Documenti di Didattica
Documenti di Professioni
Documenti di Cultura
Dosing Pump
Caricato da
niceseshaDescrizione originale:
Copyright
Formati disponibili
Condividi questo documento
Condividi o incorpora il documento
Hai trovato utile questo documento?
Questo contenuto è inappropriato?
Segnala questo documentoCopyright:
Formati disponibili
Dosing Pump
Caricato da
niceseshaCopyright:
Formati disponibili
S R Metering Pumps & Systems.
INDEX
Sr. No.
Description
Page No.
1.
OPERATING
-------- 02
2.
INSTALLATION
--------- 02
3.
PIPE LINE
--------- 02
4.
PREOPERATION CHECK-LIST
--------- 03
5.
CALLIBERATION
--------- 04
6.
ASSEMBLING & DISMANTLING PROCEDURE - 05
7.
MAINTAINENCE
--------- 07
8.
TROUBLE SHOOTING CHART
--------- 08
9.
PUMP SECTION DRAWING & PART LIST --------- ANNEXURE 1 & 2
(HD SERIES & SL SERIES)
10.
PLUNGER, HEAD & VALVE ASSEMBLY --------- ANNEXURE 3
11.
EXPLODED VIEW
--------- ANNEXURE 4
12.
PIPING INSTRUCTIONS 1 & 2
--------- ANNEXURE 5 & 6
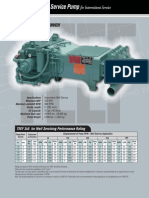
PUMP SR. NO.
MODEL
CAPACITY
L.P.H.
PRESSURE
Kg. / Sq. Cm.
PLUNGER DIA.
S. P. M.
GEAR RATIO
VALVE
1/1
Email: info@srmetering.com
S R Metering Pumps & Systems.
OPERATION
S. R. make plunger pumps are simple piston and cylinder operation. The forward
movement (discharge stroke) of the plunger activates (opens) discharge valve and shuts off
suction valve enabling the liquid in the head to flow out of the head, from the discharge end.
Backward movement (suction stroke) of plunger activates (opens) suction valve and shuts off
discharge valve causing the liquid to enter the head from the suction end.
Simple gear and eccentric mechanism drive the plunger. By rotating the control barrel
mounted on the top, the eccentricity is varied (increased or decreased) resulting in the increase or
decrease of stroke length. The stroke length can be varied from 0% to 100% by means of the
control barrel; thus the liquid discharge is varied accordingly.
Installation Instructions
1. The pump should be mounted on a surface, which is flat and leveled.
2. All piping connecting the pump should be supported so that no stress is placed on pump
fittings.
3. Flush and blow out all pipelines before connecting the pump.
4. Install shut off valves with unions on the suction and discharge side to facilitate servicing.
5. A safety valve must always be provided immediately after the discharge port.
6. If a smooth flow is required a pulsation-damping chamber should be installed immediately
after the discharge port.
7. Install a strainer of adequate size on the suction side.
8. A flooded suction is essential for optimum service.
9. The suction piping must be absolutely airtight. Test the piping with air pressure and soap
solution for any leaks.
Pipe Line
a)
General information
i. Use piping to withstand maximum working pressure.
ii. Use piping material that is resistant to corrosion by the pumped media. Connection to the
pump liquid end should be carefully selected.
iii. Piping should be as short as possible and slopped in a manner to prevent trapping of vapor
in pockets. Vapor present in liquid end will cause inaccurate pump delivery.
iv. Install full flow type of valves with union/flanges on the suction and discharge side to
facilitate servicing.
v. Provide for pipe expansion when hot fluids are to be pumped. Support piping so the pipe
forces are not transferred to the pump. Never spring in piping to make connections.
b)
Suction piping
i. If possible, use tubing for the suction line, which has smooth inner surface and can be bent
into long sweeping bends, thus decreasing frictional flow losses.
ii. Suction piping must be absolutely air tight to ensure accurate pumping.
iii. It is preferable to have the suction of the pump flooded by having the liquid end located
below the lowest level of fluid in the supply tank.
iv. When suction piping is long, particularly at stroke speeds greater than 100strokes per
minute (SPM), the size of piping should be larger than the liquid end suction fitting to
prevent starving of the pump.
v. Any measures to prevent foreign matter from entering the head will give trouble free
service.
vi. Sealed piping, sufficient suction pressure, and properly adjusted packing are absolutely
necessary for accurate and stable pump operation.
2/2
Email: info@srmetering.com
S R Metering Pumps & Systems.
c)
Discharge piping
i. Install adequate size pipe to prevent excessive pressure losses on the discharge stroke of the
pump. Maximum pressure at the discharge fitting on the liquid end must be kept at or
below the maximum pressure rating as shown on the nameplate. The peak flow of this type
pump during the discharge stroke is approximately three times the average flow rate
(because of harmonic motion of the plunger) and discharge piping should be sized
accordingly.
ii. The pump will not deliver a controlled flow if discharge pressure is less than the suction
pressure. To guarantee proper functioning of the pump, the back pressure at the discharge
end must be at least 0.5kg/sq.cm to 2 Kg/sq.cm. (7psi to28Psi) higher than the suction
pressure. If these pressure conditions cannot be attained by the stated discharge head, a
spring loaded back pressure valve must be installed on the discharge side. The pump
produces the required pressure to overcome the back pressure or discharge pressure in the
discharge side.
iii. A pressure relief valve must always be provided immediately after the discharge port. Pipe
the outlet of the relief valve back to the suction tank (do not pipe back into pump suction
line.
d)
Precautions (piping).
When planning pipe installation the following must be AVOIDED.
1. Lengthy pipelines of small diameter.
2. Sharp bends.
3. The use of suction hoses whose walls are so thin that they contract during suction.
4. Suction lines drawing from the lowest point of the reservoir.
5. Long vertical rises immediately after the delivery outlet of the pump.
6. Filters whose elements cannot be changed or cleaned.
7. Piping relief valve discharge back to the suction line.
8. Shut off valves (isolating valves) in the delivery line, unless a safety valve is installed before
the shut off valve to prevent excess pressure build up.
9. When handling suspension, pipeline systems, which do not feed the pump with a uniform
well-mixed medium or tend to deposit sediment or cannot be drained during shut down.
10. Pump heads must not be subjected to any strain by the weight or vibration of the pipeline
system.
11. Pipelines and pump must be so installed that inspection overhaul or repairs can be easily
carried out.
CHECK LIST BEFORE OPERATION
1.
2.
3.
4.
5.
6.
Check for the correct oil level in the gearbox.
Make sure if all the tie down bolts are tight.
Make sure if the suction lines are filled with system fluid.
Check if the pipes are installed properly.
All shut-off valves should be open.
Check if the pressure relief valve is mounted before the first isolation valve on the discharge
line.
WARNING
1.
2.
3.
4.
5.
6.
7.
8.
Install adequate size pipe to prevent Starving & excessive pressure losses.
Do not run the pump without oil.
Use only recommended (approved) oils.
Do not rotate the control barrel below 0 % & above 100 % setting
Do not disturb or remove any bolts on the drive end.
Do not run the pump without the coupling guard.
Only use Genuine spares.
Never spring in piping to make connections
3/3
Email: info@srmetering.com
S R Metering Pumps & Systems.
INITIAL RUNNING
1. Start the pump for a moment and ensure the preferred direction of rotation as indicated.
2. On initial start up, run the pump for 30 to 40 seconds. Repeat the same for approximately 10
times. During these start runs listen for any abnormal noise, and if you notice any, refer the
trouble-shooting chart.
3. Set the stroke length to maximum capacity and run the pump for 30 minutes without any
discharge pressure. Check the discharge lines for indication of flow.
Precautions:
When the pump has to be started frequently against full system pressure it is necessary to
have the system-piping layout as shown in illustration. When starting the pump against full
system pressure first the bypass valve is fully open and then it is gradually closed to load the
pump to bring it to system pressure. This is absolutely necessary to protect the pump from shock
loading.
It is essential that the suction lines of controlled volume pumps be absolutely free of
entrapped air vapor, to prevent gas entrapment into liquid end. Liquid ends are designed to
rapidly discharge any small bubbles that may enter. However large amount of gas in the liquid
end is alternatively compressed and expanded with each plunger stroke and causes inaccuracies
in pumping. In severe cases the liquid end may become vapor bound and cease pumping
altogether.
CALIBRATION
General:
The metering pumps are calibrated on our test stands under the following conditions:
a) Suction lift 0.3 m. / Positive suction head of 2.5 m.
b) Discharge Pressure as specified by the customer.
------The required pressure is obtained by an adjustable throttle valve on the discharge side.
The final Calibration must be done under actual conditions at site.
Capacity calibration:
After the initial running of the pump and adjustment of the gland packing, test runs
should be made to determine the exact capacity of the controlled volume pump under the specific
operating conditions for various stroke length settings. The pump should be calibrated at four
stroke length settings to determine its characteristics throughout the entire range. The settings
normally used are 100%, 75%, 50%, and 25% stroke length. Two methods of measuring the
capacity in a given time can be used.
(1) Measure the drop of liquid level from calibrated vessel on suction side. (This is preferred to
any other method.)
(2) Measure the quantity collected from the discharge side of the pump.
Check the capacity several times at four different stroke length settings. Record the readings on
linear graph paper.
For all stable conditions these points should describe a straight line.
4/4
Email: info@srmetering.com
S R Metering Pumps & Systems.
ASSEMBLING AND DISASSEMBLING PROCEDURE
Dismantling the liquid end assembly
Plunger Pump
1. Remove all the pipes & pipe fittings from the valve holder of the pump.
2. Loosen the plunger lock nut & unscrew the Plunger retainer from the crosshead. Unscrew the
bolts on the valve holder plate & remove the valve assembly.
3. Unscrew the bolts of the Head. Pull out the Head.
Dismantling the Hydraulic assembly( Hydraulic Diaphragm Pump)
Diaphragm Pump
1. Drain the oil in the oil chamber.
2. Loosen the plunger lock nut & unscrew the Plunger retainer from the crosshead.
3. Unscrew the vacuum body from the actuator body.
4. Unscrew the Pressure relief valve from the actuator body.
* NoteDo not change the factory setting of the PRV lock nut.
5. Unscrew the bolts on the valve holder plate, on liquid head, & remove the valve assembly.
6. Unscrew the bolts of the Head. Pull out the Head along with the Diaphragm.
7. Unscrew the bolts of adaptor plate (or actuator body in case of size 2 & 3. ) & oil chamber
Assembly procedure of Hydraulic End & liquid End. ( Hydraulic Diaphragm Pump)
Diaphragm Pump
1. Locate the refill gate & guide assembly in the Actuator body & fix the circklip on the refill
guide.
2. Place the plunger in the plunger guide & bolt it to the actuator body.
3. Bolt the adaptor plate to the actuator body,( Not applicable to size 2 & 3)
4. Tighten the vacuum assembly to the actuator Body.
5. Tighten the PRV assembly to the actuator body.
* NoteDo not change the factory setting of the PRV lock nut.
6. Bolt the hydraulic assembly to the oil chamber.
7. Place the gland in the groove of the liquid head.
8. Place the Diaphragm on the liquid head & bolt the liquid head assembly to the actuator body.
9. Reassemble the valve & valve holder to the liquid head.
10. Fill Hydraulic oil in the oil Camber.
11. Remove the air in the hydraulic assembly. (* The pump will not function properly air is
entrapped in the hydraulic assembly.)
Air Bleeding Procedure ( Hydraulic Diaphragm Pump)
1. Unscrew the PRV from the actuator body.(Check oil level in oil Chamber.)
2. Set the pump at 10 % To 20 % stroke & start the pump.
3. Some air will start coming out of the PRV hole of the actuator body. When air will
stop coming out , it indicates that all the air is Bled out of the hydraulic assembly.
4. Stop the pump after 2 to 3 minutes & reassemble the PRV assembly in the actuator
body.
5. Start the pump to get the desired flow.
Dismantling stroke adjustment mechanism assembly.
1.
2.
3.
4.
Remove back cover plate bolts and washers and take out back cover plate.
Rotate barrel in decreasing direction and set pump stroke at zero percentage.
Loosen the grub screws of the barrel and remove it.
Remove the bolts of the S. L. indicator. Unscrew the S. L. indicator from the Control screw
to remove it.
5. Remove the top cover bolts and washers. Remove the top cover and thrust plate.
6. Hold the Control screw by right hand and eccentric strap by left hand. Lift the Control screw
to disengage the eccentric strap from the eccentric.
7. Pull the stroke adjustment mechanism and take out the crosshead and eccentric strap
assembly.
5/5
Email: info@srmetering.com
S R Metering Pumps & Systems.
Dismantling the slider housing assembly
1. Remove side and bearing end cover bolts and washers and take out the bearing end cover by
slightly tapping both ends of the worm shaft. Keep the worm shaft lose in the housing.
2. Tighten the grub screws at the bottom of the housing and push the drive shaft assembly up
till slider housing assembly comes out from the top bore of the housing.
3. Dismantle worm wheel from the slider housing after knocking out the spring dowels.
ASSEMBLY PROCEDURE
1. Place the worm shaft in the housing pushing it along with the bearing through the side cover
bores.
2. Lightly push and tap the side covers locating them on the worm shaft bearing and the
housing bores. Fix the side cover and ensure that the worm wheel moves freely. Replace the
oil seals.
3. Assemble the slider housing assembly.
4. Insert the control assembly with the crosshead end through the yoke side and simultaneously
insert slider in the slider housing assembly.
5. Fix the yoke locating in the crosshead.
6. Fix top cover and check if the thrust plate is not tightened (thrust plate should just rotate by
hand).
7. Assemble all the rest of the parts in the reverse sequence of dismantling
ZERO SETTING
1. Keep the grub screw, of the control barrel loose, and fix the barrel on Control screw.
2. Tighten the barrel fixing grub screw and turn the knob of the barrel in decreasing direction.
3. Check the pump stroke on cross head while turning the worm shaft by hand. Rotate the
control barrel till no movement is felt on the cross head, even when the worm shaft is
moving.
4. Match the bottom edge of the control barrel with the 0% mark of S. L. indicator.
5. Tighten the grub screw at the set position.
6/6
Email: info@srmetering.com
S R Metering Pumps & Systems.
MAINTENANCE
Accurate records in the early stages of pump operation will reveal the type and amount
of maintenance that will be required. A preventive maintenance program based on these record
will ensure trouble free operation. It is not possible in these instructions to forecast the life of
such parts as the valves, gland packing and other contact parts with the product you are handling.
Corrosion rates and conditions of operations affect the useful life of these materials so an
individual metering must be gauged according to particular service conditions.
Lubrication:
The gear reservoir of the pump main housing should be filled with the recommended
gear lubricant to the oil level mark. If the oil level is less remove the breather plug and with the
help of funnel fill the oil in the reservoir up to the recommended level.
The oil should be changed every 500 hours of operation or every 3 months -whichever is
earlier. Use only recommended oil. Do not overfill.
RECOMMENDED GEAR OILS:
1] Caltex
: 460
2] IOC
: Servocyl 460
3] H.P.
: Enklo 460
4] Bharat Refinery : Macoma 460
Checklist after every 48 hrs.
1.
2.
3.
4.
Check oil level in the gearbox.
Inspect the liquid end for indication of leakage. Glands to be tightened as gently as possible.
Grease / Oil all lubricating points.
Oil the crosshead every 48 hours.
Note (For plunger Pump only) :- During operation if leakage occurs the gland nut
should be tightened a little (1/6turnes or less) until leakage is minimized. The packing should be
allowed to resettle for at least 5 minutes between adjustments. It is advisable to tolerate a little
leakage at the gland as the leaking liquid will help to lubricate and cool the packing and plunger,
greatly extending the life of both.
7/7
Email: info@srmetering.com
S R Metering Pumps & Systems.
TROUBLE SHOOTING CHART
----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------DIFFICULTY
PROBABLE CAUSE
REMEDY
----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------Pump does not
1. Coupling disconnected
Connect and align
start.
2. Faulty power source
Check power source
3.
Blown fuse
Replace
4.
Broken wire
Locate and repair
5.
Wired improperly
Check diagram
6.
Motor not running
Check Power Source, Check wiring
diagram
No delivery
1.
Supply tank empty
Fill the liquid
2.
Lines clogged
Clean and Flush
3.
Closed line valves
Open pipeline valves
4.
Suction or discharge
Clean and inspect
NRVs held open with solids
Delivery erratic
Low Delivery
6.
Vapor Lock, cavitation
Increase suction Pressure
7.
Strainer clogged
Remove mesh & clean
8.
Prime lost
Check for suction pipeline leak.
9.
Pipeline Blockage
Locate & clear pipelines
10.
Shut off valve closed
Open valves
1. Leak in suction line
Locate & correct
2. Pump cavitating
Increase suction pressure
3. Entrained air or gas in product
Consult Factory for suggested venting
4. Motor speed erratic
Check voltage, frequency
5. Fouled Suction/ delivery NRV
Clean, Replace if necessary
1. Motor speed too low
Check voltages, frequency, wiring
2. Discharge and suction check
Clean, replace if damaged
& terminal connections
valves worn or dirty
3.
Pressure Safety valve open
Reset PSV.
4.
Calibration system error
Evaluate & correct
5.
Product viscosity too high
Lower viscosity by increasing product
Temperature, Increase pump capacity.
6. Pump cavitating
Increase suction
pressure Cool product
as necessary
7. Heavy gland leakage
Inspect & replace if
deteriorated
8. Bypass leakage
Correct for by-pass valve leakage.
8/8
Email: info@srmetering.com
S R Metering Pumps & Systems.
----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------DIFFICULTY
PROBABLE CAUSE
REMEDY
-----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
Delivery gradually
Delivery higher than
Suction/discharge NRV leakage
1.
Leak in suction line
Locate & Correct
2.
PSV set too low
Readjust
3.
Stroke adjustment creeping
Consult Factory
4.
Strainer Fouled
Clean, replace mesh
5.
Product Change
Check viscosity
6.
Bypass leakage
Correct for by-pass valve leakage
7.
Gland Leakage
Inspect & replace if damaged
1. Suction pressure higher than
rated
discharge pressure
Noisy gearing
Pump loses oil
Pump over heats
Install backpressure valve or consult
Factory for piping recommendations
2. Back pressure valve set too low
Increase setting
1. Discharge pressure too high
Reduce pressure
1. Leaky oil seal
Replace
2.
Leaky gasket
Replace
3.
Gear box over filled
Remove excess oil
Leaky grub screws on drive end
Replace, use Teflon
cover
tape
4.
Knocking
Clean & Replace, if damaged
1.
Water hammer
Install dampner
2.
Worn bearing, gear
Replace
3.
End play in worm shaft
Correct for shaft play by shims
4.
Play in plunger
Tighten cross head nut
5.
Loose Thrust plate
Tighten Top cover screws
1.
Oil level too low
Fill oil in gear box
2.
Gear box over filled
Remove excess oil
3.
Wrong shaft rotation
Correct shaft rotation
4.
Thrust plate over tightened
Correct thrust plate play by tightening
& proper shims
Motor overheats
1.
Motor overloaded
Check operating conditions
2.
Low voltage
Check power supply
3.
Loose wire
Trace & correct
4.
Over tightened gland
Correct by loosening gland nut.
-----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
S R Metering Pumps & Systems.
K-36, M. I. D. C., Ambad,
Nashik-422010,
Maharashtra State, India.
Tel : (91 253 ) 6604491/2383372
Tel- Fax : (91 253) 6603321
9/9
Email: info@srmetering.com
Potrebbero piacerti anche
- Value Of Work Done A Complete Guide - 2020 EditionDa EverandValue Of Work Done A Complete Guide - 2020 EditionNessuna valutazione finora
- 800D SeriesDocumento3 pagine800D Seriesvkeie0206Nessuna valutazione finora
- EFCO Maschinenbau India Private Limited: Job Card - Isolation ValveDocumento2 pagineEFCO Maschinenbau India Private Limited: Job Card - Isolation ValveDebasis Pattnaik DebaNessuna valutazione finora
- Released: Company Document No: Document ClassDocumento32 pagineReleased: Company Document No: Document ClassShajahan AsanarNessuna valutazione finora
- QAP For Conical StrainerDocumento2 pagineQAP For Conical StrainersatishchidrewarNessuna valutazione finora
- 13-OM-QC-PL-MS-06 - MS FIXED TUBE TYPE EXCHANGER'S INSPECTION & CLEANING (Rev.00)Documento7 pagine13-OM-QC-PL-MS-06 - MS FIXED TUBE TYPE EXCHANGER'S INSPECTION & CLEANING (Rev.00)SANDEEP100% (1)
- WPS Sa 517Documento2 pagineWPS Sa 517DHANANNJAI SINGH -Nessuna valutazione finora
- Charging & Discharging of CapacitorDocumento4 pagineCharging & Discharging of CapacitorHemanth GedelaNessuna valutazione finora
- Risks in Facility Build Quality and Project Handover: What Happened?Documento3 pagineRisks in Facility Build Quality and Project Handover: What Happened?musaismail8863Nessuna valutazione finora
- Mov ItpDocumento1 paginaMov ItpMussab Salih100% (1)
- Vendor Fabrication Shop Site Construction: QA/QC Inspections: Inspection Test PlanDocumento2 pagineVendor Fabrication Shop Site Construction: QA/QC Inspections: Inspection Test PlanSuraj ShettyNessuna valutazione finora
- User'S Manual: MANUAL NO - GL240-UM-153Documento150 pagineUser'S Manual: MANUAL NO - GL240-UM-153Ta100% (1)
- LBC-125 SpecificationDocumento1 paginaLBC-125 Specificationastiadi engineeringNessuna valutazione finora
- Belzona 1111ps EnglDocumento2 pagineBelzona 1111ps EnglNikolay GuerreroNessuna valutazione finora
- Valve Storage ProcedureDocumento2 pagineValve Storage Procedurenisus4everNessuna valutazione finora
- Eadips Manual Engl PDFDocumento390 pagineEadips Manual Engl PDFbkarabasevicNessuna valutazione finora
- Eagle Burgmann API PlanDocumento43 pagineEagle Burgmann API PlanONURNessuna valutazione finora
- FW3315 - Centrifugal Pump Check ListDocumento1 paginaFW3315 - Centrifugal Pump Check ListRachel FloresNessuna valutazione finora
- New SSIV InstallationDocumento12 pagineNew SSIV InstallationDidiNessuna valutazione finora
- ASME B31.3 Process Piping: 13. Inspection, Examination & TestingDocumento37 pagineASME B31.3 Process Piping: 13. Inspection, Examination & TestingMohamed Al-OdatNessuna valutazione finora
- Membrane Purification System (MPS) Project Chemical Cleaning ReportDocumento8 pagineMembrane Purification System (MPS) Project Chemical Cleaning ReportEdy Iswanto0% (1)
- Itp Jib Crane Rev.1Documento1 paginaItp Jib Crane Rev.1Roger MahilumNessuna valutazione finora
- Bifold UpdatedDocumento8 pagineBifold UpdatedGopinath GunasekaranNessuna valutazione finora
- MNT-INTG-2007OP - Maintenance Welding InspectionDocumento43 pagineMNT-INTG-2007OP - Maintenance Welding InspectionNatarajan MurugesanNessuna valutazione finora
- EZR RegulatorDocumento40 pagineEZR RegulatorBranko BabicNessuna valutazione finora
- Technical Doc 1 - Technical Scope of Work Drs Eac181Documento25 pagineTechnical Doc 1 - Technical Scope of Work Drs Eac181bhargavpansuria09Nessuna valutazione finora
- MP 4 0004 060Documento4 pagineMP 4 0004 060husen123 alhusadaNessuna valutazione finora
- Orbinox VG08 Knife Gate ValveDocumento8 pagineOrbinox VG08 Knife Gate ValveYorkistNessuna valutazione finora
- Coke Crusher - Lubrication Pumps Run in TestDocumento26 pagineCoke Crusher - Lubrication Pumps Run in TestsayedNessuna valutazione finora
- Installation, Operation & Maintenance Manual: Virgo Engineers LimitedDocumento47 pagineInstallation, Operation & Maintenance Manual: Virgo Engineers LimitedSreenivasNessuna valutazione finora
- ITP For Hydraulic BarrierDocumento4 pagineITP For Hydraulic Barriermoytabura96Nessuna valutazione finora
- Damage / Discrepancy ReportDocumento2 pagineDamage / Discrepancy ReportScott YoungNessuna valutazione finora
- 4.1 - ANX-1 Definition of Mechanical Completion PDFDocumento18 pagine4.1 - ANX-1 Definition of Mechanical Completion PDFLegend AnbuNessuna valutazione finora
- 206B-FF Flange Facer ManualDocumento22 pagine206B-FF Flange Facer ManualKmelt39Nessuna valutazione finora
- FAT Precedure - R 072 Nitrogen PackageDocumento10 pagineFAT Precedure - R 072 Nitrogen PackageBudi UtomoNessuna valutazione finora
- Area Handover FormDocumento1 paginaArea Handover FormsivagaaneshNessuna valutazione finora
- Re-Welding, Expansion & HT ProcedureDocumento6 pagineRe-Welding, Expansion & HT Proceduresuria qaqcNessuna valutazione finora
- SP 2154Documento26 pagineSP 2154Anoop gokhaleNessuna valutazione finora
- Method Statement For Ultrasonic Testing: DCSM Project 2019Documento5 pagineMethod Statement For Ultrasonic Testing: DCSM Project 2019Thinh NguyenNessuna valutazione finora
- Burckhardt Compression (India) PVT - LTD.: 1.0 MaterialsDocumento2 pagineBurckhardt Compression (India) PVT - LTD.: 1.0 MaterialsYOGESHNessuna valutazione finora
- Nqd-Valve Installation ReportDocumento21 pagineNqd-Valve Installation ReportprathameshNessuna valutazione finora
- Instruction Sheet: W-Series Hydraulic Torque WrenchesDocumento40 pagineInstruction Sheet: W-Series Hydraulic Torque WrenchesShag Shaggy100% (1)
- Installation Instructions For Commercial RO SystemsDocumento22 pagineInstallation Instructions For Commercial RO SystemsMfundo DlaminiNessuna valutazione finora
- Camx 2015 Vaidya UabDocumento11 pagineCamx 2015 Vaidya UabJuNeng NigLtdNessuna valutazione finora
- Samson Globe Control ValveDocumento12 pagineSamson Globe Control ValveShishir DwivediNessuna valutazione finora
- Butterfly Valve Operation Manual PDFDocumento16 pagineButterfly Valve Operation Manual PDFLuis GonzalezNessuna valutazione finora
- Chapter 5 - Conclusion & RecommendationDocumento4 pagineChapter 5 - Conclusion & RecommendationMohamad Shukri0% (1)
- Procedure For Rapid Chloride Penetration Test: 1.1 Personnel, Material, and Equipment RequirementsDocumento3 pagineProcedure For Rapid Chloride Penetration Test: 1.1 Personnel, Material, and Equipment RequirementsShyamNessuna valutazione finora
- SP-2154 - 2015valves Technical SpecificationDocumento23 pagineSP-2154 - 2015valves Technical Specificationarjunprasannan7Nessuna valutazione finora
- Earth Moving Equipment ChekclistDocumento2 pagineEarth Moving Equipment ChekclistBakri Bin SapilahNessuna valutazione finora
- Newcr SS: ABC-TPEF-EKUF1-PX2365-002620-001/Z01Documento1 paginaNewcr SS: ABC-TPEF-EKUF1-PX2365-002620-001/Z01eke23Nessuna valutazione finora
- Instruction Manual Enardo 2000 2500 Series Emergency Pressure Relief Vents North America Only en 122600 3Documento8 pagineInstruction Manual Enardo 2000 2500 Series Emergency Pressure Relief Vents North America Only en 122600 3Ramon GarciaNessuna valutazione finora
- Tank Fabrication & ErectionDocumento72 pagineTank Fabrication & ErectionPramod GrNessuna valutazione finora
- Procedure For Earthing PitDocumento2 pagineProcedure For Earthing PitMohammed Jahir HusainNessuna valutazione finora
- Cameron Ball ValvesDocumento31 pagineCameron Ball ValvesJosé Roberto Alejo MirandaNessuna valutazione finora
- Factors Contributing To Foarming Crude OilDocumento11 pagineFactors Contributing To Foarming Crude OilSang Duong Van100% (1)
- NT2-L3-M-000!21!00022 MS For Oil Flushing of The Fuel Oil Piping SystemDocumento15 pagineNT2-L3-M-000!21!00022 MS For Oil Flushing of The Fuel Oil Piping SystemHuynh Thanh TamNessuna valutazione finora
- CR QapDocumento2 pagineCR QapSimbu ArasanNessuna valutazione finora
- Prosedur Penetran TestingDocumento11 pagineProsedur Penetran TestingIkhsan DalimuntheNessuna valutazione finora
- BW Filmfill EngDocumento4 pagineBW Filmfill EngkylegazeNessuna valutazione finora
- Designed Concrete MixDocumento6 pagineDesigned Concrete MixniceseshaNessuna valutazione finora
- Eminentlabs ProfileDocumento2 pagineEminentlabs ProfileniceseshaNessuna valutazione finora
- Trident PaperDocumento6 pagineTrident PaperniceseshaNessuna valutazione finora
- Astm A36 1997 PDFDocumento5 pagineAstm A36 1997 PDFnicesesha0% (1)
- SCT Assembly Indtruction PDFDocumento27 pagineSCT Assembly Indtruction PDFniceseshaNessuna valutazione finora
- Urban Bus SpecificationsDocumento210 pagineUrban Bus SpecificationsMohsin RiazNessuna valutazione finora
- Hydraulic Jack or Hydraulic PressDocumento8 pagineHydraulic Jack or Hydraulic PressAnand HaseNessuna valutazione finora
- 4003q1 Specimen PaperDocumento16 pagine4003q1 Specimen Paperwatson0% (1)
- Predator Generator ManualDocumento28 paginePredator Generator Manualcasa gutierrezNessuna valutazione finora
- Operating Instructions and Maintenance Manual For LV AC Induction MotorsDocumento22 pagineOperating Instructions and Maintenance Manual For LV AC Induction MotorsAlwyzz Happie RaamzzNessuna valutazione finora
- (ME - 514A: Alternative Energy Resources) : Natural GasDocumento11 pagine(ME - 514A: Alternative Energy Resources) : Natural GasMarvin ArnaizNessuna valutazione finora
- Engineering Declaration Unit # 2 JindalDocumento16 pagineEngineering Declaration Unit # 2 JindalVIBHAV100% (1)
- Royal Enfield BulletDocumento7 pagineRoyal Enfield BulletHeenakshi VermaNessuna valutazione finora
- Dynaco g101 g102 Dump Pump PDFDocumento6 pagineDynaco g101 g102 Dump Pump PDFnbgearsNessuna valutazione finora
- 4plas Troubleshooting Guide Id111 PDFDocumento12 pagine4plas Troubleshooting Guide Id111 PDFJohn WayneNessuna valutazione finora
- New Holland B110 Backhoe Loader Service Repair Manual PDFDocumento35 pagineNew Holland B110 Backhoe Loader Service Repair Manual PDFfjjskekdmmekm33% (6)
- Tata Company HistoryDocumento3 pagineTata Company HistorySushmita JkNessuna valutazione finora
- 95ZV Cargador Frontal KawazakiDocumento194 pagine95ZV Cargador Frontal Kawazakibernardo angeles rojas100% (3)
- Makeshift Arsenal by LoweryDocumento37 pagineMakeshift Arsenal by LoweryD50% (2)
- DNGF PR 200 Dbs 1009-2-1 3 Fire Protection System Design Basis and PhilosophyDocumento21 pagineDNGF PR 200 Dbs 1009-2-1 3 Fire Protection System Design Basis and Philosophychy_id100% (2)
- NGL-PIAAP-00007-0712 Depropanizer PDFDocumento2 pagineNGL-PIAAP-00007-0712 Depropanizer PDFHairunnisaNessuna valutazione finora
- Risk Asses 65-Piping Fabricated and Assembly - H03Documento11 pagineRisk Asses 65-Piping Fabricated and Assembly - H03Rochdi BahiriNessuna valutazione finora
- Introduce LP&MP CompressorDocumento1 paginaIntroduce LP&MP CompressorchuminhNessuna valutazione finora
- Hybrid EngineDocumento20 pagineHybrid EngineThirumaaran GopalanNessuna valutazione finora
- Wellsite GeologyDocumento6 pagineWellsite GeologyLeonardo CarrilloNessuna valutazione finora
- Structural Topics Problems SolvedDocumento10 pagineStructural Topics Problems Solvedامين الزريقي50% (4)
- MTU Marine Spec 16V4000M93 PDFDocumento2 pagineMTU Marine Spec 16V4000M93 PDFsmithworkNessuna valutazione finora
- 250kva Tech SpecsDocumento3 pagine250kva Tech Specscrawn06Nessuna valutazione finora
- Bomba Triplex TEEF 5 de in Gardner DenverDocumento2 pagineBomba Triplex TEEF 5 de in Gardner DenverPeponSera100% (2)
- Service FGWilsonDocumento70 pagineService FGWilsonbrahimNessuna valutazione finora
- Manual L3-56 15521 Deno, Deno Compressors L3-56 INSTALLATION, OPERATION & MAINTENANCE MANUAL L3-SeriesDocumento47 pagineManual L3-56 15521 Deno, Deno Compressors L3-56 INSTALLATION, OPERATION & MAINTENANCE MANUAL L3-Seriestm5u2r100% (1)
- Portable Inverter Generator: 2000 Max Watts / 1700 Rated WattsDocumento30 paginePortable Inverter Generator: 2000 Max Watts / 1700 Rated WattsWilmer SuarezNessuna valutazione finora
- Preliminary Tech. Doc. OG120C TG 5Documento17 paginePreliminary Tech. Doc. OG120C TG 5Михаил Гуляев100% (1)
- A Catalogue of Crude Oil and Oil Product PropertiesDocumento24 pagineA Catalogue of Crude Oil and Oil Product PropertiesToapanta FredyNessuna valutazione finora
- Sulphuric Acid Handbook 1000265717Documento268 pagineSulphuric Acid Handbook 1000265717robertluisNessuna valutazione finora