IV > III
(4) III > IV > I > II
23. X and Y in the reaction sequence
are given by the set
(1) Carboxamide, Carbonitrile
(2) Carboxylic acid, Carbonitrile
(3) RCOOH, RCOOCH3
(4) RCONH2, RCOCH3
24. Which of the following organic acid decolourises
bromine water as well as forms anhydride
(1) HOOCCOOH
(2) HOOCCH2COOH
25. The product, A, B and C in the reaction sequence
are
(1) HCHO, HCOONa, CH3OH
(2) HCHO, Na2CO3, NaHCO3
(3) HCHO, HCOONa, (COONa)2
(4) HCHO, HCOONa, Na2CO3
26. The end product C in the following sequence of
chemical reaction is
(1) Acetaldehyde oxime
(2) Formaldehyde oxime
(3) Methyl nitrate
(4) Acetoneoxime
27. Which of the following carboxylic acids undergoes
decarboxylation easily ?
28.
The compound (B) is
(1) CH3CH2OH
(2) CH3CH2COCl
(3) CH2=CHCOOH
(4) CH3 CHCl COOH
29. A compound undergoes the following sequence of
reactions :
The compound C is
(1) 1-Nitropropane
(2) 2-Nitropropane
(3) 2-Aminopropanoic acid
(4) 2-Hydroxypropanamide
30. In a set of the given reactions, acetic acid yields a
product C
31. In the given reaction final compound (C) is
HO O
32. Which of the following sets of reagents X & Y will
convert propanoic acid into alanine (an amino acid)
(1) Br2
(2) Br2/P
(3) Br2/P
(4) Br2/HBr
NaNH2
NaOH
NH3
NaNH2
33. Which of the following has the highest pKa value ?
34. (A), (B) and (C) are three dicarboxylic acids such
that
(A)
(1) adipic acid,
(2) Malonic acid,
(3) adipic acid,
(4) Malonic acid,
(B)
malonic acid,
adipic acid,
succinic acid
succinic acid
(C)
succinic acid
succinic acid
malonic acid
adipic acid
35. The identical CO bond lengths in carboxylate ions
are due to
(1) Resonance
(2) Presence of carbonyl group
(3) Presence of alkyl group
(4) None of these
36. Consider the following sequence of reaction
Identify A, B, C and D :
A
B
(1) F,
COOH,
(2) CHO,
COOH,
(3) Br,
COOH,
(4) Br,
-COOH,
C
COCH3,
COCl,
COCl,
COCl,
D
COC3H7
COC2H5
COC2H5
CHO
37. CH3COCl can react with
(1) C6H5OH
(2) C6H5NH2
(3)
(4) All of these
38. Which is the correct statement in regards to
CH3COCl
(1) It is reduced to C2H5OH by LiAlH4
(2) It is reduced to CH3CHO when H2 is passed into
it, in the presence of Pd/BaSO4 in boiling xylene
(3) It forms ethyl acetate on reaction with
C2H5OH
(4) All of these
39. The end product in the relation
is
(1) CH3CHO
(2) CH3COCH3
(3) CH3COOC2H5
(4) (CH3CO)2O
40. The reaction is called
(1) Claisen reduction
(2) Claisen condensation
(3) Bouveault-Blanc reduction
(4) Tischenko reduction
41. The reaction of acetaldehyde in the presence of
Al(OC2H5)3 produces
(1) CH3CH(OH)CH2CHO
(2) CH3CH=CHCHO
(3) CH3COOC2H5
(4) No reaction
42. An aliphatic carboxylic acid of molecular formula
C2H4O2 on reaction with PCl5 gives a compound Y.
Y when heated with sodium salt of the acid
produces
(1) Ethyl acetate
(2) Ethyl acetoacetate
(3) Methyl methanoate
(4) Ethanoic anhydride
43. The end product in the following series of reactions
is
(1) CH4
(2) CH3OH
(3) acetonitrile
(4) ammonium acetate
44. Among the given compounds, the most susceptible
to nucleophilic attack at the carbonyl group is
(1) MeCOOCOMe
(2) MeCHO
(3) MeCOOMe
(4) MeCOCl
45. Esterification is fastest in case of
(1) CH3COOH
(2) HCOOH
(3) CH3CH2COOH
(4) (CH3)2CHCOOH
46.
(1) CH3COOH, CH3COONH4 and CH3CONH2
(2) CH3COCl, CH3CONH2 and C2H5COONH4
(3) C2H5COOH, C2H5CONH4 and C2H5CONH2
(4) C2H5CONH4, C2H5CONH2 and C2H5COOH
47. Which of the following esters cannot udergo Claisen
self condensation
(1) CH3CH2CH2CH2COOC2H5
(2) C6H5COOC2H5
(3) C6H11CH2COOC2H5
(4) C6H5CH2COOC2H5
48. Let us consider an esterfication of isotopically
labelled carboxylic acid
49.
Alcohol (Y) gives Lucas test within one minute.
Thus, (X) and (Y) respectively are
(1) CH3COOC2H5 ; (CH3)3(COH)
(2) HCOOC3H7 ; (CH3)2CHOH
(3) C2H5COOCH3 ; (C2H5)3COH
(4) HCOOC3H7 ; (CH3)3COH
50. Methyl acetate on treating with excess of C2H5MgBr
products
Potrebbero piacerti anche
- Learning Chart Aliphatic Compounds-331Documento1 paginaLearning Chart Aliphatic Compounds-331john nash0% (1)
- Laidler 5Documento116 pagineLaidler 5Teresa Cano100% (1)
- Alkene Revision SlideDocumento73 pagineAlkene Revision SlideNeet2023 Don'twastetimeNessuna valutazione finora
- Alkyne Revision SlideDocumento43 pagineAlkyne Revision SlideAditya RamNessuna valutazione finora
- AK - Carbonyl CompoundDocumento8 pagineAK - Carbonyl Compoundmgupta13marNessuna valutazione finora
- Practice Questions For CET-Organic ChemistryDocumento4 paginePractice Questions For CET-Organic ChemistrySantosh KareNessuna valutazione finora
- Aldehyde J Ketone Amd Carboxylic MCQDocumento5 pagineAldehyde J Ketone Amd Carboxylic MCQSaransh KumarNessuna valutazione finora
- Aldehydes Ketones Carboxylic AcidsDocumento22 pagineAldehydes Ketones Carboxylic AcidsvenkithebossNessuna valutazione finora
- Ald Keto Carboxylic AcidDocumento6 pagineAld Keto Carboxylic AcidCY Shivam SinghNessuna valutazione finora
- Aldehydes, Ketones and Carboxylic AcidsDocumento7 pagineAldehydes, Ketones and Carboxylic Acidskavitha2511977Nessuna valutazione finora
- Sub Topic - Iv. Poly Halogen Compounds: Halo Alkanes and HaloarenesDocumento3 pagineSub Topic - Iv. Poly Halogen Compounds: Halo Alkanes and HaloarenesmsNessuna valutazione finora
- CHM s2Documento9 pagineCHM s2kolapo feyisetanNessuna valutazione finora
- Jee 2014 Booklet7 HWT Oxygen Containing Organic Compounds IIDocumento10 pagineJee 2014 Booklet7 HWT Oxygen Containing Organic Compounds IIvarunkohliinNessuna valutazione finora
- 12 - Cbs - Aldehydes Ketones Carboxylic AcidsDocumento6 pagine12 - Cbs - Aldehydes Ketones Carboxylic AcidsShauryaNessuna valutazione finora
- Question Bank Class Xii (Chemistry) Unit 5: Alcohols, Phenols & Ethers Multiple Choice QuestionsDocumento21 pagineQuestion Bank Class Xii (Chemistry) Unit 5: Alcohols, Phenols & Ethers Multiple Choice QuestionsSahilNessuna valutazione finora
- NCERT Solutions Class 12 Chemistry Chapter 10 Haloalkenes and HaloarenesDocumento31 pagineNCERT Solutions Class 12 Chemistry Chapter 10 Haloalkenes and HaloarenesVidyakulNessuna valutazione finora
- National Standard Examination in Chemistry 2014: QP Code C 203Documento15 pagineNational Standard Examination in Chemistry 2014: QP Code C 203Karan TejwaniNessuna valutazione finora
- 34 Alcohols & Ethers - Problems For Practice - Level 1Documento14 pagine34 Alcohols & Ethers - Problems For Practice - Level 1Abuturab MohammadiNessuna valutazione finora
- Alkane Revision SlideDocumento51 pagineAlkane Revision SlideNeet2023 Don'twastetimeNessuna valutazione finora
- Chemistry Haloalkanes and Haloarenes PDFDocumento40 pagineChemistry Haloalkanes and Haloarenes PDFGanesh KrishnaNessuna valutazione finora
- Aldehyde KetoneDocumento5 pagineAldehyde Ketonehareharanbt22Nessuna valutazione finora
- 12 Carboxyloc AcidDocumento3 pagine12 Carboxyloc Acidimu4u_786Nessuna valutazione finora
- Alcohol & EtherDocumento217 pagineAlcohol & EtherAmitNessuna valutazione finora
- Alcohols, Phenols MCQDocumento13 pagineAlcohols, Phenols MCQSnekha TNessuna valutazione finora
- Sample Question Paper 2021-22 Term 1 Subject: ChemistryDocumento10 pagineSample Question Paper 2021-22 Term 1 Subject: ChemistryNishi Kant MishraNessuna valutazione finora
- Sample Question Paper 2021-22 Term 1 Subject: ChemistryDocumento16 pagineSample Question Paper 2021-22 Term 1 Subject: Chemistrysarthak MongaNessuna valutazione finora
- DPP 04Documento10 pagineDPP 041234dvsvNessuna valutazione finora
- Chem Class 12 WorksheetDocumento8 pagineChem Class 12 WorksheetBHAVYA KUSHWAHANessuna valutazione finora
- Alkyl HalideDocumento8 pagineAlkyl HalideMegh Raj BhattNessuna valutazione finora
- WORK BOOK - Exercise in ChemistryDocumento28 pagineWORK BOOK - Exercise in ChemistryTikeshwar SharmaNessuna valutazione finora
- Class XII MOCK TEST TERMI 2021 CHEMISTRYDocumento10 pagineClass XII MOCK TEST TERMI 2021 CHEMISTRYSumit KumarNessuna valutazione finora
- Answers To ROH Tutorial PDFDocumento12 pagineAnswers To ROH Tutorial PDFCorvo Haosen Al-Han0% (1)
- Carbonyl CompoundDocumento197 pagineCarbonyl CompoundAmitNessuna valutazione finora
- Chem Book 2 TestDocumento3 pagineChem Book 2 TestHishq DhimanNessuna valutazione finora
- NSEC Solved Paper 2010Documento7 pagineNSEC Solved Paper 2010whatismyusername1947Nessuna valutazione finora
- C12 - ALDEHYDES KETONES AND CARBOXYLIC ACIDS (1) .9cfd4beDocumento4 pagineC12 - ALDEHYDES KETONES AND CARBOXYLIC ACIDS (1) .9cfd4beakashkishore363Nessuna valutazione finora
- MCQ Halo Alkanes and ArenesDocumento27 pagineMCQ Halo Alkanes and ArenessarahNessuna valutazione finora
- Section-I (Single Correct Choice) : HC CH 1.1eq Nanh Nanh Nanh X XDocumento14 pagineSection-I (Single Correct Choice) : HC CH 1.1eq Nanh Nanh Nanh X XPriyansh YadavNessuna valutazione finora
- Haloalkanes and HaloarenesDocumento14 pagineHaloalkanes and HaloarenesKalpesh BishnoiNessuna valutazione finora
- Class 12 - Aldehydes, Ketones and Carboxylic Acids - 24577953Documento4 pagineClass 12 - Aldehydes, Ketones and Carboxylic Acids - 24577953Aryan KhandkaNessuna valutazione finora
- CLASS: 10+2 Subject: ChemistryDocumento5 pagineCLASS: 10+2 Subject: ChemistryVeer KaurNessuna valutazione finora
- 12TH CBSE DPP 37. Aldehydes, Ketones and Carboxylic Acids MCQ ASSERTION REASON CS QDocumento20 pagine12TH CBSE DPP 37. Aldehydes, Ketones and Carboxylic Acids MCQ ASSERTION REASON CS Q123Nessuna valutazione finora
- Unit 12 Aldehysdes Ketones and Carboxylic AcidsDocumento4 pagineUnit 12 Aldehysdes Ketones and Carboxylic Acidspavankumar3905syNessuna valutazione finora
- Chemistry 12Documento3 pagineChemistry 12Anonymous WxtxTR2Nessuna valutazione finora
- Aldehydes KetonesDocumento51 pagineAldehydes Ketonesadarsh mohanNessuna valutazione finora
- 09-Final With SolutionsDocumento27 pagine09-Final With SolutionsDanielle Wood100% (2)
- Aieee 2010Documento6 pagineAieee 2010zubairmaj3417Nessuna valutazione finora
- Jee 2014 Booklet5 HWT HalidesDocumento12 pagineJee 2014 Booklet5 HWT Halidesvarunkohliin100% (2)
- Corbonyl CompOUND AND Corboxilic AcidDocumento12 pagineCorbonyl CompOUND AND Corboxilic AcidApex InstituteNessuna valutazione finora
- Sample Paper - 6Documento8 pagineSample Paper - 6rajneesh kumarNessuna valutazione finora
- Halogen DerivativesOrganic Chem Class XIIDocumento32 pagineHalogen DerivativesOrganic Chem Class XIIDwaipayan Pradhan100% (2)
- Organic C CCCC CCCCDocumento88 pagineOrganic C CCCC CCCCKugan KishurNessuna valutazione finora
- Aldehyde, Ketone and Carboxylic AcidDocumento10 pagineAldehyde, Ketone and Carboxylic Acidgoodgirlz946Nessuna valutazione finora
- CLS Aipmt 19 20 XII Che Study Package 4 Level 1 Chapter 10Documento36 pagineCLS Aipmt 19 20 XII Che Study Package 4 Level 1 Chapter 10Utkarsh KumarNessuna valutazione finora
- JEE - Chemistry - P - Block Elements 17 - 18Documento57 pagineJEE - Chemistry - P - Block Elements 17 - 18official.archit234Nessuna valutazione finora
- Solutions CH 1 NcertDocumento40 pagineSolutions CH 1 NcertRadhika BasistaNessuna valutazione finora
- Lakhmir Singh Chemistry Class 10 Solutions Chapter 4 - Carbon and Its CompoundsDocumento27 pagineLakhmir Singh Chemistry Class 10 Solutions Chapter 4 - Carbon and Its CompoundsS.SreerevanthNessuna valutazione finora
- Topic 10 Paper 1Documento30 pagineTopic 10 Paper 1RawanMazen SharifNessuna valutazione finora
- Multiple Choice Questions: Question Bank Class: Xii, Chemistry Unit 4: Haloalknaes & HaloarenesDocumento27 pagineMultiple Choice Questions: Question Bank Class: Xii, Chemistry Unit 4: Haloalknaes & HaloarenesAkshita BoroNessuna valutazione finora
- ch9 AlkynesDocumento7 paginech9 AlkynesApichat JunsodNessuna valutazione finora
- Graphene Oxide: Fundamentals and ApplicationsDa EverandGraphene Oxide: Fundamentals and ApplicationsAyrat M. DimievNessuna valutazione finora
- E 42 1 024 S TeX PDFDocumento2 pagineE 42 1 024 S TeX PDFjohn nashNessuna valutazione finora
- Amines For Iit JeeDocumento3 pagineAmines For Iit Jeejohn nashNessuna valutazione finora
- Probability: Etoos Academy Pvt. LTDDocumento28 pagineProbability: Etoos Academy Pvt. LTDjohn nashNessuna valutazione finora
- 00 Classnote-577390ae36c75Documento12 pagine00 Classnote-577390ae36c75john nashNessuna valutazione finora
- Assignment Mole Concept JH Sir-4283 RedactedDocumento22 pagineAssignment Mole Concept JH Sir-4283 Redactedjohn nashNessuna valutazione finora
- Solubility of Asphalt Materials in Trichloroethylene: Standard Test Method ForDocumento3 pagineSolubility of Asphalt Materials in Trichloroethylene: Standard Test Method ForMohamed Maamoun T.Nessuna valutazione finora
- Synthesis of Asprin Lab ReportDocumento3 pagineSynthesis of Asprin Lab ReportRachelleNessuna valutazione finora
- Slug CatcherDocumento16 pagineSlug Catchermuhammad_asim_10Nessuna valutazione finora
- Flat Products Made of Steel BS EN10028 - 2Documento26 pagineFlat Products Made of Steel BS EN10028 - 2Javier OrnaNessuna valutazione finora
- Investigating Anglo-Saxon Population Movement Using Strontium Stable Isotope AnalysisDocumento58 pagineInvestigating Anglo-Saxon Population Movement Using Strontium Stable Isotope AnalysisAnnemieke DoornbosNessuna valutazione finora
- Projector Lift - Manual and Tech SpecsDocumento3 pagineProjector Lift - Manual and Tech SpecsbeamaxNessuna valutazione finora
- T040032 00Documento17 pagineT040032 00Doanh HoangNessuna valutazione finora
- Conostan STD Brochure For AAS or ICPDocumento14 pagineConostan STD Brochure For AAS or ICPDewi WulandhariNessuna valutazione finora
- Sudare S690QLDocumento16 pagineSudare S690QLgivaliNessuna valutazione finora
- Sucrose EsteresDocumento72 pagineSucrose EsteresWaltoy DinizNessuna valutazione finora
- Dehydration ProcessesDocumento43 pagineDehydration ProcessesKatib Sultan100% (6)
- Installation Manual - Brazed Heat Exchangers - UK PDFDocumento2 pagineInstallation Manual - Brazed Heat Exchangers - UK PDFesteban vasquezNessuna valutazione finora
- Revision Notes On Heat TransferDocumento11 pagineRevision Notes On Heat TransferAnonymous vRpzQ2BLNessuna valutazione finora
- Solutions To 7.012 Problem Set 1Documento4 pagineSolutions To 7.012 Problem Set 1attiqueNessuna valutazione finora
- Enzyme PPT 12 PDFDocumento42 pagineEnzyme PPT 12 PDFAnonymous wY9ogndU100% (1)
- KHU MHD HandoutDocumento42 pagineKHU MHD Handoutmiguel san martinNessuna valutazione finora
- Clariant Brochure Home Care 2017 enDocumento42 pagineClariant Brochure Home Care 2017 ensrushtiNessuna valutazione finora
- Wave C11Documento8 pagineWave C11Wajira Sanjaya PereraNessuna valutazione finora
- Continuous CastingDocumento11 pagineContinuous CastingakritiNessuna valutazione finora
- Silicon ExicipientDocumento12 pagineSilicon ExicipientArif ShaikhNessuna valutazione finora
- Automatic Grease Lubricators White PaperDocumento5 pagineAutomatic Grease Lubricators White PaperPaul RuckNessuna valutazione finora
- Northern Black Polished Ware in IndiaDocumento19 pagineNorthern Black Polished Ware in IndiaMohit Sony100% (1)
- Rock Engineering Design of Post-Tensioned Anchors For DamsDocumento13 pagineRock Engineering Design of Post-Tensioned Anchors For Damszepfer100% (1)
- Common Fragrance and Flavor Materials Preparation Properties and Uses PDFDocumento2 pagineCommon Fragrance and Flavor Materials Preparation Properties and Uses PDFSummer0% (1)
- 1600060Documento4 pagine1600060danyNessuna valutazione finora
- Behr Labor Technik Extraction En-1Documento28 pagineBehr Labor Technik Extraction En-1MilanVukic100% (1)
- 7 Stream Gauging-2Documento54 pagine7 Stream Gauging-2ChampNessuna valutazione finora
- What Is A BatteryDocumento2 pagineWhat Is A Batteryshahzad444Nessuna valutazione finora