Documenti di Didattica
Documenti di Professioni
Documenti di Cultura
Definitions
Caricato da
Taichi Everlast0 valutazioniIl 0% ha trovato utile questo documento (0 voti)
32 visualizzazioni3 pagineTitolo originale
definitions.doc
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Formati disponibili
DOC, PDF, TXT o leggi online da Scribd
Condividi questo documento
Condividi o incorpora il documento
Hai trovato utile questo documento?
Questo contenuto è inappropriato?
Segnala questo documentoCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Formati disponibili
Scarica in formato DOC, PDF, TXT o leggi online su Scribd
0 valutazioniIl 0% ha trovato utile questo documento (0 voti)
32 visualizzazioni3 pagineDefinitions
Caricato da
Taichi EverlastCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Formati disponibili
Scarica in formato DOC, PDF, TXT o leggi online su Scribd
Sei sulla pagina 1di 3
COMPUTER GRAPHICS
(Short Answer type Questions)
Q 1. Can you tell which major components (hardware and software) are
needed for computer graphics?
Ans. Besides the basic computer, some special devices and software may be
required especially for computer graphics. For hardware, a special high-resolution,
color monitor is often demanded and some input tools, e.g. mouse and joy-sticker,
and hard-copy devices, e.g. high-resolution color printer, may be required. For
software, some special purpose utilities (device-dependent and device independent)
are needed for handling processing in computer graphics.
Q 2. Can you list at least three important applications of computer graphics?
Ans. There are many interesting applications of computer graphics. Three common
applications are graphic user interface (GUI), computer-aided design (CAD), and
computer games.
Q 3. Define Computer Graphics.
Ans. Computer graphics remains one of the most existing and rapidly growing
computer fields. Computer graphics may be defined as a pictorial representation or
graphical representation of objects in a computer.
Q 4. What is meant by scan code?
Ans. When a key is pressed on the keyboard, the keyboard controller places a code
carry to the key pressed into a part of the memory called as the keyboard buffer.
This code is called as the scan code.
Q 5. What does refreshing of the screen mean?
Ans. Some method is needed for maintaining the picture on the screen. Refreshing
of screen is done by keeping the phosphorus glowing to redraw the picture
repeatedly. i.e. by quickly directing the electronic beam back to the same points.
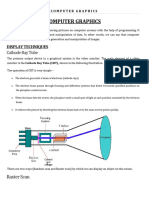
Q 6. Define Random Scan/Raster Scan displays.
Ans. Random scan is a method in which the display is made by the electronic
beam, which is directed, only to the points or part of the screen where the picture is
to be drawn. The Raster scan system is a scanning technique in which the electrons
sweep from top to bottom and from left to right. The intensity is turned on or off to
light and unlight the pixel.
Q 7. Explain the merits and demerits of Penetration techniques.
Ans. The merits and demerits of the Penetration techniques are as follows:
1. It is an inexpensive technique.
2. It has only four colors.
3. The quality of the picture is not good when it is compared to other techniques.
4. It can display color scans in monitors.
Q 8. Explain the merits and demerits of DVST.
Ans. The merits and demerits of direct view storage tubes (DVST) are as follows:
1. It has a flat screen.
2. Refreshing of screen is not required.
3. Selective or part erasing of screen is not possible.
4. It has poor contrast.
5. Performance is inferior to the refresh CRT.
Q 9. What do you mean by emissive and non-emissive displays?
Ans. EMISSIVE:
The emissive display converts electrical energy into light energy. The plasma
panels, thin film
electro-luminescent displays are the examples.
NON-EMISSIVE:
They are optical effects to convert the sunlight or light from any other source to
graphic form. Liquid crystal display is an example.
Q 10. Explain the merits and demerits of Plasma panel display.
Ans. ADVANTAGES:
1. Refreshing is not required.
2. Produce a very steady image free of Flicker.
3. Less bulky than a CRT.
DISADVANTAGES:
1. Poor resolution of up to 60 d.p.i.
2. It requires complex addressing and wiring.
3. It is costlier than CRT.
Q 11. What is persistence?
Ans. The time it takes the emitted light from the screen to decay one tenth of its
original intensity is called as persistence.
Q 12. What is resolution?
Ans. The maximum number of points that can be displayed without an overlap on
a CRT is called as resolution.
Q 13. What is Aspect Ratio?
Ans. The ratio of vertical points to the horizontal points necessary to produce
length of lines in both directions of the screen is called Aspect Ratio. Usually the
aspect ratio is .
Potrebbero piacerti anche
- Traktor Signatures Set-Up DubfireDocumento1 paginaTraktor Signatures Set-Up DubfireAndres Fernando Rodriguez JaramilloNessuna valutazione finora
- CS602 Short Notes (1 To 22)Documento60 pagineCS602 Short Notes (1 To 22)Zain AhmedNessuna valutazione finora
- Electronic Control System ComponentsDocumento7 pagineElectronic Control System ComponentsTri WahyuningsihNessuna valutazione finora
- .. Uploads Question Bank Btech 4sem Cse CG Important Question With Answer (UNIT-I)Documento13 pagine.. Uploads Question Bank Btech 4sem Cse CG Important Question With Answer (UNIT-I)هارون المقطريNessuna valutazione finora
- Short Answer Type QuestionsDocumento6 pagineShort Answer Type QuestionsHIDEINPRE08Nessuna valutazione finora
- Computer Graphics - Important Question and AnswersDocumento9 pagineComputer Graphics - Important Question and AnswersR Anirudh ChelseaNessuna valutazione finora
- For Academic Use OnlyDocumento17 pagineFor Academic Use OnlyPrakhar SrivastavaNessuna valutazione finora
- Computer Graphics Viva QuestionDocumento8 pagineComputer Graphics Viva QuestionRugved TatkareNessuna valutazione finora
- Graphics 1Documento6 pagineGraphics 1Surendra Singh ChauhanNessuna valutazione finora
- Chapter-I Q.1: Why We Need Computer Graphics ?Documento25 pagineChapter-I Q.1: Why We Need Computer Graphics ?Chandan SrivastavaNessuna valutazione finora
- Section C - Tapescript and Answer Keys 243Documento7 pagineSection C - Tapescript and Answer Keys 243certo2011Nessuna valutazione finora
- Computer GraphicDocumento11 pagineComputer GraphicKidus SeleshiNessuna valutazione finora
- Computer Graphics IntroDocumento7 pagineComputer Graphics IntroraceacademyrbNessuna valutazione finora
- Cs2401 Computer Graphiccs Question Bank With AnswersDocumento11 pagineCs2401 Computer Graphiccs Question Bank With Answersathirayan100% (1)
- Display UnitDocumento28 pagineDisplay UnitGuty HuancaNessuna valutazione finora
- Color CRT MonitorsDocumento8 pagineColor CRT MonitorsSahilNessuna valutazione finora
- Question and AnswerDocumento15 pagineQuestion and AnswerIT Department HODNessuna valutazione finora
- 5cs4 4 CGMT Guess Paper Solution 8492Documento73 pagine5cs4 4 CGMT Guess Paper Solution 8492PratapNessuna valutazione finora
- Chapter 1: Overview of Graphics SystemsDocumento9 pagineChapter 1: Overview of Graphics SystemsprincejiNessuna valutazione finora
- DC105 Module1 Lesson2 - Graphics and VisualizationDocumento12 pagineDC105 Module1 Lesson2 - Graphics and VisualizationsdfNessuna valutazione finora
- Computer Graphics Questions and AnswersDocumento8 pagineComputer Graphics Questions and AnswersAneeshia SasidharanNessuna valutazione finora
- Assignment 1 Computer Graphics NicoleDocumento5 pagineAssignment 1 Computer Graphics NicoleSimbarashe HlanyaNessuna valutazione finora
- Display Devices Assignm3ntDocumento15 pagineDisplay Devices Assignm3ntakhil rankaNessuna valutazione finora
- Computer Graphics - HandoutsDocumento26 pagineComputer Graphics - HandoutsSaqib HayatNessuna valutazione finora
- CG VivaDocumento10 pagineCG VivaSantOsh JamaDarNessuna valutazione finora
- Random Scan and Raster Scan DisplayDocumento8 pagineRandom Scan and Raster Scan DisplayAyush SharmaNessuna valutazione finora
- Final - Sheet 2018 04 01 Part1Documento30 pagineFinal - Sheet 2018 04 01 Part1Lee CangNessuna valutazione finora
- Assignment:-1: Introduction To Computer Graphics QuestionsDocumento16 pagineAssignment:-1: Introduction To Computer Graphics QuestionsDrashti PatelNessuna valutazione finora
- CG Unit-1 Computer GraphicsDocumento25 pagineCG Unit-1 Computer GraphicsIshanika SharmaNessuna valutazione finora
- Sample Study Material: NTA UGC-NET Computer Science and ApplicationsDocumento71 pagineSample Study Material: NTA UGC-NET Computer Science and ApplicationsSrinivas JupalliNessuna valutazione finora
- Display DevicesDocumento25 pagineDisplay DevicesReyansh RoyNessuna valutazione finora
- CAD Display DevicesDocumento38 pagineCAD Display DevicesMrinal ShahNessuna valutazione finora
- Computer GraphicsDocumento6 pagineComputer GraphicsLady BugNessuna valutazione finora
- CG Lab Exam Viva QuestionsDocumento3 pagineCG Lab Exam Viva Questionsvasanthi2014Nessuna valutazione finora
- Graphics NotesDocumento16 pagineGraphics NotesSamuel EbenezerNessuna valutazione finora
- CGM Lec-4Documento11 pagineCGM Lec-4RAKESH KUMARNessuna valutazione finora
- Cathode Ray TubeDocumento17 pagineCathode Ray TubesandhyaNessuna valutazione finora
- DisplaysDocumento12 pagineDisplaysPlay ZoneNessuna valutazione finora
- Asics of Omputer Raphics: Chapter DetailsDocumento14 pagineAsics of Omputer Raphics: Chapter Detailsdamannaughty100% (1)
- CG Unit 1Documento22 pagineCG Unit 1VINAYAK CODMNessuna valutazione finora
- Unit-I: 1.what Is Scan Conversion?Documento10 pagineUnit-I: 1.what Is Scan Conversion?sNessuna valutazione finora
- Graphics UNIT 1 NotesDocumento39 pagineGraphics UNIT 1 NotesmalathiNessuna valutazione finora
- Computer Graphics: Week 4: Presentation By: Ms. Ifrah MansoorDocumento48 pagineComputer Graphics: Week 4: Presentation By: Ms. Ifrah MansoorAyesha RahimNessuna valutazione finora
- Fa20-Bcs-042 A2Documento3 pagineFa20-Bcs-042 A2waleedNessuna valutazione finora
- Digital Image ProcessingDocumento14 pagineDigital Image Processingnirankari_satishNessuna valutazione finora
- 51 - Graphics and Multimedia - CGDocumento22 pagine51 - Graphics and Multimedia - CGashishshrivastava340Nessuna valutazione finora
- UNIT 1:: Overview of Graphics System Characteristics of Cathode-Ray Tube (CRT)Documento37 pagineUNIT 1:: Overview of Graphics System Characteristics of Cathode-Ray Tube (CRT)Devang JoshiNessuna valutazione finora
- ICT STD VI - Output DevicesDocumento4 pagineICT STD VI - Output DevicesPatrick mdaganoNessuna valutazione finora
- CG Assignment-2 With SolutionDocumento11 pagineCG Assignment-2 With SolutionSelzer ProfitNessuna valutazione finora
- CG AssignmentDocumento47 pagineCG AssignmentdddddhwNessuna valutazione finora
- Computer Graphics QBDocumento19 pagineComputer Graphics QBAruna BajpaiNessuna valutazione finora
- Chapter 2Documento11 pagineChapter 2ibrahin mahamedNessuna valutazione finora
- CG UNIT !VVZVZDocumento32 pagineCG UNIT !VVZVZSaad ChaudharyNessuna valutazione finora
- Computer GraphicsDocumento22 pagineComputer GraphicsJaimin PatelNessuna valutazione finora
- Bangabandhu Sheikh Mujibur Rahman Science & Technology University, Gopalgonj-8100Documento17 pagineBangabandhu Sheikh Mujibur Rahman Science & Technology University, Gopalgonj-8100Bisnu SarkarNessuna valutazione finora
- 2 Lecture2Documento31 pagine2 Lecture2Format BookNessuna valutazione finora
- Output DevicesDocumento12 pagineOutput DevicesflolimNessuna valutazione finora
- Lecture - 5, 7 CAD System & HardwareDocumento24 pagineLecture - 5, 7 CAD System & Hardwaresyed yousafNessuna valutazione finora
- TFT-LCD Modules " Improving Video Performance/ Reducing CostDocumento7 pagineTFT-LCD Modules " Improving Video Performance/ Reducing CostAnonymous O5WK6kiLiV100% (1)
- Architecture of Computers and Parallel Systems Part 8: Computer Display UnitsDocumento28 pagineArchitecture of Computers and Parallel Systems Part 8: Computer Display UnitsGojko RatkovićNessuna valutazione finora
- Digital Signal Processing: A Practical Guide for Engineers and ScientistsDa EverandDigital Signal Processing: A Practical Guide for Engineers and ScientistsValutazione: 4.5 su 5 stelle4.5/5 (7)
- Selecting Video Monitors For The Home Features Of The Best Video MonitorDa EverandSelecting Video Monitors For The Home Features Of The Best Video MonitorNessuna valutazione finora
- IO-Link Interface DescriptionDocumento22 pagineIO-Link Interface DescriptionJoão Vitor TeixeiraNessuna valutazione finora
- Electrical Engineering Department: Practical Work (Lab 2) Dee 20023 Semiconductor Devices Program: Dep / DTKDocumento7 pagineElectrical Engineering Department: Practical Work (Lab 2) Dee 20023 Semiconductor Devices Program: Dep / DTKSarahmei MeiNessuna valutazione finora
- Excel Tips 2013 (Javed Iqbal Awan We Creat PDF Chemistry 03078162003)Documento7 pagineExcel Tips 2013 (Javed Iqbal Awan We Creat PDF Chemistry 03078162003)waqarNessuna valutazione finora
- DVLS VUV Analyzer User Manual: Based On ASTM D8071Documento22 pagineDVLS VUV Analyzer User Manual: Based On ASTM D8071Duy DangNessuna valutazione finora
- Mukesh Dubey Resume June 2019Documento2 pagineMukesh Dubey Resume June 2019Mukesh DubeyNessuna valutazione finora
- What Is Unijunction Transistor (UJT)Documento6 pagineWhat Is Unijunction Transistor (UJT)khan yousafzaiNessuna valutazione finora
- FST DFS Gardner DenverDocumento4 pagineFST DFS Gardner DenverEric DunnNessuna valutazione finora
- Microsoft Teams EnglishDocumento14 pagineMicrosoft Teams Englishapi-321004552Nessuna valutazione finora
- PAT GR 10 Learner 1 April 2016Documento19 paginePAT GR 10 Learner 1 April 2016khadijaosman33% (3)
- Managing Hotspot Clients With RadiusDocumento34 pagineManaging Hotspot Clients With Radiusiosmaris2331Nessuna valutazione finora
- Basic Electrical &electronics Engineering Lab Practice Course ContentsDocumento2 pagineBasic Electrical &electronics Engineering Lab Practice Course ContentsBhanoth MohanNessuna valutazione finora
- Chapter 4 Network SecurityDocumento10 pagineChapter 4 Network SecurityalextawekeNessuna valutazione finora
- Inverter Documents-OM Textiles 4MW Rev00Documento18 pagineInverter Documents-OM Textiles 4MW Rev00Kalayanaraman Ramakrishnan100% (1)
- Dyna Line, ButtonsDocumento20 pagineDyna Line, Buttonsgus459Nessuna valutazione finora
- Acceleration of Convolutional Neural Network Using FFT Based Split ConvolutionsDocumento5 pagineAcceleration of Convolutional Neural Network Using FFT Based Split ConvolutionsMUPPALLA HEMA VARSHITANessuna valutazione finora
- ENT ReadmeDocumento2 pagineENT ReadmegaNessuna valutazione finora
- How To Install Dev-C++ and GLUTDocumento15 pagineHow To Install Dev-C++ and GLUTMelquior PaniniNessuna valutazione finora
- 30 B 5 C 7Documento16 pagine30 B 5 C 7Irfan shagooNessuna valutazione finora
- As400 Subfile Programming Part II Basic CodingDocumento13 pagineAs400 Subfile Programming Part II Basic Codingmaka123Nessuna valutazione finora
- Finite Element in PLS-CADDDocumento11 pagineFinite Element in PLS-CADDMuhammad usman hayatNessuna valutazione finora
- AWS Academy Cloud Architecting Module 12 Student Guide: 200-ACACAD-20-EN-SGDocumento53 pagineAWS Academy Cloud Architecting Module 12 Student Guide: 200-ACACAD-20-EN-SGM Rizki AsriyandaNessuna valutazione finora
- Composite and Inverse FunDocumento14 pagineComposite and Inverse FunNiejay Arcullo LlagasNessuna valutazione finora
- Fortune - Tafadzwa - Madzivo - Infrastructure & Cyber Security OfficerDocumento4 pagineFortune - Tafadzwa - Madzivo - Infrastructure & Cyber Security OfficerFortune Tafadzwa MadzivoNessuna valutazione finora
- OOADDocumento21 pagineOOADNamelessNessuna valutazione finora
- Subnetting ItexampracticeDocumento12 pagineSubnetting ItexampracticeMohammad Tayyab KhusroNessuna valutazione finora
- Itt320 Quiz (Question)Documento9 pagineItt320 Quiz (Question)tesqNessuna valutazione finora
- P780Documento50 pagineP780Shailesh BhanushaliNessuna valutazione finora
- Ansys Airfoil 2DDocumento11 pagineAnsys Airfoil 2Dmonidogar88Nessuna valutazione finora