Documenti di Didattica
Documenti di Professioni
Documenti di Cultura
MECHANICS (ME10001) : Aluminum
Caricato da
RahulTitolo originale
Copyright
Formati disponibili
Condividi questo documento
Condividi o incorpora il documento
Hai trovato utile questo documento?
Questo contenuto è inappropriato?
Segnala questo documentoCopyright:
Formati disponibili
MECHANICS (ME10001) : Aluminum
Caricato da
RahulCopyright:
Formati disponibili
MECHANICS (ME10001)
Tutorial 9: Torsion
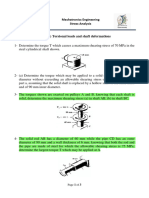
1. An aluminum tube of 40 mm inner diameter and 50
mm outer diameter is rigidly fixed to an aluminum
circular flange. The assembly is fixed to a wall by
two steel bolts of 10 mm diameter. The allowable
shear stress and bearing stress of steel are 45 MPa
and 90 MPa respectively. For aluminum, the
allowable shear stress and bearing stress are 30MPa
and 60 MPa, respectively. (a) Determine the
maximum torsion T the system can withstand and
(b) the angle of twist of the tube for the T computed
in part (a). GAluminum =28 GPa. [(a) 282.74 N-m (b)
0.32o ]
2. What must be the length of a 5 mm diameter aluminum wire so that it could be twisted
through one complete revolution without exceeding a shear stress of 42 MPa. Given
GAluminum =27 GPa. [10.1 m]
3. Knowing that each portion of the shaft AD consists
of a solid circular rod, determine (a) the portion of
the shaft in which the maximum shearing stress
occurs, (b) the magnitude of that stress. [(a) Shaft
BC (b) 57.3 MPa]
4. A solid aluminum shaft of 50 mm diameter is to be replaced by a hollow steel shaft of 50
mm outside diameter. Both the shafts are 1000 mm in length and should undergo same
angle of twist by the application of 200 N-m torque at the ends. Shear modulus of
elasticity for steel is three times that of the aluminum. Find the dimensions of the steel
shaft. [45.18 mm]
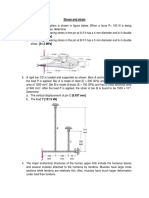
5. Two gears are attached to two 50 mm diameter
steel shafts. The gear at B has a 200 mm pitch
diameter; the gear at C, a 400 mm diameter pitch
diameter. Through what angle will end A turn if a
torque of 560 N-m is applied at A and end D of the
second shaft is prevented from rotating? Given G =
84 MPa [0.195 rad]
6. The preliminary design of a large shaft connecting a
motor to a generator calls for the use of hollow shaft with
inner and outer diameter of 100 mm and 150 mm,
respectively. Knowing that the allowable shearing stress
is 85 MPa, determine the maximum torque which may be
transmitted (a) by the shaft as designed, (b) by a solid
shaft of the same weight, (c) by a hollow shaft of same
weight and of 200 mm outside diameter. [(a) 45.2 kN-m
(b) 23.3 kN-m (c) 70.4 kN-m]
7. The torque shown are exerted on
pulleys B, C and D. Knowing that
the entire shaft is made of steel (G
= 27 GPa), determine the angle of
twist between (a) C and B, (b) D
and B. [(a) 8.54o (b) 2.11o]
8. Two solid steel shafts, each of 30 mm
diameter, are connected by gear shown.
Knowing that G = 77 GPa, determine the angle
through which end A rotates when a 200 N-m
torque T is applied at A. [A = 3.79o]
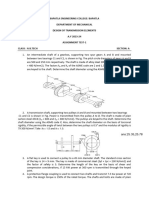
9. The design specifications of 1.2 m long solid circular transmission shaft require that the
angle of twist of the shaft not exceed 4 when a torque of 680 N-m is applied. Determine
the required diameter of the shaft, knowing that the shaft is made of a steel with an
allowable shearing stress of 83 MPa and a modulus of rigidity of 77 GPa. [d = 35.2 mm]
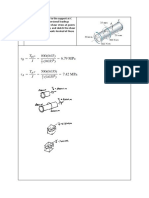
10. Two 5 mm thick cylinders AC and BD are
glued together at the overlapping portion BC.
(a) Determine the maximum torque the
system can withstand, without exceeding the
shear stress limit of 5 MPa at the glued joint.
(b) Assuming no slippage at the glued joint, at
this torque, what would be the angle of twist
of end A with respect to B? G = 80GPa for
the cylinder materials. Dimensions are in mm.
[(a) T = 785.4 N-m (b) AB = 0.256o]
11. The composite shaft shown is to be twisted by
applying the torques shown. Knowing that the
modulus of rigidity is 77 GPa for the steel and 39 GPa
for the brass, determine the largest angle of twist of
end B relative to end A if the following allowable
stresses are not to be exceeded steel = 100 MPa and
brass = 55 MPa. [all = 7.27o]
12. A 120 mm diameter solid steel shaft transmits 400 kW at 2 Hz. (a) Determine the
maximum shear stress, (b) what would be the required shaft diameter to operate at 4 Hz.
At the same maximum stress? [(a) 93.72 MPa (b) 95.24 mm]
Potrebbero piacerti anche
- Strength of Materials Chapter 3 ProblemsDocumento3 pagineStrength of Materials Chapter 3 ProblemsNEIVER ALEVIS CASTRO JULIONessuna valutazione finora
- Sheet 4 Torsional Loads and Shaft Deformations - MechatronicsDocumento3 pagineSheet 4 Torsional Loads and Shaft Deformations - MechatronicsAhmed AlaaNessuna valutazione finora
- Civl 2120 Ch3 QsDocumento2 pagineCivl 2120 Ch3 QsTina ChenNessuna valutazione finora
- Department of Civil Engineering CEA 1120 - Tutorial Sheet # 9 TorsionDocumento2 pagineDepartment of Civil Engineering CEA 1120 - Tutorial Sheet # 9 TorsionSijuKalladaNessuna valutazione finora
- Torque (Examples and Seatwork)Documento4 pagineTorque (Examples and Seatwork)Laurence PaulNessuna valutazione finora
- Problemas de Concentracion de EsfuerzosDocumento7 pagineProblemas de Concentracion de EsfuerzosJonathan MendozaNessuna valutazione finora
- MDB Prob Set TorsionDocumento2 pagineMDB Prob Set TorsionFerrolinoLouieNessuna valutazione finora
- STL203SDocumento6 pagineSTL203SClaudioNessuna valutazione finora
- Thapar Institute Torsion TutorialDocumento1 paginaThapar Institute Torsion TutorialSimranjeet SinghNessuna valutazione finora
- Tutorial 4Documento6 pagineTutorial 4Ysgn MysgnNessuna valutazione finora
- Assignment QuestionDocumento15 pagineAssignment QuestionPratik WalimbeNessuna valutazione finora
- HW 6Documento4 pagineHW 6Dan RiversNessuna valutazione finora
- SOM AssignmentDocumento6 pagineSOM Assignmentshreyas shahNessuna valutazione finora
- BMCS 2323 – MEKANIK PEPEJAL I TUTORIAL 3A: ELASTIC TORSION & ANGLE OF TWISTDocumento3 pagineBMCS 2323 – MEKANIK PEPEJAL I TUTORIAL 3A: ELASTIC TORSION & ANGLE OF TWISTW. M. HaziqNessuna valutazione finora
- Template Mechanics 3Documento10 pagineTemplate Mechanics 3Gerald B. APOSTOLNessuna valutazione finora
- torsionDocumento26 paginetorsionkidowapoNessuna valutazione finora
- Ce234 Topic 06-07Documento31 pagineCe234 Topic 06-07Nicholas Bonn SingNessuna valutazione finora
- Dme Question BankDocumento4 pagineDme Question BankRavi Patil100% (1)
- 212-Chpt 5Documento8 pagine212-Chpt 5zainabcomNessuna valutazione finora
- QB Unit-3,4,5Documento7 pagineQB Unit-3,4,5Agranshu BhardwajNessuna valutazione finora
- 12ME5DCDM2Documento3 pagine12ME5DCDM2Abhyudaya SinghNessuna valutazione finora
- Me 2303 - Design of Machine Elements December 2010Documento3 pagineMe 2303 - Design of Machine Elements December 2010Ilaya Perumal K0% (1)
- Prob SheetDocumento20 pagineProb SheetAditya ShuklaNessuna valutazione finora
- 4363 111 Machine Design IDocumento6 pagine4363 111 Machine Design Iyogesh_b_k100% (2)
- ME 331 - DESIGN OF MACHINE ELEMENTS EXAMDocumento5 pagineME 331 - DESIGN OF MACHINE ELEMENTS EXAMarumugam_rNessuna valutazione finora
- PMD ModelDocumento8 paginePMD ModelDamodara SatyaDeva MadhukarNessuna valutazione finora
- GATE - IES QuestionsDocumento4 pagineGATE - IES QuestionsMahesh Chandrabhan ShindeNessuna valutazione finora
- Previous Exam QuestionsDocumento8 paginePrevious Exam QuestionssallyreffatNessuna valutazione finora
- ShaftsDocumento1 paginaShaftsNhlaka ZuluNessuna valutazione finora
- DME Assignment 1Documento2 pagineDME Assignment 1sumikannuNessuna valutazione finora
- IIT BOMBAY ME201 SOLID MECHANICS Tutorial 3Documento3 pagineIIT BOMBAY ME201 SOLID MECHANICS Tutorial 3Kunal ShroteNessuna valutazione finora
- Unit 4 AssignmentsDocumento5 pagineUnit 4 AssignmentsbattuarunNessuna valutazione finora
- Dte Assignment-1 A.Y 23-24Documento2 pagineDte Assignment-1 A.Y 23-24asfvkjsv asgbaegbNessuna valutazione finora
- Common Subject Code: Shivaji University, KolhapurDocumento10 pagineCommon Subject Code: Shivaji University, Kolhapursatyamchgl2010Nessuna valutazione finora
- 16mu315 - Machine Design Question Bank: Ut Yt B TDocumento3 pagine16mu315 - Machine Design Question Bank: Ut Yt B THarishNessuna valutazione finora
- Problem Set 4Documento5 pagineProblem Set 4Jobelle SDNessuna valutazione finora
- Question Bank - DMEDocumento6 pagineQuestion Bank - DMEBdhdhshNessuna valutazione finora
- B.Tech Exam Design of Machine Members QuestionsDocumento8 pagineB.Tech Exam Design of Machine Members Questionsprk74Nessuna valutazione finora
- DME 1 Question BankDocumento5 pagineDME 1 Question BankRahul YedduNessuna valutazione finora
- Mechanics of Solid I Torsion Chapter SummaryDocumento42 pagineMechanics of Solid I Torsion Chapter SummaryFuaad Abdirizak ElmiNessuna valutazione finora
- BMS College of Engineering, Bangalore-560019: January 2015 Semester End Make Up ExaminationsDocumento2 pagineBMS College of Engineering, Bangalore-560019: January 2015 Semester End Make Up ExaminationsAbhyudaya SinghNessuna valutazione finora
- Mechanics of Solids: Torsion Chapter QuestionsDocumento1 paginaMechanics of Solids: Torsion Chapter QuestionsMelvin Shady PereiraNessuna valutazione finora
- Screws, Fasteners, and Nonpermanent Joint DesignDocumento5 pagineScrews, Fasteners, and Nonpermanent Joint DesignMohamed AshrafNessuna valutazione finora
- Design strength of steel connectionsDocumento9 pagineDesign strength of steel connectionsCrisnico PeligrinoNessuna valutazione finora
- TUK University Exams June 2016 Mechanical Engineering Technology Advanced Machine DesignDocumento8 pagineTUK University Exams June 2016 Mechanical Engineering Technology Advanced Machine DesignCharles OndiekiNessuna valutazione finora
- 07a6ec05 Designofmachinemembers IIDocumento11 pagine07a6ec05 Designofmachinemembers IIzahid_polyNessuna valutazione finora
- Final Design Work SheetDocumento7 pagineFinal Design Work SheetKINDUNessuna valutazione finora
- DME - Assignment - IDocumento3 pagineDME - Assignment - ISathis KumarNessuna valutazione finora
- R7310305-Design of Machine Members-I2Documento4 pagineR7310305-Design of Machine Members-I2slv_prasaad100% (1)
- 0326 Me 2303 Design of Machine ElementsDocumento3 pagine0326 Me 2303 Design of Machine ElementsSaravanan MathiNessuna valutazione finora
- Snist Dom Previous PaperDocumento9 pagineSnist Dom Previous PaperKapil Siddhant DevulapalliNessuna valutazione finora
- Dme Home Assignment 2019-20Documento4 pagineDme Home Assignment 2019-20VenkateshNessuna valutazione finora
- ME-311 Cotter and Coupling - 2018Documento2 pagineME-311 Cotter and Coupling - 2018VishnuNessuna valutazione finora
- Assignment 1Documento4 pagineAssignment 1sonawanepmsNessuna valutazione finora
- Assignment 2 (Solution)Documento9 pagineAssignment 2 (Solution)Nurul Amira AmiruddinNessuna valutazione finora
- Strength of Materials 4th Ed by Ferdinand L Singer Andrew Pytel Www07MettkDocumento21 pagineStrength of Materials 4th Ed by Ferdinand L Singer Andrew Pytel Www07Mettkvjereme100% (3)
- Composite Structures of Steel and Concrete: Beams, Slabs, Columns and Frames for BuildingsDa EverandComposite Structures of Steel and Concrete: Beams, Slabs, Columns and Frames for BuildingsNessuna valutazione finora
- CB and Transducer Where Do I ConnectDocumento20 pagineCB and Transducer Where Do I ConnectAries dNessuna valutazione finora
- .Uateacherhomeworkshow Fileid B1+Preliminary+for+Schools+PRACTICE+TESTS+2020 PDFDocumento204 pagine.Uateacherhomeworkshow Fileid B1+Preliminary+for+Schools+PRACTICE+TESTS+2020 PDFAlexa YNessuna valutazione finora
- BT Chuong1Documento14 pagineBT Chuong1Chu Thái AnhNessuna valutazione finora
- Geotechnical Report SummaryDocumento35 pagineGeotechnical Report SummaryEr navneet jassiNessuna valutazione finora
- Partial Loading Optimal Control - Steam Turbine EffDocumento6 paginePartial Loading Optimal Control - Steam Turbine EffLTE002Nessuna valutazione finora
- Effect of ComEffect of Compression Ratio On Ground Grid Designpression Ratio On Ground Grid DesignDocumento6 pagineEffect of ComEffect of Compression Ratio On Ground Grid Designpression Ratio On Ground Grid Designnitinatp1978Nessuna valutazione finora
- Modave2005 PDFDocumento298 pagineModave2005 PDFpolickNessuna valutazione finora
- MIL-DTL-5541 Rev F - Part5Documento1 paginaMIL-DTL-5541 Rev F - Part5David WongNessuna valutazione finora
- Spring RatingDocumento6 pagineSpring Ratingbrowar444Nessuna valutazione finora
- PHYS 2425 Exp 1 ManualDocumento11 paginePHYS 2425 Exp 1 ManualSagar ShahiNessuna valutazione finora
- How Newton Discovered Gravity's Inverse Square RuleDocumento19 pagineHow Newton Discovered Gravity's Inverse Square RuleAnnNessuna valutazione finora
- Using ACF and PACF To Select MA (Q) or AR (P) ModelsDocumento3 pagineUsing ACF and PACF To Select MA (Q) or AR (P) ModelsbboyvnNessuna valutazione finora
- Exp 4 BiochemDocumento5 pagineExp 4 BiochemLê ThắngNessuna valutazione finora
- Design and Control of Hybrid Multi-Stage Inverter For AC DrivesDocumento219 pagineDesign and Control of Hybrid Multi-Stage Inverter For AC DrivesMd Didarul IslamNessuna valutazione finora
- ROHR2 Program System for Static and Dynamic Piping AnalysisDocumento33 pagineROHR2 Program System for Static and Dynamic Piping Analysisaddai262Nessuna valutazione finora
- Determination of Power System Voltage Stability Using Modal AnalysisDocumento7 pagineDetermination of Power System Voltage Stability Using Modal Analysiswvargas926Nessuna valutazione finora
- 2 English Paper2Documento7 pagine2 English Paper2Sri HarshaNessuna valutazione finora
- 18 N 40 BDocumento8 pagine18 N 40 BEudis HernandezNessuna valutazione finora
- Dysfunctional Performance MeasurementDocumento7 pagineDysfunctional Performance Measurement321daiqiNessuna valutazione finora
- Safety Devices ENGDocumento22 pagineSafety Devices ENGshank100Nessuna valutazione finora
- QbasQbase Radiology3 Croppede Radiology3 CroppedDocumento175 pagineQbasQbase Radiology3 Croppede Radiology3 CroppedZubair Lone100% (4)
- Year 8 Revision Paper (1) 2023 For YouDocumento13 pagineYear 8 Revision Paper (1) 2023 For Youa sohanaNessuna valutazione finora
- Introduction To Reliability. WARWICK MANUFACTURING GROUPDocumento37 pagineIntroduction To Reliability. WARWICK MANUFACTURING GROUPAlexis Lopez100% (2)
- LX200 Classic ManualDocumento64 pagineLX200 Classic ManualKeri Sawyer100% (1)
- ES223 - LECTURE - 06 - Equilibrium of A Rigid BodyDocumento15 pagineES223 - LECTURE - 06 - Equilibrium of A Rigid BodyserhatNessuna valutazione finora
- Physics Investigatory ProjectDocumento18 paginePhysics Investigatory ProjectPrakruti modi100% (1)
- 4.forces and Laws of MotionExercise PDFDocumento88 pagine4.forces and Laws of MotionExercise PDFPriyanshu RajNessuna valutazione finora
- Generalization of Smoluchowski's Diffusion EquationDocumento4 pagineGeneralization of Smoluchowski's Diffusion EquationDanieleRinaldoNessuna valutazione finora
- Sensorless PMSMDocumento35 pagineSensorless PMSMShirosh AyeshmanthaNessuna valutazione finora
- Opel Astra CodesDocumento17 pagineOpel Astra CodesIvan RimacNessuna valutazione finora