Documenti di Didattica
Documenti di Professioni
Documenti di Cultura
Dnarnanotes
Caricato da
api-343673679Titolo originale
Copyright
Formati disponibili
Condividi questo documento
Condividi o incorpora il documento
Hai trovato utile questo documento?
Questo contenuto è inappropriato?
Segnala questo documentoCopyright:
Formati disponibili
Dnarnanotes
Caricato da
api-343673679Copyright:
Formati disponibili
DNA/RNA Notes
Central Dogma: the process of DNA being transcribed into mRNA and mRNA being
translated into a protein; the flow of genetic information from DNA to RNA to protein
DNA=Deoxyribonucleic Acid
Stores genetic information (genes)
Double stranded (creates a D
ouble Helix)
RNA=Ribonucleic Acid
Single stranded
Gene: section of DNA that codes for a protein
DNA and RNA are both Nucleic Acid polymers
Monomer is a Nucleotide
Nucleotide
Adenine, Thymine, Guanine, C
y tosine, U
racil
Made of a Phosphate, Ribose/Deoxyribose Sugar, and a Nitrogenous Base
Nucleoside consists only of the Ribose/Deoxyribose Sugar and Nitrogenous
Base
Base Pairs: Nucleotides only bind to their complementary nucleotides, forming base
pairs
Adenine binds with T
hymine in DNA or U
racil in RNA (A-T/U or T/U-A)
Cytosine binds with G
uanine (C-G or G-C)
RNA types
mRNA: messenger RNA
rRNA: ribosomal RNA
tRNA: transfer RNA
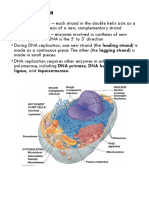
RNA Polymerase: Enzyme that splits the DNA double helix and transcribes DNA into
mRNA
Promoter: Section of DNA where RNA Polymerase binds to initiate transcription
Intron: non-coding portion of mRNA (is removed while in the nucleus)
Exon: coding portion of mRNA (is not removed)
Transcription: process of transcribing DNA into mRNA
Translation: process of translating mRNA into protein, consists of three stages
Initiation: mRNA binds to Ribosome, first tRNA molecule binds
Elongation: tRNA molecules bind to mRNA codons, leaving behind a growing
chain of amino acids
Termination: mRNA chain and amino acid chain are released from Ribosome
Codon: 3-nucleotide coding sections of mRNA
Each codon corresponds to a specific amino acid
Anticodon: 3-nucleotide section of tRNA that binds to a single, specific, corresponding
codon of mRNA
Mutation: permanent change in DNA sequence
Point mutation: a single nucleotide in the DNA sequence is r eplaced with a
different nucleotide
Missense mutation: a point mutation that replaces a single amino acid in
the protein with a different amino acid
Nonsense mutation: a point mutation that creates a premature s
top
codon which prematurely ends translation
Silent mutation: a point mutation that replaces a single nucleotide in a
codon with a different nucleotide, but does NOT change the amino acid
being coded for by the codon
Frameshift mutation: a mutation that shifts the reading frame of the DNA
sequence, changing all subsequent codons
Insertion mutation: a frameshift mutation that adds a nucleotide into the
DNA sequence
Deletion mutation: a frameshift mutation that removes a single
nucleotide from the DNA sequence
Potrebbero piacerti anche
- BIOLS102-UOB-Chapter 12Documento7 pagineBIOLS102-UOB-Chapter 12Noor JanahiNessuna valutazione finora
- Genetics, Variation and Natural SelectionDocumento71 pagineGenetics, Variation and Natural Selectionjordan griersonNessuna valutazione finora
- PK Bio Nucliec AcidsDocumento36 paginePK Bio Nucliec Acidsvinaya raviNessuna valutazione finora
- Chapter 16 Chromosomes, Genes and DNADocumento47 pagineChapter 16 Chromosomes, Genes and DNAZin Min KhantNessuna valutazione finora
- 1 - DNA Structure, Transcription, & TranslationDocumento3 pagine1 - DNA Structure, Transcription, & Translationmohanofficial285Nessuna valutazione finora
- Transcription and Translation 2014Documento32 pagineTranscription and Translation 2014Shilpa KantariaNessuna valutazione finora
- Lecture 7, Ch. 17Documento12 pagineLecture 7, Ch. 17S. SpencerNessuna valutazione finora
- BIO121 Chapter 9 From DNA To ProteinDocumento47 pagineBIO121 Chapter 9 From DNA To ProteinggttettanNessuna valutazione finora
- Ch. 14 - Gene Expression - From Gene To ProteinDocumento9 pagineCh. 14 - Gene Expression - From Gene To ProteinMeera RaoNessuna valutazione finora
- TranscriptionDocumento29 pagineTranscriptionRochelle Ann CunananNessuna valutazione finora
- Module 10Documento7 pagineModule 10Sri Harsha BairisettyNessuna valutazione finora
- Dna and Rna: Molecule of HeredityDocumento74 pagineDna and Rna: Molecule of Heredityalfani wahyuNessuna valutazione finora
- Physio Protein SynthesisDocumento3 paginePhysio Protein SynthesisM.TAYYAB KHANNessuna valutazione finora
- The Central DogmaDocumento7 pagineThe Central DogmaTobias Domenite P.Nessuna valutazione finora
- Gene ExpressionDocumento2 pagineGene Expressionvuminhtut66Nessuna valutazione finora
- BC Lec M6 Lesson 3Documento21 pagineBC Lec M6 Lesson 3Mershonthel MarquezNessuna valutazione finora
- 4.9 Chapter 4 - Protein Synthesis - TranscriptionDocumento19 pagine4.9 Chapter 4 - Protein Synthesis - Transcriptionlilpidas54Nessuna valutazione finora
- Protein Synthesis: Indian Institute of Technology PatnaDocumento29 pagineProtein Synthesis: Indian Institute of Technology PatnaHritik KumarNessuna valutazione finora
- Ch. 16 Molecular Basis of Inheritance: o o o o o o o oDocumento7 pagineCh. 16 Molecular Basis of Inheritance: o o o o o o o oAniket BinwadeNessuna valutazione finora
- Dna, Replikasi, Transkripsi Dan Translasi DR - Ruswana Anwar, Spog Pembimbing DR - Herman Wibisono MS, SpandDocumento41 pagineDna, Replikasi, Transkripsi Dan Translasi DR - Ruswana Anwar, Spog Pembimbing DR - Herman Wibisono MS, Spandyuyu tuptupNessuna valutazione finora
- Protein Synthesis NotesDocumento17 pagineProtein Synthesis Notesapi-655732711100% (1)
- In-Depth Steps Towards Nucleic Acid and Protein SynthesisDocumento21 pagineIn-Depth Steps Towards Nucleic Acid and Protein SynthesisGbenga AjaniNessuna valutazione finora
- Cyto Unit 3Documento3 pagineCyto Unit 3Vince CarrilloNessuna valutazione finora
- DNA, RNA and ProteinsDocumento47 pagineDNA, RNA and ProteinsShanice RhuleNessuna valutazione finora
- Protein Synthesis: 1) Nucleus: The First Stage of Protein Synthesis Occurs Here. It Is Named TranscriptionDocumento3 pagineProtein Synthesis: 1) Nucleus: The First Stage of Protein Synthesis Occurs Here. It Is Named TranscriptionmohammedNessuna valutazione finora
- 05b. Part 2 of Nucleic Acids For BSRadTechDocumento26 pagine05b. Part 2 of Nucleic Acids For BSRadTechBea Abigail BrocalNessuna valutazione finora
- Understanding The Genetic Materials DNA ReplicationDocumento44 pagineUnderstanding The Genetic Materials DNA Replicationnoeme babiaNessuna valutazione finora
- Protein Synthesis ReviewDocumento3 pagineProtein Synthesis ReviewTheGeekSquadNessuna valutazione finora
- DNA, RNA, and Protein SynthesisDocumento19 pagineDNA, RNA, and Protein SynthesisAnonymous qMToncNessuna valutazione finora
- BCH Lecture 8Documento38 pagineBCH Lecture 8AnniezaMohamedNessuna valutazione finora
- Module 8 - Nucleic Acids and Central DogmaDocumento52 pagineModule 8 - Nucleic Acids and Central DogmaPauline Grace CadusaleNessuna valutazione finora
- Science ReviewerDocumento5 pagineScience Reviewerronderenz22Nessuna valutazione finora
- Q3 WEEK 4 Protein SynthesisDocumento65 pagineQ3 WEEK 4 Protein SynthesisAdonis SanielNessuna valutazione finora
- Transcription and TranslationDocumento43 pagineTranscription and TranslationSaqlain Ali ShahNessuna valutazione finora
- Transcription and TranslationDocumento42 pagineTranscription and TranslationConnor EnglandNessuna valutazione finora
- DNA Overview Central DogmaDocumento56 pagineDNA Overview Central DogmaBukhari DiangkaNessuna valutazione finora
- DNA Replication and Protein SynthesisDocumento53 pagineDNA Replication and Protein SynthesisDeborah Chloe EnriquezNessuna valutazione finora
- DNA, Genes and Protein SynthesisDocumento2 pagineDNA, Genes and Protein SynthesisAlexis ReezeNessuna valutazione finora
- Transcription Kezia Joice BautistaDocumento43 pagineTranscription Kezia Joice BautistaKeziajoicee Bautista0% (1)
- Biology: Third QuarterDocumento126 pagineBiology: Third QuarterHill A. D.Nessuna valutazione finora
- Heredity: 10 - AmaziahDocumento33 pagineHeredity: 10 - AmaziahAlice KrodeNessuna valutazione finora
- Transcription and Translation Power PointDocumento21 pagineTranscription and Translation Power Pointapi-176402481Nessuna valutazione finora
- LG 11-14Documento56 pagineLG 11-14hasan.hmu2004Nessuna valutazione finora
- Dna ProcessesDocumento28 pagineDna Processesvivas.kznne.9Nessuna valutazione finora
- DNA Replication: Ligase, and TopoisomeraseDocumento26 pagineDNA Replication: Ligase, and TopoisomeraseNikki AlbiosNessuna valutazione finora
- 22 - Protein BiosynthesisDocumento34 pagine22 - Protein Biosynthesisمحمد صالح ابراهيم محمدNessuna valutazione finora
- Transcription and TranslationDocumento35 pagineTranscription and TranslationJaneNessuna valutazione finora
- Nucleic AcidsDocumento46 pagineNucleic AcidsM. MalonesNessuna valutazione finora
- Transciption and TranslationDocumento31 pagineTransciption and TranslationDuduetsang MosalakataneNessuna valutazione finora
- Central Dogma of Biology: DNA RNA ProteinDocumento16 pagineCentral Dogma of Biology: DNA RNA Proteinmungil_alifNessuna valutazione finora
- Central Dogma of Biology: DNA RNA ProteinDocumento16 pagineCentral Dogma of Biology: DNA RNA ProteinJessa Lynn E. AcalaNessuna valutazione finora
- Nucleic Acids and Protein Synthesis PDFDocumento55 pagineNucleic Acids and Protein Synthesis PDFAleine Leilanie Oro0% (1)
- Structure and Functions of DNADocumento37 pagineStructure and Functions of DNARaj kumar paswanNessuna valutazione finora
- CH 7 Nucleic AcidsDocumento8 pagineCH 7 Nucleic AcidsInes Ait Si SelmiNessuna valutazione finora
- Rna Protein Synthesis VocabDocumento1 paginaRna Protein Synthesis VocabChastity MiddlebrooksNessuna valutazione finora
- Protein SynthesisDocumento21 pagineProtein SynthesisAnthony MoloneyNessuna valutazione finora
- Biochemistry - PPT 01Documento28 pagineBiochemistry - PPT 01Rasel IslamNessuna valutazione finora
- Ribosomes and Protein SynthesisDocumento15 pagineRibosomes and Protein SynthesisRichard ShakespeareNessuna valutazione finora
- Biology XII (12th Grade/Class) MCQs KEYDocumento268 pagineBiology XII (12th Grade/Class) MCQs KEYInni CallmeinniNessuna valutazione finora
- The Chemistry, Properties and Tests of Precious Stones by Mastin, John, 1865Documento67 pagineThe Chemistry, Properties and Tests of Precious Stones by Mastin, John, 1865Gutenberg.org100% (1)
- Production: Ethers, Aliphatic)Documento6 pagineProduction: Ethers, Aliphatic)Harsh ShahNessuna valutazione finora
- Amu 2 (2017)Documento23 pagineAmu 2 (2017)Deep JattNessuna valutazione finora
- Woodward Fieser RuleDocumento28 pagineWoodward Fieser RuleRakesh Kotta100% (3)
- Organic Chem ReactionsDocumento7 pagineOrganic Chem ReactionsTeo Jia Ming NickolasNessuna valutazione finora
- Final Exam Review Fall 2009 AnswersDocumento14 pagineFinal Exam Review Fall 2009 AnswersCharisma SubaNessuna valutazione finora
- Chem100 SS 2022Documento23 pagineChem100 SS 2022Cheng FuNessuna valutazione finora
- The Periodic Table SongDocumento2 pagineThe Periodic Table SongMa Odessa MatiasNessuna valutazione finora
- Experiment 11, 12, 13 Classification Tests For Amines and SynthesisDocumento19 pagineExperiment 11, 12, 13 Classification Tests For Amines and SynthesisDenise Yanci DemiarNessuna valutazione finora
- sANa OllDocumento43 paginesANa OllPeejayNessuna valutazione finora
- Rare Earth Elements (Metals) - ListDocumento3 pagineRare Earth Elements (Metals) - Listasset68Nessuna valutazione finora
- Periodic Table of Elements W Standard State PubChemDocumento1 paginaPeriodic Table of Elements W Standard State PubChemSHENIVEL BANTENessuna valutazione finora
- Chapter 7Documento259 pagineChapter 7Hafizszul Feyzul100% (1)
- Why Use Silicones in Personal Care Part 1Documento8 pagineWhy Use Silicones in Personal Care Part 1JulioNessuna valutazione finora
- Solids Conveying Edu Ctors Data SheetDocumento11 pagineSolids Conveying Edu Ctors Data SheetBenny GomezNessuna valutazione finora
- Manufacturing of Fly Ash Brick and Finding The Optimal Mix of Materials With Replacement of Cement by Lime Sludge and GypsumDocumento4 pagineManufacturing of Fly Ash Brick and Finding The Optimal Mix of Materials With Replacement of Cement by Lime Sludge and GypsumshivaNessuna valutazione finora
- Dibutyltin Dilaurate TDSDocumento1 paginaDibutyltin Dilaurate TDSBoro TerakolNessuna valutazione finora
- 01 Sulphuric AcidDocumento22 pagine01 Sulphuric AcidreetajesuNessuna valutazione finora
- Process Aluminum SulfateDocumento1 paginaProcess Aluminum SulfateAquaniDia HnataVionNessuna valutazione finora
- APARECE REYES Comparison of The Effectiveness of Activated Carbon From Cocos Nucifera Chemically Activated by Lemon Juice and Sodium Chloride For Water PurificationDocumento32 pagineAPARECE REYES Comparison of The Effectiveness of Activated Carbon From Cocos Nucifera Chemically Activated by Lemon Juice and Sodium Chloride For Water PurificationellaNessuna valutazione finora
- Nuclear Charge Increases.: (Do Not Mention Shielding Effect)Documento3 pagineNuclear Charge Increases.: (Do Not Mention Shielding Effect)sfndmnfmnNessuna valutazione finora
- Bromination GreenDocumento3 pagineBromination GreenAlex BorneNessuna valutazione finora
- Group 8: AbsorptionDocumento15 pagineGroup 8: AbsorptionSambiri PisiraiNessuna valutazione finora
- High Performance Concrete and Applications by Shah and AhmedDocumento307 pagineHigh Performance Concrete and Applications by Shah and AhmedSumanNessuna valutazione finora
- InorganicDocumento105 pagineInorganicKishan Gupta100% (6)
- Comparision of CTE Values of Different MaterialsDocumento107 pagineComparision of CTE Values of Different MaterialsPurvesh NanavatiNessuna valutazione finora
- Preparation of Red and Grey Elemental Selenium For Food FortificationDocumento11 paginePreparation of Red and Grey Elemental Selenium For Food FortificationLaras NovitasariNessuna valutazione finora
- Battery TechnologyDocumento44 pagineBattery Technologyvishnu100% (1)
- Kathon LXDocumento15 pagineKathon LXIvanovich RuizNessuna valutazione finora