Documenti di Didattica
Documenti di Professioni
Documenti di Cultura
Ketoasidosis Diabetikum
Caricato da
Dyah AyuTitolo originale
Copyright
Formati disponibili
Condividi questo documento
Condividi o incorpora il documento
Hai trovato utile questo documento?
Questo contenuto è inappropriato?
Segnala questo documentoCopyright:
Formati disponibili
Ketoasidosis Diabetikum
Caricato da
Dyah AyuCopyright:
Formati disponibili
Ketoasidosis diabetikum
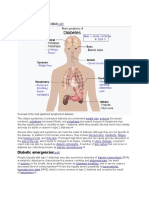
Definisi
Diabetic ketoacidosis (DKA) is an acute, major, life-threatening complication of diabetes. DKA mainly
occurs in patients with type 1 diabetes, but it is not uncommon in some patients with type 2 diabetes
(most likely latent autoimmune diabetes of adults [LADA] or Flatbush diabetes).
Ketoasidosis diabetes adalah keadaan akut dan komplikasi yang mengancam nyawa pada penderita
diabetes. Umumnya DKA terjadi pada pasien diabetes tipe 1, namun bukan hal yang jarang KAD
terjadi pada pasien dengan diabetes tipe 2.
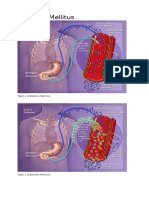
DKA is a state of absolute or relative insulin deficiency aggravated by ensuing hyperglycemia,
dehydration, and acidosis-producing derangements in intermediary metabolism. The most common
causes are underlying infection, disruption of insulin treatment, and new onset of diabetes. (See
Etiology.)
KAD adalah suatu keadaan
DKA is defined clinically as an acute state of severe uncontrolled diabetes associated with
ketoacidosis that requires emergency treatment with insulin and intravenous fluids. (See Treatment
and Management and Medications.)
Biochemically, DKA is defined as an increase in the serum concentration of ketones greater than 5
mEq/L, a blood glucose level greater than 250 mg/dL (although it is usually much higher), and a blood
(usually arterial) pH less than 7.3. Ketonemia and ketonuria are characteristic, as is a serum
bicarbonate level of 18 mEq/L or less (less than 5 mEq/L is indicative of severe DKA). These
biochemical changes are frequently associated with increased anion gap, increased serum osmolarity
and increased serum uric acid
Potrebbero piacerti anche
- Diabetic Ketoacidosis, A Simple Guide To The Condition, Diagnosis, Treatment And Related ConditionsDa EverandDiabetic Ketoacidosis, A Simple Guide To The Condition, Diagnosis, Treatment And Related ConditionsNessuna valutazione finora
- Types of DementiaDocumento6 pagineTypes of DementiaDyah Ayu100% (1)
- Type 2 Diabetes MellitusDocumento24 pagineType 2 Diabetes Mellitusdr. M.F. Romdhoni100% (1)
- Diabetic Ketoacidosis PDFDocumento11 pagineDiabetic Ketoacidosis PDFCsr ArsNessuna valutazione finora
- LuiDocumento1 paginaLuiMary LyonNessuna valutazione finora
- Oajbs Id 000530Documento8 pagineOajbs Id 000530Aldy RanggaNessuna valutazione finora
- Complicaciones en DiabetesDocumento10 pagineComplicaciones en DiabetesJhaann Franco UPNessuna valutazione finora
- Cad BMJ 2013Documento6 pagineCad BMJ 2013kathy1905Nessuna valutazione finora
- Diabetic KetoacidosisDocumento7 pagineDiabetic KetoacidosisetengNessuna valutazione finora
- DKA, EDKA and Lactic AcidosisDocumento3 pagineDKA, EDKA and Lactic AcidosisAvinash BeezadhurNessuna valutazione finora
- Clinical Review: Diabetic Ketoacidosis in AdultsDocumento8 pagineClinical Review: Diabetic Ketoacidosis in AdultscitrahmahNessuna valutazione finora
- Dysfunction of The Endocrine Pancreas:: Diabetes MellitusDocumento27 pagineDysfunction of The Endocrine Pancreas:: Diabetes Mellitushasan ismaelNessuna valutazione finora
- AJGP 05 2019 Focus Willix Hyperglycaemic Presentations WEBDocumento5 pagineAJGP 05 2019 Focus Willix Hyperglycaemic Presentations WEBmystatNessuna valutazione finora
- Euglycemic Diabetic KetoacidosisDocumento6 pagineEuglycemic Diabetic KetoacidosisMuhammad BilalNessuna valutazione finora
- New Microsoft Word DocumentDocumento6 pagineNew Microsoft Word DocumentKawther El-FikyNessuna valutazione finora
- Diabetic KetoacidosisDocumento85 pagineDiabetic Ketoacidosismohamed mowafeyNessuna valutazione finora
- Askep KAD RevisiDocumento27 pagineAskep KAD RevisiEcho PeweNessuna valutazione finora
- Laboratory FindingsDocumento22 pagineLaboratory FindingseffiniasiregarNessuna valutazione finora
- Management of Diabetic Ketoacidosis in Adults - A Narrative ReviewDocumento12 pagineManagement of Diabetic Ketoacidosis in Adults - A Narrative Reviewghr9cjy5npNessuna valutazione finora
- 194-Article Text-600-1-10-20200829Documento5 pagine194-Article Text-600-1-10-20200829arifcetungtakNessuna valutazione finora
- Dka 1Documento5 pagineDka 1Terlalu TampanNessuna valutazione finora
- Diabetes - Used As Example OnlyDocumento15 pagineDiabetes - Used As Example OnlyKiana DouglasNessuna valutazione finora
- Oxidative Stress and DiabetesDocumento8 pagineOxidative Stress and DiabetesSAVA ADINANessuna valutazione finora
- Diabetes Mellitus DiagnosisDocumento10 pagineDiabetes Mellitus DiagnosisIsmail Hossain SujanNessuna valutazione finora
- Diabetes MellitusDocumento13 pagineDiabetes Mellitusdreneavalentinstefan100% (1)
- Cetoacidosis y Edo Hiperglicemico HiperO 2013Documento19 pagineCetoacidosis y Edo Hiperglicemico HiperO 2013RosolinaNessuna valutazione finora
- Hyperglycemic Crise1Documento146 pagineHyperglycemic Crise1Vincent ReyesNessuna valutazione finora
- Acute. KetoacidosisdocxDocumento12 pagineAcute. KetoacidosisdocxShara SampangNessuna valutazione finora
- Diabetic KetoacidosisDocumento4 pagineDiabetic KetoacidosispreetyNessuna valutazione finora
- Diabetes Mellitus Is A Group of Metabolic Diseases Characterized byDocumento67 pagineDiabetes Mellitus Is A Group of Metabolic Diseases Characterized byBivek TimalsinaNessuna valutazione finora
- 06.disorder of Carbohydrate MetabolismDocumento47 pagine06.disorder of Carbohydrate MetabolismRizka NizarNessuna valutazione finora
- Type 1 Diabetes Mellitus: PathoDocumento6 pagineType 1 Diabetes Mellitus: PathoMary JoyceNessuna valutazione finora
- Prenatal Genetic Testing For Monogenic Diabetes Due To Glucokinase Deficiency (December 2023) What's NewDocumento33 paginePrenatal Genetic Testing For Monogenic Diabetes Due To Glucokinase Deficiency (December 2023) What's NewAntenehNessuna valutazione finora
- A Review of The Hybrid Description of Diabetes MellitusDocumento4 pagineA Review of The Hybrid Description of Diabetes MellitusIJRDPM JOURNALNessuna valutazione finora
- Euglycemic KetoacidosisDocumento7 pagineEuglycemic KetoacidosisMuhammad BilalNessuna valutazione finora
- Diabetes Emergencia Umpierrez 2016Documento11 pagineDiabetes Emergencia Umpierrez 2016Nathalie GandoNessuna valutazione finora
- WJD 12 514Documento11 pagineWJD 12 514josimarNessuna valutazione finora
- Aiims Dka ProtocolDocumento9 pagineAiims Dka Protocolbbboghara100% (1)
- Emergencies in Diabetes e Diabetic Ketoacidosis and Hyperosmolar Hyperglycaemic StateDocumento4 pagineEmergencies in Diabetes e Diabetic Ketoacidosis and Hyperosmolar Hyperglycaemic StateUmmi LatifahNessuna valutazione finora
- Tatalaksana Kad 1Documento7 pagineTatalaksana Kad 1Nurul Kamilah SadliNessuna valutazione finora
- IJPRDocumento6 pagineIJPRUlvi DitasariNessuna valutazione finora
- Ketoasidosis DiabetikDocumento6 pagineKetoasidosis DiabetikSahril RamadhanNessuna valutazione finora
- Diagnosis and Management HiperglikemiDocumento13 pagineDiagnosis and Management HiperglikemiTasya SylviaNessuna valutazione finora
- Diabetes MellitusDocumento29 pagineDiabetes MellitusSyed MaazNessuna valutazione finora
- Management of Diabetic Ketoacidosis in The Emergency DepartmentDocumento7 pagineManagement of Diabetic Ketoacidosis in The Emergency DepartmentnandarNessuna valutazione finora
- Pediatric KADDocumento6 paginePediatric KADBrotherhood of KryptonianNessuna valutazione finora
- Diabetic NephropathyDocumento35 pagineDiabetic NephropathyIstanli CarrascalNessuna valutazione finora
- Diabetes Mellitus Type 2Documento19 pagineDiabetes Mellitus Type 2Ann MaraeNessuna valutazione finora
- Diabetes Mellitus, Often Simply Referred To As Diabetes, Is A Group of Metabolic Diseases inDocumento3 pagineDiabetes Mellitus, Often Simply Referred To As Diabetes, Is A Group of Metabolic Diseases inGanesh BalaNessuna valutazione finora
- Crtical Endocrine 2Documento24 pagineCrtical Endocrine 2JorgeNessuna valutazione finora
- Acute Diabetes ComplicationsDocumento7 pagineAcute Diabetes ComplicationsHala Salah IbrahimNessuna valutazione finora
- Diabetes Mellitus Type 2Documento16 pagineDiabetes Mellitus Type 2Roland Jireh MarananNessuna valutazione finora
- Diabetes Mellitus (Etiology, Classification, and Diagnosis)Documento6 pagineDiabetes Mellitus (Etiology, Classification, and Diagnosis)ayu permata dewiNessuna valutazione finora
- Presented By-Kamini SinghDocumento52 paginePresented By-Kamini SinghSupriyati RahayuNessuna valutazione finora
- Diabetic Ketoacidosis in The Emergency DepartmentDocumento19 pagineDiabetic Ketoacidosis in The Emergency DepartmentMichael NovilloNessuna valutazione finora
- Dka - PPT - 090339Documento8 pagineDka - PPT - 090339Floida Rose KatterNessuna valutazione finora
- Classification: Blood Sugar Insulin Hormone Pancreas HyperglycemiaDocumento20 pagineClassification: Blood Sugar Insulin Hormone Pancreas Hyperglycemiabammu21Nessuna valutazione finora
- Diabetic Ketoacidosis (DKA) : in The Established Patient, DKA Results FromDocumento3 pagineDiabetic Ketoacidosis (DKA) : in The Established Patient, DKA Results FromOber SánchezNessuna valutazione finora
- Diabetes MellitusDocumento19 pagineDiabetes MellitusHaleelu Abdul JaleelNessuna valutazione finora
- 01b. ACUTE COMPLICATIONS (KAD & HONK)Documento42 pagine01b. ACUTE COMPLICATIONS (KAD & HONK)febriNessuna valutazione finora
- Management of Diabetic Ketoacidosis in Children and Adolescents With Type 1 Diabetes MellitusDocumento11 pagineManagement of Diabetic Ketoacidosis in Children and Adolescents With Type 1 Diabetes MellitusYaritza Barraza RojasNessuna valutazione finora
- Smiths FractureDocumento4 pagineSmiths FractureDyah AyuNessuna valutazione finora
- Ketoasidosis DiabetikumDocumento1 paginaKetoasidosis DiabetikumDyah AyuNessuna valutazione finora
- Smiths FractureDocumento4 pagineSmiths FractureDyah AyuNessuna valutazione finora
- Ketoasidosis DiabetikumDocumento1 paginaKetoasidosis DiabetikumDyah AyuNessuna valutazione finora
- Ketoasidosis DiabetikumDocumento1 paginaKetoasidosis DiabetikumDyah AyuNessuna valutazione finora
- Pain During Menstruation or Dysmenorrhea Occurs in 50Documento3 paginePain During Menstruation or Dysmenorrhea Occurs in 50Dyah AyuNessuna valutazione finora
- Ketoasidosis DiabetikumDocumento1 paginaKetoasidosis DiabetikumDyah AyuNessuna valutazione finora
- Ketoasidosis DiabetikumDocumento1 paginaKetoasidosis DiabetikumDyah AyuNessuna valutazione finora
- Ketoasidosis DiabetikumDocumento1 paginaKetoasidosis DiabetikumDyah AyuNessuna valutazione finora
- Ketoasidosis DiabetikumDocumento1 paginaKetoasidosis DiabetikumDyah AyuNessuna valutazione finora
- Ketoasidosis DiabetikumDocumento1 paginaKetoasidosis DiabetikumDyah AyuNessuna valutazione finora
- Ketoasidosis DiabetikumDocumento1 paginaKetoasidosis DiabetikumDyah AyuNessuna valutazione finora
- Ketoasidosis DiabetikumDocumento1 paginaKetoasidosis DiabetikumDyah AyuNessuna valutazione finora
- Ketoasidosis DiabetikumDocumento1 paginaKetoasidosis DiabetikumDyah AyuNessuna valutazione finora
- Pemeriksaan Fisik MataDocumento18 paginePemeriksaan Fisik MataDyah AyuNessuna valutazione finora
- CA Nasofaring ENTDocumento5 pagineCA Nasofaring ENTDyah AyuNessuna valutazione finora
- Management of InfertilityDocumento3 pagineManagement of InfertilityDyah AyuNessuna valutazione finora
- Pemeriksaan Fisik MataDocumento18 paginePemeriksaan Fisik MataDyah AyuNessuna valutazione finora
- Neonatal JaundiceDocumento8 pagineNeonatal JaundiceDyah AyuNessuna valutazione finora
- Thyroid Causing DementiaDocumento2 pagineThyroid Causing DementiaDyah AyuNessuna valutazione finora