Documenti di Didattica
Documenti di Professioni
Documenti di Cultura
Actvity Sheets Genetics
Caricato da
api-340406981Titolo originale
Copyright
Formati disponibili
Condividi questo documento
Condividi o incorpora il documento
Hai trovato utile questo documento?
Questo contenuto è inappropriato?
Segnala questo documentoCopyright:
Formati disponibili
Actvity Sheets Genetics
Caricato da
api-340406981Copyright:
Formati disponibili
SAN FELIPE NERI PAROCHIAL SCHOOL
PAASCU ACCREDITED LEVEL II
SCIENCE DEPARTMENT
NAME : _______________________
_____________
DATE : _______________________
SECTION
SCORE
: _____________
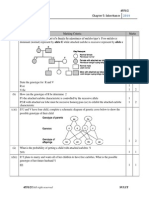
ACTIVITY # 1
Objectives:
1. Diagram and complete a Punnett square
2. Give the genotypic and phenotypic percentages of the offspring
3. Infer the unknown phenotypes of individuals on the basis of the known
phenotypes
BACKGROUND: A long time ago, in a galaxy far, far away, a great race of beings lived
on a planet called ZORK. The inhabitants were known as Zorkonians. They are made
up of 10 basic genes (unit) that code for their appearance. Each one of these genes is
made up 2 alleles (traits). With this in mind, there are 1,024 different possible
combinations for their appearance! This is called their phenotype or their physical
appearance. If we look at their genes, there are 59,049 different combinations of the
alleles! This is called the genotype or genetic makeup. Remember that we use letters
for the alleles that control the genes and one letter or allele is inherited from each
parent. You will be using Zorks, who use the same genetic principles as a pea plant, to
see how genes are passed on and inherited. You will be using Punnett Squares to do
this.
Here are some things to help you. You must understand these concepts and terms! I
will use traits from the table on the next page as examples.
Phenotype: The physical appearance or what the gene makes an organism look like.
Examples would be two eyes, yellow hair, and green lips from a zork.
1. Dominant: The trait that is shown the most. Example: Green hair is dominant over
yellow hair.
2. Recessive: The trait that is hidden. In this example: yellow hair.
Genotype: The genetic makeup of an organism. We use letters for the genotype.
Remember that you need to look at the genotype to see what the phenotype will be.
Example: There is a Gene or unit for hair color in a zork. The alleles or traits (individual
genes) for hair color would be yellow and green. There are 2 alleles for each gene and
we use letters for each allele. The capital letters are the dominant alleles and the lower
case letters are the recessive alleles.
Gene
Allele
Hair color
1. Green color = G
2. Yellow color = g
Parents Signature: _______________ Teachers Signature: _______________
_______
Date:
SAN FELIPE NERI PAROCHIAL SCHOOL
PAASCU ACCREDITED LEVEL II
SCIENCE DEPARTMENT
1. Heterozygous: The term used for different alleles. There is always
one dominant and one recessive allele. Example: Gg. There is only one
possibility for this!
2. Homozygous: The term used for having the same alleles. This will be either 2
dominant alleles or 2 recessive alleles. Example: GG or gg. There are 2 possibilities
for this!
Please refer back to this to help you as you work through this assignment. You will use
the table on the next page to complete the problems that follow. Everything you need is
in the table! The following are the traits of a Zork, which we will use to study genetics.
You will be studying one family. Be sure to read each problem carefully, because in
each case the information is built upon the previous problem.
Parents Signature: _______________ Teachers Signature: _______________
_______
Date:
SAN FELIPE NERI PAROCHIAL SCHOOL
PAASCU ACCREDITED LEVEL II
SCIENCE DEPARTMENT
SINGLE CROSS PROBLEMS
1. Cross a heterozygous green skinned zork with a yellow skinned zork.
A. What do the possible offspring look like?
2. Cross a homozygous two horned zork with a heterozygous two horned zork.
A. What are the genotypes of the possible offspring?
3. Cross a heterozygous green haired zork with a heterozygous green haired zork.
A. What are the genotypes and phenotypes of the possible offspring?
4. Cross a green lipped zork with a heterozygous purple lipped zork.
A. What are the number of phenotypes and genotypes of the offspring? Hint:
Count what is in the boxes!
5. Tork, who is homozygous for tall meets Vorkina, who is short.
A. What are the phenotypes and genotypes if they were to have offspring?
Parents Signature: _______________ Teachers Signature: _______________
_______
Date:
SAN FELIPE NERI PAROCHIAL SCHOOL
PAASCU ACCREDITED LEVEL II
SCIENCE DEPARTMENT
6. Tork and Vorkina have two children. One is a boy named Torky and the other is a girl
named Vorki. Many years later, Torky meets and marries a girl named Morkalina who is
short.
A. What are the possibilities for the height of their offspring?
Hint: Look at 5A for information on Torky.
7. Vorki the daughter meets a zork named Spork, who is heterozygous for tall.
A. How many will be tall? How many will be short?
How many will be Tt? How many will be tt?
How many will be TT?
8. Torky has green hair and Morkalina has yellow hair. They have four children and all
of them have green hair. What phenotype and genotype must Torky be?
9. Spork and Vorki both have three eyes.
A. What would their offspring look like?
10. Using problems 5-9, give the phenotypes and genotypes of Tork, Vorkina, Torky,
Morkalina, Spork and Vorki based ONLY on the traits given in the problems.
Parents Signature: _______________ Teachers Signature: _______________
_______
Date:
SAN FELIPE NERI PAROCHIAL SCHOOL
PAASCU ACCREDITED LEVEL II
SCIENCE DEPARTMENT
NAME: _______________________
DATE : _______________________
SECTION : _____________
SCORE : _____________
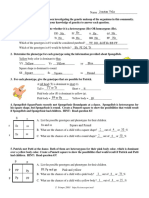
ACTIVITY # 2
Objectives:
1. Solve problems related to sex-linked traits.
SEX-LINKED TRAITS
1. Read the given problem below.
A normal daughter of a man with hemophilia, a recessive sex-linked trait, marries
a man who is normal for the trait.
Key: XH =normal Xh =hemophiliac
Guide Questions:
1. What is the genotype of the male?
2. What is the genotype of the female?
3. What percent of the couples daughter will become hemophiliac?
4. What is the chance that a son will be hemophiliac?
5. What is the ratio of children who is normal to those who have hemophilia?
Parents Signature: _______________ Teachers Signature: _______________
_______
Date:
SAN FELIPE NERI PAROCHIAL SCHOOL
PAASCU ACCREDITED LEVEL II
SCIENCE DEPARTMENT
2. Read the given problem below.
Red-green color blindness is caused by an X-linked recessive allele. A color-blind
woman marries a man with normal vision
Key: XB =normal vision Xb =color blindness
Guide Questions:
1. What is the genotype of the mother/wife?
2. What is the genotype of the father/husband?
3. What percent is a chance that a male child will be color blind?
4. What percent is a chance that the couples daughter will be color blind?
5. What is the ratio of children with normal vision to those who will be color blind?
Parents Signature: _______________ Teachers Signature: _______________
_______
Date:
Potrebbero piacerti anche
- Staar Eoc 2016test Bio F 7Documento39 pagineStaar Eoc 2016test Bio F 7api-293216402Nessuna valutazione finora
- Kami Export - Mendel Webquest SHORT KEYDocumento3 pagineKami Export - Mendel Webquest SHORT KEYNicolle Herrera Blandon100% (1)
- Bio102 General Biology II SummaryDocumento47 pagineBio102 General Biology II SummaryIkenna Okpala100% (1)
- Day 4. Warm-Up. STAAR® Blitz. Science. BiologyDocumento2 pagineDay 4. Warm-Up. STAAR® Blitz. Science. BiologyRaul Ramirez RangelNessuna valutazione finora
- Chapter 2 The Chromosomal Basis of HeredityDocumento50 pagineChapter 2 The Chromosomal Basis of Heredityvimbee alipoonNessuna valutazione finora
- Transcription Kezia Joice BautistaDocumento43 pagineTranscription Kezia Joice BautistaKeziajoicee Bautista0% (1)
- Cot Lesson Plan GeneticsDocumento10 pagineCot Lesson Plan GeneticsPrincess Ronquillo - DuqueNessuna valutazione finora
- Lab 13: Mendelian Laws and Paterns of InheritanceDocumento24 pagineLab 13: Mendelian Laws and Paterns of InheritanceNau MaanNessuna valutazione finora
- The Impact of BiotechnologyDocumento10 pagineThe Impact of BiotechnologyaizerzapNessuna valutazione finora
- Biol-111 - Mendelian Genetics WorksheetDocumento10 pagineBiol-111 - Mendelian Genetics WorksheetKing JoshNessuna valutazione finora
- Protein Synthesis Worksheet: 1. Filling The BlanksDocumento3 pagineProtein Synthesis Worksheet: 1. Filling The BlanksFelix SimsungNessuna valutazione finora
- Nicha-Cellcycle-Overview 1Documento6 pagineNicha-Cellcycle-Overview 1api-452284231100% (1)
- Mutations WorksheetDocumento3 pagineMutations Worksheetapi-293001217Nessuna valutazione finora
- Evolution Test CH 10 and 11 Review Sheet ANSWERSDocumento4 pagineEvolution Test CH 10 and 11 Review Sheet ANSWERSAlex IoannouNessuna valutazione finora
- The Historical Development of Biotechnology: Biotechnology: An Agricultural Revolution By: Ray V. HerrenDocumento24 pagineThe Historical Development of Biotechnology: Biotechnology: An Agricultural Revolution By: Ray V. HerrenRhan AlcantaraNessuna valutazione finora
- DNA - Student NotesDocumento23 pagineDNA - Student NotesCola ChauNessuna valutazione finora
- 7th Grade Cells and Heredity Planning GuideDocumento10 pagine7th Grade Cells and Heredity Planning Guideapi-232424041Nessuna valutazione finora
- ConstellationsDocumento85 pagineConstellationsDivya NayakaNessuna valutazione finora
- Dihybrid ProblemsDocumento7 pagineDihybrid Problemsbrenden chapmanNessuna valutazione finora
- Class: 8 Science Chapter - 8 Cell - Structure and FunctionsDocumento10 pagineClass: 8 Science Chapter - 8 Cell - Structure and FunctionsAmiteshwar SinghNessuna valutazione finora
- Jose P. Laurel Sr. High SchoolDocumento8 pagineJose P. Laurel Sr. High SchoolEricha SolomonNessuna valutazione finora
- Linkage: Linkage, Recombination & Gene MappingDocumento11 pagineLinkage: Linkage, Recombination & Gene MappingKhushbuNessuna valutazione finora
- Activity Sheet PhotosynthesisDocumento4 pagineActivity Sheet Photosynthesisapi-34040698140% (5)
- Segregation, Assortment, and Dominance RelationshipsDocumento39 pagineSegregation, Assortment, and Dominance RelationshipsAyaNessuna valutazione finora
- Science 9 Rubrics: Health and Fitness Plan Primer RubricsDocumento6 pagineScience 9 Rubrics: Health and Fitness Plan Primer Rubricsapi-340406981Nessuna valutazione finora
- Genes in DevelopmentDocumento13 pagineGenes in DevelopmentCyrosNessuna valutazione finora
- BIOLOGY Form 5 Chapter 5 InheritanceDocumento52 pagineBIOLOGY Form 5 Chapter 5 InheritanceShephard Png93% (15)
- Structure of Organic CompoundsDocumento27 pagineStructure of Organic CompoundsBetty Weiss100% (1)
- Test Bank For Brain Behavior An Introduction To Biological Psychology 3rd Edition by Bob L GarrettDocumento21 pagineTest Bank For Brain Behavior An Introduction To Biological Psychology 3rd Edition by Bob L GarrettlilymelanieuangerNessuna valutazione finora
- Student Exploration: Cell StructureDocumento8 pagineStudent Exploration: Cell Structurelingesh tamizhanNessuna valutazione finora
- WORKSHEET 14.4 Inheritance of TraitsDocumento5 pagineWORKSHEET 14.4 Inheritance of TraitsafzalNessuna valutazione finora
- Bscbo 301 PDFDocumento418 pagineBscbo 301 PDFparik kakani100% (1)
- Cell Bio Assignment - Plasma Membrane and Basement MembraneDocumento2 pagineCell Bio Assignment - Plasma Membrane and Basement Membranerahul mauryaNessuna valutazione finora
- Grade 9 Ubd 4th Heat ElectricityDocumento15 pagineGrade 9 Ubd 4th Heat Electricityapi-340406981100% (14)
- Stem Cell Plasticity-Building The Brain of Dreams: by Sally TempleDocumento22 pagineStem Cell Plasticity-Building The Brain of Dreams: by Sally TempleGagan KarwarNessuna valutazione finora
- Spongebob GeneticsDocumento2 pagineSpongebob Geneticsapi-250125823Nessuna valutazione finora
- IB Biology HL/SL: Auxins and Plant GrowthDocumento2 pagineIB Biology HL/SL: Auxins and Plant GrowthINDRANI GOSWAMINessuna valutazione finora
- Plant Behavioural Strategies For SurvivalDocumento3 paginePlant Behavioural Strategies For SurvivalNancyNguyen16Nessuna valutazione finora
- Angiosperm Classification and The APGDocumento2 pagineAngiosperm Classification and The APGAnsev CivasNessuna valutazione finora
- Unit 5 Genetics Guided Notes Page 7 Non-MendellanDocumento11 pagineUnit 5 Genetics Guided Notes Page 7 Non-MendellanCurt NormanNessuna valutazione finora
- Chapter 8 - Linkage, Crossing Over Chromosome Mapping in Eukaryotes 5 DecDocumento44 pagineChapter 8 - Linkage, Crossing Over Chromosome Mapping in Eukaryotes 5 DecselowestNessuna valutazione finora
- Polytene and Lampbrush ChromosomesDocumento3 paginePolytene and Lampbrush Chromosomesneeru.bhagatNessuna valutazione finora
- Bio Eoc Review PacketDocumento29 pagineBio Eoc Review Packetapi-267855902Nessuna valutazione finora
- Koonin EV 2015Documento5 pagineKoonin EV 2015leNessuna valutazione finora
- Lecture 1 (DNA - The Genetic Material)Documento43 pagineLecture 1 (DNA - The Genetic Material)M Luqman HakimNessuna valutazione finora
- Using Punnett SquaresDocumento11 pagineUsing Punnett Squaresapi-287347668Nessuna valutazione finora
- BioEOC PracticekeyDocumento21 pagineBioEOC PracticekeyEnerya AbalosNessuna valutazione finora
- BioSci 101 Test 2 NotesDocumento12 pagineBioSci 101 Test 2 NotesPianomanSuperman100% (1)
- Gene Mapping: Biology 20Documento5 pagineGene Mapping: Biology 20Soham SenguptaNessuna valutazione finora
- Plant Taxonomy NotesDocumento38 paginePlant Taxonomy Notesopolla nianorNessuna valutazione finora
- Dicot-Monocot Stem AnatomyDocumento6 pagineDicot-Monocot Stem AnatomyAdlet100% (1)
- Gregor MendelDocumento3 pagineGregor MendelAimee GutierrezNessuna valutazione finora
- Psilophyta To SphenophytaDocumento39 paginePsilophyta To Sphenophytajaninamariesarmiento100% (1)
- POGIL Cell Size-KEYDocumento5 paginePOGIL Cell Size-KEYKali WarnkeNessuna valutazione finora
- Replication in EukaryotesDocumento8 pagineReplication in EukaryotesnaliniNessuna valutazione finora
- StramenopilaDocumento21 pagineStramenopilaMarlyn AmanteNessuna valutazione finora
- DNADocumento37 pagineDNAGhafoor AzamNessuna valutazione finora
- EMTecson Mendoza Biotech R & D in The PhilippinesDocumento8 pagineEMTecson Mendoza Biotech R & D in The PhilippinesChua Yee LingNessuna valutazione finora
- CHAPTER 4 BOTANY - Review Questions and AnswersDocumento7 pagineCHAPTER 4 BOTANY - Review Questions and AnswersPam GarciaNessuna valutazione finora
- Biology 1A03 Exam ReviewDocumento69 pagineBiology 1A03 Exam Review0xVi3tfireNessuna valutazione finora
- Tissues: Chapter - 6Documento17 pagineTissues: Chapter - 6Aditya Jha100% (1)
- Chapter7 MC QuizDocumento19 pagineChapter7 MC Quizsmishra_97Nessuna valutazione finora
- Carbohydrates Identification 10th GradeDocumento5 pagineCarbohydrates Identification 10th GradeAndres Felipe MarroquinNessuna valutazione finora
- Chapter 2. Fundamentals of Genetics: Short QuestionsDocumento16 pagineChapter 2. Fundamentals of Genetics: Short QuestionsShouryaNessuna valutazione finora
- Karyotype Analysis in Zea Mays L. Var. Everta (Popcorn) Cultivated Within Owerri, Southeast NigeriaDocumento6 pagineKaryotype Analysis in Zea Mays L. Var. Everta (Popcorn) Cultivated Within Owerri, Southeast NigeriaImpact JournalsNessuna valutazione finora
- DNA Teacher V.Documento3 pagineDNA Teacher V.Angela Joan YedersbergerNessuna valutazione finora
- Approval Sheet: Name: Andi Nurlaeli Reg - No: 071404159 Group: IV (Fourth)Documento12 pagineApproval Sheet: Name: Andi Nurlaeli Reg - No: 071404159 Group: IV (Fourth)Lhely Andi NurlaeliNessuna valutazione finora
- AP Biology - Chapter 29 Discussion AnswersDocumento3 pagineAP Biology - Chapter 29 Discussion Answersangel91me6371100% (1)
- Punnett Square Practice Worksheet: Bobtails in Cats Are Recessive. Normal Tails Are DominantDocumento2 paginePunnett Square Practice Worksheet: Bobtails in Cats Are Recessive. Normal Tails Are DominantZaxbiyNessuna valutazione finora
- Biotechnology and Food Safety: Proceedings of the Second International SymposiumDa EverandBiotechnology and Food Safety: Proceedings of the Second International SymposiumDonald D. BillsValutazione: 5 su 5 stelle5/5 (1)
- MotionDocumento10 pagineMotionapi-34040698150% (2)
- 9 Learning StrategiesDocumento3 pagine9 Learning Strategiesapi-340406981Nessuna valutazione finora
- ClimateDocumento5 pagineClimateapi-340406981Nessuna valutazione finora
- MoleDocumento5 pagineMoleapi-340406981Nessuna valutazione finora
- VolcanoDocumento8 pagineVolcanoapi-340406981Nessuna valutazione finora
- Chemical BondingDocumento5 pagineChemical Bondingapi-340406981Nessuna valutazione finora
- Volcanoes 3 FinalDocumento106 pagineVolcanoes 3 Finalapi-340406981Nessuna valutazione finora
- GeneticsDocumento28 pagineGeneticsapi-340406981Nessuna valutazione finora
- Projectile MotionDocumento11 pagineProjectile Motionapi-340406981Nessuna valutazione finora
- Impulse Momentum Check ItDocumento38 pagineImpulse Momentum Check Itvenkateshyadav2116Nessuna valutazione finora
- 8 Project ProposalDocumento3 pagine8 Project Proposalapi-340406981Nessuna valutazione finora
- Activity Sheet Body SystemDocumento8 pagineActivity Sheet Body Systemapi-340406981Nessuna valutazione finora
- 0708 EnergyDocumento42 pagine0708 EnergybittuchintuNessuna valutazione finora
- ClimateDocumento14 pagineClimateapi-340406981Nessuna valutazione finora
- Bonding Types Ionic Covalent MetallicDocumento43 pagineBonding Types Ionic Covalent Metallicapi-236069914100% (1)
- Circulatory SystemDocumento22 pagineCirculatory SystemAliAshalNessuna valutazione finora
- ExtinctionsDocumento20 pagineExtinctionsapi-340406981Nessuna valutazione finora
- The Mole ConceptDocumento8 pagineThe Mole Conceptapi-340406981Nessuna valutazione finora
- Respiratorysystem 16Documento35 pagineRespiratorysystem 16api-340406981Nessuna valutazione finora
- Grade 9 Ubd 3rd VolcanoDocumento1 paginaGrade 9 Ubd 3rd Volcanoapi-340406981Nessuna valutazione finora
- Remodeled Plan 2nd Quarter Chemical BondingDocumento34 pagineRemodeled Plan 2nd Quarter Chemical Bondingapi-340406981Nessuna valutazione finora
- Grade 9 Ubd 4th Motion EnergyDocumento1 paginaGrade 9 Ubd 4th Motion Energyapi-340406981Nessuna valutazione finora
- Grade 9 Ubd 3rd Climate ConstellationDocumento1 paginaGrade 9 Ubd 3rd Climate Constellationapi-340406981Nessuna valutazione finora
- Remodeled Plan 2nd Quarter MoleDocumento23 pagineRemodeled Plan 2nd Quarter Moleapi-340406981100% (1)
- Mouse Genetics SeDocumento5 pagineMouse Genetics SeReflexNessuna valutazione finora
- Life Sciences Grade 12 Informal Test GeneticsDocumento4 pagineLife Sciences Grade 12 Informal Test GeneticsTonyy MichNessuna valutazione finora
- Baby - Lab MoDocumento6 pagineBaby - Lab MoArjayNessuna valutazione finora
- IGA 10e SM Chapter 06Documento71 pagineIGA 10e SM Chapter 06duabgelor100% (6)
- Non Mendelian PrinciplesDocumento38 pagineNon Mendelian PrinciplesEzra Denise Lubong RamelNessuna valutazione finora
- Kami Export - Jonatan Veliz - Sponge BobDocumento2 pagineKami Export - Jonatan Veliz - Sponge BobJonatan VNessuna valutazione finora
- Genetics Review Sheet 2017Documento7 pagineGenetics Review Sheet 2017anon_865386332Nessuna valutazione finora
- Genotype Phenotype WorksheetDocumento3 pagineGenotype Phenotype WorksheetJohn G Villar100% (1)
- Got Lactase?: Pedigrees and The Inheritance of Lactose IntoleranceDocumento6 pagineGot Lactase?: Pedigrees and The Inheritance of Lactose IntoleranceNoelNessuna valutazione finora
- Heredity DefinitionDocumento7 pagineHeredity DefinitionArianz GamingNessuna valutazione finora
- 18 - Murren (2015) Limits and Costs of Phenotype and PlasticityDocumento9 pagine18 - Murren (2015) Limits and Costs of Phenotype and PlasticityClaivert FelixNessuna valutazione finora
- More Punnett Square Practice: Solution: B B BB BB BB BBDocumento3 pagineMore Punnett Square Practice: Solution: B B BB BB BB BBAMYRA BatesNessuna valutazione finora
- 1-OG Genetics PowerpointDocumento54 pagine1-OG Genetics PowerpointElizabeth DeanNessuna valutazione finora
- OEB50 Assignment1Documento17 pagineOEB50 Assignment1Adrian GuzmanNessuna valutazione finora
- Life Sciences P2 Survival KitDocumento35 pagineLife Sciences P2 Survival KitMashamba CoutinhoNessuna valutazione finora
- Human Characteristics WorksheetDocumento3 pagineHuman Characteristics WorksheetijbfvosdjbNessuna valutazione finora
- Between-Individual Differences in Behavioural Plasticity Within Populations. Causes and Consequences - Dingemanse & Wolf - 2013Documento9 pagineBetween-Individual Differences in Behavioural Plasticity Within Populations. Causes and Consequences - Dingemanse & Wolf - 2013vmsolartecNessuna valutazione finora
- Universal Haplotype-Based Noninvasive Prenatal Testing For Single Gene DiseasesDocumento12 pagineUniversal Haplotype-Based Noninvasive Prenatal Testing For Single Gene DiseasestestNessuna valutazione finora
- Genetics, Evolution, Development, and PlasticityDocumento8 pagineGenetics, Evolution, Development, and PlasticityMerryNessuna valutazione finora
- Section A Answer ALL Question. Write Your Answers in The Spaces Provided in This BookletDocumento8 pagineSection A Answer ALL Question. Write Your Answers in The Spaces Provided in This BookletJoy BoehmerNessuna valutazione finora
- PDF Ib Biology Answers - CompressDocumento60 paginePDF Ib Biology Answers - CompressValentina VegaNessuna valutazione finora
- Clinical Pharmacology & Pharmacotherapy: International Journal ofDocumento2 pagineClinical Pharmacology & Pharmacotherapy: International Journal offakhrur rozyNessuna valutazione finora
- Populations Review Questions KEYDocumento23 paginePopulations Review Questions KEYtanusehdev17Nessuna valutazione finora