Documenti di Didattica
Documenti di Professioni
Documenti di Cultura
Mechanics Problem Set - 2
Caricato da
Perry EsguerraTitolo originale
Copyright
Formati disponibili
Condividi questo documento
Condividi o incorpora il documento
Hai trovato utile questo documento?
Questo contenuto è inappropriato?
Segnala questo documentoCopyright:
Formati disponibili
Mechanics Problem Set - 2
Caricato da
Perry EsguerraCopyright:
Formati disponibili
Mechanics Set II (Dynamics, Kinematics, Statics)
Sky Hook The science fiction writer R. A. Heinlein describes a "skyhook" satellite that consists of a long rope placed in
orbit at the equator, aligned along a radius from the center of the earth, and moving so that the rope appears suspended in
space above a fixed point on the equator. The bottom of the rope hangs free just above the surface of the earth (radius R).
Assuming that the rope has uniform mass per unit length (and that the rope is strong enough to resist breaking!), find the
length of the rope.
1)
An articulated contraption consists of three rhombuses
whose sides are in the proportions 3:2:1. The vertex A3 moves along
a horizontal direction with a constant speed V. Determine the speeds
of the vertices A1, A2, B2 at the moment that all the angles of the
contraption are right angles.
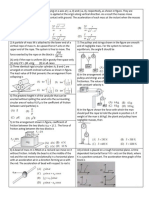
3. A block of mass M rests on
a fixed plane inclined at angle
. You apply a horizontal force of Mg on the block, as shown in the figure on the
left. (a) Assume that the friction force between the block and the plane is large
enough to keep the block at rest. What are the normal and friction forces (call them
N and f ) that the plane exerts on the block?
(b) Let the coefficient of static friction be . For what range of angles will the block
remain still?
4. A rope wraps an angle around a pole. You grab one end and pull with a tension T0. The other end is attached to a large
object, say, a boat. If the coefficient of static friction between the rope and the pole is , what is the largest force the rope
can exert on the boat, if the rope is not to slip around the pole?
5. A. A ladder of mass M and length L leans against a frictionless wall. If the coefficient of friction with the ground is ,
what is the smallest angle the ladder can make with the ground and not slip? (assume that the mass distribution along the
length of the ladder is uniform)
B. Now assume that a person of mass m stands on the ladder of the way-up. In this case, what is the smallest angle the
ladder can make with the ground and not slip? (approximate the person as a point mass )
6. An inclined plane with inclined angle and mass M is placed on a frictionless table. A piece of wood with friction
coefficient < tan is put on the inclined plane (see
figure). A horizontal force F acts on the system as shown
F
in the figure. What is the range of magnitude of F where
m
M
the piece of wood can remain stationary on the inclined
plane?
7. With two fingers, you hold an ice cream cone motionless upside down,as shown in the
figure. The mass of the cone is m, and the coefficient of static friction between your fingers
and the cone is . When viewed from the side, the angle of the tip is 2. What is the
minimum normal force you must apply with each finger in order to hold up the cone? In
terms of , what is the minimum value of that allows you to hold up the cone? Assume that
you can supply as large a normal force as needed.
8. Three identical cylinders are arranged as in the figure.
The coefficient of friction between the cylinders is 1,
and between the cylinders and the floor is 2. What minimum values must 1 and 2
exceed so that the system can be in static equilibrium?
Potrebbero piacerti anche
- Phys101 8 hw2Documento2 paginePhys101 8 hw2mirsad türkerNessuna valutazione finora
- Tugas Mek I-9 OktDocumento2 pagineTugas Mek I-9 OktAlifani SofiNessuna valutazione finora
- Force and Friction WorksheetDocumento2 pagineForce and Friction WorksheetAdil AliNessuna valutazione finora
- Energi Momentum Dan Dinamika Rotasi Pelatihan Osn 2012Documento7 pagineEnergi Momentum Dan Dinamika Rotasi Pelatihan Osn 2012Ivandito HerdayandityaNessuna valutazione finora
- Momento Linear e Centro de Massa: Resolução de Problemas de MecânicaDocumento4 pagineMomento Linear e Centro de Massa: Resolução de Problemas de MecânicaThales FreireNessuna valutazione finora
- Energy and Momentum - Level 3Documento8 pagineEnergy and Momentum - Level 3Kusharg rahejaNessuna valutazione finora
- MotionDocumento17 pagineMotionJohnNessuna valutazione finora
- Prob01s - H C VermaDocumento6 pagineProb01s - H C VermaManoj KumarNessuna valutazione finora
- Ovchinkin Problems in PhysicsDocumento16 pagineOvchinkin Problems in PhysicsDeekshaNessuna valutazione finora
- Application of Newton's Second Law: Challenge Problems Problem 1: Painter On A PlatformDocumento9 pagineApplication of Newton's Second Law: Challenge Problems Problem 1: Painter On A PlatformBoldie LutwigNessuna valutazione finora
- PHY102 Iitk Home AssignmentDocumento3 paginePHY102 Iitk Home AssignmentJaya Aditya ChandrasekarNessuna valutazione finora
- Particle Dynamics SheetDocumento27 pagineParticle Dynamics SheetAkhilesh SoniNessuna valutazione finora
- Assignment 1 Due DateDocumento7 pagineAssignment 1 Due DateArunnarenNessuna valutazione finora
- Assignment 2 - Mechanics 2Documento2 pagineAssignment 2 - Mechanics 2Marcos Aaron TherthensNessuna valutazione finora
- IIT Physics Sample Paper 1 Rotational Kinematics & DynamicsDocumento2 pagineIIT Physics Sample Paper 1 Rotational Kinematics & DynamicsVikash TiwariNessuna valutazione finora
- SpringerDocumento10 pagineSpringerMonico AlejoNessuna valutazione finora
- THE DESIGN OF PYRAMID ROOFSDocumento24 pagineTHE DESIGN OF PYRAMID ROOFSrosario59100% (4)
- Part - I: Subjective Questions: Section (A) : Calculation of Centre of MassDocumento14 paginePart - I: Subjective Questions: Section (A) : Calculation of Centre of MassRaman GoyalNessuna valutazione finora
- PHY5113 TUTORIAL N0 3 Questions PDFDocumento9 paginePHY5113 TUTORIAL N0 3 Questions PDFAlbertNessuna valutazione finora
- Rigid Body DynamicsDocumento5 pagineRigid Body Dynamicsrockingjoe0% (1)
- Practice-Problems For Kleppner Mechanics 2nd EditionDocumento2 paginePractice-Problems For Kleppner Mechanics 2nd Editiongayatri rainaNessuna valutazione finora
- Laws of Motion WorksheetDocumento5 pagineLaws of Motion WorksheetHarishNessuna valutazione finora
- Practice Sheet WPEDocumento9 paginePractice Sheet WPENaveen JaferNessuna valutazione finora
- RotaionalDocumento19 pagineRotaionalSujay BhattacharyaNessuna valutazione finora
- Exercise Set 11Documento3 pagineExercise Set 11Mr MemeNessuna valutazione finora
- Mit RotationDocumento7 pagineMit RotationKrrish BhallaNessuna valutazione finora
- Assignment#1Documento4 pagineAssignment#1Anoosha ArshadNessuna valutazione finora
- Center of Mass, LM, CollisionsDocumento11 pagineCenter of Mass, LM, CollisionsChinmay MandaveNessuna valutazione finora
- Problems of The 53Rd-25Th International-Rudolf Ortvay Problem Solving Contest in Physics 17 February-27 February 2023Documento13 pagineProblems of The 53Rd-25Th International-Rudolf Ortvay Problem Solving Contest in Physics 17 February-27 February 2023Francisco LuNessuna valutazione finora
- 1053 Exam 3Documento12 pagine1053 Exam 3cortesamNessuna valutazione finora
- Rigid Body Dynamics ExplainedDocumento27 pagineRigid Body Dynamics ExplainedB AbhinavNessuna valutazione finora
- Static EquilibriumDocumento18 pagineStatic EquilibriumMustafa BasitNessuna valutazione finora
- Problem Solving Circular Motion Dynamics: Challenge Problems Problem 1: Double Star SystemDocumento10 pagineProblem Solving Circular Motion Dynamics: Challenge Problems Problem 1: Double Star SystemVongNessuna valutazione finora
- Problem Set MechanicsDocumento2 pagineProblem Set MechanicsPrateek KumarNessuna valutazione finora
- AJC TutorialDocumento4 pagineAJC TutorialYong Ming HengNessuna valutazione finora
- ProblemsDocumento9 pagineProblemsSiddhartha MoralesNessuna valutazione finora
- Last Name: - : University of Waterloo Final Examination Fall 2014Documento13 pagineLast Name: - : University of Waterloo Final Examination Fall 2014YuChenQianNessuna valutazione finora
- PhysicsLabI Exp5Documento9 paginePhysicsLabI Exp5Jessica RossNessuna valutazione finora
- Problem Set 6Documento4 pagineProblem Set 6sagarnitishpirtheeNessuna valutazione finora
- Draw A Picture!: You May Treat The Child As A Point ParticleDocumento24 pagineDraw A Picture!: You May Treat The Child As A Point Particlebat.laughNessuna valutazione finora
- Advanced HandoutDocumento8 pagineAdvanced Handoutparthkalra1981Nessuna valutazione finora
- Practice FinalDocumento4 paginePractice FinalChennaiSuperkingsNessuna valutazione finora
- Phys101 8 hw5Documento1 paginaPhys101 8 hw5mirsad türkerNessuna valutazione finora
- Classical 093Documento33 pagineClassical 093Julian David Henao EscobarNessuna valutazione finora
- Physics 1 Recitation 7 RotationDocumento10 paginePhysics 1 Recitation 7 RotationAlexNessuna valutazione finora
- CPP1 RotationaldynamicsDocumento14 pagineCPP1 RotationaldynamicsBNessuna valutazione finora
- Er. Shravan Katiyar: Physics For Iit-Jee (Main & Advanced)Documento4 pagineEr. Shravan Katiyar: Physics For Iit-Jee (Main & Advanced)ShreyanshNessuna valutazione finora
- Assignment Sheet - 23 - (Rotation-2) - (AM) - Date - 11.8.2008Documento10 pagineAssignment Sheet - 23 - (Rotation-2) - (AM) - Date - 11.8.2008Pranjal SinghalNessuna valutazione finora
- Chapter Questions Newton S LawsDocumento8 pagineChapter Questions Newton S LawsJunLi CaiNessuna valutazione finora
- Indonesian Regional Physics Olympiad 2022 1Documento4 pagineIndonesian Regional Physics Olympiad 2022 1Marcus PoonNessuna valutazione finora
- Physics Practice Midterm 1Documento11 paginePhysics Practice Midterm 1ahkeeraNessuna valutazione finora
- IIT-JEE Download Sample Question PapersDocumento3 pagineIIT-JEE Download Sample Question PapersSayan Kumar KhanNessuna valutazione finora
- Colombian Olympiad PhysicsDocumento120 pagineColombian Olympiad Physicssanits591100% (8)
- Smoothings of Piecewise Linear Manifolds. (AM-80), Volume 80Da EverandSmoothings of Piecewise Linear Manifolds. (AM-80), Volume 80Valutazione: 5 su 5 stelle5/5 (1)
- SPP-2010-103 Approximate Expressions for Revival TimesDocumento4 pagineSPP-2010-103 Approximate Expressions for Revival TimesPerry EsguerraNessuna valutazione finora
- Evolution of A Spin-1/2 System Subject To Pulsed Magnetic FieldsDocumento4 pagineEvolution of A Spin-1/2 System Subject To Pulsed Magnetic FieldsPerry EsguerraNessuna valutazione finora
- A. Two Spheres: Physics Questions 6Documento1 paginaA. Two Spheres: Physics Questions 6Perry EsguerraNessuna valutazione finora
- Physics Questions 3Documento1 paginaPhysics Questions 3Perry EsguerraNessuna valutazione finora
- Fractional Damped-Coupled Oscillator of Two Identical MassesDocumento4 pagineFractional Damped-Coupled Oscillator of Two Identical MassesPerry EsguerraNessuna valutazione finora
- Physics Questions 1Documento1 paginaPhysics Questions 1Perry EsguerraNessuna valutazione finora
- Mechanics ProblemsDocumento1 paginaMechanics ProblemsPerry EsguerraNessuna valutazione finora
- Persistent 2D Random Walk With Geometrically Shrinking Steps With Four DirectionsDocumento5 paginePersistent 2D Random Walk With Geometrically Shrinking Steps With Four DirectionsPerry EsguerraNessuna valutazione finora
- SPP-2010-3B-05 Agapito Et AlDocumento3 pagineSPP-2010-3B-05 Agapito Et AlPerry EsguerraNessuna valutazione finora
- Electricity and Magnetism ProblemsDocumento1 paginaElectricity and Magnetism ProblemsPerry EsguerraNessuna valutazione finora
- Physics shock wave and increasing gravity questionsDocumento1 paginaPhysics shock wave and increasing gravity questionsPerry EsguerraNessuna valutazione finora
- Physics Questions 5Documento1 paginaPhysics Questions 5Perry EsguerraNessuna valutazione finora
- Mechanics Problem Set - 20Documento1 paginaMechanics Problem Set - 20Perry EsguerraNessuna valutazione finora
- Physics Questions 2Documento1 paginaPhysics Questions 2Perry EsguerraNessuna valutazione finora
- Mechanics Problem Set - 19Documento1 paginaMechanics Problem Set - 19Perry EsguerraNessuna valutazione finora
- Particle Physics Exercise 1Documento1 paginaParticle Physics Exercise 1Perry EsguerraNessuna valutazione finora
- Mechanics Problem Set - 18Documento1 paginaMechanics Problem Set - 18Perry EsguerraNessuna valutazione finora
- Particle Physics Exercise 2Documento1 paginaParticle Physics Exercise 2Perry EsguerraNessuna valutazione finora
- Mechanics Problem Set - 17Documento1 paginaMechanics Problem Set - 17Perry EsguerraNessuna valutazione finora
- Mechanics Problem Set - 17Documento1 paginaMechanics Problem Set - 17Perry EsguerraNessuna valutazione finora
- Mechanics Problem Set - 13Documento1 paginaMechanics Problem Set - 13Perry EsguerraNessuna valutazione finora
- Mechanics Set 16 Constants of MotionDocumento1 paginaMechanics Set 16 Constants of MotionPerry EsguerraNessuna valutazione finora
- Circular Orbits Central Forces Mechanics ProblemsDocumento1 paginaCircular Orbits Central Forces Mechanics ProblemsPerry EsguerraNessuna valutazione finora
- Mechanics Problem Set - 15Documento1 paginaMechanics Problem Set - 15Perry EsguerraNessuna valutazione finora
- Mechanics Problem Set - 12Documento1 paginaMechanics Problem Set - 12Perry EsguerraNessuna valutazione finora
- Mechanics Problem Set - 9Documento1 paginaMechanics Problem Set - 9Perry EsguerraNessuna valutazione finora
- Mechanics Problem Set - 14Documento1 paginaMechanics Problem Set - 14Perry EsguerraNessuna valutazione finora
- Circular Orbits Central Forces Mechanics ProblemsDocumento1 paginaCircular Orbits Central Forces Mechanics ProblemsPerry EsguerraNessuna valutazione finora
- Mechanics Problem Set - 10Documento1 paginaMechanics Problem Set - 10Perry EsguerraNessuna valutazione finora
- Mechanics Problem Set - 9Documento1 paginaMechanics Problem Set - 9Perry EsguerraNessuna valutazione finora
- Lightwave Maya 3D TutorialsDocumento8 pagineLightwave Maya 3D TutorialsrandfranNessuna valutazione finora
- CG Module 1 NotesDocumento64 pagineCG Module 1 Notesmanjot singhNessuna valutazione finora
- Nikola Tesla Was Murdered by Otto Skorzeny.Documento12 pagineNikola Tesla Was Murdered by Otto Skorzeny.Jason Lamb50% (2)
- Gauss Contest: Grade 8Documento4 pagineGauss Contest: Grade 8peter100% (1)
- PDFViewer - JSP 3Documento46 paginePDFViewer - JSP 3Kartik ChaudharyNessuna valutazione finora
- CP 343-1Documento23 pagineCP 343-1Yahya AdamNessuna valutazione finora
- IEQ CompleteDocumento19 pagineIEQ Completeharshal patilNessuna valutazione finora
- Daftar Spesifikasi Teknis Pembangunan Gedung Kantor BPN BojonegoroDocumento6 pagineDaftar Spesifikasi Teknis Pembangunan Gedung Kantor BPN BojonegoroIrwin DarmansyahNessuna valutazione finora
- Flexibility Personal ProjectDocumento34 pagineFlexibility Personal Projectapi-267428952100% (1)
- Private Schools Provide Better EducationDocumento2 paginePrivate Schools Provide Better EducationcitraNessuna valutazione finora
- Lesson 2 Socio Anthropological View of The SelfDocumento12 pagineLesson 2 Socio Anthropological View of The SelfAilyn RamosNessuna valutazione finora
- CIRC 314-AN 178 INP EN EDENPROD 195309 v1Documento34 pagineCIRC 314-AN 178 INP EN EDENPROD 195309 v1xloriki_100% (1)
- 11bg USB AdapterDocumento30 pagine11bg USB AdapterruddyhackerNessuna valutazione finora
- Fundermax Exterior Technic 2011gb WebDocumento88 pagineFundermax Exterior Technic 2011gb WebarchpavlovicNessuna valutazione finora
- Oecumenius’ Exegetical Method in His Commentary on the RevelationDocumento10 pagineOecumenius’ Exegetical Method in His Commentary on the RevelationMichał WojciechowskiNessuna valutazione finora
- Acuity Assessment in Obstetrical TriageDocumento9 pagineAcuity Assessment in Obstetrical TriageFikriNessuna valutazione finora
- Casio AP-80R Service ManualDocumento41 pagineCasio AP-80R Service ManualEngkiong Go100% (1)
- LSUBL6432ADocumento4 pagineLSUBL6432ATotoxaHCNessuna valutazione finora
- Juan Martin Garcia System Dynamics ExercisesDocumento294 pagineJuan Martin Garcia System Dynamics ExercisesxumucleNessuna valutazione finora
- Sibuyan Island ResiliencyDocumento12 pagineSibuyan Island ResiliencyEndangeredSpeciesNessuna valutazione finora
- Philippines' Legal Basis for Claims in South China SeaDocumento38 paginePhilippines' Legal Basis for Claims in South China SeaGeeNessuna valutazione finora
- Fraktur Dentoalevolar (Yayun)Documento22 pagineFraktur Dentoalevolar (Yayun)Gea RahmatNessuna valutazione finora
- Chemistry Implementation: Name: Rasheed Campbell School: Kingston College Candidate #.: Centre #: 100057Documento12 pagineChemistry Implementation: Name: Rasheed Campbell School: Kingston College Candidate #.: Centre #: 100057john brownNessuna valutazione finora
- TILE QUOTEDocumento3 pagineTILE QUOTEHarsh SathvaraNessuna valutazione finora
- 2019 Course CatalogDocumento31 pagine2019 Course CatalogDeepen SharmaNessuna valutazione finora
- The Impact of Employees' Commitment Towards Food Safety at Ayana Resort, BaliDocumento58 pagineThe Impact of Employees' Commitment Towards Food Safety at Ayana Resort, Balirachelle agathaNessuna valutazione finora
- Nickel-Metal Hydride Battery Safety Data SheetDocumento8 pagineNickel-Metal Hydride Battery Safety Data SheetYeong WheeNessuna valutazione finora
- O2 Orthodontic Lab Catalog PDFDocumento20 pagineO2 Orthodontic Lab Catalog PDFplayer osamaNessuna valutazione finora
- Elements of ClimateDocumento18 pagineElements of Climateእኔ እስጥፍNessuna valutazione finora
- Ultrasonic Weld Examination ProcedureDocumento16 pagineUltrasonic Weld Examination ProcedureramalingamNessuna valutazione finora