Documenti di Didattica
Documenti di Professioni
Documenti di Cultura
Rte 141 Note Book 11
Caricato da
api-3314715680 valutazioniIl 0% ha trovato utile questo documento (0 voti)
33 visualizzazioni2 pagineTitolo originale
rte 141 note book 11
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Formati disponibili
DOCX, PDF, TXT o leggi online da Scribd
Condividi questo documento
Condividi o incorpora il documento
Hai trovato utile questo documento?
Questo contenuto è inappropriato?
Segnala questo documentoCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Formati disponibili
Scarica in formato DOCX, PDF, TXT o leggi online su Scribd
0 valutazioniIl 0% ha trovato utile questo documento (0 voti)
33 visualizzazioni2 pagineRte 141 Note Book 11
Caricato da
api-331471568Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Formati disponibili
Scarica in formato DOCX, PDF, TXT o leggi online su Scribd
Sei sulla pagina 1di 2
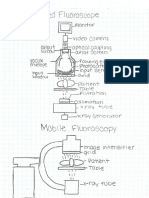
NOTE BOOK # 11
The X-Ray Tube Components
The X-ray rube is where the electrical production of x-rays is possible. There are
certain components that are important in making this production work. Every tube
has to have a source of electrons, an appropriate target material, high voltage, and
a vacuum. Every tube has to have a cathode and anode in order to create a
potential difference and create photons. There is a tubing house envelope or
glass envelope (3) is used as protection. It helps cool the tube, absorbs of
focus radiation, and isolates high voltages.
The Cathode is the negative side of the tube, the function of this side is to produce
a thermionic cloud, conduct high voltage between the gap of itself and the anode,
and focus the stream of electrons to the positive side. This is a complex device and
is often referred to by the cathode assembly. The assembly includes the filament,
focusing cup, and associated wiring.
Filament (5): Most x-rays will have a dual filament. It is made up of
tungsten, because of its high melting point, and its difficulty to be vaporized.
The length and width of this filament will have a great impact of the detail of
the images that are created. The overall function of the filament is to provide
sufficient resistance to the flow of electrons so that heat s produced and will
cause thermionic emission to occur.
Focusing Cup (12): This helps control the electron cloud. The electrons
repel each other & want to spread out. The cup forces them to stay together
and stay in a small stream that heads toward to the target. Usually it is made
of nickel.
Electron Beam (11): This is the electrons making its move across the gap to
the anode target, that is being controlled by the focusing cup.
The filament circuit (2): This circuit controls the tube current, the more
electrons that are boiled off the higher the tube current.
The X-Ray Beam (10): The effective beam is the beam that goes strait
toward the patient. The bouncing of the beam is caused by the anode heal
effect. Which is based upon the angle of the anode itself.
The Anode is the other side of the x-ray tube, which is known as the positive side.
Tis side has 3 functions, it serves as a target surface for high voltage electrons from
the filament, the source of x-ray photons, and it serves as the primary thermal
conductor. The anode target surface is where the high speed electrons from the
filament are suddenly stopped resulting in the photon production. The assembly of
the anode consists of the stator and rotor, which serves as a path for the high
voltage flow during the exposure. The faster the anode rotates, the better the heat
dissipation is, which heat is the number 1 reason that tubes fail. Now to describe
the components on the anode side, that are shown in the drawing of the x-ray tube.
The tungsten anode (4): This is the point of the anode where the electrons
strike, which than directs the x-ray beam. Tungsten is chosen because of its
high atomic number, high thermal conductivity level, and it high melting
point.
NOTE BOOK # 11
Molybdenum neck and base (9): may assist with the dissipation of heath
in heavy load situations.
Bearing (6): Reducing rotational friction caused by the rotor.
Armature (7): Apart of the rotating of the anode. Which is induced with
current.
Rotating Portion (8): showing where the actual rotation is occurring, which
contains the bearings inside.
Stator Electromagnets (1): The device that is actually causing the rotation
of the anode, which increases the target area. This allows the anode to have
much high heat capacities.
Potrebbero piacerti anche
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeDa EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeValutazione: 4 su 5 stelle4/5 (5794)
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeDa EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeValutazione: 4.5 su 5 stelle4.5/5 (537)
- Rte 142 Notebok 10Documento2 pagineRte 142 Notebok 10api-331471568Nessuna valutazione finora
- Rte 142 Notebook 10 Lab ResultsDocumento2 pagineRte 142 Notebook 10 Lab Resultsapi-331471568Nessuna valutazione finora
- Rte 142 Notebook 10 Fluoro EquationsDocumento3 pagineRte 142 Notebook 10 Fluoro Equationsapi-331471568Nessuna valutazione finora
- Rte 142 Notebook 10 Digital Vs ItDocumento2 pagineRte 142 Notebook 10 Digital Vs Itapi-331471568Nessuna valutazione finora
- Rte 142 Notebook 5Documento2 pagineRte 142 Notebook 5api-331471568Nessuna valutazione finora
- Scan0010 Fluro DrawingDocumento1 paginaScan0010 Fluro Drawingapi-331471568Nessuna valutazione finora
- Rte 142 Notebook 2Documento4 pagineRte 142 Notebook 2api-331471568Nessuna valutazione finora
- Rte 142 PSP Imaging PlateDocumento1 paginaRte 142 PSP Imaging Plateapi-331471568Nessuna valutazione finora
- Rte 142 Notebook 10 TimelineDocumento2 pagineRte 142 Notebook 10 Timelineapi-331471568Nessuna valutazione finora
- Notebook 3 142Documento3 pagineNotebook 3 142api-331471568Nessuna valutazione finora
- Rte 142 Notebook 4Documento4 pagineRte 142 Notebook 4api-331471568Nessuna valutazione finora
- Rte 141 Notebook 6Documento3 pagineRte 141 Notebook 6api-331471568Nessuna valutazione finora
- Rte 142 Notebook 1Documento4 pagineRte 142 Notebook 1api-331471568Nessuna valutazione finora
- Scan0008 Cassette LayersDocumento1 paginaScan0008 Cassette Layersapi-331471568Nessuna valutazione finora
- Rte 141 Notebook 7Documento3 pagineRte 141 Notebook 7api-331471568Nessuna valutazione finora
- Rte 142 Notebook 12Documento2 pagineRte 142 Notebook 12api-331471568Nessuna valutazione finora
- Rte 142 Notebook 11Documento2 pagineRte 142 Notebook 11api-331471568Nessuna valutazione finora
- Rte 142 Notebook 8Documento5 pagineRte 142 Notebook 8api-331471568Nessuna valutazione finora
- Rte 142 Notebook 6Documento2 pagineRte 142 Notebook 6api-331471568Nessuna valutazione finora
- Rte 142 Notebook 9Documento4 pagineRte 142 Notebook 9api-331471568Nessuna valutazione finora
- Rte 141 Notebook 13Documento3 pagineRte 141 Notebook 13api-331471568Nessuna valutazione finora
- Waveforms of Rectification PowerpointDocumento9 pagineWaveforms of Rectification Powerpointapi-331471568Nessuna valutazione finora
- Rte 141 Note Book 15Documento2 pagineRte 141 Note Book 15api-331471568Nessuna valutazione finora
- Rte 142 Noebook 7Documento4 pagineRte 142 Noebook 7api-331471568Nessuna valutazione finora
- Note Book 10Documento3 pagineNote Book 10api-331471568Nessuna valutazione finora
- Note Book 9Documento1 paginaNote Book 9api-331471568Nessuna valutazione finora
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Da EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Valutazione: 4 su 5 stelle4/5 (98)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceDa EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceValutazione: 4 su 5 stelle4/5 (895)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersDa EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersValutazione: 4.5 su 5 stelle4.5/5 (344)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingDa EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingValutazione: 3.5 su 5 stelle3.5/5 (399)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceDa EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceValutazione: 4 su 5 stelle4/5 (588)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerDa EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerValutazione: 4.5 su 5 stelle4.5/5 (271)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaDa EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaValutazione: 4.5 su 5 stelle4.5/5 (266)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItDa EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItValutazione: 4.5 su 5 stelle4.5/5 (838)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryDa EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryValutazione: 3.5 su 5 stelle3.5/5 (231)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealDa EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealValutazione: 4 su 5 stelle4/5 (73)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureDa EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureValutazione: 4.5 su 5 stelle4.5/5 (474)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnDa EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnValutazione: 4.5 su 5 stelle4.5/5 (234)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyDa EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyValutazione: 3.5 su 5 stelle3.5/5 (2259)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaDa EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaValutazione: 4 su 5 stelle4/5 (45)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreDa EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreValutazione: 4 su 5 stelle4/5 (1090)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Da EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Valutazione: 4.5 su 5 stelle4.5/5 (120)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesDa EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesValutazione: 4 su 5 stelle4/5 (821)
- Generator ProtectionDocumento5 pagineGenerator ProtectionThirumalNessuna valutazione finora
- Physics LODocumento39 paginePhysics LOAbdullah MohamedNessuna valutazione finora
- QB PSC Unit-IDocumento4 pagineQB PSC Unit-IManigandan PriyaNessuna valutazione finora
- Nano and Micro PTFEDocumento22 pagineNano and Micro PTFERazvan ScarlatNessuna valutazione finora
- Born-Oppenheimer ApproximationDocumento6 pagineBorn-Oppenheimer ApproximationSup FansNessuna valutazione finora
- Section 6 Magnetism Electromagnetism - UnlockedDocumento43 pagineSection 6 Magnetism Electromagnetism - UnlockedgesNessuna valutazione finora
- Bearing Dynamic Static Load Carrying Capacity PDFDocumento11 pagineBearing Dynamic Static Load Carrying Capacity PDFmanimeczNessuna valutazione finora
- IX Final Exam Science 2021-22 - Google FormsDocumento4 pagineIX Final Exam Science 2021-22 - Google FormsKing RajdeepNessuna valutazione finora
- X X F DX X F: Applications of Integration Plane Areas by IntegrationDocumento17 pagineX X F DX X F: Applications of Integration Plane Areas by IntegrationLee Anthony ChingNessuna valutazione finora
- M.SC Phy, I Yr, P-II Clas MechDocumento172 pagineM.SC Phy, I Yr, P-II Clas MechAMIT VAIDNessuna valutazione finora
- DC To AC Inverter With DSCDocumento23 pagineDC To AC Inverter With DSCUsamah FarooquiNessuna valutazione finora
- X Ray DiffractionDocumento122 pagineX Ray DiffractionNayan Raj ShandilyaNessuna valutazione finora
- Chapter 1 Chem Kinetics Auto Saved)Documento127 pagineChapter 1 Chem Kinetics Auto Saved)Mohd IzzudinNessuna valutazione finora
- Blade Calculations For Water Turbines of The Banki Type: Citation For Published Version (APA)Documento24 pagineBlade Calculations For Water Turbines of The Banki Type: Citation For Published Version (APA)Anonymous Hy5Ir9QXNessuna valutazione finora
- Physics Assignment 4Documento2 paginePhysics Assignment 4happyworryNessuna valutazione finora
- Analytic Solution of Stokes Second Problem For Second-Grade FluidDocumento9 pagineAnalytic Solution of Stokes Second Problem For Second-Grade FluidricljrNessuna valutazione finora
- Chemistry Unit 1Documento7 pagineChemistry Unit 1Natasha Liliane LootNessuna valutazione finora
- Dynamics HWDocumento21 pagineDynamics HWthebigdick619Nessuna valutazione finora
- Define An IndicatrixDocumento4 pagineDefine An IndicatrixTYron AnotidaNessuna valutazione finora
- Colision Entre Cartogeno Pampeano y Rio de La Plata PDFDocumento13 pagineColision Entre Cartogeno Pampeano y Rio de La Plata PDFMaria Ines LombardoNessuna valutazione finora
- FluidStatics PracticeProblemsDocumento12 pagineFluidStatics PracticeProblemsDavid Sulis100% (1)
- LC and AC CircuitsDocumento35 pagineLC and AC CircuitsAmy LangMui Locke100% (11)
- Catalytic Reaction Transport and Kinetics - W7Documento46 pagineCatalytic Reaction Transport and Kinetics - W7Nabilahtul FullahNessuna valutazione finora
- 1 Microwave Theory and TechniqesDocumento77 pagine1 Microwave Theory and TechniqesKomal Khurana71% (7)
- Physical Sciences Baseline Test Gr11Documento7 paginePhysical Sciences Baseline Test Gr11Midyondzi ngobeniNessuna valutazione finora
- Summary Notes - Topic 3 Waves - Edexcel Physics IGCSEDocumento5 pagineSummary Notes - Topic 3 Waves - Edexcel Physics IGCSEVarsha PNessuna valutazione finora
- Material PropertiesDocumento2 pagineMaterial PropertiesCelineKevinNessuna valutazione finora
- Venturi, Orifice, RotameterDocumento34 pagineVenturi, Orifice, RotameterVinod VadithyaNessuna valutazione finora
- My SVPWMprojectDocumento68 pagineMy SVPWMprojectHari Reddy100% (1)
- 3.3.2 Current Capacity of The CableDocumento11 pagine3.3.2 Current Capacity of The CableardiwilagagunNessuna valutazione finora