Documenti di Didattica
Documenti di Professioni
Documenti di Cultura
Specialist Mathematics: Written Examination 1
Caricato da
Garrison LiuTitolo originale
Copyright
Formati disponibili
Condividi questo documento
Condividi o incorpora il documento
Hai trovato utile questo documento?
Questo contenuto è inappropriato?
Segnala questo documentoCopyright:
Formati disponibili
Specialist Mathematics: Written Examination 1
Caricato da
Garrison LiuCopyright:
Formati disponibili
Victorian Certificate of Education
2013
SUPERVISOR TO ATTACH PROCESSING LABEL HERE
STUDENT NUMBER
Letter
Figures
Words
SPECIALIST MATHEMATICS
Written examination 1
Friday 8 November 2013
Reading time: 9.00 am to 9.15 am (15 minutes)
Writing time: 9.15 am to 10.15 am (1 hour)
QUESTION AND ANSWER BOOK
Structure of book
Number of
questions
Number of questions
to be answered
Number of
marks
40
Students are permitted to bring into the examination room: pens, pencils, highlighters, erasers,
sharpeners and rulers.
Students are not permitted to bring into the examination room: notes of any kind, a calculator of any
type, blank sheets of paper and/or white out liquid/tape.
Materials supplied
Question and answer book of 11 pages with a detachable sheet of miscellaneous formulas in the
centrefold.
Working space is provided throughout the book.
Instructions
Detach the formula sheet from the centre of this book during reading time.
Write your student number in the space provided above on this page.
All written responses must be in English.
Students are NOT permitted to bring mobile phones and/or any other unauthorised electronic
devices into the examination room.
VICTORIAN CURRICULUM AND ASSESSMENT AUTHORITY 2013
2013 SPECMATH EXAM 1
THIS PAGE IS BLANK
2013 SPECMATH EXAM 1
Instructions
Answer all questions in the spaces provided.
Unless otherwise specified, an exact answer is required to a question.
In questions where more than one mark is available, appropriate working must be shown.
Unless otherwise indicated, the diagrams in this book are not drawn to scale.
Take the acceleration due to gravity to have magnitude g m/s2, where g = 9.8.
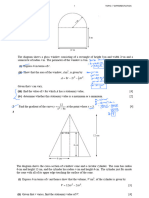
Question 1 (3 marks)
A body of mass 10 kg is held in place on a smooth plane inclined at 30 to the horizontal by a
tension force, T newtons, acting parallel to the plane.
a. On the diagram below, show all other forces acting on the body and label them.
1 mark
30
b.
Find the value of T.
2 marks
TURN OVER
2013 SPECMATH EXAM 1
Question 2 (4 marks)
1
Evaluate
x5
x2 5 x + 6 dx .
0
2013 SPECMATH EXAM 1
Question 3 (4 marks)
The coordinates of three points are A(1, 2, 4), B(1, 0, 5) and C(3, 5, 2).
a.
Find AB .
b.
The points A, B and C are the vertices of a triangle.
Prove that the triangle has a right angle at A.
c.
Find the length of the hypotenuse of the triangle.
1 mark
2 marks
1 mark
TURN OVER
2013 SPECMATH EXAM 1
Question 4 (6 marks)
a. State the maximal domain and the range of y = arccos(1 2x).
b.
2 marks
Sketch the graph of y = arccos(1 2x) over its maximal domain. Label the endpoints with
their coordinates.
2 marks
c.
Find the gradient of the tangent to the graph of y = arccos(1 2x) at x =
1
.
4
2 marks
2013 SPECMATH EXAM 1
Question 5 (5 marks)
A container of water is heated to boiling point (100 C) and then placed in a room that has a
constant temperature of 20 C. After five minutes the temperature of the water is 80 C.
dT
a. Use Newtons law of cooling
= k (T 20) , where T C is the temperature of the water
dt
3
at time t minutes after the water is placed in the room, to show that e 5k = .
4
b.
Find the temperature of the water 10 minutes after it is placed in the room.
2 marks
3 marks
TURN OVER
2013 SPECMATH EXAM 1
Question 6 (4 marks)
Find the value of c, where c R, such that the curve defined by
y2 +
3e( x 1)
=c
x2
has a gradient of2 where x = 1.
2013 SPECMATH EXAM 1
Question 7 (6 marks)
The position vector ~r(t ) of a particle moving relative to an origin O at time t seconds is given by
r (t ) = 4 sec(t ) ~i + 2 tan(t ) j, t 0,
~
2
where the components are measured in metres.
x2 y 2
= 1.
16 4
a.
Show that the cartesian equation of the path of the particle is
b.
Sketch the path of the particle on the axes below, labelling any asymptotes with their
equations.
2 marks
2 marks
c.
Find the speed of the particle, in ms1, when t =
.
4
2 marks
TURN OVER
2013 SPECMATH EXAM 1
10
Question 8 (4 marks)
Find all solutions of z4 2z2 + 4 = 0, z C in cartesian form.
11
2013 SPECMATH EXAM 1
Question 9 (4 marks)
The shaded region below is enclosed by the graph of y = sin(x) and the lines y = 3x and x = .
3
This region is rotated about the x-axis.
y
3
x=
y = 3x
1
y = sin(x)
O
Find the volume of the resulting solid of revolution.
END OF QUESTION AND ANSWER BOOK
SPECIALIST MATHEMATICS
Written examinations 1 and 2
FORMULA SHEET
Directions to students
Detach this formula sheet during reading time.
This formula sheet is provided for your reference.
VICTORIAN CURRICULUM AND ASSESSMENT AUTHORITY 2013
SPECMATH
Specialist Mathematics formulas
Mensuration
area of a trapezium:
1 a+b h
(
)
2
curved surface area of a cylinder:
2rh
volume of a cylinder:
r2h
volume of a cone:
sine rule:
1 2
r h
3
1 Ah
3
4 r3
3
1 bc sin A
2
a
b
c
= =
sin A sin B sin C
cosine rule:
c2 = a2 + b2 2ab cos C
volume of a pyramid:
volume of a sphere:
area of a triangle:
Coordinate geometry
ellipse:
( x h )2 + ( y k )2
a2
b2
= 1
hyperbola:
( x h )2 ( y k )2
a2
b2
=1
Circular (trigonometric) functions
cos2(x) + sin2(x) = 1
1 + tan2(x) = sec2(x) cot2(x) + 1 = cosec2(x)
sin(x + y) = sin(x) cos(y) + cos(x) sin(y) sin(x y) = sin(x) cos(y) cos(x) sin(y)
cos(x + y) = cos(x) cos(y) sin(x) sin(y) cos(x y) = cos(x) cos(y) + sin(x) sin(y)
tan( x + y ) =
tan( x) + tan( y )
1 tan( x) tan( y )
tan( x y ) =
tan( x) tan( y )
1 + tan( x) tan( y )
cos(2x) = cos2(x) sin2(x) = 2 cos2(x) 1 = 1 2 sin2(x)
tan(2 x) =
sin(2x) = 2 sin(x) cos(x)
function
sin1
cos1
tan1
domain
[1, 1]
[1, 1]
2 , 2
[0, ]
,
2 2
range
2 tan( x)
1 tan 2 ( x)
SPECMATH
Algebra (complex numbers)
z = x + yi = r(cos + i sin ) = r cis
z = x 2 + y 2 = r < Arg z
z1 r1
z1z2 = r1r2 cis(1 + 2)
= cis
z2 r2 ( 1 2 )
zn = rn cis(n) (de Moivres theorem)
Calculus
d n
x = nx n 1
dx
x n dx =
1 n +1
x + c, n 1
n +1
d ax
e = ae ax
dx
e ax dx =
1 ax
e +c
a
1
d
( log e ( x) ) =
dx
x
d
( sin(ax) ) = a cos(ax)
dx
1
dx = log e x + c
x
d
( cos(ax) ) = a sin(ax)
dx
1
cos( ax) dx = sin(ax) + c
a
d
( tan(ax) ) = a sec2 (ax)
dx
sec 2 (ax) dx =
d
1
sin 1 ( x) =
dx
1 x2
x
dx = sin 1 + c, a > 0
a
a2 x2
1
d
cos 1 ( x) =
dx
1 x2
x
dx = cos 1 + c, a > 0
a
a2 x2
d
1
tan 1 ( x) =
dx
1 + x2
( )
( )
(
(
(
1
sin( ax) dx = cos(ax) + c
a
1
tan(ax) + c
a
x
dx = tan 1 + c
a +x
a
2
product rule:
dv
du
d
( uv ) = u + v
dx
dx
dx
quotient rule:
du
dv
v
u
d u
dx
dx
=
dx v
v2
chain rule:
dy dy du
=
dx du dx
Eulers method:
If
acceleration:
a=
dy
= f ( x), x0 = a and y0 = b, then xn + 1 = xn + handyn + 1 = yn + hf(xn)
dx
d 2x
dt
dv
dv d 1
= v = v2
dt
dx dx 2
1
1
constant (uniform) acceleration: v = u + ats = ut + at2v2 = u2 + 2ass = (u + v)t
2
2
TURN OVER
SPECMATH
Vectors in two and three dimensions
r = x~i + y j + zk~
| ~r | = x 2 + y 2 + z 2 = r
~ 1. ~ 2
r = r r cos = x x + y y + z z
1 2
1 2
1 2
1 2
Mechanics
momentum:
p = mv
equation of motion:
R = ma
friction:
F N
END OF FORMULA SHEET
Potrebbero piacerti anche
- Math Minutes - 8th GradeDocumento112 pagineMath Minutes - 8th Gradeklatifdg91% (23)
- Formula Matematik Dan Nota RingkasDocumento9 pagineFormula Matematik Dan Nota RingkasPurawin Subramaniam100% (11)
- Math 365 Sample ExamsDocumento13 pagineMath 365 Sample ExamsNab Tor100% (1)
- Test Bank for Precalculus: Functions & GraphsDa EverandTest Bank for Precalculus: Functions & GraphsValutazione: 5 su 5 stelle5/5 (1)
- Maatthheem Maattiiccs: FI Iiit TJ JEDocumento5 pagineMaatthheem Maattiiccs: FI Iiit TJ JEheroNessuna valutazione finora
- 02 - Mathematics - July 2006Documento6 pagine02 - Mathematics - July 2006vishaljalanNessuna valutazione finora
- Time: 3 Hours 06 - Mathematics - July 2008 Marks: 100 PG - 1Documento6 pagineTime: 3 Hours 06 - Mathematics - July 2008 Marks: 100 PG - 1SURAJ SINGHNessuna valutazione finora
- 09a1bs01 Mathematics 1Documento5 pagine09a1bs01 Mathematics 1Ansh PratapNessuna valutazione finora
- Kcet - Mathematics - 2016: Version Code: C - 3Documento13 pagineKcet - Mathematics - 2016: Version Code: C - 3Kamalesh ShenoyNessuna valutazione finora
- Some Important Formulae, Definitions and Results in MathematicsDocumento12 pagineSome Important Formulae, Definitions and Results in Mathematicsparchure123100% (1)
- Multivariable Calculus Sample ExamDocumento5 pagineMultivariable Calculus Sample ExamFaithBoaz21Nessuna valutazione finora
- 03 - Mathematics - March 2007Documento6 pagine03 - Mathematics - March 2007vishaljalanNessuna valutazione finora
- Anderson Sec 2010 AM Prelim - P2Documento5 pagineAnderson Sec 2010 AM Prelim - P2math3matics3Nessuna valutazione finora
- Notes and Formulae MathematicsDocumento9 pagineNotes and Formulae MathematicsNurAinKhalidNessuna valutazione finora
- NH Mathematics All 2015Documento20 pagineNH Mathematics All 2015Leandro SoaresNessuna valutazione finora
- AMath Trial P1 07Documento10 pagineAMath Trial P1 07Norazman Chik MohamadNessuna valutazione finora
- Revised Diagnostic Test KeyDocumento10 pagineRevised Diagnostic Test KeyKristine RepolloNessuna valutazione finora
- ISI KolkataDocumento32 pagineISI KolkatagaurishkorpalNessuna valutazione finora
- Applied Calculus: Credit Hour: 3Documento39 pagineApplied Calculus: Credit Hour: 3bigbangmelvanNessuna valutazione finora
- KVPY 2013 Stream SB SX Solved PaperDocumento39 pagineKVPY 2013 Stream SB SX Solved PaperSoumya DansanaNessuna valutazione finora
- 05 - Mathematics - March 2008Documento6 pagine05 - Mathematics - March 2008vishaljalanNessuna valutazione finora
- Math Stats Booklet 1Documento20 pagineMath Stats Booklet 1Koh Boon HaoNessuna valutazione finora
- STPM Mathematics T Past Year Question P1 P2 P3Documento19 pagineSTPM Mathematics T Past Year Question P1 P2 P3Sou Voyage0% (3)
- Maths Model Test Paper For Summative Assessment - 1Documento13 pagineMaths Model Test Paper For Summative Assessment - 1Apex InstituteNessuna valutazione finora
- Information About The Final Exam: XdydxDocumento2 pagineInformation About The Final Exam: Xdydxswagmaster11Nessuna valutazione finora
- XcosxdxDocumento5 pagineXcosxdxWelyab PaulaNessuna valutazione finora
- Notes and Formulae SPM Mathematics Form 1 - 3 Notes Solid GeometryDocumento9 pagineNotes and Formulae SPM Mathematics Form 1 - 3 Notes Solid GeometryJarnice Ling Yee ChingNessuna valutazione finora
- ISI Sample Question 2015 For B.stat & B.mathDocumento9 pagineISI Sample Question 2015 For B.stat & B.mathMota Chashma100% (1)
- 15aimo 2Documento10 pagine15aimo 2Hoàng LongNessuna valutazione finora
- Notes and Formulae SPM Mathematics Form 1 - 3 Notes Solid GeometryDocumento9 pagineNotes and Formulae SPM Mathematics Form 1 - 3 Notes Solid GeometrySharmini RajagopalNessuna valutazione finora
- Additional Mathematics 2010 November Paper 13Documento8 pagineAdditional Mathematics 2010 November Paper 13Sharifa McLeodNessuna valutazione finora
- Batch XII PDFDocumento4 pagineBatch XII PDFArun KumarNessuna valutazione finora
- Mathematics Engg Practice Test Paper-1Documento5 pagineMathematics Engg Practice Test Paper-1Indra Pratap Sengar100% (1)
- MHT CET 2016 Version 11Documento16 pagineMHT CET 2016 Version 11JitNessuna valutazione finora
- TKGS 2010 Sec 4 MYE AMDocumento8 pagineTKGS 2010 Sec 4 MYE AMdreamydamselNessuna valutazione finora
- Baulkham Hills 2013 3U HY & SolutionsDocumento12 pagineBaulkham Hills 2013 3U HY & SolutionsSumNessuna valutazione finora
- Have A Safe and Happy Break: Math 122 FinalDocumento17 pagineHave A Safe and Happy Break: Math 122 FinalDavid VarkeyNessuna valutazione finora
- Mathematics 1Documento4 pagineMathematics 1Vinay KandulaNessuna valutazione finora
- 0606 w10 QP 13Documento8 pagine0606 w10 QP 13Kimberley Fnick ChanNessuna valutazione finora
- Solution Total DistributionsDocumento5 pagineSolution Total Distributions8rztNessuna valutazione finora
- KVPY 2012 Stream SB SX Solved PaperDocumento32 pagineKVPY 2012 Stream SB SX Solved PaperAnkitKambojNessuna valutazione finora
- Quiz 1 (Chapter 14) - SolutionsDocumento12 pagineQuiz 1 (Chapter 14) - Solutionsxperia30Nessuna valutazione finora
- Chapter 2: Trigonometric FunctionsDocumento10 pagineChapter 2: Trigonometric FunctionsSaidin AhmadNessuna valutazione finora
- Additional Mathematics 2003 November Paper 1Documento8 pagineAdditional Mathematics 2003 November Paper 1lornarifaNessuna valutazione finora
- TrigonometryDocumento23 pagineTrigonometryTitis PohanNessuna valutazione finora
- Mathematical Methods (Cas) : Written Examination 1Documento15 pagineMathematical Methods (Cas) : Written Examination 1Peele TanNessuna valutazione finora
- Sample Paper MATH Extended PaperM2 EDocumento6 pagineSample Paper MATH Extended PaperM2 EHarry Mak HollamNessuna valutazione finora
- Trigonometric Ratios to Transformations (Trigonometry) Mathematics E-Book For Public ExamsDa EverandTrigonometric Ratios to Transformations (Trigonometry) Mathematics E-Book For Public ExamsValutazione: 5 su 5 stelle5/5 (1)
- Ten-Decimal Tables of the Logarithms of Complex Numbers and for the Transformation from Cartesian to Polar Coordinates: Volume 33 in Mathematical Tables SeriesDa EverandTen-Decimal Tables of the Logarithms of Complex Numbers and for the Transformation from Cartesian to Polar Coordinates: Volume 33 in Mathematical Tables SeriesNessuna valutazione finora
- Analytic Geometry: Graphic Solutions Using Matlab LanguageDa EverandAnalytic Geometry: Graphic Solutions Using Matlab LanguageNessuna valutazione finora
- Transformation of Axes (Geometry) Mathematics Question BankDa EverandTransformation of Axes (Geometry) Mathematics Question BankValutazione: 3 su 5 stelle3/5 (1)
- De Moiver's Theorem (Trigonometry) Mathematics Question BankDa EverandDe Moiver's Theorem (Trigonometry) Mathematics Question BankNessuna valutazione finora
- Application of Derivatives Tangents and Normals (Calculus) Mathematics E-Book For Public ExamsDa EverandApplication of Derivatives Tangents and Normals (Calculus) Mathematics E-Book For Public ExamsValutazione: 5 su 5 stelle5/5 (1)
- Circles (Geometry) Mathematics Question BankDa EverandCircles (Geometry) Mathematics Question BankNessuna valutazione finora
- 10.3 The Six Circular Functions and Fundamental IdentitiesDocumento26 pagine10.3 The Six Circular Functions and Fundamental IdentitiesJerico VillanuevaNessuna valutazione finora
- BD S1e03Documento24 pagineBD S1e03BAFSNessuna valutazione finora
- Act Math FormulasDocumento9 pagineAct Math FormulasMiles100% (1)
- Chap.5 Eigenvalues EigenvectorsDocumento34 pagineChap.5 Eigenvalues EigenvectorsndarubagusNessuna valutazione finora
- Lab04 GLS554Documento13 pagineLab04 GLS554Muhammad IrfanNessuna valutazione finora
- Composite and Inverse FunctionsDocumento22 pagineComposite and Inverse FunctionsriskyNessuna valutazione finora
- Chapter 2Documento57 pagineChapter 2jacob quizonNessuna valutazione finora
- Mcs 013Documento21 pagineMcs 013D.J. VykNessuna valutazione finora
- Lecture 3Documento11 pagineLecture 3lvrevathiNessuna valutazione finora
- Differentiation Pastpaper Question'sDocumento13 pagineDifferentiation Pastpaper Question'sUrnext bestalternw100% (1)
- Apollonius of PergaDocumento29 pagineApollonius of PergaVicky FelicianoNessuna valutazione finora
- S. Mandelbrojt (Auth.) - Dirichlet Series - Principles and Methods (1971, Springer Netherlands)Documento174 pagineS. Mandelbrojt (Auth.) - Dirichlet Series - Principles and Methods (1971, Springer Netherlands)luisufspaiandreNessuna valutazione finora
- Chapter 3: Laplace Transform: FT FsDocumento29 pagineChapter 3: Laplace Transform: FT FsTekdNessuna valutazione finora
- C4 Partial Fractions B - QuestionsDocumento1 paginaC4 Partial Fractions B - QuestionsHin Wa LeungNessuna valutazione finora
- CBSE Class 9 Mathematics SA1 2011 Question PaperDocumento12 pagineCBSE Class 9 Mathematics SA1 2011 Question PaperravilullaNessuna valutazione finora
- Inverse and Analytic Functions PDFDocumento9 pagineInverse and Analytic Functions PDFjayroldparcedeNessuna valutazione finora
- Revision Worksheet Class 9 MathDocumento1 paginaRevision Worksheet Class 9 MathRead And GrowNessuna valutazione finora
- Summary MATH1131 AlgebraDocumento42 pagineSummary MATH1131 AlgebraClinton3011Nessuna valutazione finora
- Class 10 Math Sample Paper2Documento7 pagineClass 10 Math Sample Paper2Bharath RajNessuna valutazione finora
- CONTEXTUALIZATION in MathDocumento7 pagineCONTEXTUALIZATION in MathRhodabie MelendresNessuna valutazione finora
- Indefinite Integration: Chapter HighlightsDocumento52 pagineIndefinite Integration: Chapter HighlightsAditya WanwadeNessuna valutazione finora
- Rising 7th Grade Summer Math PacketDocumento7 pagineRising 7th Grade Summer Math Packetapi-252496044Nessuna valutazione finora
- Polynomial FunctionsDocumento29 paginePolynomial FunctionsJessel PalermoNessuna valutazione finora
- MP Straight LinesDocumento8 pagineMP Straight LinesYeswa Preetham ReddyNessuna valutazione finora
- Elliptic Grid - Assignment # 3 (2012420071) - WaseemDocumento7 pagineElliptic Grid - Assignment # 3 (2012420071) - WaseemWaseem SakhawatNessuna valutazione finora
- Derivation of The NavierDocumento13 pagineDerivation of The NaviersumiNessuna valutazione finora
- Lesson 4 - NTH Term of Arithmetic SequenceDocumento3 pagineLesson 4 - NTH Term of Arithmetic SequenceCarolyn Ancheta-DaquioagNessuna valutazione finora
- Cert-Ece Mathematics: Final CoachingDocumento7 pagineCert-Ece Mathematics: Final CoachingHary KrizNessuna valutazione finora
- Application of The Concept of Sequence and Arithmetic Series in Economics 1Documento17 pagineApplication of The Concept of Sequence and Arithmetic Series in Economics 1ARFIAN TANJUNGNessuna valutazione finora