Documenti di Didattica
Documenti di Professioni
Documenti di Cultura
F&G System
Caricato da
JayJayTitolo originale
Copyright
Formati disponibili
Condividi questo documento
Condividi o incorpora il documento
Hai trovato utile questo documento?
Questo contenuto è inappropriato?
Segnala questo documentoCopyright:
Formati disponibili
F&G System
Caricato da
JayJayCopyright:
Formati disponibili
EPS - Fire And Gas
Page 1 of 6
This package is divided into the following main headings:
l
l
l
l
l
Introduction
Objectives
Principles of Operation
Summary
Self Test
Introduction
The overall aim of a Fire and Gas System is to monitor all air spaces where a fire or
accumulation of a potentially flammable mixture may occur and to detect these events, alert
personnel and initiate timely executive actions in order to minimize the consequences of the
event.
Objectives
Upon completion of this package, you should be able to:
l
l
l
l
l
Explain which automatic executive actions are initiated upon fire detection.
List the different types of fire detection system in use.
Describe the different types of gas detectors in use.
Explain what considerations are given to the selection of detectors for different types of area.
List the interfaces between the fire and gas system and other systems.
Principles of Operation
The Fire and Gas system consists of a fire and gas control panel located in the CCR and a number of
detectors located at various points throughout the facility. The fire and gas panel is integrated into the
overall Process Shutdown and Monitoring System thereby providing the operator with a display of the
complete status of the facility.
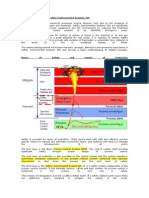
The EPF will normally be subdivided into a number of separate fire zones each with its own set of fire
and gas detectors and separate fire protection. Subdivision is determined on an individual basis for each
plant and such factors as naturally occurring fire barriers (fire walls, bulkheads, physical separation),
capacity of the fire water system and the specific hazards present in each area are considered. For
compact plants where there are no inherent fire barriers, the entire process area and wellhead area is
considered a single fire zone. In general, the installation of fire walls for the sole purpose of dividing one
part of the plant from another for the purposes of zoning is not considered.
Typical zoning would be:
l
Wellhead area (Zone 1)
https://elc.melun.eur.slb.com/onlinetraining/well_testing/eps/control/f&g/fire-gas-body.htm 22/11/2005
EPS - Fire And Gas
l
l
l
l
Page 2 of 6
Process area (Zone 2)
Central control room (Zone 3)
Electrical rooms (Zone 4)
Utilities area (Zone 5)
The operator interface with the fire and gas system is the CCR Panel and/or workstations. Individual gas
LEL levels are displayed.
Maintenance bypass facilities are provided to facilitate online testing of the fire and gas system. Fire and
gas alarms are displayed on the first-up alarm annunciator.
All input and output signals to the fire and gas panel are individually hardwired.
The fire and gas system automatically initiates fire protection systems on detection of fire.
The fire and gas system interfaces with the ESD system to initiate automatic shutdown and/or blowdown
of the process plant.
Fire Detection
Fires are detected using a combination of the following:
l
l
l
l
Fusible loop heat detection (plastic tube)
Infrared flame detectors
Rate of rise heat detectors
Smoke detectors
The selection of detector type considers the probable type of fire in each area and the limitations of each
detector with respect to its ability to detect a fire in the specific environment. (i.e., smoke detection is
only suitable for use in confined spaces such as control rooms and switchgear rooms.) In high risk areas
and in areas where the consequential damage from a fire is great, two types of detection shall be used.
Typical selection of fire detection would be:
l
l
l
l
The wellhead area - fusible loop heat detection system.
Process area - fusible loop heat detection and infrared flame detectors.
Control room and electrical rooms - optical smoke detectors and infrared flame detectors.
Enclosed machinery spaces - infrared flame detectors and rate of rise heat detectors. (In general,
ventilation rates in these areas are too high for smoke detectors to work satisfactorily.)
To reduce the incidence of spurious trips, IR flame detectors and smoke detectors will be voted on the
basis of any two detectors in the area. Sensing a fire shall cause executive action. Detection by a single
detector shall initiate a fire alarm. Where voting is employed, there shall be a minimum of three
detectors of the same type in a fire zone.
Automatic Executive Actions
Upon fire detection, the following executive actions shall be automatically initiated, wherever
applicable:
https://elc.melun.eur.slb.com/onlinetraining/well_testing/eps/control/f&g/fire-gas-body.htm 22/11/2005
EPS - Fire And Gas
l
l
l
l
Page 3 of 6
Isolation and disposal of hydrocarbon inventories.
Isolate energy supplies by shutdown of equipment .
Release of active fire protection systems (where installed).
Start firewater pumps.
The first two actions are initiated by the fire and gas system and executed via the process ESD system.
Active fire protection systems are released directly by the fire and gas system.
Facilities for remote and local manual release of fire protection are also provided.
Gas Detection
Gas detection systems are designed to detect potentially hazardous accumulations of flammable and
toxic gas. (Toxic gas detection is only installed when the crude oil is predicted to contain H 2S.) The
presence of gas will be detected using a combination of the following types of detectors:
l
l
l
l
Catalytic type flammable gas detectors
Point type infrared gas detectors
Open path type infrared gas detectors
Catalytic type H 2S detectors
H2 S detectors raise alarms at 10 ppm and 20 ppm but do not initiate any executive actions.
The selection of detector type considers the type of gas which can be present in each area, the ventilation
systems and the physical layout of the equipment in the area.
When selecting gas detectors, consideration is also given to the long term reliability and stability of the
detectors. Infrared detectors are more expensive than catalytic types but do not suffer from the problems
of catalyst poisoning which reduces the sensitivity of catalytic types. Furthermore, IR detectors
incorporate fault monitoring circuitry to alert operators if a detector fails or loses sensitivity. Loss of
sensitivity of a catalytic type detector can only be determined by testing the detector. For this reason,
infrared detectors are recommended for longer term contracts where the saving in maintenance and
detector replacement will offset the higher capital cost of the detectors.
It is also possible to cover a larger area of the plant with a smaller number of detectors using open path
type IR technology. For this reason, open path type detectors are recommended for coverage of large
open areas irrespective of the duration of the contract.
Gas detection is always installed in or adjacent to the ventilation inlets serving control rooms,
switchrooms and enclosed equipment spaces.
Catalytic type flammable gas detectors initiate alarms and shutdowns as follows:
l
l
l
One detector sensing gas at 20% LEL - low gas warning.
One detector sensing gas at 60% LEL - high gas alarm.
Two detectors in the same zone sensing gas at 60% LEL - shutdown and blowdown of the plant.
Point type infrared gas detectors (if used) initiate alarms and shutdowns as follows:
https://elc.melun.eur.slb.com/onlinetraining/well_testing/eps/control/f&g/fire-gas-body.htm 22/11/2005
EPS - Fire And Gas
l
l
l
Page 4 of 6
One detector sensing gas at 20% LEL - gas warning.
Two detectors in the same zone sensing gas at 20% LEL - shutdown and blowdown of the plant.
One detector sensing gas at 60% LEL - shutdown and blowdown of the plant.
Open path type infrared gas detectors (if used) shall initiate alarms and shutdowns as follows:
l
l
One detector sensing gas at 1 LEL meter - low gas warning.
One detector sensing gas at 3 LEL meters - shutdown and blowdown of the plant.
Gas detection levels are displayed in the central control room to allow the operator to assess the
magnitude, location and extent of a gas release.
A typical selection of detectors would be:
l
l
l
l
l
Wellhead area - Two open path IR gas detectors
Process area - Four open path IR gas detectors, four point type IR gas detectors
Control room - Two point type IR gas detectors (one inside, one in ventilation inlet)
Electrical room - Two point type IR gas detectors (one inside, one in ventilation inlet)
Enclosed machinery space - Two point type IR gas detectors (one inside, one in ventilation inlet)
To achieve the same level of coverage with catalytic type detectors the following would be a typical
selection:
l
l
l
l
l
Wellhead area - Four detectors
Process area - Twelve detectors
Control room - Six detectors (three inside, three in ventilation inlet)
Electrical room - Six detectors (three inside, three in ventilation inlet)
Enclosed machinery space - Six detectors (three inside, three in ventilation inlet)
Manual Detection
In addition to automatic detection of fire and gas, it is essential to provide a means by which personnel
throughout the installation can quickly alert the operator at the continuously manned CCR of any
hazardous event and its approximate location.
Therefore two separate manual detection systems are provided.
1. The first system is for general alarm and comprises a number of Manual Alarm Call (MAC)
break-glass stations located at strategic locations throughout the facility. These will initiate an
alarm on the alarm annunciator in the CCR and an audible alarm outdoors in the process facility.
2. The other is intended to be used in the event of a process incident and shall initiate a Surface
Process Shutdown (SPS) via the process ESD system.
Alarms
An audible alarm is installed in the process area (and visual alarm in high noise areas) to alert operators
in the area of potentially hazardous situations. This alarm sounds automatically for the following events:
l
l
Manual call point operated
Fire alarm for any reason
https://elc.melun.eur.slb.com/onlinetraining/well_testing/eps/control/f&g/fire-gas-body.htm 22/11/2005
EPS - Fire And Gas
l
l
Page 5 of 6
Flammable gas detected at any level
Toxic gas detected
Interface with Other Systems
Process ESD System
Rig Systems (Offshore Installations)
From process F&G System:
l
l
l
l
Start firewater pump
Fire detected
Gas detected (low level)
Gas detected (high level)
From rig to process F&G System
l
l
Fire detected
Gas detected
Summary
In this training page, we have discussed the following points:
l
l
l
l
The types of fire detectors in use.
The types of smoke and gas detectors in use.
The automatic executive actions taken upon fire detection.
The suitability of detectors for the area's in which they work.
Self Test
1.
2.
3.
4.
5.
6.
7.
8.
9.
10.
List the four types of fire detector currently in use.
Explain the voting system employed for use with IR detectors and smoke detectors.
Explain what executive actions are initiated upon fire detection.
List the four types of gas detectors currently in use.
What is the function and limitations of the H 2S detectors.
What are the advantages/disadvantages of IR detectors compared with catalytic type detectors.
Which types of detectors would you expect to find in the well head area?
Which types of detectors would you expect to find in the control room?
What minimum events must raise an alarm in the process area?
What other systems interface with the Fire and Gas system?
Your feedback about the information presented in this topic is welcome.
https://elc.melun.eur.slb.com/onlinetraining/well_testing/eps/control/f&g/fire-gas-body.htm 22/11/2005
EPS - Fire And Gas
Page 6 of 6
Send any comments, suggestions, or questions to Lee_Dixon-Cave.
A list of references on this topic is available.
You can access the original graphics presented in this topic and use them to build your own
presentations.
https://elc.melun.eur.slb.com/onlinetraining/well_testing/eps/control/f&g/fire-gas-body.htm 22/11/2005
Potrebbero piacerti anche
- KOC-E-004 Pt. 2Documento18 pagineKOC-E-004 Pt. 2Nagarajakumar DNessuna valutazione finora
- Essentials On Safety Instrumented SystemsDocumento9 pagineEssentials On Safety Instrumented Systemstibi1000Nessuna valutazione finora
- FNG Detectors SpecificationsDocumento33 pagineFNG Detectors Specificationssuhailfarhaan100% (1)
- Gas and Fire Detection in Tank AreasDocumento3 pagineGas and Fire Detection in Tank Areasstavros7Nessuna valutazione finora
- Hockney-Falco Thesis: 1 Setup of The 2001 PublicationDocumento6 pagineHockney-Falco Thesis: 1 Setup of The 2001 PublicationKurayami ReijiNessuna valutazione finora
- Instrument Engineer ManualDocumento31 pagineInstrument Engineer ManualRonald ImmanuelNessuna valutazione finora
- Sensorselection and PlacementDocumento4 pagineSensorselection and Placementnirbhay111Nessuna valutazione finora
- Fire ProtectionDocumento14 pagineFire ProtectionTeguh SetionoNessuna valutazione finora
- DP Transmitter Interface Level Measurement Principle, Limitations, Selection, Installation, Design & CalibrationDocumento12 pagineDP Transmitter Interface Level Measurement Principle, Limitations, Selection, Installation, Design & CalibrationsubbaraoNessuna valutazione finora
- Eng Standard F&G SystemsDocumento16 pagineEng Standard F&G Systemsytd7524Nessuna valutazione finora
- Fire & Gas Capability BrochureDocumento7 pagineFire & Gas Capability BrochureNazeeruddin MohammedNessuna valutazione finora
- Proceedings-Agile Technical Conference 2020Documento201 pagineProceedings-Agile Technical Conference 2020Enpak ArsalanNessuna valutazione finora
- Fire and Gas Detection in ProcessDocumento50 pagineFire and Gas Detection in ProcessRizwan FaridNessuna valutazione finora
- PM - Man.6590-Fire and Gas Solution Manual (SM)Documento52 paginePM - Man.6590-Fire and Gas Solution Manual (SM)gil ClaroNessuna valutazione finora
- Managing Obsolete Technologies - Strategies and PracticesDocumento30 pagineManaging Obsolete Technologies - Strategies and PracticescarakooloNessuna valutazione finora
- DH 81 Open Path Detectors atDocumento4 pagineDH 81 Open Path Detectors atAnthonyNessuna valutazione finora
- BIS - RFID - School Children - F PDFDocumento12 pagineBIS - RFID - School Children - F PDF27051995Nessuna valutazione finora
- Fire & Gas Detection SystemDocumento35 pagineFire & Gas Detection SystemShakeel AhmedNessuna valutazione finora
- ISATR84Documento6 pagineISATR84checito49100% (1)
- Temperature Measuring Instruments Selection & ApplicationDocumento70 pagineTemperature Measuring Instruments Selection & ApplicationIrfan AliNessuna valutazione finora
- On-Line Gas ChromatographsDocumento52 pagineOn-Line Gas Chromatographstuanlq73Nessuna valutazione finora
- Scada BasicsDocumento41 pagineScada Basicskarkey82Nessuna valutazione finora
- SIL Explained: Fluid Power Actuators and Control SystemsDocumento8 pagineSIL Explained: Fluid Power Actuators and Control Systemsprihartono_diasNessuna valutazione finora
- Basic Fundamentals of Safety Instrumented Systems SISDocumento3 pagineBasic Fundamentals of Safety Instrumented Systems SIScalixtohenriquezNessuna valutazione finora
- Calculate IDMT Over Current Relay Setting 50 51 Electrical Notes Articles PDFDocumento5 pagineCalculate IDMT Over Current Relay Setting 50 51 Electrical Notes Articles PDFVelu SamyNessuna valutazione finora
- Sabp J 900Documento9 pagineSabp J 900Hassan MokhtarNessuna valutazione finora
- F&G Detection System: Fire & Gas Detection LayoutDocumento15 pagineF&G Detection System: Fire & Gas Detection LayoutRamesh IyerNessuna valutazione finora
- "Namur Standard" Sensors: Process Control - Factory Automation - Explosion Protection - Machine SafetyDocumento2 pagine"Namur Standard" Sensors: Process Control - Factory Automation - Explosion Protection - Machine SafetySaqueib Khan100% (1)
- Fire and Gas in The Process Industry Jon Hind PaperDocumento40 pagineFire and Gas in The Process Industry Jon Hind PaperLieu Dinh PhungNessuna valutazione finora
- IOT Based School Children Transportation Safety SystemDocumento3 pagineIOT Based School Children Transportation Safety Systemkadudula pranavi kumariNessuna valutazione finora
- Foundation Fieldbus Safety InstrumentedDocumento20 pagineFoundation Fieldbus Safety InstrumentedmoralesmjyNessuna valutazione finora
- IDC Conference 2012 - Proof Test Procedure Effectiveness On Safety Instrumented SystemsDocumento25 pagineIDC Conference 2012 - Proof Test Procedure Effectiveness On Safety Instrumented SystemsNaresh BajajNessuna valutazione finora
- Loop Calibration PrinciplesDocumento4 pagineLoop Calibration PrinciplesrenvNessuna valutazione finora
- Detector Placement and ConfigurationDocumento35 pagineDetector Placement and Configurationasimozma100% (1)
- REVISED Flow Measurement Course Syllabus-NewDocumento2 pagineREVISED Flow Measurement Course Syllabus-NewKevin Pelaez CardenasNessuna valutazione finora
- Evolution of Process Hazard Analysis in An Oil & Gas Pipeline Company: From Ad-Hoc To An Enterprise Standard PracticeDocumento10 pagineEvolution of Process Hazard Analysis in An Oil & Gas Pipeline Company: From Ad-Hoc To An Enterprise Standard PracticeMarcelo Varejão CasarinNessuna valutazione finora
- Flow ComputersDocumento11 pagineFlow ComputersKarthik ChockkalingamNessuna valutazione finora
- Partial Stroke Testing With Positioners and or Logic SolversDocumento6 paginePartial Stroke Testing With Positioners and or Logic Solversusman379Nessuna valutazione finora
- Level Transmitter - DP TypeDocumento1 paginaLevel Transmitter - DP TypeSreejesh SundaresanNessuna valutazione finora
- Industrial VariablesDocumento59 pagineIndustrial VariablesMuhamad RidzwanNessuna valutazione finora
- MAFMA Multi Attribute Failure Mode AnalyDocumento17 pagineMAFMA Multi Attribute Failure Mode AnalyRubenNessuna valutazione finora
- Smart Meter Verification & ProvingDocumento7 pagineSmart Meter Verification & ProvingdianyvgnNessuna valutazione finora
- Process Analyzer Sampling System TrainingDocumento3 pagineProcess Analyzer Sampling System TrainingPhilNessuna valutazione finora
- Oil&Gas Hazard ZonesDocumento31 pagineOil&Gas Hazard ZonesrakicbgNessuna valutazione finora
- Appendix-2 SRS 03112016Documento15 pagineAppendix-2 SRS 03112016Qayyum KhanNessuna valutazione finora
- F&GS LeakDetection SIL PDFDocumento44 pagineF&GS LeakDetection SIL PDFAlvaro José Rodríguez Talavera100% (1)
- Sensepoint XCD TechMan MAN0873 Iss8 0913 EMEAIDocumento84 pagineSensepoint XCD TechMan MAN0873 Iss8 0913 EMEAImusajcNessuna valutazione finora
- Hazardous Classification Under Electrical SafetyDocumento98 pagineHazardous Classification Under Electrical SafetyMark WardNessuna valutazione finora
- Fire & Gas System (FGS) Integrity Analysis: KenexisDocumento51 pagineFire & Gas System (FGS) Integrity Analysis: KenexisBaba JohnehNessuna valutazione finora
- Distributed Control System Slide Group 8 FinalDocumento20 pagineDistributed Control System Slide Group 8 FinalTakudzwa MatangiraNessuna valutazione finora
- 01 Installation of Ratio Flow ControllersDocumento1 pagina01 Installation of Ratio Flow ControllersBrandon TrocNessuna valutazione finora
- Desmoke System p.155-173Documento19 pagineDesmoke System p.155-173Just RysdanNessuna valutazione finora
- Dissolved Oxygen Analyzer Working Principle Instrumentation ToolsDocumento3 pagineDissolved Oxygen Analyzer Working Principle Instrumentation ToolsAbarajithan RajendranNessuna valutazione finora
- Hazardous Area ClassificationDocumento7 pagineHazardous Area Classificationhassenova.kNessuna valutazione finora
- Flow-X Flow ComputerDocumento12 pagineFlow-X Flow ComputerKuan Yue ChanNessuna valutazione finora
- Fire PreventionDocumento26 pagineFire PreventionABHISHEKNessuna valutazione finora
- Basics of Sample System DesigningDocumento14 pagineBasics of Sample System DesigningJAY PARIKHNessuna valutazione finora
- Fire & Gas Detection and Alarm SystemsDocumento17 pagineFire & Gas Detection and Alarm Systemseliud03Nessuna valutazione finora
- Fire Detection SystemDocumento38 pagineFire Detection Systemkhalid najjarNessuna valutazione finora
- Fire Detection & Alarm SystemDocumento30 pagineFire Detection & Alarm SystemmohideenNessuna valutazione finora
- Topic IV Fire and Gas SystemDocumento13 pagineTopic IV Fire and Gas SystemJulius ChavezNessuna valutazione finora
- OTIS Elevator Weekly Inspection Checklist Revision 28 December 2019.Documento2 pagineOTIS Elevator Weekly Inspection Checklist Revision 28 December 2019.JayJayNessuna valutazione finora
- 2015 Highlander Product Information: Matrix SiennaDocumento10 pagine2015 Highlander Product Information: Matrix SiennaJayJayNessuna valutazione finora
- How To Calibrate Level Troll PDFDocumento3 pagineHow To Calibrate Level Troll PDFJayJayNessuna valutazione finora
- MS-MP01473 IT HandbookDocumento30 pagineMS-MP01473 IT HandbookJayJayNessuna valutazione finora
- Ap Lifting Gear Limited: Offshore Time Sheet/Job Completion CertificateDocumento1 paginaAp Lifting Gear Limited: Offshore Time Sheet/Job Completion CertificateJayJayNessuna valutazione finora
- Electrical TroubleshootingDocumento9 pagineElectrical TroubleshootingJayJay40% (5)
- Vacant PositionsDocumento3 pagineVacant PositionsJayJayNessuna valutazione finora
- Img 20150510 0001Documento2 pagineImg 20150510 0001api-284663984Nessuna valutazione finora
- Python in Hidrology BookDocumento153 paginePython in Hidrology BookJuan david Gonzalez vasquez100% (1)
- Registration ListDocumento5 pagineRegistration ListGnanesh Shetty BharathipuraNessuna valutazione finora
- Precursor Effects of Citric Acid and Citrates On Zno Crystal FormationDocumento7 paginePrecursor Effects of Citric Acid and Citrates On Zno Crystal FormationAlv R GraciaNessuna valutazione finora
- The Palestinian Centipede Illustrated ExcerptsDocumento58 pagineThe Palestinian Centipede Illustrated ExcerptsWael HaidarNessuna valutazione finora
- Dutch Iris Eng 9734 HappyPattyCrochetDocumento68 pagineDutch Iris Eng 9734 HappyPattyCrochetFrancisca Rico100% (6)
- Pioneer 1019ah-K Repair ManualDocumento162 paginePioneer 1019ah-K Repair ManualjekNessuna valutazione finora
- Ch-10 Human Eye Notes FinalDocumento27 pagineCh-10 Human Eye Notes Finalkilemas494Nessuna valutazione finora
- Song Book Inner PagesDocumento140 pagineSong Book Inner PagesEliazer PetsonNessuna valutazione finora
- Math F112Documento3 pagineMath F112ritik12041998Nessuna valutazione finora
- ABARI-Volunteer Guide BookDocumento10 pagineABARI-Volunteer Guide BookEla Mercado0% (1)
- Safety Data Sheet SDS For CB-G PG Precision Grout and CB-G MG Multipurpose Grout Documentation ASSET DOC APPROVAL 0536Documento4 pagineSafety Data Sheet SDS For CB-G PG Precision Grout and CB-G MG Multipurpose Grout Documentation ASSET DOC APPROVAL 0536BanyuNessuna valutazione finora
- OM CommandCenter OI SEP09 enDocumento30 pagineOM CommandCenter OI SEP09 enGabriely MuriloNessuna valutazione finora
- Job Satisfaction VariableDocumento2 pagineJob Satisfaction VariableAnagha Pawar - 34Nessuna valutazione finora
- W.C. Hicks Appliances: Client Name SKU Item Name Delivery Price Total DueDocumento2 pagineW.C. Hicks Appliances: Client Name SKU Item Name Delivery Price Total DueParth PatelNessuna valutazione finora
- Been There, Done That, Wrote The Blog: The Choices and Challenges of Supporting Adolescents and Young Adults With CancerDocumento8 pagineBeen There, Done That, Wrote The Blog: The Choices and Challenges of Supporting Adolescents and Young Adults With CancerNanis DimmitrisNessuna valutazione finora
- Vitamins - CyanocobalaminDocumento12 pagineVitamins - CyanocobalaminK PrashasthaNessuna valutazione finora
- Manuel SYL233 700 EDocumento2 pagineManuel SYL233 700 ESiddiqui SarfarazNessuna valutazione finora
- Inspección, Pruebas, Y Mantenimiento de Gabinetes de Ataque Rápido E HidrantesDocumento3 pagineInspección, Pruebas, Y Mantenimiento de Gabinetes de Ataque Rápido E HidrantesVICTOR RALPH FLORES GUILLENNessuna valutazione finora
- Sundar Pichai PDFDocumento6 pagineSundar Pichai PDFHimanshi Patle100% (1)
- 9400 Series - Catalogue - AccessoriesDocumento86 pagine9400 Series - Catalogue - AccessoriesSaulo Leonardo Fabelo FontesNessuna valutazione finora
- DB Lecture Note All in ONEDocumento85 pagineDB Lecture Note All in ONEyonasante2121Nessuna valutazione finora
- Pubb-0589-L-Rock-mass Hydrojacking Risk Related To Pressurized Water TunnelsDocumento10 paginePubb-0589-L-Rock-mass Hydrojacking Risk Related To Pressurized Water Tunnelsinge ocNessuna valutazione finora
- The Linguistic Colonialism of EnglishDocumento4 pagineThe Linguistic Colonialism of EnglishAdriana MirandaNessuna valutazione finora
- Toh736 - 84000 The Dharani of Parnasavari PDFDocumento24 pagineToh736 - 84000 The Dharani of Parnasavari PDFJames LeeNessuna valutazione finora
- SIVACON 8PS - Planning With SIVACON 8PS Planning Manual, 11/2016, A5E01541101-04Documento1 paginaSIVACON 8PS - Planning With SIVACON 8PS Planning Manual, 11/2016, A5E01541101-04marcospmmNessuna valutazione finora
- 4.2.4.5 Packet Tracer - Connecting A Wired and Wireless LAN InstructionsDocumento5 pagine4.2.4.5 Packet Tracer - Connecting A Wired and Wireless LAN InstructionsAhmadHijaziNessuna valutazione finora
- ST Arduino Labs CombinedDocumento80 pagineST Arduino Labs CombineddevProNessuna valutazione finora
- SEILDocumento4 pagineSEILGopal RamalingamNessuna valutazione finora