Documenti di Didattica
Documenti di Professioni
Documenti di Cultura
1st-Trial 07-08
Caricato da
api-253679034Titolo originale
Copyright
Formati disponibili
Condividi questo documento
Condividi o incorpora il documento
Hai trovato utile questo documento?
Questo contenuto è inappropriato?
Segnala questo documentoCopyright:
Formati disponibili
1st-Trial 07-08
Caricato da
api-253679034Copyright:
Formati disponibili
7002 - 7002
. - :
. . 6 .02 -
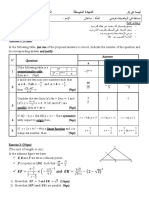
1st exercise: (3pts)
Choose the correct answer and justify
No.
Questions
1.
4x 2 9
the equation
0
2x 3
a
has a unique
3
solution x
2
Answers
b
has 2 solutions
3
3
and x
x
2
2
c
has a unique
3
solution x
2
triangle ABC is
isosceles at B
triangle ABC is
scalene
triangle ABC is right
and isosceles at A
internally
tangent
not intersecting
externally tangent
Given a triangle ABC of
sides AB 2 3 cm ,
2.
3.
4.
6 2
and
AC
2
BC 1 3 cm then
4152 2303
8101
The two circles C 0, 8 and
C ' 0' , 18 such that
00' 50 are
2nd exercise: (3pts)
(C) is a circle of center O and diameter [AC] such that AC 5 10 2 40 2 3 5 . B is a point such
that BO
5 2 1 2 2 1 2 2 (unit of length is dm)
1. Write AC in the form a b where a and b are two natural integers to be determined. ( pt)
2. Show that BO 2 10 and justify that B belongs to (C) (1 pts)
3. Calculate AB if BC 4 5 then deduce that the triangle ABC is right isosceles at B(1pt)
Remark: you can only draw a sketch
3rd exercise: (2 pts)
Consider the two polynomials: P(x) = (a2 - 5)x2 + 6x + c -2 and Q(x) = -4x2 + (b2 10)x - 2
1. Find a, b, and c so that P(x) and Q(x) are identical. (1pt)
2. Find b so that x = 1 is a root of Q(x). ( pt)
1
3. a) Verify that 4( x 1)(x ) 4 x 2 6 x 2 ( pt)
2
b) Find the roots of Q(x) when b = 4 ( pt)
2/1
- - - 2002
4th exercise: (5 pts)
Part A: Consider the two real numbers: x
3 96
36
2 27 2 4 and y 4 75
2
3
2
1. Show that x 4 6 3 ( pt)
2. Write y in the form of a b 3 where a and b are two integers to be determined. ( pt)
Part B: 1. Let x and y represent the lengths of the bases of the
trapezoid ABCD. Indicate the length of [AB] and that of
[CD]. Justify by calculation. (1pt)
2. [BH] is the height relative to [CD], let CH = 2cm, and
BCH 60o
a. Show that BC = 4cm, then deduce BH using two
different ways. (1 pts)
b. Give an approximate value rounded to the nearest
0.001 of BH. ( pt)
c. Calculate the exact area of the trapezoid ABCD (1pt)
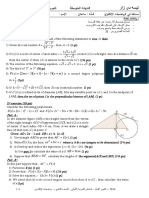
5th exercise: (3pts)
Given a square ABCD of side x cm (x > 2).
The sides [AB] and [AD] are decreased by 2cm each to obtain AEFG.
1. Find the nature of AEFG (1pt)
2. Determine the area of the shaded region in the form of a(x - b)
where a and b are natural integers to be determined. (1pt)
3. Deduce the value of x so that the area of the shaded region is
16cm2. (1pt)
60o
C
2cm
2cm
E
B
x
G
2cm
D
6th exercise: (3pts)
Given a circle (C) of center O and radius R. [AB] is a fixed diameter and M is a variable point on (C). The
circle (C1) of center M and radius MA cuts (C) in A and E. Let D be the point diametrically opposite to A in
(C1).
1. Draw a figure. ( pt)
2. Determine the nature of each of the following triangles ADE and AEB. Deduce that the points B, E
and D are collinear. (1pt)
3. Show that (OM) and (BD) are parallel. Deduce that BD = 2R ( pt)
4. Choose the correct answer and justify.
a. The point B is
i. variable
ii. fixed
b. The point D is
i. variable
ii. fixed
c. The length BD is
i. constant
ii. variable
From the above questions, deduce the path on which the point D moves when M moves on (C). ( pt)
2/2
- - - 2002
Potrebbero piacerti anche
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeDa EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeValutazione: 4 su 5 stelle4/5 (5794)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreDa EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreValutazione: 4 su 5 stelle4/5 (1090)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItDa EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItValutazione: 4.5 su 5 stelle4.5/5 (838)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceDa EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceValutazione: 4 su 5 stelle4/5 (895)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceDa EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceValutazione: 4 su 5 stelle4/5 (588)
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeDa EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeValutazione: 4.5 su 5 stelle4.5/5 (537)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersDa EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersValutazione: 4.5 su 5 stelle4.5/5 (344)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureDa EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureValutazione: 4.5 su 5 stelle4.5/5 (474)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesDa EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesValutazione: 4 su 5 stelle4/5 (821)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Da EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Valutazione: 4.5 su 5 stelle4.5/5 (120)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerDa EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerValutazione: 4.5 su 5 stelle4.5/5 (271)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingDa EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingValutazione: 3.5 su 5 stelle3.5/5 (399)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyDa EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyValutazione: 3.5 su 5 stelle3.5/5 (2259)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Da EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Valutazione: 4 su 5 stelle4/5 (98)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaDa EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaValutazione: 4.5 su 5 stelle4.5/5 (266)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryDa EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryValutazione: 3.5 su 5 stelle3.5/5 (231)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnDa EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnValutazione: 4.5 su 5 stelle4.5/5 (234)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealDa EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealValutazione: 4 su 5 stelle4/5 (73)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaDa EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaValutazione: 4 su 5 stelle4/5 (45)
- 4-1 Right Triangle TrigonometryDocumento4 pagine4-1 Right Triangle TrigonometryKhoon Yu TanNessuna valutazione finora
- 2nd-Trial 18-19Documento2 pagine2nd-Trial 18-19api-253679034Nessuna valutazione finora
- Lycée Des Arts: Mathematics 9 - Grade. Name: - . - . - . - . - "Factorizing Techniques" E.S-8Documento3 pagineLycée Des Arts: Mathematics 9 - Grade. Name: - . - . - . - . - "Factorizing Techniques" E.S-8api-253679034Nessuna valutazione finora
- Lycée Des Arts: ConclusionDocumento2 pagineLycée Des Arts: Conclusionapi-253679034Nessuna valutazione finora
- Lycée Des Arts: Mathematics 9 - Grade. Name: - . - . - . - . - " " E.S-5Documento1 paginaLycée Des Arts: Mathematics 9 - Grade. Name: - . - . - . - . - " " E.S-5api-253679034Nessuna valutazione finora
- Lycée Des Arts: Areas & Perimeters of Plane FiguresDocumento2 pagineLycée Des Arts: Areas & Perimeters of Plane Figuresapi-253679034Nessuna valutazione finora
- Lycée Des Arts: Mathematics 9 - Grade Name: - . - . - . - . - . "Overview About Special Quadrilaterals"Documento4 pagineLycée Des Arts: Mathematics 9 - Grade Name: - . - . - . - . - . "Overview About Special Quadrilaterals"api-253679034Nessuna valutazione finora
- 1st-Trial 13-14Documento2 pagine1st-Trial 13-14api-253679034Nessuna valutazione finora
- 1st-Trial 09-10Documento2 pagine1st-Trial 09-10api-253679034Nessuna valutazione finora
- 1st-Trial 21-22Documento2 pagine1st-Trial 21-22api-253679034Nessuna valutazione finora
- 1st-Trial 11-12Documento2 pagine1st-Trial 11-12api-253679034Nessuna valutazione finora
- 1st-Trial 10-11Documento2 pagine1st-Trial 10-11api-253679034Nessuna valutazione finora
- 1st-Trial 08-09Documento2 pagine1st-Trial 08-09api-253679034Nessuna valutazione finora
- 1st-Trial 12-13Documento2 pagine1st-Trial 12-13api-253679034Nessuna valutazione finora
- Midyear 19-20Documento2 pagineMidyear 19-20api-253679034Nessuna valutazione finora
- 1st-Trial 16-17Documento2 pagine1st-Trial 16-17api-253679034Nessuna valutazione finora
- 1st-Trial 14-15Documento2 pagine1st-Trial 14-15api-253679034Nessuna valutazione finora
- Correction-Standards For Midterm 19-20Documento2 pagineCorrection-Standards For Midterm 19-20api-253679034Nessuna valutazione finora
- Midterm 19-20Documento2 pagineMidterm 19-20api-253679034Nessuna valutazione finora
- 1st-Trial 19-20Documento2 pagine1st-Trial 19-20api-253679034Nessuna valutazione finora
- Midyear 19-20Documento2 pagineMidyear 19-20api-253679034Nessuna valutazione finora
- Correction of Midyear 19-20Documento1 paginaCorrection of Midyear 19-20api-253679034Nessuna valutazione finora
- Midyear 19-20Documento2 pagineMidyear 19-20api-253679034Nessuna valutazione finora
- 1st-Trial 15-16Documento2 pagine1st-Trial 15-16api-253679034Nessuna valutazione finora
- Midterm 19-20Documento2 pagineMidterm 19-20api-253679034Nessuna valutazione finora
- 8 THDocumento3 pagine8 THapi-253679034Nessuna valutazione finora
- 3rd-Trial 17-18Documento2 pagine3rd-Trial 17-18api-253679034Nessuna valutazione finora
- Mathematics - Grade Name: - . - . - . - . " Statistics" W.S-14Documento2 pagineMathematics - Grade Name: - . - . - . - . " Statistics" W.S-14api-253679034Nessuna valutazione finora
- Your Warm Up Today Is The R.1&R.2 Review Ws On Itunes U.: R.3 Right Triangles in Q1Documento13 pagineYour Warm Up Today Is The R.1&R.2 Review Ws On Itunes U.: R.3 Right Triangles in Q1api-444439435Nessuna valutazione finora
- Grade 10 Trigonometry IdDocumento10 pagineGrade 10 Trigonometry IdDjemi SiswantoNessuna valutazione finora
- Mensuration Square Shaped Figure 2D and 3DDocumento11 pagineMensuration Square Shaped Figure 2D and 3DAbdullah Al Noman MarufNessuna valutazione finora
- G10 Standard - Iii Preboard 2022-23 - QP (Set B)Documento7 pagineG10 Standard - Iii Preboard 2022-23 - QP (Set B)sahanaaarunNessuna valutazione finora
- Lecture20 Double and Half-Angle IdentitiesDocumento4 pagineLecture20 Double and Half-Angle Identitiesmarchelo_cheloNessuna valutazione finora
- One Shot Straight LinesDocumento164 pagineOne Shot Straight LinesAaryan Chodankar100% (1)
- Class 10 Maths Solved HSLC QuestionsDocumento152 pagineClass 10 Maths Solved HSLC QuestionsLalchhanhima ChhanaNessuna valutazione finora
- Types of Triangles GCSE WorksheetDocumento14 pagineTypes of Triangles GCSE WorksheetSouvik GhoshNessuna valutazione finora
- Module 1 - CirclesDocumento27 pagineModule 1 - CirclesHenry Languisan50% (2)
- Math Reviewer 2nd Quarter Grade 10Documento5 pagineMath Reviewer 2nd Quarter Grade 10Joshua GariandoNessuna valutazione finora
- Medieval Islamic World: The Compendious Book On Calculation by Completion and BalancingDocumento2 pagineMedieval Islamic World: The Compendious Book On Calculation by Completion and BalancingRonaldNessuna valutazione finora
- PRMO Assignment - 10: X P X X XDocumento4 paginePRMO Assignment - 10: X P X X XaumoghNessuna valutazione finora
- 826e7d61cdcb2db132f6b543be299df4Documento14 pagine826e7d61cdcb2db132f6b543be299df4shweta051Nessuna valutazione finora
- Mathematics Assignment P8Documento17 pagineMathematics Assignment P8chandraNessuna valutazione finora
- To Draw Their Projections Means F.V, T.V. & S.V. What Is Usually Asked in The Problem?Documento37 pagineTo Draw Their Projections Means F.V, T.V. & S.V. What Is Usually Asked in The Problem?Amit MakhijaNessuna valutazione finora
- 8-Mathematics - Quiz 8 Solutions - 22 Sept. 2021Documento12 pagine8-Mathematics - Quiz 8 Solutions - 22 Sept. 2021Francis John BuacNessuna valutazione finora
- Trigonometry FormulasDocumento3 pagineTrigonometry Formulasakshat yadavNessuna valutazione finora
- UPCAT Mathematics Practice Questions Set 2Documento10 pagineUPCAT Mathematics Practice Questions Set 2Irishmae HervasNessuna valutazione finora
- PolygonsDocumento8 paginePolygonsDaisuke InoueNessuna valutazione finora
- 00 Guided Notes Circles DALDocumento14 pagine00 Guided Notes Circles DALarfan ardiyantoNessuna valutazione finora
- Math ChapterDocumento6 pagineMath ChapterRavi AutiNessuna valutazione finora
- Exercise Quadratic Equations and Application ProblemsDocumento1 paginaExercise Quadratic Equations and Application ProblemsNobleNessuna valutazione finora
- Homework Book AnswersDocumento15 pagineHomework Book AnswersDeez NutsNessuna valutazione finora
- Interactive Classroom Circles and CircumferenceDocumento28 pagineInteractive Classroom Circles and CircumferenceLLLNessuna valutazione finora
- Aops Community 1972 Amc 12/ahsmeDocumento8 pagineAops Community 1972 Amc 12/ahsmeQWERTY111Nessuna valutazione finora
- PRECALCULUS TOS-MidtermDocumento2 paginePRECALCULUS TOS-MidtermJERLYN MACADONessuna valutazione finora
- Sulit 1449/1 Matematik Kertas 1 Oktober 2013Documento19 pagineSulit 1449/1 Matematik Kertas 1 Oktober 2013Siti Rohani Mohd KadriNessuna valutazione finora
- POGIME FinalDocumento4 paginePOGIME FinalJerry XiaoNessuna valutazione finora
- School: Grade Level: Grade 8 Teacher: Learning Area: QuadrilateralsDocumento22 pagineSchool: Grade Level: Grade 8 Teacher: Learning Area: QuadrilateralsAdonis FabillaranNessuna valutazione finora