Documenti di Didattica
Documenti di Professioni
Documenti di Cultura
CHG 4160 Assignment 2
Caricato da
Zachary ComeauCopyright
Formati disponibili
Condividi questo documento
Condividi o incorpora il documento
Hai trovato utile questo documento?
Questo contenuto è inappropriato?
Segnala questo documentoCopyright:
Formati disponibili
CHG 4160 Assignment 2
Caricato da
Zachary ComeauCopyright:
Formati disponibili
CHG 4160 Assignment 2
Zachary Comeau, 6876641
Question 1:
a) 5ATGGCGAACCTTGGCTGGATG3
b) 3TACCGCTTGGAACCGACCTAC5
c) Transcription is the process whereby DNA is transcribed to RNA, a first step of
gene expression. RNA polymerase binds genomic DNA, with the assistance of
a variety of transcription factors, and transcribes the DNA into single
stranded RNA (with thymine being swapped for uracil). Further modifications
to the RNA may be performed in the nucleus including polyadenylation,
capping, and splicing. Now, a transcript of the gene in question the RNA exits
the nucleus to be translated into a protein.
mRNA transcript: 5AUGGCGAACCUUGGCUGGAUG3
d) Translation is the process whereby mRNA is translated, via codons, into an
amino acid sequence which, once processed, will become a functional
protein. A beginning step to this process is the assembly of ribosomes on the
mRNA at the start codon (DNA: ATG, RNA: AUG). The ribosomal subunits then
move along the mRNA reading each codon and attaching the corresponding
amino acid to a growing amino acid chain in a process known as elongation.
Once a stop codon is reached (UAA, UAG, or UGA) the chain of amino acids,
or polypeptide, is released for further processing (folding and etc. to
eventually become a protein) and the ribosomal subunits separate.
Amino acid sequence: Methionine Alanine Asparagine Leucine Glycine
Tryptophan Methionine
The stop codon used is UGA
e)
Question 3 (as theres no question 2 on the assignment handout):
a) pBluescript plasmid
b) Start with purified cell DNA, order oligos so I can perform PCR against my
gene of interest, amplify and purify my gene of interest. Find an appropriate
cut site on the plasmid that will allow for ligation of my gene of interest into
the plasmid. Cut the plasmid with (usually) two restriction enzymes, ligate in
my gene of interest, purify the resulting modified plasmid.
Use either chemically or electrically competent cells, heat shock them with
your plasmid, then grow them. Most plasmids will code for an antibiotic
resistance gene (commonly ampicillin). By growing transformed cells on the
appropriate antibiotic plate one can be sure that any colonies that grow will
have taken up the modified plasmid of interest.
c) GGGTAGAATTCAATCG
CCCATCTTAAGTTAGC
GGGTAG
CCCATCTTAA
GTTAGC
AATTCAATCG
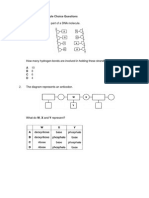
Question 4:
One can either use oligo-nucleotides probes for cDNA clones, or anti-body probes.
The first method involves taking a known protein sequence, translating it into all
possible mRNA sequences and in turn generating radiolabeled DNA oligonucleotides
which will hybridize to the clone of interest and appear on X-ray film. The second
method involves transforming bacterial cells such that they express the protein of
interest, performing a protein-membrane absorption, and then probing the
membrane with a primary antibody (coded for the protein) and a secondary
antibody (coded for the primary antibody) which, upon binding of both, will either
produce a colored or fluorescent product, allowing for individual colonies of interest
to be identified.
Question 5:
Sequences (red represents the primers):
Forward Primer Sequence: AGTCAGTGGAACAAGCCGAG
Reverse Primer Sequence: CTGCCGAAATGTATGATGGGC
Primers bind to the red highlighted sequences
Sequence to be amplified (reverse primer binds)
5AGTCAGTGGAACAAGCCGAGTAAGCCAAAAACCAACATGAAGCACATGGCTGGTGCTGC
AGCAGCTGGGGCAGTGGTGGGGGGCCTTGGCGGCTACATGCTGGGAAGTGCCATGAGCA
GGCCCATCATACATTTCGGCAG3
Complementary sequence (forward primer binds)
5TGGGCCTGCTCATGGCACTTCCCAGCATGTAGCCGCCAAGGCCCCCCACCACTGCCCCA
GCTGCTGCAGCACCAGCCATGTGCTTCATGTTGGTTTTTGGCTTACTCGGCTTGTTCCACTGA
CT3
PCR steps:
DNA is heat denatured at 94-95C
Annealing occurs at about 68C. Primers bind to their respective sequences (red,
above)
Elongation is performed, at about 72C, as the DNA polymerase (commonly TAQ)
travels from the 5 -> 3 end of the primers, upon reaching the end of each primer
adding the appropriate nucleotides to create 2 (double stranded) strands of DNA
(from one).
The whole process is then repeated allowing for an exponential increase in the
amount of DNA strands.
Potrebbero piacerti anche
- Air Emissions ReportDocumento19 pagineAir Emissions ReportZachary ComeauNessuna valutazione finora
- TheoryDocumento2 pagineTheoryZachary ComeauNessuna valutazione finora
- Athletic LetterDocumento2 pagineAthletic LetterZachary ComeauNessuna valutazione finora
- Refresher Referee Course ApplicationDocumento3 pagineRefresher Referee Course ApplicationZachary ComeauNessuna valutazione finora
- Preschool WorksheetDocumento14 paginePreschool WorksheetZachary ComeauNessuna valutazione finora
- Swim Kids Worksheet 1-10Documento20 pagineSwim Kids Worksheet 1-10Zachary Comeau80% (5)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItDa EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItValutazione: 4.5 su 5 stelle4.5/5 (838)
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeDa EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeValutazione: 4.5 su 5 stelle4.5/5 (537)
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeDa EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeValutazione: 4 su 5 stelle4/5 (5794)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Da EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Valutazione: 4 su 5 stelle4/5 (98)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceDa EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceValutazione: 4 su 5 stelle4/5 (894)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingDa EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingValutazione: 3.5 su 5 stelle3.5/5 (399)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureDa EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureValutazione: 4.5 su 5 stelle4.5/5 (474)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryDa EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryValutazione: 3.5 su 5 stelle3.5/5 (231)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceDa EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceValutazione: 4 su 5 stelle4/5 (587)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaDa EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaValutazione: 4.5 su 5 stelle4.5/5 (265)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealDa EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealValutazione: 4 su 5 stelle4/5 (73)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerDa EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerValutazione: 4.5 su 5 stelle4.5/5 (271)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersDa EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersValutazione: 4.5 su 5 stelle4.5/5 (344)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaDa EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaValutazione: 4 su 5 stelle4/5 (45)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnDa EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnValutazione: 4.5 su 5 stelle4.5/5 (234)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyDa EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyValutazione: 3.5 su 5 stelle3.5/5 (2219)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreDa EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreValutazione: 4 su 5 stelle4/5 (1090)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Da EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Valutazione: 4.5 su 5 stelle4.5/5 (119)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesDa EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesValutazione: 4 su 5 stelle4/5 (821)
- Replicacion ADNDocumento2 pagineReplicacion ADNSebastian NeculqueoNessuna valutazione finora
- DNA Structure RevealedDocumento44 pagineDNA Structure Revealedevacarlina1721Nessuna valutazione finora
- H2 DNA and Genomics QuestionsDocumento18 pagineH2 DNA and Genomics QuestionsWesley TanNessuna valutazione finora
- hssb0800t StudygdbDocumento17 paginehssb0800t StudygdbyawahabNessuna valutazione finora
- Bio Practice Questions For Final Exam Biol 1101Documento5 pagineBio Practice Questions For Final Exam Biol 1101Megadirectioner 21Nessuna valutazione finora
- Protein Translation ProcessDocumento8 pagineProtein Translation ProcessKempetsNessuna valutazione finora
- DNA Damage and RepairDocumento7 pagineDNA Damage and RepairAparna AbiNessuna valutazione finora
- Have Your Dna and Eat It TooDocumento4 pagineHave Your Dna and Eat It Tooapi-32133818Nessuna valutazione finora
- Virulence and PathogenesisDocumento52 pagineVirulence and PathogenesisAlmoatazbellah AbdallahNessuna valutazione finora
- 12 Fire Letters - 1 DNA Strand Template (1 Fire Letter Sequence 144 Vector Codes)Documento1 pagina12 Fire Letters - 1 DNA Strand Template (1 Fire Letter Sequence 144 Vector Codes)RobertNessuna valutazione finora
- DNA Fingerprinting for IdentificationDocumento28 pagineDNA Fingerprinting for IdentificationWiwin SyaifudinNessuna valutazione finora
- Semester 2 Biochem TimetableDocumento1 paginaSemester 2 Biochem TimetablesophiecabNessuna valutazione finora
- Protein Synthesis - Transcription and TranslationDocumento61 pagineProtein Synthesis - Transcription and Translationblackmoneygrabber100% (1)
- Rnahybrid: Microrna Target Prediction Easy, Fast and FlexibleDocumento4 pagineRnahybrid: Microrna Target Prediction Easy, Fast and FlexibleJorge Hantar Touma LazoNessuna valutazione finora
- P20 VWRCVQ65052.1000 Coa 031122an70 enDocumento1 paginaP20 VWRCVQ65052.1000 Coa 031122an70 enbotond77Nessuna valutazione finora
- Recombinant DNA ToolsDocumento23 pagineRecombinant DNA ToolskrystenNessuna valutazione finora
- Restriction EnzymeDocumento45 pagineRestriction Enzymedrsubhash81Nessuna valutazione finora
- Principle, Analysis, Application and Challenges of Next-Generation Sequencing: A ReviewDocumento30 paginePrinciple, Analysis, Application and Challenges of Next-Generation Sequencing: A ReviewShahid HanifNessuna valutazione finora
- Harper's Illustrated Biochemistry PDFDocumento1 paginaHarper's Illustrated Biochemistry PDFDilip ReddyNessuna valutazione finora
- Gene Expression and Regulation - University of LeicesterDocumento5 pagineGene Expression and Regulation - University of LeicesterAriqa FatinaNessuna valutazione finora
- Name: SurnameDocumento2 pagineName: SurnameMichele Leigh ChenaultNessuna valutazione finora
- Chapter On TranscriptomicsDocumento13 pagineChapter On TranscriptomicsMazhar FarNessuna valutazione finora
- Protein Synthesis ACEDocumento14 pagineProtein Synthesis ACEZhiTing96Nessuna valutazione finora
- Transcription & Translation ColoringDocumento2 pagineTranscription & Translation ColoringKristen LindstromNessuna valutazione finora
- MCQ On PCR (Polymerase Chain Reaction) - MCQ Biology - Learning Biology Through MCQsDocumento6 pagineMCQ On PCR (Polymerase Chain Reaction) - MCQ Biology - Learning Biology Through MCQsPpa Gpat Amit100% (2)
- Cracking The Secret MessageDocumento8 pagineCracking The Secret MessageEvette dela PenaNessuna valutazione finora
- 6 BIO462 Chapter 6Documento21 pagine6 BIO462 Chapter 6Syafiqah SuhaimiNessuna valutazione finora
- DNA Puzzle Kit: Teacher'S Manual and Student GuideDocumento3 pagineDNA Puzzle Kit: Teacher'S Manual and Student GuideClven Fernandez0% (1)
- Biochemistry 8th Edition Campbell Test BankDocumento17 pagineBiochemistry 8th Edition Campbell Test BankchristinecohenceyamrgpkjNessuna valutazione finora
- DNA Structure and Function - First Lecture (4822)Documento17 pagineDNA Structure and Function - First Lecture (4822)Ashley Ramos LópezNessuna valutazione finora