Documenti di Didattica
Documenti di Professioni
Documenti di Cultura
Lesson 3 - Ship Stability 2
Caricato da
amirsyawal87Copyright
Formati disponibili
Condividi questo documento
Condividi o incorpora il documento
Hai trovato utile questo documento?
Questo contenuto è inappropriato?
Segnala questo documentoCopyright:
Formati disponibili
Lesson 3 - Ship Stability 2
Caricato da
amirsyawal87Copyright:
Formati disponibili
8/24/16
3.1 DEFINE BUOYANCY
3.1.1 WHAT IS BUOYANCY?
Buoyancy is basically , the ability of something to float or rise in a fluid . Simple as that ,
more scientifically buoyancy refers to a force that aries from the pressure exerted on an
object by a fluid (a liquid or a gas ). Since its a force we call it the buoyant force .
SHIP STABILITY
BOUYANCY
SECARA RINGKASNYA . . .
The ability of an object to float in water or air
The power of a liquid to make someone or something float
The ability of someone or something to continue to be happy , strong through the
difficult times
3.1.2 FORCE OF BUOYANCY AS
AN UPWARD FORCE ON A
FLOATING OBJECT CREATED BY
THE PRESSURE OF LIQUID ON
THE
OBJECT
When weight
is added to a ship , draft and displacement increase in the same
amount freeboard and reserve buoyancy decrease
When a ship is floating at rest in calm water , it is acted upon by two sets of forces
a)the downward force of gravity
b)the upward force of buoyancy
The force of gravity is a resultant or composite force including the weights of all
portions of the ships structure , equipment , cargo , and personnel . The force of
gravity may be considered as a single force , which acts downward through the ships
center of gravity(G)
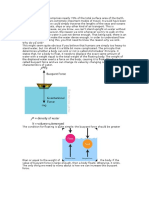
The force of buoyancy is also a composite force which result from the pressure of the water
on the ships hull . A good example of the immersing container in a tank of water as shown
below
3.1.3 THE BUOYANCY FORCE
IS EQUAL TO THE
DISPLACEMENT OF A
FLOATING OBJECT
8/24/16
3.2 CONCEPT OF RESERVE
BUOYANCY
3.2.1 WHAT IS RESERVE BUOYANCY ?
3.2.2 IMPORTANCE OF
RESERVED BUOYANCY
Reserved is an enclosed , watertight volume of the vessel above the water line . It is
important to a vessels stability the portion of the vessel considered effective
contribute to a vessels righting arm when heeled .
The shaded section is the underwater volume of the hull . The unshaded part is known as reserve buoyancy and
can be simply described as the volume of the vessel above the water line .
The buoyancy also important for the vessels safe operation at sea .
It also contribute to a vessel seaworthiness , and provide a buffer against flooding
(loss of a portion of buoyancy , sea loss buoyancy method ) .
For example; the more you load the boat , the greater its displacement , the more it will sink in the water , the less
reserve buoyancy . Every boat must have sufficient reserve buoyancy to opereate safely: do not overload your
vessel . Commercial vessels have a load line assigned to them and it is an offence to proceed to sea .
3.2.3 HOW FREEBOARD IS RELATED TO
RESERVE BUOYANCY
Freeboard is the distance from the waterline to the top of the deck plating at the side of the
deck amidships
3.2.4 THE PURPOSE OF LOADLINE
3.2.5 THE REQUIREMENTS FOR
MAINTAINING WATERTIGHT
INTERGRITY
Ensure all watertight decks and bulkheads are inspected periodically to verify that
there are no unprotected openings or improper penetrations that will allow
progressive flooding and that closure devices (watertight door, duct closers, etc.) are
in place and in working order
Purpose of loadline is to allot a maximum legal limit up to which a ship can be loaded . By
prescribing such limits , the risk of having the vessel sailing with inadequate freeboard and
buoyancy can be limited . A vessel should be having sufficient freeboard at all the times ,
any exceptions made will result in insufficient stability and excessive stress on the ship s hull .
This is where loadline play an important role , as it make the task of detecting ehether the
vessel is over-loaded and it is freeboard tremendously easy and effortless .
Ensure all crew members are familiar with the locations of the watertight doors
(WTDs) and weather tight closures throughout their vessels. Knowing the locations of
such WTDs and weather tight closures should be part of the crew member vessel
familiarization process.
Ensure WTDs and hatches are closed while at sea and as otherwise specified in the
stability guidance provided to the master or individual in charge. The importance of
keeping WTDs and hatches closed should be emphasized on a regular basis (e.g. at
safety meetings). WTDs and hatches should be opened only briefly to allow passage
and labeled appropriately to remind crew members to close them. If they must
remain open to permit work, WTDs and hatches should be attended at all times so
that they can immediately be closed. Any WTDs permitted to be open while the
vessel is underway should be secured during drills to ensure they work properly.
Implement a WTD inspection program to ensure each WTD is regularly inspected and
properly maintained. As part of the inspection of each WTD, the following should be
examined:
Ensure compartments and external hull structures fitted with ventilation
ducts that have hinged covers with gaskets, hinges, sealing surfaces and
securing mechanisms are regularly inspected and properly maintained (see
above for guidance).
straightness of the knife edge;
the door assembly for twisting or warp-age;
evidence of loose, missing seized ordamaged components;
permanent set in gasket material, cracks in the gasket;
gaps at gasket joints;
paint, rust, or other foreign material on gaskets,knife-edges and working parts; binding and difficult
operations;
loose or excessively tight dogs.
Rotating spindles of the dog, handles and hinges, and other points of friction should be lubricated to
prevent seizing and allow proper closure. If fitted, the spindle packing should also be examined.
8/24/16
Ensure watertight hatches, dogged manholes, bolted manhole covers, and
access plates are given similar examinations, focusing on the sealing
surfaces and the method by which the hatch is secured. Gasket materials
should be replaced whenever they are found insufficient. Regardless of the
type of hatch or access, every component that secures the device, such as
dogs, wing nuts, or bolts should be inspected, lubricated and free, and
repaired or replaced as necessary to ensure they operate properly. As with
watertight doors, hatches and accesses should be labeled to indicate they
remain closed while underway. Most importantly, all securing devices must
be used when the hatch or access is closed. Improper closure of a hatch
will not prevent flooding.
Ensure electrical cables and conduits, piping runs, remote valve actuators, and other
components that penetrate watertight bulkheads, decks, and compartments are
inspected frequently and properly maintained. Each may have a unique sealing
method involving glands with packing assemblies, penetration seals, or other
methods. Frequent inspection and proper maintenance of these various fittings and
assemblies will assist in minimizing the possibility of progressive flooding.
Potrebbero piacerti anche
- TOWING PREPDocumento7 pagineTOWING PREPMico SantosNessuna valutazione finora
- DefinitionsDocumento3 pagineDefinitionsAhmed AboelmagdNessuna valutazione finora
- Presentation AnchorDocumento35 paginePresentation AnchorHan Thu WynnNessuna valutazione finora
- ch1 Framing SystemDocumento12 paginech1 Framing Systemموبليات حسين المصريNessuna valutazione finora
- B) First Trim Correction: Trim LCF Forward of Midships LCF Aft of MidshipsDocumento6 pagineB) First Trim Correction: Trim LCF Forward of Midships LCF Aft of MidshipsCezar100% (1)
- Calculating ship stability using hydrostatic curvesDocumento10 pagineCalculating ship stability using hydrostatic curvesjonas lintagNessuna valutazione finora
- Chapter13 Mercator Charts and Plotting SheetsDocumento3 pagineChapter13 Mercator Charts and Plotting SheetsYasser MetaweaNessuna valutazione finora
- Unit IDocumento24 pagineUnit IsomasundaramNessuna valutazione finora
- DTS - Ship Const & StabDocumento12 pagineDTS - Ship Const & StabYASHKAR VERMA100% (2)
- Seamanship - DefinitionDocumento2 pagineSeamanship - DefinitionFrenzie Mae Vasquez Rivera0% (1)
- DS Stability Questions 33p 298q PDFDocumento33 pagineDS Stability Questions 33p 298q PDFVardiasNessuna valutazione finora
- DNV Grain LoadingDocumento1 paginaDNV Grain LoadingfodrioNessuna valutazione finora
- Ship's Construction PPDocumento26 pagineShip's Construction PPRabiul Islam RobinNessuna valutazione finora
- Topic 2 - Cargo Handling and StowageDocumento17 pagineTopic 2 - Cargo Handling and StowageHemonNessuna valutazione finora
- AnchoringDocumento12 pagineAnchoringDryanmNessuna valutazione finora
- Dynamic UKC BookletDocumento19 pagineDynamic UKC BookletOllivier AmaruNessuna valutazione finora
- Navigation SQADocumento13 pagineNavigation SQACherian KuttyNessuna valutazione finora
- SHIP HANDLING AND MANUEVERING Week 2Documento55 pagineSHIP HANDLING AND MANUEVERING Week 2Anthony Steve Lomillo100% (1)
- Collision Regulations: Part A - GeneralDocumento23 pagineCollision Regulations: Part A - GeneralTheoNessuna valutazione finora
- Here Is All You Wanted To Know About Draft Survey CalculationsDocumento22 pagineHere Is All You Wanted To Know About Draft Survey CalculationsPanagiotis MouzenidisNessuna valutazione finora
- Oic Deck c13Documento51 pagineOic Deck c13Mikhail Roy Dela CruzNessuna valutazione finora
- 3.structural Damages During Cargo Operations DAY 3Documento16 pagine3.structural Damages During Cargo Operations DAY 3cicileana100% (1)
- 47 5815 MT222 2015 1 1 1 Ch.6 Transverse Statical Stability-ADocumento23 pagine47 5815 MT222 2015 1 1 1 Ch.6 Transverse Statical Stability-AManoj KumarNessuna valutazione finora
- Intro To NADocumento11 pagineIntro To NAAnshuman SharmaNessuna valutazione finora
- ANCHOR SystemDocumento32 pagineANCHOR SystemenglisgoNessuna valutazione finora
- Word Ship HandlingDocumento9 pagineWord Ship Handlingrigel100% (1)
- Solutions: Grain CargoesDocumento3 pagineSolutions: Grain CargoesKirtishbose Chowdhury100% (1)
- Intact BuoyancyDocumento62 pagineIntact BuoyancyGuillermoNessuna valutazione finora
- Methods of Preventing Grain From ShiftingDocumento4 pagineMethods of Preventing Grain From ShiftingGovinda Koshyari100% (1)
- Ocean Currents NEWDocumento11 pagineOcean Currents NEWVikram Das100% (1)
- D Watch 2 ReportingDocumento18 pagineD Watch 2 ReportingCezar M. Barranta Jr.Nessuna valutazione finora
- f2 (2) (1) Reviewer Chief Officer Materials.Documento20 paginef2 (2) (1) Reviewer Chief Officer Materials.Alden Almaquer Delizo100% (1)
- Navigation 01Documento8 pagineNavigation 01Khian LiNessuna valutazione finora
- Squat: What in Fact Is Squat and Why Is Squat Relevant For Shipping?Documento8 pagineSquat: What in Fact Is Squat and Why Is Squat Relevant For Shipping?Abhay Kinra100% (2)
- Calculation of Draft SurveyDocumento27 pagineCalculation of Draft Surveysaif100% (1)
- Vts PROCEDURESDocumento26 pagineVts PROCEDURESAlexandro Vincente100% (1)
- Phase 1 Naval Arch Theory QuestionsDocumento6 paginePhase 1 Naval Arch Theory QuestionsSam UelNessuna valutazione finora
- Marine Communication PhrasesDocumento8 pagineMarine Communication PhrasesBhupender RamchandaniNessuna valutazione finora
- Surface Ocean Current Circulation & Principal SeasDocumento50 pagineSurface Ocean Current Circulation & Principal SeasDENWIL VINCENT MONERANessuna valutazione finora
- Design criteria for anchoring systems and operationsDocumento17 pagineDesign criteria for anchoring systems and operationsCelal Bozdogan100% (1)
- 10a.1 - Ship Handling HydrodynamicsDocumento34 pagine10a.1 - Ship Handling HydrodynamicsRaghav Sood100% (1)
- Trim or Longitudinal StabilityDocumento5 pagineTrim or Longitudinal StabilityA JSprNessuna valutazione finora
- RudderDocumento23 pagineRudderAktarojjaman MiltonNessuna valutazione finora
- D1MC Semester 1 / Ship Stability / April 2006/capt - MARDocumento37 pagineD1MC Semester 1 / Ship Stability / April 2006/capt - MARMohd Azril NaharudinNessuna valutazione finora
- 1 What Is The Reasons For A General Inspection of HoldsDocumento2 pagine1 What Is The Reasons For A General Inspection of HoldsMark Gapasangra100% (1)
- Stresses On Ship StructureDocumento72 pagineStresses On Ship Structure187Ranjan Kumar100% (1)
- P020213 Stability BookDocumento115 pagineP020213 Stability BookPETERNessuna valutazione finora
- 15 Precise PilotingDocumento32 pagine15 Precise PilotingErnestoDom100% (3)
- nav 04 - pilot card - копияDocumento4 paginenav 04 - pilot card - копияКонстантин КулаковNessuna valutazione finora
- Bnwas 2Documento22 pagineBnwas 2gopuNessuna valutazione finora
- SCOTVEC STABILITY THEORYDocumento25 pagineSCOTVEC STABILITY THEORYMohan KrishnanNessuna valutazione finora
- IMO Code Timber Deck Cargoes and Bulk Oil Cargo ShipsDocumento6 pagineIMO Code Timber Deck Cargoes and Bulk Oil Cargo ShipsMorganNessuna valutazione finora
- DefinitionsDocumento4 pagineDefinitionssaif100% (1)
- Rolling Period ExplainedDocumento3 pagineRolling Period ExplainedGary LampenkoNessuna valutazione finora
- Bulk Grain Cargoes LoadingDocumento27 pagineBulk Grain Cargoes LoadingMohit Anand100% (1)
- Bridge Watchkeeping, Emergencies, Ship Handling & Manoeuvering V1Documento163 pagineBridge Watchkeeping, Emergencies, Ship Handling & Manoeuvering V1Sachin Kumar MittalNessuna valutazione finora
- Initial Transverse Metacenter CugalDocumento19 pagineInitial Transverse Metacenter CugalPete KatipunanNessuna valutazione finora
- Survey and Examination of Ships' Lifting AppliancesDocumento24 pagineSurvey and Examination of Ships' Lifting Applianceshpss77100% (1)
- Survey and Examination of Ships' Lifting AppliancesDocumento24 pagineSurvey and Examination of Ships' Lifting Applianceshpss77100% (1)
- Jurnal Terindeks Malaysia 2018.07Documento6 pagineJurnal Terindeks Malaysia 2018.07mirNessuna valutazione finora
- COLREGs Course - Application of Rule 18 in Narrow Channels or Fairways Where Rule 9 AppliesDocumento3 pagineCOLREGs Course - Application of Rule 18 in Narrow Channels or Fairways Where Rule 9 Appliesamirsyawal87Nessuna valutazione finora
- Describe The Connection Between "Diurnal Variation" & "Relative Humidity"Documento35 pagineDescribe The Connection Between "Diurnal Variation" & "Relative Humidity"amirsyawal87Nessuna valutazione finora
- Can Peer Education Make A Difference? Evaluation of A South African Adolescent Peer Education Program To Promote Sexual and Reproductive HealthDocumento10 pagineCan Peer Education Make A Difference? Evaluation of A South African Adolescent Peer Education Program To Promote Sexual and Reproductive Healthamirsyawal87Nessuna valutazione finora
- OCIMF - Mooring Equipment Guidelines (MEG) : Joe Megeed - Technical Adviser (Engineering)Documento19 pagineOCIMF - Mooring Equipment Guidelines (MEG) : Joe Megeed - Technical Adviser (Engineering)Fernando Raúl LADINO100% (1)
- Blind Pilotage PDFDocumento6 pagineBlind Pilotage PDFamirsyawal87Nessuna valutazione finora
- Passage Plan Appraisal - MeteorologyDocumento26 paginePassage Plan Appraisal - Meteorologyamirsyawal87Nessuna valutazione finora
- T2 Pilot LadderDocumento33 pagineT2 Pilot Ladderamirsyawal87Nessuna valutazione finora
- Define INS & IBS and State Their Purpose: Integrated Navigation System (Ins)Documento8 pagineDefine INS & IBS and State Their Purpose: Integrated Navigation System (Ins)amirsyawal87Nessuna valutazione finora
- Four Stroke Diesel EngineDocumento17 pagineFour Stroke Diesel Engineamirsyawal87Nessuna valutazione finora
- Catalogue 2018Documento161 pagineCatalogue 2018amirsyawal87Nessuna valutazione finora
- Navigational Safety in The Straits of Malacca: Current and Future ConcernDocumento32 pagineNavigational Safety in The Straits of Malacca: Current and Future Concernamirsyawal87100% (1)
- 6 Methods of Data Collection PDFDocumento30 pagine6 Methods of Data Collection PDFKristine Agustin100% (4)
- VDR PDFDocumento9 pagineVDR PDFamirsyawal87Nessuna valutazione finora
- Waterline: Load Line or Water Line (PositionedDocumento13 pagineWaterline: Load Line or Water Line (Positionedamirsyawal87Nessuna valutazione finora
- VDR N SVDRDocumento41 pagineVDR N SVDRamirsyawal87Nessuna valutazione finora
- INS N IBSDocumento37 pagineINS N IBSamirsyawal87Nessuna valutazione finora
- LESSON 5 - Effect of Slack Tanks Group 5Documento1 paginaLESSON 5 - Effect of Slack Tanks Group 5amirsyawal87100% (1)
- LESSON 7 - Loss of Intact of Bouyancy Group 7Documento2 pagineLESSON 7 - Loss of Intact of Bouyancy Group 7amirsyawal87100% (1)
- Rasc Starfinder English BW PDFDocumento2 pagineRasc Starfinder English BW PDFamirsyawal87Nessuna valutazione finora
- Lesson 4 - Fresh Water Allowance Group 4Documento3 pagineLesson 4 - Fresh Water Allowance Group 4amirsyawal87Nessuna valutazione finora
- What Is Trim?: Changed by Moving Masses Already On Board Forward or AFTDocumento2 pagineWhat Is Trim?: Changed by Moving Masses Already On Board Forward or AFTamirsyawal87Nessuna valutazione finora
- Marine Aluminum Accommodation Ladder - Buy Accommodation Ladder, Marine Accommodation Ladder, Aluminum Accommodation Ladder Product OnDocumento11 pagineMarine Aluminum Accommodation Ladder - Buy Accommodation Ladder, Marine Accommodation Ladder, Aluminum Accommodation Ladder Product Onamirsyawal87Nessuna valutazione finora
- Safe Anchoring Factors to ConsiderDocumento8 pagineSafe Anchoring Factors to ConsiderSetiadi MargonoNessuna valutazione finora
- LESSON 2 - DisplacementDocumento2 pagineLESSON 2 - Displacementamirsyawal87Nessuna valutazione finora
- Understand ship stability with principles of draught, trim and hydrostatic particularsDocumento2 pagineUnderstand ship stability with principles of draught, trim and hydrostatic particularsamirsyawal87Nessuna valutazione finora
- 2014-Safe Passage Pamphlet - Straits of MalaccaDocumento9 pagine2014-Safe Passage Pamphlet - Straits of Malaccadhaneshbhor100% (5)
- FMHM GTU Study Material E-Notes Unit-2 04042021064559PMDocumento13 pagineFMHM GTU Study Material E-Notes Unit-2 04042021064559PMDarshana GajjarNessuna valutazione finora
- Hydraulic Principles Unit2l1Documento26 pagineHydraulic Principles Unit2l1KJDNKJZEFNessuna valutazione finora
- Section - 06 Displacement ProceduresDocumento4 pagineSection - 06 Displacement ProceduresIbrahim DewaliNessuna valutazione finora
- Calculation of Draft SurveyDocumento27 pagineCalculation of Draft Surveysaif100% (1)
- Practical 2 GuideDocumento2 paginePractical 2 GuideJeffrey PiggottNessuna valutazione finora
- Effects of Density on Ship Draft and DisplacementDocumento33 pagineEffects of Density on Ship Draft and Displacementjeth saganaNessuna valutazione finora
- Buoyancy and Stability ExplainedDocumento47 pagineBuoyancy and Stability ExplainedPhilimond SegieNessuna valutazione finora
- Buoyant Force of WaterDocumento2 pagineBuoyant Force of Watermrdkm37Nessuna valutazione finora
- Density: Density Is Mass Per Unit Volume of A Substance. (G/CC)Documento7 pagineDensity: Density Is Mass Per Unit Volume of A Substance. (G/CC)حمامة السلامNessuna valutazione finora
- Density Teaching PackDocumento32 pagineDensity Teaching Packvinaazfiana75% (4)
- sc-1114-2011 (Abhaya Case)Documento229 paginesc-1114-2011 (Abhaya Case)PGurusNessuna valutazione finora
- Phases Complete: Select All That ApplyDocumento2 paginePhases Complete: Select All That ApplyMarc Ronald de LeonNessuna valutazione finora
- Work5450 ShortDocumento38 pagineWork5450 ShortMohamed IbrahimNessuna valutazione finora
- Storage Tank Design Calculation - Api 650Documento21 pagineStorage Tank Design Calculation - Api 650miteshpatel191100% (1)
- Development of A Standard Method For Measuring The Buoyancy-to-Weight Ratio For Oil Spill Containment BoomDocumento28 pagineDevelopment of A Standard Method For Measuring The Buoyancy-to-Weight Ratio For Oil Spill Containment Boomjohny BavitoNessuna valutazione finora
- 13 Calculations - v1 - 6404250 - 01Documento77 pagine13 Calculations - v1 - 6404250 - 01Eslam Atif AzkolNessuna valutazione finora
- UPCH15EXDocumento13 pagineUPCH15EXHizbar ArsjadNessuna valutazione finora
- General Interview Questions GMEDocumento19 pagineGeneral Interview Questions GMEAthul P PNessuna valutazione finora
- B. Meter: Introductory Physics 1 Test #1 - Unit 1 To 3 Multiply Choices - Answer All QuestionsDocumento7 pagineB. Meter: Introductory Physics 1 Test #1 - Unit 1 To 3 Multiply Choices - Answer All Questionscondoleeza smithNessuna valutazione finora
- ASTM C474 - Standard Test Methods For Joint Treatment Materials For Gypsum Board ConstructionDocumento12 pagineASTM C474 - Standard Test Methods For Joint Treatment Materials For Gypsum Board Constructionedd11040% (1)
- Physics in Details g10-12Documento131 paginePhysics in Details g10-12Andrea Maluba100% (2)
- ASTM D2395-83 (1997) E1 Specific Gravity of Wood and Wood-Based MaterialsDocumento8 pagineASTM D2395-83 (1997) E1 Specific Gravity of Wood and Wood-Based MaterialsĐỗ Thanh TùngNessuna valutazione finora
- Solution Derivations For Capa #14: I o Liq 3Documento10 pagineSolution Derivations For Capa #14: I o Liq 3tony lordNessuna valutazione finora
- Air Purge or Air Bubbler Level Measurement Instrumentation ToolsDocumento7 pagineAir Purge or Air Bubbler Level Measurement Instrumentation Toolskali bangonNessuna valutazione finora
- Archimedes Principle Determines Copper Block DensityDocumento4 pagineArchimedes Principle Determines Copper Block DensityAhmad Shahir ShakriNessuna valutazione finora
- PerforationDocumento3 paginePerforationTeguh Akbar HarahapNessuna valutazione finora
- Lab Manual Physics I Sem 1 2022-2023Documento41 pagineLab Manual Physics I Sem 1 2022-2023ahmad yasinNessuna valutazione finora
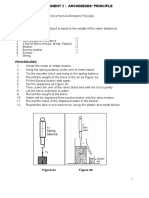
- Experiment 2: Archimedes' Principle: ObjectiveDocumento2 pagineExperiment 2: Archimedes' Principle: Objective1031 NakiudinNessuna valutazione finora
- Tructure of CBSE Class 9 Maths Sample Paper 2019 Is As FollowsDocumento32 pagineTructure of CBSE Class 9 Maths Sample Paper 2019 Is As FollowsHARISHNessuna valutazione finora
- Chemistry LiquidsDocumento20 pagineChemistry LiquidsNishanth Thamizh SelvanNessuna valutazione finora