Documenti di Didattica
Documenti di Professioni
Documenti di Cultura
DragonBoard 410C Cheat Sheet
Caricato da
made_up-down65Titolo originale
Copyright
Formati disponibili
Condividi questo documento
Condividi o incorpora il documento
Hai trovato utile questo documento?
Questo contenuto è inappropriato?
Segnala questo documentoCopyright:
Formati disponibili
DragonBoard 410C Cheat Sheet
Caricato da
made_up-down65Copyright:
Formati disponibili
Jonathan Diaz
Vocabulary and Acronyms
MIPI-DSI (Mobile Industry Processing Interface - Display Serial Interface
IP - Internet Protocol - communication protocol for sending data/packets across a
network
(e.g. computer to computer)
VoIP - Voice over Internet Protocol - voice communication through IP.
PSTN - Public Switched Telephone Network - traditional telephone service.
SIP - Session Initiation Protocol - communication protocol that controls multimedia
communications, phone/voice, video, messaging.
ATA - Analog Telephone Adapter - device that connects an analog device (e.g. telephone,
fax) to a digital network (VoIP)
ADC - Analog-to-Digital Converter - device that converts an analog signal to a
digitalsignal.
DAC - Digital-to-Analog Converter - device that converts a digital signal to an analog
signal.
RTP - Real-time Transport Protocol.
API - Application Programming Interface.
UDP - User Datagram Protocol.
TCP - Transmission Control Protocol.
SSL - Secure Sockets Layer
TLS - Transport Layer Security
SCTP - Stream Control Transmission Protocol
SDP - Session Description Protocol
MSML - Media Server Markup Language
XML - Extensible Markup Language
IPvX - Internet Protocol version X - First accepted internet protocol was
IPv4, its successor is IPv6
GTK - GIMP Tool Kit - tool kit used to create GUIs.
GUI - Graphical User Interface - an interface (for interactions between the
user and the software) using visuals (e.g. video games)
ICE - Interactive Connectivity Establishment - similar to SIP; a
communication protocol but where one can discover public IPs to communicate
to/with.
Protocol - set of rules for how systems communicate.
Datagrams - basic piece of data to be sent
Packets - grouping transmitted data into nice blocks
Internet Protocol Suite - also known as IP; a communications protocol
Codecs - coder-decoder, encodes or decodes a digital signal
o encoded signals are for transmission, storage, or encryption
o decoded signals are for playback or editing
Containers - file formats, contains the codecs
1
Jonathan Diaz
GStreamer - multimedia framework that allows for audio/video playback,
editing, streaming, recording
IoT - Internet of Things.
IDE - Integrated Development Environment.
SDK - Software Development Kit - Software developing tools used to create applications
for a certain software/hardware platform(i.e. Android).
NDK - Native Development Kit - tool used to write programs in C/C++ for Android
devices.
AVD - Android Virtual Device - A tool which allows one to emulate an actual Android
device virtually on ones computer.
ADB - Android Debug Bridge - A command line tool which lets one communicate with a
connected Android device or an emulated virtual device.
APK - Android Application Package - file format which is used for distributing and
installing application software on Android.
API - Application Programming Interface - set of routines, protocols and tools for
building software applications.
Script - an executable file (automates a process).
Fastboot - a method to install an OS using a USB and a computer.
Flashing - overwriting existing OS or firmware.
PMIC(Power Management Integrated Circuits) - are integrated circuits (or a system
block in a system-on-a-chip device) for managing power requirements of the host system.
A PMIC is often included in battery-operated devices such as mobile phones and portable
media players.
Daemon - A background process that runs on each
Device/ Emulator
Vocabulary and Acronyms
MIPI-DSI (Mobile Industry Processing Interface - Display Serial Interface
IP - Internet Protocol - communication protocol for sending data/packets across a
network
(e.g. computer to computer)
VoIP - Voice over Internet Protocol - voice communication through IP.
PSTN - Public Switched Telephone Network - traditional telephone service.
SIP - Session Initiation Protocol - communication protocol that controls multimedia
communications, phone/voice, video, messaging.
ATA - Analog Telephone Adapter - device that connects an analog device (e.g. telephone,
fax) to a digital network (VoIP)
2
Jonathan Diaz
ADC - Analog-to-Digital Converter - device that converts an analog signal to a
digitalsignal.
DAC - Digital-to-Analog Converter - device that converts a digital signal to an analog
signal.
RTP - Real-time Transport Protocol.
API - Application Programming Interface.
UDP - User Datagram Protocol.
TCP - Transmission Control Protocol.
SSL - Secure Sockets Layer
TLS - Transport Layer Security
SCTP - Stream Control Transmission Protocol
SDP - Session Description Protocol
MSML - Media Server Markup Language
XML - Extensible Markup Language
IPvX - Internet Protocol version X - First accepted internet protocol was
IPv4, its successor is IPv6
GTK - GIMP Tool Kit - tool kit used to create GUIs.
GUI - Graphical User Interface - an interface (for interactions between the
user and the software) using visuals (e.g. video games)
ICE - Interactive Connectivity Establishment - similar to SIP; a
communication protocol but where one can discover public IPs to communicate
to/with.
Protocol - set of rules for how systems communicate.
Datagrams - basic piece of data to be sent
Packets - grouping transmitted data into nice blocks
Internet Protocol Suite - also known as IP; a communications protocol
Codecs - coder-decoder, encodes or decodes a digital signal
- encoded signals are for transmission, storage, or encryption
- decoded signals are for playback or editing
Containers - file formats, contains the codecs
GStreamer - multimedia framework that allows for audio/video playback,
editing, streaming, recording
IoT - Internet of Things.
IDE - Integrated Development Environment.
SDK - Software Development Kit - Software developing tools used to create
applications for a certain software/hardware platform(i.e. Android).
NDK - Native Development Kit - tool used to write programs in C/C++ for
Android devices.
AVD - Android Virtual Device - A tool which allows one to emulate an actual
Android device virtually on ones computer.
ADB - Android Debug Bridge - A command line tool which lets one
communicate with a connected Android device or an emulated virtual device.
3
Jonathan Diaz
APK - Android Application Package - file format which is used for distributing
and installing application software on Android.
API - Application Programming Interface - set of routines, protocols and tools
for building software applications.
Script - an executable file (automates a process).
Fastboot - a method to install an OS using a USB and a computer.
Flashing - overwriting existing OS or firmware.
PMIC(Power Management Integrated Circuits) - are integrated circuits (or a
system block in a system-on-a-chip device) for managing power requirements of the
host system. A PMIC is often included in battery-operated devices such as mobile
phones and portable media players.
Daemon - A background process that runs on each
Device/ Emulator
Features and Overview for the DragonBoard 410c
Feature Highlights
OS Support: Android 5.1 (Lollipop) on Linux Kernel 3.10, Linux based on
Debian 8.0, and Windows 10 IoT Core
CPU: Quad-core ARM Cortex A53 at up to 1.2 GHz per core with both 32-bit
and 64-bit support
Memory/storages: 1GB LPDDR3 533MHz / 8GB eMMC 4.5 / SD 3.0 (UHS-I)
The maximun DDR is 533Mhz
The LPDDR3 is a 32bit width bus implementation interfacing directly to
the APQ8016 build-in LPDDR controller.
The eMMC is an 8bit implementation interfacing with APQ8016 SDC1
interface supporting eMMC 4.5 specifications.
Graphics: Qualcomm Adreno 306 GPU with support for advanced APIs,
including OpenGL ES 3.0, OpenCL, DirectX, and content security
Video: 1080p@30fps HD video playback and capture with H.264 (AVC), and
720p playback with H.265 (HEVC)
Camera Support: Integrated ISP with support for image sensors up to 13MP
Connectivity and Location:
Wi-Fi 802.11 b/g/n 2.4GHz, integrated digital core
Bluetooth 4.1, integrated digital core
Qualcomm IZat location technology Gen8C
On-board Wi-Fi, BT and GPS antenna
I/O Interfaces: HDMI Full-size Type A connector, one micro USB (device mode
only), two USB 2.0 (host mode only), micro SD card slot
Note: Micro USB (device mode) and USB 2.0 (host mode) are mutually exclusive
and cannot be operated at the same time
4
Jonathan Diaz
Expansion:
One 40-pin low speed expansion connector: UART, SPI, I2S, I2C x2, GPIO x12,
DC power
One 60-pin high speed expansion connector: 4L MIPI-DSI, USB, I2C x2, 2L+4L
MIPI-CSI
Footprint for one optional 16-pin analog expansion connector for stereo
headset/line-out, speaker and analog line-in.
The board can be made compatible with Arduino using an add-on mezzanine
board
13.5 MP camera input support.(Integrated ISP with support for image sensors up
to 13MP)
Jonathan Diaz
Alternative front view for the GPS/BLUETOOTH/WLAN Module.
Overview.
(J8) Low Speed Expansion Connector
APQ8016 Snapdragon Processor
(U9) Power Management PMIC
(J7) Analog Expansion Connector
6
Jonathan Diaz
WLAN/Bluetooth/GPS
(J1) Power Jack
(J5) uSD Card Socket
(J6) HDMI Type A Port
(J9) High Speed Connector
10
(J4) Micro USB Type B Connector
11
Bluetooth/WLAN LEDs
12
(J3) USB Host2 Connector
13
User LEDs 1-4
14
(J2) USB Host1 Connector
15
(S3-4) Vol+/Vol- Buttons
16
(S2) Power Button
17
Bluetooth/WLAN Antenna
18
GPS Antenna
19
(S6) Boot Switches
Jonathan Diaz
OS Support - Images to download
To mount ISO (image) --- Install first Win32 disk imager in your PC ..
https://sourceforge.net/projects/win32diskimager/?source=typ_redirect
Optional -Also install format SD-card in your PC - this program can format " erase the
content of your SD card", so you can reuse the SD-card again to install or save other
stuffs in it.
https://www.sdcard.org/downloads/formatter_4/
Procedure :
1.
Start the Disk Imager tool and install the ISO file (your OS)
2.
Plug In the programmed SD-card into the board
3.
Connect a Mouse and Keyboard to the board
4.
Connect a monitor with an HDMI cable to the board
1.
Set the boot switches S6 to 0100 (boot from SD-card)
2.
Plug the power supply into the board
3.
The board should start up and show a Dialog from which
you can choose the Operating System to install
4.
Choose the displayed Operating system (Android) and click
Install. This will flash the OS on the board eMMC
5.
Once you see the programming successful dialog proceed
with the next step
6.
unplug the power cord
7.
remove the SD-card
8.
reset the boot switches S6 to 0000
9.
Plug in the power cord. The system should now boot into
your chosen Operating System
0100
0000
Android 5.1 (Lollipop) on Linux Kernel 3.10
http://builds.96boards.org/releases/dragonboard410c/qualcomm/android/latest/dragonboard410
c_sdcard_install_android-*.zip
Linux based on Debian 8.0
http://builds.96boards.org/releases/dragonboard410c/linaro/debian/latest/dragonboard410c_sdc
ard_install_debian-*.zip
Installing from SD-card (requirements)
SD-card: In order to install Linux directly from SD-card you need a SD-card with
at least 4GB in size.
A monitor capable of 1080p resolution. A monitor with lower resolution might
not be able to display the high resolution output by the board.
8
Jonathan Diaz
Mouse and keyboard (this works excellent for me http://www.amazon.com/GearHead-KB3800TPW-Keyboard-Wireless/dp/B005LRAQTW )
For Windows 10 ( probably )
https://developer.qualcomm.com/blog/windows-10-and-dragonboard-410c-perfect-start-iotdevelopmEnt
Development Environment
http://www.oracle.com/technetwork/java/javase/downloads/index.html
(Java
SDK)
https://developer.android.com/studio/index.html
https://git-scm.com/download (git bash)
(Android Studio)
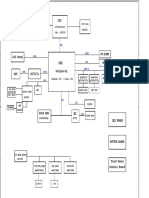
System Block Diagram
Display Interface
Jonathan Diaz
USB PORTS
Power Supply
The 410c board supports these requirements as follows:
+1.8V : Driven by two PMIC(Power Management Integrated Circuits) LDOs, LDO15
and LDO16, each can provide 55mA. The PM8916 allows connecting the two LDOs in
parallel to provide 110mA on a 1.8V rail which meets the 96Boards requirement.
10
Jonathan Diaz
+5V : Driven by the 4A 5.0V buck switcher (U13). This buck switcher powers both USB
limit current devices (each at 1.18A max). The remaining capacity provides a max current
of 1.64A to the Low Speed Expansion Connector, for a total of 8.2W which meets the
96Boards requirements.
SYS_DCIN: Can serves as the boards main power source or can receive power from the
board.
Power Supply for the DragonBoard 410c Rev. C is about the range of 6.5 VDC-18 VDC
The DragonBoard 410c can't be powered by using USB Type C
SY8104ADC
SY8104 is a high-efficiency 500 kHz synchronous buck DC-DC converter
4.0A
over a
voltage
4.5V to
the
provides
current.
SY8104
operates
wide input
range of
16V, and
integrates
main
11
Jonathan Diaz
switch and synchronous switch with very low RDS (ON), in order to minimize conduction
losses. Low output voltage ripple and small external inductor and capacitor size and switching
frequency of 500 kHz to achieve.
SY8104 uses real-time PWM architecture to achieve fast transient response high step-down
applications
SY8104 General the Description
at The SY8104 IS A 500 kHz High Efficiency Synchronous the DC-STEP-Down Converter
Capable of Delivering the DC 4.0A Current. At The SY8104 Operates over the INPUT A Wide
Voltage the Range from 4.5V to 16V and integrates the with main Switch and Synchronous
Switch Very Low RDS (ON) to minimize the conduction loss. Low output voltage ripple and
small external inductor and capacitor sizes are achieved with 500 kHz switching frequency. It
adopts the instant PWM architecture to achieve fast transient responses for high step down
applications
12
Jonathan Diaz
DragonBoard 410c Pinout Information
13
Jonathan Diaz
Low Speed Expansion Connector
14
Jonathan Diaz
15
Jonathan Diaz
High Speed Expansion Connector
16
Jonathan Diaz
17
Jonathan Diaz
Analog Expansion Connector
18
Potrebbero piacerti anche
- Multimedia HardWareDocumento18 pagineMultimedia HardWareRohan GuptaNessuna valutazione finora
- LoppDocumento7 pagineLoppMaroine CharityNessuna valutazione finora
- Computer Parts Full Form List A To Z 629Documento17 pagineComputer Parts Full Form List A To Z 629a68126634Nessuna valutazione finora
- Embedded Linux On ARM Cortex-A8Documento2 pagineEmbedded Linux On ARM Cortex-A8JOHNSON JOHNNessuna valutazione finora
- CaseStudy Atmel Sam9 Odb Data Logger enDocumento7 pagineCaseStudy Atmel Sam9 Odb Data Logger enromoNessuna valutazione finora
- Part B&C - Cat3Documento16 paginePart B&C - Cat3Keesha DeepakNessuna valutazione finora
- Aviation Analytics and The Internet of Things: Dr. Paul Comitz, Self-Employed Aaron Kersch, The Boeing CompanyDocumento6 pagineAviation Analytics and The Internet of Things: Dr. Paul Comitz, Self-Employed Aaron Kersch, The Boeing CompanydeepaneceNessuna valutazione finora
- Albis Onu HdmiDocumento2 pagineAlbis Onu HdmioomariniNessuna valutazione finora
- TERASIC DE1 SOC VIP DemoDocumento4 pagineTERASIC DE1 SOC VIP DemoBryan ProcukNessuna valutazione finora
- Android Is A LinuxDocumento5 pagineAndroid Is A Linuxvivaan2Nessuna valutazione finora
- Glossary Computer HardwareDocumento5 pagineGlossary Computer HardwareNahid MamunNessuna valutazione finora
- A To Z Computer Related Full FormDocumento15 pagineA To Z Computer Related Full FormMeena Sharma100% (1)
- Computer Related Full Form Board PDFDocumento9 pagineComputer Related Full Form Board PDFxsaaNessuna valutazione finora
- Set - Top Box (STB)Documento20 pagineSet - Top Box (STB)AbinayaNessuna valutazione finora
- Lab No. 01: Ans: Operating SystemDocumento2 pagineLab No. 01: Ans: Operating SystemMàhàvěęř ŔámèśhNessuna valutazione finora
- Computer DictionaryDocumento6 pagineComputer DictionaryMuhammad Haris KharaNessuna valutazione finora
- Android: An Open Platform For Mobile DevelopmentDocumento18 pagineAndroid: An Open Platform For Mobile DevelopmentRevathi RevaNessuna valutazione finora
- Gregory Levin: JIRA, JIRA Agile, Segger Studio 4.x, JlinkDocumento9 pagineGregory Levin: JIRA, JIRA Agile, Segger Studio 4.x, JlinkrecruiterkkNessuna valutazione finora
- Question Bank Solutions (Module-5) - IOT - 15CS81Documento32 pagineQuestion Bank Solutions (Module-5) - IOT - 15CS81Sai Suhas MkNessuna valutazione finora
- Geek Speak Glossary A Managers Guide To IT TerminologyDocumento20 pagineGeek Speak Glossary A Managers Guide To IT TerminologyjohnbullasNessuna valutazione finora
- A To Z Computer Related Full FormDocumento20 pagineA To Z Computer Related Full FormNoob PlayerNessuna valutazione finora
- Microchip Conectivity 00001181L PDFDocumento20 pagineMicrochip Conectivity 00001181L PDFFernando LizarragaNessuna valutazione finora
- Computer Basics and NetworksDocumento40 pagineComputer Basics and Networksapi-249547905Nessuna valutazione finora
- Schematic Diagram of Ip Camera With EthernetDocumento18 pagineSchematic Diagram of Ip Camera With EthernetnguyenminhtuanengineNessuna valutazione finora
- Computer Ports.20121027.000243Documento2 pagineComputer Ports.20121027.000243anon_313601587Nessuna valutazione finora
- Personal Digital AssistantDocumento18 paginePersonal Digital AssistantVikasNessuna valutazione finora
- Audio and Video Streamingppt3357Documento55 pagineAudio and Video Streamingppt3357Kadar Fadar Ne EiNessuna valutazione finora
- Android TurorialDocumento179 pagineAndroid TurorialSrinivas MahantiNessuna valutazione finora
- Test ScenariosDocumento7 pagineTest ScenariosMehr Fathima50% (2)
- Summer Internship Presentation On Embedded Systems Through RaspberryDocumento44 pagineSummer Internship Presentation On Embedded Systems Through Raspberryayush.agarwal9325360% (1)
- Android: Next Generation Mobile ComputingDocumento7 pagineAndroid: Next Generation Mobile ComputingSuhasini BadamNessuna valutazione finora
- ICT TerminologyDocumento8 pagineICT TerminologySaurabh M. SaleNessuna valutazione finora
- Mcpherson Aes2015Documento7 pagineMcpherson Aes2015Pedro CiminiNessuna valutazione finora
- 5.3 Unit-V Developing Applications Through IoT ToolsDocumento8 pagine5.3 Unit-V Developing Applications Through IoT ToolsGostudy LifeNessuna valutazione finora
- Yc Yc Yc Yc Yc Yc Yc Yc Yc Yc Yc YcDocumento7 pagineYc Yc Yc Yc Yc Yc Yc Yc Yc Yc Yc YcintriguegirlNessuna valutazione finora
- Android TurorialDocumento216 pagineAndroid TurorialSrinivas MahantiNessuna valutazione finora
- Expansion Slots and CardsDocumento4 pagineExpansion Slots and CardsUma SoniNessuna valutazione finora
- Atlas Media Server II TELCO DatasheetDocumento3 pagineAtlas Media Server II TELCO DatasheetLaszlo ZoltanNessuna valutazione finora
- SpecsDocumento67 pagineSpecsAzlan MahmudNessuna valutazione finora
- MSIT 616 - Research #1: IntranetsDocumento41 pagineMSIT 616 - Research #1: IntranetsveeNessuna valutazione finora
- Experiment 9Documento29 pagineExperiment 9Aman SharmaNessuna valutazione finora
- Hardware FamiliarizationDocumento42 pagineHardware FamiliarizationLeandro IsidroNessuna valutazione finora
- Peripherals Updated Js2019 Clo1 Week3Documento52 paginePeripherals Updated Js2019 Clo1 Week3somerandomhedgehogNessuna valutazione finora
- ESP-WROOM-02: What Is The "Internet of Things"?Documento7 pagineESP-WROOM-02: What Is The "Internet of Things"?KOKONessuna valutazione finora
- Summary:: Raj Kumar ThavtiDocumento4 pagineSummary:: Raj Kumar ThavtiRaj kumarNessuna valutazione finora
- Ict Assignment 1Documento11 pagineIct Assignment 1Iliya SuhaimiNessuna valutazione finora
- FarSync TE1e E1 PCIe Adapter DatasheetDocumento5 pagineFarSync TE1e E1 PCIe Adapter Datasheetyame asfiaNessuna valutazione finora
- Unit - 4: Building IOT With Galileo/ArdunioDocumento41 pagineUnit - 4: Building IOT With Galileo/Ardunio16TUCS228 SRIDHAR T.SNessuna valutazione finora
- DSP CasestudyDocumento23 pagineDSP CasestudyShayani BatabyalNessuna valutazione finora
- Quickspecs: HP Ipaq Rx3700 Series Mobile Media CompanionDocumento12 pagineQuickspecs: HP Ipaq Rx3700 Series Mobile Media CompanionhuicholeNessuna valutazione finora
- Multimedia Hardware: Ms P KadebuDocumento40 pagineMultimedia Hardware: Ms P Kadebusharon mkdauendaNessuna valutazione finora
- Computer Hardware: Computer Parts and PortsDocumento14 pagineComputer Hardware: Computer Parts and PortsSanduni GamageNessuna valutazione finora
- Terminos en InglesDocumento15 pagineTerminos en InglesRicardo OchoaNessuna valutazione finora
- Media Fundamentals of A Communications App: Kenny Oladosu & Johnny BregarDocumento54 pagineMedia Fundamentals of A Communications App: Kenny Oladosu & Johnny BregarsubuhpramonoNessuna valutazione finora
- Tech GlossaryDocumento11 pagineTech Glossaryapi-3837264100% (1)
- GrafanaCon LA IoT Workshop PDFDocumento30 pagineGrafanaCon LA IoT Workshop PDFThe FannyNessuna valutazione finora
- GrafanaCon LA IoT Workshop PDFDocumento30 pagineGrafanaCon LA IoT Workshop PDFThe FannyNessuna valutazione finora
- Desmo Uliers 2012Documento12 pagineDesmo Uliers 2012Anonymous UI7JawqNessuna valutazione finora
- CppForJavaProgrammers 1Documento44 pagineCppForJavaProgrammers 1HansNessuna valutazione finora
- Unattended Install Help PDFDocumento4 pagineUnattended Install Help PDFSeptian Wahyu PriyonoNessuna valutazione finora
- The Docker Book James TurnbullDocumento410 pagineThe Docker Book James TurnbullAlex100% (1)
- Exit Mock With AnswerDocumento25 pagineExit Mock With AnswerBkibru aetsubNessuna valutazione finora
- 04 - Muse Ed - SR-02-0-PCB - 090327Documento48 pagine04 - Muse Ed - SR-02-0-PCB - 090327Moises PerelloNessuna valutazione finora
- Profibus Encoder ConnectionDocumento74 pagineProfibus Encoder ConnectionRoberto CedilloNessuna valutazione finora
- Speech Timer For Contests and Debates: Arduino-Based Fridge Monitor and Data LoggerDocumento76 pagineSpeech Timer For Contests and Debates: Arduino-Based Fridge Monitor and Data LoggerZaw ZawNessuna valutazione finora
- Structures & Pointers in C ProgrammingDocumento91 pagineStructures & Pointers in C ProgrammingRohit GhoshalNessuna valutazione finora
- 02 - Mpi - ShuDocumento15 pagine02 - Mpi - ShuUsama JavedNessuna valutazione finora
- CH 10 FunctionsDocumento30 pagineCH 10 FunctionsVatsala B RNessuna valutazione finora
- Aos CH 2.3Documento47 pagineAos CH 2.3Efrain Sanjay AdhikaryNessuna valutazione finora
- Restoring The Memory On An Excel CNC With Fanuc 0 ControlDocumento4 pagineRestoring The Memory On An Excel CNC With Fanuc 0 ControlmalexorozcoNessuna valutazione finora
- X Virtual ServerDocumento8 pagineX Virtual ServerAnitosh SahaNessuna valutazione finora
- IIS 7: The Administrator's GuideDocumento8 pagineIIS 7: The Administrator's GuidearivsNessuna valutazione finora
- DCA 2019 BatchDocumento25 pagineDCA 2019 BatchWjajshs UshdNessuna valutazione finora
- HMC Enhanced Gui Quick Start Guide 1.0: Classic GUI To Enhanced GUI Mappings and Enhanced GUI ImprovementsDocumento15 pagineHMC Enhanced Gui Quick Start Guide 1.0: Classic GUI To Enhanced GUI Mappings and Enhanced GUI ImprovementsRajeev GhoshNessuna valutazione finora
- Enhanced Table Maintenance With Automatic Change Recording - My Experiments With ABAPDocumento6 pagineEnhanced Table Maintenance With Automatic Change Recording - My Experiments With ABAPpraneeth abapNessuna valutazione finora
- Solarwinds Network Management Guide: Revision: H2Cy10Documento20 pagineSolarwinds Network Management Guide: Revision: H2Cy10arun0076@gmail.comNessuna valutazione finora
- MediaTek - MediaTek Dimensity 900Documento4 pagineMediaTek - MediaTek Dimensity 900Logo XNessuna valutazione finora
- Rhcsa and Rhce SyllabusDocumento9 pagineRhcsa and Rhce SyllabusSandip PudasainiNessuna valutazione finora
- Diego 1Documento22 pagineDiego 1acs_spNessuna valutazione finora
- Presentation Sheet C++Documento13 paginePresentation Sheet C++HassanHusniNessuna valutazione finora
- 1、USB 2.0+3.0 Slim External DVDRW 20130822Documento2 pagine1、USB 2.0+3.0 Slim External DVDRW 20130822Carlos TorresNessuna valutazione finora
- Psat-1 3 4Documento7 paginePsat-1 3 4Suresh SinghNessuna valutazione finora
- Zabbix Manual v1.6Documento314 pagineZabbix Manual v1.6alexander.rozhkov100% (2)
- Simple Template Checklist Free Excel DownloadDocumento2 pagineSimple Template Checklist Free Excel DownloadDeepak SinghNessuna valutazione finora
- How To Connect Palo Alto Next Generation Firewall VM To GNS 3Documento20 pagineHow To Connect Palo Alto Next Generation Firewall VM To GNS 3Ankur SaxenaNessuna valutazione finora
- Hashicorp Certified Terraform Associate Practice Questions - IntermediateDocumento31 pagineHashicorp Certified Terraform Associate Practice Questions - Intermediateingeduardo23100% (1)
- (DELL) 一款七寸平板电脑原理图JWT - V1A - 0721 - 16P2 PDFDocumento30 pagine(DELL) 一款七寸平板电脑原理图JWT - V1A - 0721 - 16P2 PDFsamuelNessuna valutazione finora
- DO180 ExamDocumento4 pagineDO180 ExamadgsdfgNessuna valutazione finora
- Microsoft Azure Infrastructure Services for Architects: Designing Cloud SolutionsDa EverandMicrosoft Azure Infrastructure Services for Architects: Designing Cloud SolutionsNessuna valutazione finora
- ITIL® 4 Create, Deliver and Support (CDS): Your companion to the ITIL 4 Managing Professional CDS certificationDa EverandITIL® 4 Create, Deliver and Support (CDS): Your companion to the ITIL 4 Managing Professional CDS certificationValutazione: 5 su 5 stelle5/5 (2)
- CCNA Certification Study Guide, Volume 2: Exam 200-301Da EverandCCNA Certification Study Guide, Volume 2: Exam 200-301Nessuna valutazione finora
- Hacking: A Beginners Guide To Your First Computer Hack; Learn To Crack A Wireless Network, Basic Security Penetration Made Easy and Step By Step Kali LinuxDa EverandHacking: A Beginners Guide To Your First Computer Hack; Learn To Crack A Wireless Network, Basic Security Penetration Made Easy and Step By Step Kali LinuxValutazione: 4.5 su 5 stelle4.5/5 (67)
- Hacking Network Protocols: Complete Guide about Hacking, Scripting and Security of Computer Systems and Networks.Da EverandHacking Network Protocols: Complete Guide about Hacking, Scripting and Security of Computer Systems and Networks.Valutazione: 5 su 5 stelle5/5 (2)
- Evaluation of Some Websites that Offer Virtual Phone Numbers for SMS Reception and Websites to Obtain Virtual Debit/Credit Cards for Online Accounts VerificationsDa EverandEvaluation of Some Websites that Offer Virtual Phone Numbers for SMS Reception and Websites to Obtain Virtual Debit/Credit Cards for Online Accounts VerificationsValutazione: 5 su 5 stelle5/5 (1)
- The Compete Ccna 200-301 Study Guide: Network Engineering EditionDa EverandThe Compete Ccna 200-301 Study Guide: Network Engineering EditionValutazione: 5 su 5 stelle5/5 (4)
- AWS Certified Solutions Architect Study Guide: Associate SAA-C01 ExamDa EverandAWS Certified Solutions Architect Study Guide: Associate SAA-C01 ExamValutazione: 4 su 5 stelle4/5 (1)
- Cybersecurity: The Beginner's Guide: A comprehensive guide to getting started in cybersecurityDa EverandCybersecurity: The Beginner's Guide: A comprehensive guide to getting started in cybersecurityValutazione: 5 su 5 stelle5/5 (2)
- Palo Alto Networks: The Ultimate Guide To Quickly Pass All The Exams And Getting Certified. Real Practice Test With Detailed Screenshots, Answers And ExplanationsDa EverandPalo Alto Networks: The Ultimate Guide To Quickly Pass All The Exams And Getting Certified. Real Practice Test With Detailed Screenshots, Answers And ExplanationsNessuna valutazione finora
- Practical TCP/IP and Ethernet Networking for IndustryDa EverandPractical TCP/IP and Ethernet Networking for IndustryValutazione: 4 su 5 stelle4/5 (2)
- Cybersecurity: A Simple Beginner’s Guide to Cybersecurity, Computer Networks and Protecting Oneself from Hacking in the Form of Phishing, Malware, Ransomware, and Social EngineeringDa EverandCybersecurity: A Simple Beginner’s Guide to Cybersecurity, Computer Networks and Protecting Oneself from Hacking in the Form of Phishing, Malware, Ransomware, and Social EngineeringValutazione: 5 su 5 stelle5/5 (40)
- AWS Certified Solutions Architect Study Guide: Associate SAA-C02 ExamDa EverandAWS Certified Solutions Architect Study Guide: Associate SAA-C02 ExamNessuna valutazione finora
- Set Up Your Own IPsec VPN, OpenVPN and WireGuard Server: Build Your Own VPNDa EverandSet Up Your Own IPsec VPN, OpenVPN and WireGuard Server: Build Your Own VPNValutazione: 5 su 5 stelle5/5 (1)
- Computer Networking: The Complete Beginner's Guide to Learning the Basics of Network Security, Computer Architecture, Wireless Technology and Communications Systems (Including Cisco, CCENT, and CCNA)Da EverandComputer Networking: The Complete Beginner's Guide to Learning the Basics of Network Security, Computer Architecture, Wireless Technology and Communications Systems (Including Cisco, CCENT, and CCNA)Valutazione: 4 su 5 stelle4/5 (4)
- ITIL® 4 Create, Deliver and Support (CDS): Your companion to the ITIL 4 Managing Professional CDS certificationDa EverandITIL® 4 Create, Deliver and Support (CDS): Your companion to the ITIL 4 Managing Professional CDS certificationNessuna valutazione finora
- Open Radio Access Network (O-RAN) Systems Architecture and DesignDa EverandOpen Radio Access Network (O-RAN) Systems Architecture and DesignNessuna valutazione finora
- CWNA Certified Wireless Network Administrator Study Guide: Exam CWNA-108Da EverandCWNA Certified Wireless Network Administrator Study Guide: Exam CWNA-108Nessuna valutazione finora
- Microsoft Certified Azure Fundamentals Study Guide: Exam AZ-900Da EverandMicrosoft Certified Azure Fundamentals Study Guide: Exam AZ-900Nessuna valutazione finora