Documenti di Didattica
Documenti di Professioni
Documenti di Cultura
Power Electronics Half-Wave Rectifier Calculations
Caricato da
Mohab SamehTitolo originale
Copyright
Formati disponibili
Condividi questo documento
Condividi o incorpora il documento
Hai trovato utile questo documento?
Questo contenuto è inappropriato?
Segnala questo documentoCopyright:
Formati disponibili
Power Electronics Half-Wave Rectifier Calculations
Caricato da
Mohab SamehCopyright:
Formati disponibili
Faculty of Information Engineering & Technology
Electrical & Electronics Department
Course: Power Electronics (ELCT 704)
Sheet (3)
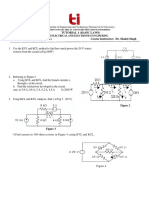
1- A 240V, 50 HZ voltage supply is feeding power to a 10 resistor through
a controlled half-wave rectifier operating at a firing angle of 120o as shown
in Figure 1.
a. Sketch the supply voltage, the load voltage and the voltage across the
thyristor (show all relevant magnitudes and angles).
b. Calculate the average output voltage and current.
c. Find the peak reverse and peak forward voltages of the thyristor.
d. Calculate the form factor and ripple factor of the current.
Figure 1
2- The battery shown in Figure 2 has a terminal voltage of 12 V and its
capacity is 100 W-h. The average charging current should be 5A. If the
battery is being charged from an uncontrolled half-wave rectifier
connected to a 60V, 50 Hz AC voltage supply, calculate
a. The conduction angle of the diode.
b. The current limiting resistance R.
c. The charging time in hours.
d. The rectifier efficiency.
e. The peak reverse voltage of the diode.
Figure 2
3- A 240V, 50 HZ AC voltage supply is used to charge a 20V battery with
internal resistance of 1 through a controlled half-wave rectifier operating
at a firing angle of 60o.
a. Sketch the waveforms for the output voltage, output current, and
thyristor voltage (show all relevant magnitudes and angles).
b. Find the input power factor of the supply neglecting the losses in the
thyristor.
Figure 3
4- A 240V, 50 HZ AC voltage supply is used to supply an R-L load as shown
in Figure 4. The resistance is 10 and the inductance is 0.1H.
a. Derive an expression for the output current in terms of the firing angle
and the extinction angle.
b. Sketch the waveforms for the output voltage, output current, resistor
voltage and thyristor voltage for a firing angle 110o (show all relevant
magnitudes and angles).
c. Calculate the average output voltage and current for the above
mentioned firing angle.
Figure 4
2
5- The 240V, 50Hz supply of the circuit shown in Figure 5 is supplying
power to a load composed of a resistance 15 in series with an inductance
0.12H. The firing angle of the thyristor is 0o (i.e., diode case) and the
operation is assumed to be continuous.
a. Sketch the waveforms of vo(t) , io(t) , vT(t) , vDF(t).
b. Obtain an expression for the output current.
c. Calculate the value of the output current at t = 0 and t = .
d. Calculate the value of the average current.
Figure 5
6- The single phase half wave circuit with free wheeling diode shown in
Figure 5 is used to supply a heavily inductive load having a constant
current of 15A from a 240V, 50 Hz ac supply.
a. Sketch the waveforms of vo(t) , iT(t) ,iDF(t), vDF(t) , vT(t).
b. Calculate the mean load voltage for firing angle 45o,135o,180o.
c. Calculate the value of the resistance in the load for a firing angle of 60o.
d. Find the peak reverse voltage and peak forward voltage for the thyristor
and the peak reverse voltage for the diode.
Potrebbero piacerti anche
- Experiment # 1: P-N Junction Diode: TheoryDocumento9 pagineExperiment # 1: P-N Junction Diode: Theorypoonginithi040% (1)
- DC-DC ConvertersDocumento30 pagineDC-DC ConvertersTema HassanNessuna valutazione finora
- SERIES AC CIRCUIT PROBLEMSDocumento4 pagineSERIES AC CIRCUIT PROBLEMSHubert Semeniano100% (1)
- ET Tut2 Ans AUT2016-17Documento6 pagineET Tut2 Ans AUT2016-17Tirumala Rao Yalla100% (1)
- (EPN (N401) :: A of atDocumento2 pagine(EPN (N401) :: A of atgeo_biNessuna valutazione finora
- Topic 3 Alternating Current Circuits I PDFDocumento20 pagineTopic 3 Alternating Current Circuits I PDFFeddy BlaizNessuna valutazione finora
- Sheet 3Documento3 pagineSheet 3geo_bi100% (1)
- GATE-2014 Electrical MeasurementsDocumento42 pagineGATE-2014 Electrical MeasurementsRamaDinakaran100% (1)
- Bangladesh University of Engineering and Technology: Group No. 4 Course No. Eee428Documento8 pagineBangladesh University of Engineering and Technology: Group No. 4 Course No. Eee428Samia SafaNessuna valutazione finora
- Proposed 15 Numerical Problems For PresentationDocumento8 pagineProposed 15 Numerical Problems For PresentationalexNessuna valutazione finora
- PEC Tutorial 3Documento3 paginePEC Tutorial 3harsh chaudharyNessuna valutazione finora
- 250 WATT Power Inverter: Power Small Appliances From Your Car or Any Other 12-Volt Source With Our 250-Watt InverterDocumento3 pagine250 WATT Power Inverter: Power Small Appliances From Your Car or Any Other 12-Volt Source With Our 250-Watt Invertertaner56Nessuna valutazione finora
- Assignment Problems HVDCDocumento2 pagineAssignment Problems HVDCSelva KumarNessuna valutazione finora
- Lab1 VHDLDocumento9 pagineLab1 VHDLGautam GowdaNessuna valutazione finora
- Electronic Devices Experiment 4Documento13 pagineElectronic Devices Experiment 4ArvinALNessuna valutazione finora
- Assignment 1Documento6 pagineAssignment 1Dr.Hesham El-BadawyNessuna valutazione finora
- Services Design Midsem - Docx AbDocumento5 pagineServices Design Midsem - Docx AbMichael Adu-boahenNessuna valutazione finora
- ECE 424: POWER ELECTRONICS II ASSIGNMENT (CAT 11Documento2 pagineECE 424: POWER ELECTRONICS II ASSIGNMENT (CAT 11Amos Atandi0% (1)
- Assignments StudentsDocumento2 pagineAssignments StudentsManju Chakraborty100% (1)
- EEE 2210-Analogue Electronics II-PrintreadyDocumento4 pagineEEE 2210-Analogue Electronics II-PrintreadyMike ShakespeareNessuna valutazione finora
- MBES - Lab 7-8 PDFDocumento23 pagineMBES - Lab 7-8 PDFDurraiz ShuaibNessuna valutazione finora
- Clipper Clamper CircuitsDocumento15 pagineClipper Clamper CircuitsAnilaSaghirNessuna valutazione finora
- Civil Services - Electrical Main Paper I & II - 1992-2012 - 7.6MBDocumento253 pagineCivil Services - Electrical Main Paper I & II - 1992-2012 - 7.6MBAnika DixitNessuna valutazione finora
- ELECS M3M4 FAsDocumento30 pagineELECS M3M4 FAsartNessuna valutazione finora
- Problem Set 2 in ELE 001Documento7 pagineProblem Set 2 in ELE 001Patrick Garcia100% (1)
- 1 (1) 4Documento10 pagine1 (1) 4Angga SeptianNessuna valutazione finora
- Sheet 6 Electronics - AnswerDocumento10 pagineSheet 6 Electronics - AnswerOla SamirNessuna valutazione finora
- Assignment IIIDocumento2 pagineAssignment IIIPrasenjit DeyNessuna valutazione finora
- Sheet 2 PDFDocumento3 pagineSheet 2 PDFOmar Nashat100% (1)
- Example 2PES2015Documento3 pagineExample 2PES2015FaizahmedNessuna valutazione finora
- Tutorial 2 PDFDocumento2 pagineTutorial 2 PDFSnehaNessuna valutazione finora
- PART IV. Instrument TransformersDocumento30 paginePART IV. Instrument TransformersuplbselesNessuna valutazione finora
- Thyristor ReportDocumento9 pagineThyristor ReportDhaval GamiNessuna valutazione finora
- Problems Chapter 5 1Documento7 pagineProblems Chapter 5 1Siva KumarNessuna valutazione finora
- EE 370 Electronic Instrument Assignment 3Documento1 paginaEE 370 Electronic Instrument Assignment 3vineet mishraNessuna valutazione finora
- Problems 5 Circuit WileyDocumento28 pagineProblems 5 Circuit WileyHelloWorld25% (4)
- Electrical System Design: Main Switch and Distribution Box SpecsDocumento4 pagineElectrical System Design: Main Switch and Distribution Box SpecsabhilashkrishnantkNessuna valutazione finora
- Eee2210 Analogue Elec II Omae Tie-PrintreadyDocumento4 pagineEee2210 Analogue Elec II Omae Tie-PrintreadyMike ShakespeareNessuna valutazione finora
- Full Wave Rectifier Guide: Circuit, Theory & UsesDocumento7 pagineFull Wave Rectifier Guide: Circuit, Theory & UsesArun PratapNessuna valutazione finora
- EEM328 Electronics Laboratory - Report4 - BJT BiasingDocumento4 pagineEEM328 Electronics Laboratory - Report4 - BJT Biasingdonatello84Nessuna valutazione finora
- Sheet 4 Electronics - AnswerDocumento7 pagineSheet 4 Electronics - AnswerOla SamirNessuna valutazione finora
- ADE Lab Manual - Analog Part PDFDocumento21 pagineADE Lab Manual - Analog Part PDFJk RinkuNessuna valutazione finora
- EXP2 Half Wave RectifierDocumento3 pagineEXP2 Half Wave RectifierMohammed Dyhia Ali50% (2)
- Schmitt TriggerDocumento4 pagineSchmitt TriggerManojkumarNessuna valutazione finora
- Ps 5Documento1 paginaPs 5Dawit B Melka100% (1)
- Experiment 1Documento12 pagineExperiment 1Jomar RosalesNessuna valutazione finora
- BJT Amplifier Sheet: Figure 1: Problem 1Documento3 pagineBJT Amplifier Sheet: Figure 1: Problem 1Ali AhmedNessuna valutazione finora
- Experiment No. 2.4 - The Squirrel-Cage Induction Motor ObjectiveDocumento3 pagineExperiment No. 2.4 - The Squirrel-Cage Induction Motor ObjectiveKristine AldayNessuna valutazione finora
- FiltersDocumento20 pagineFiltersSRINIKHIL GollaNessuna valutazione finora
- IIUM Electronics ECE 1312/ECE 1231 Final Exam Sem 1 (2012 - 2013)Documento8 pagineIIUM Electronics ECE 1312/ECE 1231 Final Exam Sem 1 (2012 - 2013)Ridhwan Asri100% (1)
- Tutorial1 8Documento9 pagineTutorial1 8Lovish BansalNessuna valutazione finora
- Assignment by Electrical Mentor: Author: BNSS Shankar, M.Tech (IITK)Documento11 pagineAssignment by Electrical Mentor: Author: BNSS Shankar, M.Tech (IITK)anjaneyuluNessuna valutazione finora
- Electrical Power and Machines IntroductionDocumento7 pagineElectrical Power and Machines Introductionshakeeb mana0% (1)
- Pages From Fundamentals of Electric Circuits 4th Ed - C. Alexander, M. Sadiku (McGraw-Hill, 2009) WWDocumento2 paginePages From Fundamentals of Electric Circuits 4th Ed - C. Alexander, M. Sadiku (McGraw-Hill, 2009) WWdabsorangejuiceNessuna valutazione finora
- Finally Power DiodeDocumento8 pagineFinally Power DiodeAndrei50% (2)
- DC effect on inductanceDocumento4 pagineDC effect on inductanceAndrei LeleaNessuna valutazione finora
- POWER ELECTROICS TUTORIALSDocumento20 paginePOWER ELECTROICS TUTORIALSSahil KumarNessuna valutazione finora
- ELEC2530 Rectifier Tutorial-1Documento2 pagineELEC2530 Rectifier Tutorial-1Khairul IkhwanNessuna valutazione finora
- Power Electronics Past QuestionsDocumento8 paginePower Electronics Past QuestionsSam MaosaNessuna valutazione finora
- Electrical and Electronic Principles 3 Checkbook: The Checkbook SeriesDa EverandElectrical and Electronic Principles 3 Checkbook: The Checkbook SeriesNessuna valutazione finora
- Lecture 5 PDFDocumento57 pagineLecture 5 PDFMohab SamehNessuna valutazione finora
- Lecture 9 PDFDocumento17 pagineLecture 9 PDFMohab SamehNessuna valutazione finora
- Lecture 2Documento57 pagineLecture 2Mohab SamehNessuna valutazione finora
- Elct 903 T8 PDFDocumento30 pagineElct 903 T8 PDFMohab SamehNessuna valutazione finora
- CamScanner Scans PDFs QuicklyDocumento4 pagineCamScanner Scans PDFs QuicklyMohab SamehNessuna valutazione finora
- Lecture 6 PDFDocumento61 pagineLecture 6 PDFMohab SamehNessuna valutazione finora
- Photovoltaic Systems Engineering Course OverviewDocumento49 paginePhotovoltaic Systems Engineering Course OverviewMohab SamehNessuna valutazione finora
- Lecture 1Documento55 pagineLecture 1Mohab SamehNessuna valutazione finora
- Lecture 7 PDFDocumento40 pagineLecture 7 PDFMohab Sameh100% (1)
- Lecture 4Documento23 pagineLecture 4Mohab SamehNessuna valutazione finora
- Lecture 3Documento41 pagineLecture 3Mohab SamehNessuna valutazione finora
- Lect - 3 - Sensor Technology PDFDocumento26 pagineLect - 3 - Sensor Technology PDFAhmedSeragNessuna valutazione finora
- Running Head: Title of Paper in Caps 1: Hadoop, Mapreduce and HDFS: A Developers PerspectiveDocumento5 pagineRunning Head: Title of Paper in Caps 1: Hadoop, Mapreduce and HDFS: A Developers PerspectiveMohab SamehNessuna valutazione finora
- Optoelectronics Homework Sheet 6Documento1 paginaOptoelectronics Homework Sheet 6Mohab SamehNessuna valutazione finora
- Dynamic Response of Measurement Systems: ME231 Measurements Laboratory Spring 1999Documento19 pagineDynamic Response of Measurement Systems: ME231 Measurements Laboratory Spring 1999Giriraj HedaNessuna valutazione finora
- StudentRecital Classical TemplateDocumento2 pagineStudentRecital Classical TemplateMohab SamehNessuna valutazione finora
- Concert MailDocumento1 paginaConcert MailMohab SamehNessuna valutazione finora
- Review: Dye Lasers: Presented By: Mohab Sameh Supervisor: Dr. Haitham OmranDocumento19 pagineReview: Dye Lasers: Presented By: Mohab Sameh Supervisor: Dr. Haitham OmranMohab SamehNessuna valutazione finora
- Step by StepDocumento18 pagineStep by StepAncil CleetusNessuna valutazione finora
- CT FinalDocumento5 pagineCT FinalMohab SamehNessuna valutazione finora
- Design ProblemDocumento8 pagineDesign ProblemMohab SamehNessuna valutazione finora
- FP ReportDocumento3 pagineFP ReportMohab SamehNessuna valutazione finora
- Computer Arithmetic: Introduction: Programmable Logic CircuitsDocumento75 pagineComputer Arithmetic: Introduction: Programmable Logic CircuitsMohab SamehNessuna valutazione finora
- Introduction To Electromagnetism and Its Application To Materials ScienceDocumento26 pagineIntroduction To Electromagnetism and Its Application To Materials ScienceMohab SamehNessuna valutazione finora
- NnoalsndolasDocumento13 pagineNnoalsndolasMohab SamehNessuna valutazione finora
- Interview QuestionsDocumento1 paginaInterview QuestionsMohab SamehNessuna valutazione finora
- DeadlinesDocumento2 pagineDeadlinesMohab SamehNessuna valutazione finora
- ChapterDocumento37 pagineChapterMohab SamehNessuna valutazione finora
- Jazz Concert Preliminary Preparations: 1. Dr. Yehia Al Razazz MeetingDocumento2 pagineJazz Concert Preliminary Preparations: 1. Dr. Yehia Al Razazz MeetingMohab SamehNessuna valutazione finora
- M.sc. Research Proposal GuideDocumento1 paginaM.sc. Research Proposal GuideMohab SamehNessuna valutazione finora
- Basic Electronics 97 Impor Tant MCQDocumento16 pagineBasic Electronics 97 Impor Tant MCQjyothir07Nessuna valutazione finora
- HP 245 G6 Notebook PC: Maintenance and Service GuideDocumento106 pagineHP 245 G6 Notebook PC: Maintenance and Service GuideStevenson QuinteroNessuna valutazione finora
- Selenium AutomationTest Part2 PDFDocumento347 pagineSelenium AutomationTest Part2 PDFBhavin Panchal100% (3)
- Remote Control User's Guide: Package Contents 700031-001)Documento2 pagineRemote Control User's Guide: Package Contents 700031-001)Howard HawkinsNessuna valutazione finora
- WP LAB Manual 12 13 Vinay Balaji TDocumento177 pagineWP LAB Manual 12 13 Vinay Balaji TSanathVsjsNessuna valutazione finora
- Verilog XL Training Material Ver2p2Documento360 pagineVerilog XL Training Material Ver2p2方瀚萩Nessuna valutazione finora
- Eclipse Instal GuideDocumento98 pagineEclipse Instal GuidebeevenNessuna valutazione finora
- Rocktron Midi Mate User ManualDocumento32 pagineRocktron Midi Mate User ManualBlack MammbaNessuna valutazione finora
- AZ-400 StudyGuide ENU FY23Q1.0Documento10 pagineAZ-400 StudyGuide ENU FY23Q1.0KarolNessuna valutazione finora
- The Mach System: AppendixDocumento28 pagineThe Mach System: AppendixkushishardhuNessuna valutazione finora
- Panasonic Th-L47et5d Chassis La35 Led TVDocumento75 paginePanasonic Th-L47et5d Chassis La35 Led TVsunny100% (1)
- Models Affected / Serial Numbers Affected:: All Imagepass-C1SDocumento5 pagineModels Affected / Serial Numbers Affected:: All Imagepass-C1SMehmet KaripNessuna valutazione finora
- ABB PLC-2 System 1772Documento170 pagineABB PLC-2 System 1772Mohsin Shaukat100% (1)
- STLDDocumento1 paginaSTLDdasari_reddy100% (1)
- HUAWEI VNS-L31C636B170 SD Card Software Upgrade Guideline DR deDocumento10 pagineHUAWEI VNS-L31C636B170 SD Card Software Upgrade Guideline DR deDr DeNessuna valutazione finora
- Oracle® Database XStream Guide 12c Release 1 (12.1)Documento316 pagineOracle® Database XStream Guide 12c Release 1 (12.1)errr33Nessuna valutazione finora
- The New Software EngineeringDocumento830 pagineThe New Software EngineeringApocalipsis2011175Nessuna valutazione finora
- SolutionswithExcelausersCookBook-1 1 PDFDocumento100 pagineSolutionswithExcelausersCookBook-1 1 PDFCarlos DelfinNessuna valutazione finora
- IBM DS8900F Enterprise Disk Storage Level 2 Quiz - TOS AttemptDocumento17 pagineIBM DS8900F Enterprise Disk Storage Level 2 Quiz - TOS AttemptMike ManselNessuna valutazione finora
- UFED Physical Analyzer v5.0 Manual March2016Documento238 pagineUFED Physical Analyzer v5.0 Manual March2016Allan StuartNessuna valutazione finora
- Shalini ReviewPaperDocumento6 pagineShalini ReviewPaperGirijambaNessuna valutazione finora
- System Requirements: Windows 8.1Documento3 pagineSystem Requirements: Windows 8.1Severine OlumaliNessuna valutazione finora
- OAS Cheat Sheet for File Locations, Commands, and Database ManagementDocumento8 pagineOAS Cheat Sheet for File Locations, Commands, and Database ManagementJuan Pablo Ochochoque YanezNessuna valutazione finora
- Application Examples Overview en PDFDocumento28 pagineApplication Examples Overview en PDFMatin AnsariNessuna valutazione finora
- ZeelProg PDCI-12 ManualDocumento9 pagineZeelProg PDCI-12 ManualCapitanSalamiNessuna valutazione finora
- Roland Cloud Manager Eng01 WDocumento8 pagineRoland Cloud Manager Eng01 WPablo Martinez MasipNessuna valutazione finora
- Adsl Router User ManualDocumento34 pagineAdsl Router User ManualRolando NoroñaNessuna valutazione finora
- Python Web FrameworkDocumento5 paginePython Web FrameworkAdli AzriNessuna valutazione finora
- Mstar CmdsDocumento9 pagineMstar CmdsAnil BpsNessuna valutazione finora
- COA MODULE Input Output OrganizationDocumento40 pagineCOA MODULE Input Output OrganizationDesyilalNessuna valutazione finora