Documenti di Didattica
Documenti di Professioni
Documenti di Cultura
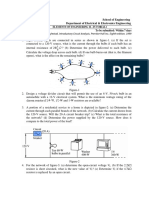
Solutions To Assignment 1 of ELEG2202
Caricato da
DuncanTitolo originale
Copyright
Formati disponibili
Condividi questo documento
Condividi o incorpora il documento
Hai trovato utile questo documento?
Questo contenuto è inappropriato?
Segnala questo documentoCopyright:
Formati disponibili
Solutions To Assignment 1 of ELEG2202
Caricato da
DuncanCopyright:
Formati disponibili
Solutions to Assignment 1 of ELEG2202
Total: 10+10+10+15+20+20+15=100
1.(10)
Independent sources can provide stable voltage or current to a network with no loss on itself, i.e.
the internal resistance or conductance is 0. It is a kind of theoretical concept which simplifies our
analysis process, while realistic sources behave in a way which deviates from ideal sources. We
can use the combination of ideal elements such as a voltage source in series with a resistor to
approximate a realistic source. However, no perfect match can be found, and only approximation
is achieved. Controlled source is also an ideal model in that it has no loss and it is used for
analytical purposes. Different from independent source, the level of voltage or current supplied
by controlled source is dependent on some other variables in a circuit, usually voltage or current,
instead of being a fixed constant.
2. (10)
(a) P (3.2V 2mA) 6.4mW .
(b) P 6V 20 A 120W .
(c) P 6V 2 5 A 60W .
(d) P 4sin 2V 8cos 2mA 32sin 2cos 2mW 12.1mW .
The above results with minus sign means the element is actually supplying power, while positive
means it is consuming power.
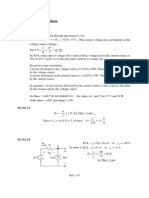
3.(10)
-2A
8V
5A
2V
-4A
10V
-3A
10V +
In order to compute the power consumed/supplied by each source, we need to know the voltage
across the source and the current flow through the source. Applying KCL to the node in the
ellipse, we can determine the current in the 2V and 8V voltage source is -2A as shown in the
graph above. Thus the power consumed by each source is:
2V voltage source: P 2V (2 A) 4W , supplying power.
8V voltage source: P 8V (2 A) 16W , supplying power.
-4A current source: P 10V (4 A) 40W , being charged.
10V voltage source: P 10V 5 A 50W , supplying power.
-3A current source: P 10V (3 A) 30W , being charged.
It can be shown that power conservation is satisfied: 4 16 40 50 30 0 .
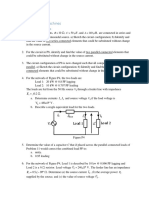
4. (15)
4
iin
N1
+
2V
vx
i4
N2
Is
6A
KVL
i3
8V
i2
4vx
First applying KVL to the central loop shown as the red arrow, we know: vx 2V 8V 10V .
According to Ohms Law, i1 10V / 4 2.5 A , i3 8V / 2 4 A , i4 2V / 2 1A . The
current of VCCS is i2 4 10 40 A .
Apply KCL at node N2, i1 i2 i3 Is 0 , so Is 46.5A .
Apply KCL at node N1, iin i1 i4 Is 6A 0 , so iin 49A .
The power provided by the dependent source is: P 8 40 320W , actually it is absorbing
power.
5. (20)
(a)
v1 v2 60V , v3 15V , v4 v5 45V
i1 27 A, i2 3 A, i3 24 A, i4 15 A, i5 9 A
(b) The absorbed powers of five circuit elements are denoted by pi i 1,,5 .
p1 v1i1 1620W
p2 v2i2 180W
p3 v3i3 360W
p4 v4i4 675W
p5 v5i5 405W
The sum of these absorbed powers is
p vi ii 0W
i 1
6. (20)
13V 10.5V
4A
(a)
0.02 R 0.035
R 0.57
I
(b) To deliver a power of 25 W to the battery, the following equation can be established :
2.5 10.5
2.5
0.035 25
0.02 0.035 R 0.02 0.035 R
R 1.003
2
(c) To present a voltage of 11 V at the terminals of the battery, the following equation must be
satisfied:
2.5
0.035 10.5 11
0.02 0.035 R
R 0.12
7. (15)
(a) Lets denote 7 sources by S1 , S 2 , S7 for the left to right , respectively. The absorbed powers
by different sources cab be found as follows:
p1 2V 5 A 10W
p2 6V (5 A) 30W
p3 4V (4 A) 16W
p4 4V 4 A 16W
p5 7V 3 A 21W
p6 3V 12 A 36W
p7 3V 9 A 27W
(b) The 4-V voltage source should be charged to be -2V.
Potrebbero piacerti anche
- Thevenin PDFDocumento12 pagineThevenin PDFHorvat ZoltánNessuna valutazione finora
- Lec2 BranchCurrentDocumento71 pagineLec2 BranchCurrentKuro ShiroNessuna valutazione finora
- Assignment 1 For CircuitsDocumento4 pagineAssignment 1 For CircuitsAmir EyniNessuna valutazione finora
- Elg2138 HW#1 Solution: P1) P2.5-2 - (The Resistor Voltage Does Not Depend On TheDocumento4 pagineElg2138 HW#1 Solution: P1) P2.5-2 - (The Resistor Voltage Does Not Depend On Thescara_dukeNessuna valutazione finora
- Electric Circuit AnalysisDocumento12 pagineElectric Circuit AnalysisMATHANKUMAR.SNessuna valutazione finora
- Assignment 2Documento5 pagineAssignment 2pappuyadav1996Nessuna valutazione finora
- Further Problems On Electricity: MBS3211 - Engineering Science For BS Electricity - TutorialsDocumento4 pagineFurther Problems On Electricity: MBS3211 - Engineering Science For BS Electricity - TutorialsCool DouglasNessuna valutazione finora
- ProblemsAC FundamentalsDocumento3 pagineProblemsAC Fundamentalskrishneel100% (1)
- Physics XII CH 7 CASE STUDY Alternating CurrentDocumento19 paginePhysics XII CH 7 CASE STUDY Alternating CurrentNjan KL16么PorottaNessuna valutazione finora
- Bai Tap Ve BJT3Documento23 pagineBai Tap Ve BJT3nguyenphuonghuy1979Nessuna valutazione finora
- Tutorial 01 (17012019)Documento6 pagineTutorial 01 (17012019)Devansh GuptaNessuna valutazione finora
- Applied One Tutorial ExcerciseDocumento18 pagineApplied One Tutorial ExcerciseABENEZER EPHREMNessuna valutazione finora
- Tutorials 1Documento20 pagineTutorials 1Sahil KumarNessuna valutazione finora
- Lecture 08Documento29 pagineLecture 08amitNessuna valutazione finora
- KNJ 2122 - Tutorial CH 1Documento3 pagineKNJ 2122 - Tutorial CH 1rpjongNessuna valutazione finora
- S1. Full Wave Bridge Rectifier - Principle of OperationDocumento7 pagineS1. Full Wave Bridge Rectifier - Principle of OperationVicNessuna valutazione finora
- Module - Ac CircuitsDocumento6 pagineModule - Ac CircuitsFalgun GeraNessuna valutazione finora
- 4d8f8analog 1, Tut SheetDocumento19 pagine4d8f8analog 1, Tut SheetmntykrNessuna valutazione finora
- C Lecjnco-' 4 Ele.E3-Vo'///Cs: /.!:::::!Y VasDocumento3 pagineC Lecjnco-' 4 Ele.E3-Vo'///Cs: /.!:::::!Y VasBhanu SharmaNessuna valutazione finora
- Tutorial Problems: Bipolar Junction Transistor (Basic BJT Amplifiers)Documento23 pagineTutorial Problems: Bipolar Junction Transistor (Basic BJT Amplifiers)vineetha nagahageNessuna valutazione finora
- Oc SC PDFDocumento5 pagineOc SC PDFVenkatasairamreddy KandulaNessuna valutazione finora
- Tutorial 2 PDFDocumento2 pagineTutorial 2 PDFSnehaNessuna valutazione finora
- Unit-2 QuestionsDocumento3 pagineUnit-2 Questionsabhioptimus00Nessuna valutazione finora
- Assign Single Phase Ac-2 (Unit-2)Documento4 pagineAssign Single Phase Ac-2 (Unit-2)Sunil JainNessuna valutazione finora
- Electric FundamentalDocumento31 pagineElectric FundamentalKein Huat ChuaNessuna valutazione finora
- Question Paper Code:: Reg. No.Documento0 pagineQuestion Paper Code:: Reg. No.aishuvc1822Nessuna valutazione finora
- Tutorial 1 PDFDocumento9 pagineTutorial 1 PDF马铃淑Nessuna valutazione finora
- Rectifier Probelems and SolutionsDocumento11 pagineRectifier Probelems and SolutionsMichael Jerlit J EEENessuna valutazione finora
- Electrical and Electronic Principles 3 Checkbook: The Checkbook SeriesDa EverandElectrical and Electronic Principles 3 Checkbook: The Checkbook SeriesNessuna valutazione finora
- TTLDocumento31 pagineTTLLembar Firdillah KurniawanNessuna valutazione finora
- Eee-III-Analog Electronic Circuits (15ee34) - AssignmentDocumento6 pagineEee-III-Analog Electronic Circuits (15ee34) - AssignmentchaitanyaNessuna valutazione finora
- Notes On Circuits Prepared by Dr. SrivastavaDocumento17 pagineNotes On Circuits Prepared by Dr. SrivastavaTarun GuptaNessuna valutazione finora
- Chapter 4 Additional Problems: X4.1 Determine The Value of The Coefficient of Coupling (Documento11 pagineChapter 4 Additional Problems: X4.1 Determine The Value of The Coefficient of Coupling (صدام حسینNessuna valutazione finora
- Analog Electronics Practice QuestionsDocumento19 pagineAnalog Electronics Practice Questionssharma_rockstarNessuna valutazione finora
- Contoh Soal Hukum Pembagi ArusDocumento7 pagineContoh Soal Hukum Pembagi ArusTomi MentariNessuna valutazione finora
- 0243Ch4Documento46 pagine0243Ch4fwoNessuna valutazione finora
- Assignment 3 Diode As A RectifierDocumento4 pagineAssignment 3 Diode As A RectifierRajesh PathakNessuna valutazione finora
- ECE590 - Tutorial 3 (UiTM)Documento5 pagineECE590 - Tutorial 3 (UiTM)NazhammerheartNessuna valutazione finora
- Tutorial 2Documento3 pagineTutorial 2rohan sinhaNessuna valutazione finora
- ENEL2EA Tutorial 3Documento5 pagineENEL2EA Tutorial 3fezileNessuna valutazione finora
- Solved Problems On RectifiersDocumento12 pagineSolved Problems On RectifiersAravind KarthikNessuna valutazione finora
- Review Problems in Series AC CircuitsDocumento4 pagineReview Problems in Series AC CircuitsVince RomanNessuna valutazione finora
- ENGN 20 HomeworkDocumento28 pagineENGN 20 HomeworkAhsan FarooquiNessuna valutazione finora
- Series Circuits-IDocumento35 pagineSeries Circuits-INatalia khanNessuna valutazione finora
- If The Switch S1 Is Closed and Switch S2 Remains Open, What Lights Will Turn On?Documento7 pagineIf The Switch S1 Is Closed and Switch S2 Remains Open, What Lights Will Turn On?Vel Murugan100% (1)
- EE 211 Sample ExamDocumento12 pagineEE 211 Sample Examlrg5092Nessuna valutazione finora
- Single-Phase - Problems - With SolutionDocumento3 pagineSingle-Phase - Problems - With SolutionVachist WangelNessuna valutazione finora
- Krishna Institute of Engineering & Technology, GhaziabadDocumento4 pagineKrishna Institute of Engineering & Technology, GhaziabadkapilkietNessuna valutazione finora
- EE 287 Circuit Theory: Presented By: Dr. Philip Yaw OkyereDocumento30 pagineEE 287 Circuit Theory: Presented By: Dr. Philip Yaw Okyeresamuel fiifi yeboahNessuna valutazione finora
- Indian Institute of Technology Department of Electrical Engineering Any FiveDocumento4 pagineIndian Institute of Technology Department of Electrical Engineering Any FiveNikhil V. JoshiNessuna valutazione finora
- Practice Problems CircuitII - 1Documento2 paginePractice Problems CircuitII - 1IbrNessuna valutazione finora
- CT Kneepoint VoltageDocumento2 pagineCT Kneepoint Voltage322399mk7086Nessuna valutazione finora
- Circuit Theory Electronic EngineeringDocumento92 pagineCircuit Theory Electronic EngineeringSubash AleNessuna valutazione finora
- Experiment 4 For B.electronicDocumento12 pagineExperiment 4 For B.electronicUmmu Umar Wa AisyahNessuna valutazione finora
- Ee TutorialDocumento2 pagineEe TutorialRajesh AgarwalNessuna valutazione finora
- Kathmandu School of Engineering University Department of Electrical & Electronics EngineeringDocumento3 pagineKathmandu School of Engineering University Department of Electrical & Electronics EngineeringUrgen TamangNessuna valutazione finora
- Lectures 6 & 7 - Uncontrolled (Diode) Rectifier Circuits: Single-Phase Center-Tapped RectifierDocumento21 pagineLectures 6 & 7 - Uncontrolled (Diode) Rectifier Circuits: Single-Phase Center-Tapped RectifierTommy ManNessuna valutazione finora
- Sheet 2Documento4 pagineSheet 2Ahmed GamalNessuna valutazione finora
- Question Paper Code: 22115: B.E./B.Tech - Degree Examinations, April/May 2011 Regulations 2008Documento5 pagineQuestion Paper Code: 22115: B.E./B.Tech - Degree Examinations, April/May 2011 Regulations 2008Vinodh GanesanNessuna valutazione finora
- B-GL-385-009 Short Range Anti-Armour Weapon (Medium)Documento171 pagineB-GL-385-009 Short Range Anti-Armour Weapon (Medium)Jared A. Lang100% (1)
- Advanced Herd Health Management, Sanitation and HygieneDocumento28 pagineAdvanced Herd Health Management, Sanitation and Hygienejane entunaNessuna valutazione finora
- Written Report SampleDocumento16 pagineWritten Report Sampleallanposo3Nessuna valutazione finora
- Consumer Protection ActDocumento34 pagineConsumer Protection ActshikhroxNessuna valutazione finora
- Employee of The Month.Documento2 pagineEmployee of The Month.munyekiNessuna valutazione finora
- Unit 1 Bearer PlantsDocumento2 pagineUnit 1 Bearer PlantsEmzNessuna valutazione finora
- DG Oil SpecificationDocumento10 pagineDG Oil SpecificationafsalmohmdNessuna valutazione finora
- Flipkart Labels 06 Jul 2022 09 52Documento37 pagineFlipkart Labels 06 Jul 2022 09 52Dharmesh ManiyaNessuna valutazione finora
- Landscape ArchitectureDocumento9 pagineLandscape Architecturelisan2053Nessuna valutazione finora
- SPFL Monitoring ToolDocumento3 pagineSPFL Monitoring ToolAnalyn EnriquezNessuna valutazione finora
- Acute Suppurative Otitis MediaDocumento41 pagineAcute Suppurative Otitis Mediarani suwadjiNessuna valutazione finora
- Thermodynamics WorksheetDocumento5 pagineThermodynamics WorksheetMalcolmJustMalcolmNessuna valutazione finora
- GrenTech Express Communication System Introduction 1.0Documento30 pagineGrenTech Express Communication System Introduction 1.0Son NguyenNessuna valutazione finora
- A Project On "Automatic Water Sprinkler Based On Wet and Dry Conditions"Documento28 pagineA Project On "Automatic Water Sprinkler Based On Wet and Dry Conditions"Srínívas SrínuNessuna valutazione finora
- Coke Drum Repair Welch Aquilex WSI DCU Calgary 2009Documento37 pagineCoke Drum Repair Welch Aquilex WSI DCU Calgary 2009Oscar DorantesNessuna valutazione finora
- Answer: C: Exam Name: Exam Type: Exam Code: Total QuestionsDocumento26 pagineAnswer: C: Exam Name: Exam Type: Exam Code: Total QuestionsMohammed S.GoudaNessuna valutazione finora
- Celula de CargaDocumento2 pagineCelula de CargaDavid PaezNessuna valutazione finora
- DP-1520 PMDocumento152 pagineDP-1520 PMIon JardelNessuna valutazione finora
- Revenue Memorandum Circular No. 55-2016: For ExampleDocumento2 pagineRevenue Memorandum Circular No. 55-2016: For ExampleFedsNessuna valutazione finora
- Emerging Technology SyllabusDocumento6 pagineEmerging Technology Syllabussw dr100% (4)
- Monitor 14sepDocumento2 pagineMonitor 14sepabhaymvyas1144Nessuna valutazione finora
- S-Sapfico-Satyanarayanamaterial 121212Documento183 pagineS-Sapfico-Satyanarayanamaterial 121212mpsing1133Nessuna valutazione finora
- Ships Near A Rocky Coast With Awaiting Landing PartyDocumento2 pagineShips Near A Rocky Coast With Awaiting Landing PartyFouaAj1 FouaAj1Nessuna valutazione finora
- An Analysis of Students' Error in Using Possesive Adjective in Their Online Writing TasksDocumento19 pagineAn Analysis of Students' Error in Using Possesive Adjective in Their Online Writing TasksKartika Dwi NurandaniNessuna valutazione finora
- Extraction of Mangiferin From Mangifera Indica L. LeavesDocumento7 pagineExtraction of Mangiferin From Mangifera Indica L. LeavesDaniel BartoloNessuna valutazione finora
- Densha: Memories of A Train Ride Through Kyushu: By: Scott NesbittDocumento7 pagineDensha: Memories of A Train Ride Through Kyushu: By: Scott Nesbittapi-16144421Nessuna valutazione finora
- 6int 2008 Dec ADocumento6 pagine6int 2008 Dec ACharles_Leong_3417Nessuna valutazione finora
- Reference GuideDocumento88 pagineReference GuideAnonymous Qm0zbNk100% (1)
- Electronics 11 02566Documento13 pagineElectronics 11 02566卓七越Nessuna valutazione finora
- Study Notes - Google Project Management Professional CertificateDocumento4 pagineStudy Notes - Google Project Management Professional CertificateSWAPNIL100% (1)