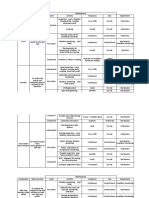
Documenti di Didattica
Documenti di Professioni
Documenti di Cultura
2502 Electrical
Caricato da
Kristine PalmesTitolo originale
Copyright
Formati disponibili
Condividi questo documento
Condividi o incorpora il documento
Hai trovato utile questo documento?
Questo contenuto è inappropriato?
Segnala questo documentoCopyright:
Formati disponibili
2502 Electrical
Caricato da
Kristine PalmesCopyright:
Formati disponibili
Basic Electrical Engineering
NEE 220
Engr. Jessica Laine M. Tumbaga
Nodal Analysis and Supernode
Engr. J.L. Tumbaga
Saturday, August 27, 2016
Nodal analysis
Nodal analysis (a.k.a node-voltage method) provides a general
procedure for analyzing circuits using node voltages as the circuit
variables. Choosing node voltages instead of element voltages as
circuit variables is convenient and reduces the number of equations
one must solve simultaneously.
Recall that a node is the point of connection between two or more
branches.
Furthermore, nodal analysis applies KCL to nd unknown
voltages.
In nodal analysis, we are interested in nding the node voltages.
Given a circuit with n nodes without voltage sources, the nodal
analysis of the circuit involves taking the following three steps.
Engr. J.L. Tumbaga
Saturday, August 27, 2016
Steps to determine NODE voltages
1. Select a node as the reference node. Assign voltages v1, v2,
vn-1 to the remaining n - 1 nodes. The voltages are referenced
with respect to the reference node.
2. Apply KCL to each of the n 1 nonreference nodes. Use Ohms
law to express the branch currents in terms of node voltages.
3. Solve the resulting simultaneous equations to obtain the
unknown node voltages.
Note: The reference node or datum node is commonly called the
ground since it is assumed to have zero potential.
Engr. J.L. Tumbaga
Saturday, August 27, 2016
Types of Ground
Common symbols for indicating a reference node. (a) common
ground, (b) ground, (c) chassis ground
When the potential of the earth is used as reference, we used earth
ground. Chassis ground is used in devices where the case,
enclosure or the chassis acts as a reference point for all circuits.
Engr. J.L. Tumbaga
Saturday, August 27, 2016
Current flows from a HIGHER potential to a LOWER potential in a
resistor.
The number of nonreference nodes is equal to the number of
independent equations that we will derive.
Engr. J.L. Tumbaga
Saturday, August 27, 2016
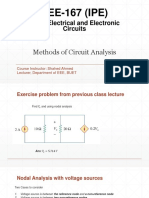
Sample Problem
Calculate the node voltages in the circuit shown above.
Ans. V1 = 13.333V, V2 = 20V
Engr. J.L. Tumbaga
Saturday, August 27, 2016
Sample Problem
Calculate the node voltages in the circuit shown above.
Ans. V1 = 4.8V, V2 = 2.4V, V3 = -2.4V
Engr. J.L. Tumbaga
Saturday, August 27, 2016
NOdal analysis with voltage sources
We now consider how voltage sources affect nodal analysis. We use
the circuit shown below for illustration. Consider the following two
possibilities.
Engr. J.L. Tumbaga
Saturday, August 27, 2016
10
CASE 1. If a voltage source is connected between the reference
node and a nonreference node, we simply set the voltage at the
nonreference node equal to the voltage of the voltage source. In the
previous circuit, for example,
V1 = 10 V
Thus, our analysis is somewhat simplied by this knowledge of the
voltage at this node.
CASE 2. If the voltage source (dependent or independent) is
connected between two nonreference nodes, the two nonreference
nodes form a generalized node or supernode, we apply both KCL
and KVL to determine the node voltages.
A SUPERNODE is formed by enclosing a (dependent or
independent) voltage source connected between two nonreference
nodes and any elements connected in parallel with it.
Engr. J.L. Tumbaga
Saturday, August 27, 2016
11
Note the following properties of a supernode.
1. The voltage source inside the supernode provides a constraint
equation needed to solve for the node voltages.
2. A supernode has no voltage of its own.
3. A supernode requires the application of both KCL and KVL
Engr. J.L. Tumbaga
Saturday, August 27, 2016
12
Sample Problem
Find the node voltages in the circuit shown below.
Ans. V1 =-7.333V, V2 = -5.333V
Engr. J.L. Tumbaga
Saturday, August 27, 2016
13
Sample Problem
Find the node voltages in the circuit shown below.
Ans. V1 =26.67V, V2 =6.667V, V3=173.33V, V4=-46.67V
Engr. J.L. Tumbaga
Saturday, August 27, 2016
14
Mesh vs Nodal analysis
MESH ANALYSIS
NODAL ANALYSIS
Used to solve mesh currents.
Employs KVL
Supermesh
Used to solve node voltages.
Employs KCL
Supernode
Engr. J.L. Tumbaga
Saturday, August 27, 2016
15
Problems
1. Solve for v1 to v3 in the circuit below using nodal analysis.
Engr. J.L. Tumbaga
Saturday, August 27, 2016
16
Problems
2. Solve for v0, i0 in the circuit below using nodal analysis.
3. In the circuit below, solve for i1, i2 and i3 using nodal analysis.
Engr. J.L. Tumbaga
Saturday, August 27, 2016
17
Toru Kumon
(Founder of Kumon)
~The End~
Engr. J.L. Tumbaga
Saturday, August 27, 2016
Potrebbero piacerti anche
- Exm Notes PMPDocumento29 pagineExm Notes PMPjay2kay5793100% (1)
- Lab 3 (Nodal and Mesh Analysis)Documento15 pagineLab 3 (Nodal and Mesh Analysis)Jing Heng0% (1)
- Employability Skills: Brush up Your ElectronicsDa EverandEmployability Skills: Brush up Your ElectronicsNessuna valutazione finora
- Maintenance Component Main Function Level Activity Frequency Line DepartmentDocumento7 pagineMaintenance Component Main Function Level Activity Frequency Line DepartmentBarathNessuna valutazione finora
- Ericsson Command LineDocumento39 pagineEricsson Command LinejulescarrelNessuna valutazione finora
- 1 s2.0 S0263876299718186 Main PDFDocumento7 pagine1 s2.0 S0263876299718186 Main PDFLeydi PatiñoNessuna valutazione finora
- Soda Ash PDFDocumento45 pagineSoda Ash PDFM TNessuna valutazione finora
- APCO Air Valve 613Documento4 pagineAPCO Air Valve 613jones0055Nessuna valutazione finora
- Network Analysis 2106Documento57 pagineNetwork Analysis 2106Sonah AlcarazNessuna valutazione finora
- Chapter 03 - Mesh AnalysisDocumento21 pagineChapter 03 - Mesh AnalysisHidayah KamaludinNessuna valutazione finora
- Chapter 3 - Methods of AnalysisDocumento20 pagineChapter 3 - Methods of AnalysisBalqis HasniNessuna valutazione finora
- EE42 100 Cch-Lecure11 071713-CleanDocumento31 pagineEE42 100 Cch-Lecure11 071713-CleanozanistzNessuna valutazione finora
- Electronic Curcuit Chapter 2.Documento25 pagineElectronic Curcuit Chapter 2.AbcdNessuna valutazione finora
- SUPERNODE Circuit Analysis (@B)Documento5 pagineSUPERNODE Circuit Analysis (@B)shivamNessuna valutazione finora
- Lec2 - DC Circuits 2Documento42 pagineLec2 - DC Circuits 2junryNessuna valutazione finora
- FEI 3103 Circuit TheoryDocumento16 pagineFEI 3103 Circuit TheorySyafnie NinieNessuna valutazione finora
- 4 Lecture NewDocumento29 pagine4 Lecture Newzohan waheedNessuna valutazione finora
- Experiment No. 9 1Documento14 pagineExperiment No. 9 1Kent Gerard SolanoNessuna valutazione finora
- Chapter 3 - Node and Mesh Analysis - Part 1Documento22 pagineChapter 3 - Node and Mesh Analysis - Part 1fayNessuna valutazione finora
- Mod 2 - 3Documento11 pagineMod 2 - 3Georji kairuNessuna valutazione finora
- Chapter 2 EEE121 Part 2Documento9 pagineChapter 2 EEE121 Part 2Ashraf RezaNessuna valutazione finora
- Lesson 3 6 Methods of AnalysisDocumento52 pagineLesson 3 6 Methods of AnalysisJoel Kelly MabaoNessuna valutazione finora
- Mod 2 - 3Documento13 pagineMod 2 - 3Georji kairuNessuna valutazione finora
- Node Analysis: Arceta Torres Fernando Pazarán Rodríguez Samy Zabdiel Urquiza López Carlos AriadDocumento7 pagineNode Analysis: Arceta Torres Fernando Pazarán Rodríguez Samy Zabdiel Urquiza López Carlos AriadYo TuNessuna valutazione finora
- Nodal AnalysisDocumento6 pagineNodal AnalysisJerome BricenioNessuna valutazione finora
- Nodal AnalysisDocumento15 pagineNodal AnalysisRNessuna valutazione finora
- Nodal Analysis NotesDocumento2 pagineNodal Analysis Notesapi-288751705Nessuna valutazione finora
- Methods of Analysis ModifiedDocumento15 pagineMethods of Analysis ModifiedNebiyou KorraNessuna valutazione finora
- EE231 Lecture 2A "Network Theorems I": By: Engr. Paolo Josemari P. ZafraDocumento28 pagineEE231 Lecture 2A "Network Theorems I": By: Engr. Paolo Josemari P. ZafraPaolo Josemari ZafraNessuna valutazione finora
- Topic 4 - Nodal Analysis (Notes)Documento15 pagineTopic 4 - Nodal Analysis (Notes)taptech004Nessuna valutazione finora
- Finding Voltages in A CircuitDocumento8 pagineFinding Voltages in A CircuitcassNessuna valutazione finora
- Mod 2 - 3 - 4Documento18 pagineMod 2 - 3 - 4Georji kairuNessuna valutazione finora
- Week 6Documento38 pagineWeek 6IGIHOZO HeritierNessuna valutazione finora
- Nodal's and Maxwell's Theorem Anore, James IvanDocumento16 pagineNodal's and Maxwell's Theorem Anore, James IvanMeiko AbrinaNessuna valutazione finora
- Lecture 2Documento9 pagineLecture 2paulamarieestrellalengascoNessuna valutazione finora
- Ece 201 Exam 2 ReviewDocumento12 pagineEce 201 Exam 2 ReviewkarlrodNessuna valutazione finora
- Electrical Science: Lecture-5: Topic-Nodal and Mesh AnalysisDocumento13 pagineElectrical Science: Lecture-5: Topic-Nodal and Mesh Analysisi_khandelwalNessuna valutazione finora
- Nodal and LoopDocumento40 pagineNodal and LoopAnindya MukherjeeNessuna valutazione finora
- Electric Circuit and Electronics NoteDocumento34 pagineElectric Circuit and Electronics NoteEzekiel JamesNessuna valutazione finora
- V8 - Chapter 3 - Methods of Analysis - Delta Wye - TE 58 A - B and CDocumento74 pagineV8 - Chapter 3 - Methods of Analysis - Delta Wye - TE 58 A - B and CMubashir KhanNessuna valutazione finora
- V4 - Chapter 3 - Methods of Analysis - Delta Wye - To Class 56 A and D PDFDocumento77 pagineV4 - Chapter 3 - Methods of Analysis - Delta Wye - To Class 56 A and D PDFasfasNessuna valutazione finora
- Series and Parallel ResistorsDocumento8 pagineSeries and Parallel ResistorsYzabelle De GuzmanNessuna valutazione finora
- AER204Electrics and Electronics-Chapter 3Documento22 pagineAER204Electrics and Electronics-Chapter 3tyoudalpenaNessuna valutazione finora
- Ues013 Ele Lec4Documento16 pagineUes013 Ele Lec4Ishan Satya PrakashNessuna valutazione finora
- Abhradeep 2212102009Documento6 pagineAbhradeep 2212102009Abhradeep SenguptaNessuna valutazione finora
- Announcements: - First Assignment PostedDocumento22 pagineAnnouncements: - First Assignment Posted1553Nessuna valutazione finora
- Laboratory Experiment 1Documento6 pagineLaboratory Experiment 1Mark Jomel MangampoNessuna valutazione finora
- Chapter 3 - Methods of Circuit Analysis and Circuit TheoremsDocumento125 pagineChapter 3 - Methods of Circuit Analysis and Circuit TheoremsAugustine JR RobertNessuna valutazione finora
- EEE121 ECA-I Lecture 05-BSE 2BDocumento7 pagineEEE121 ECA-I Lecture 05-BSE 2BMuhammad Asghar KhanNessuna valutazione finora
- Series Parallel ConfigurationsDocumento12 pagineSeries Parallel ConfigurationsRenee Pascual SalipotNessuna valutazione finora
- Chapter 3 - Methods of Circuit Analysis and Circuit TheoremsDocumento125 pagineChapter 3 - Methods of Circuit Analysis and Circuit TheoremsNaim NizamNessuna valutazione finora
- PRELIM To FINALS ELECTRIC DEVICE THEORY 1Documento9 paginePRELIM To FINALS ELECTRIC DEVICE THEORY 1Lrac semaj NarivNessuna valutazione finora
- Electric Circuit I - EEC-1003 LO3 (Chapter 8) : Slides Prepared by Electric Circuit Team at Sharjah CollegesDocumento39 pagineElectric Circuit I - EEC-1003 LO3 (Chapter 8) : Slides Prepared by Electric Circuit Team at Sharjah CollegesSaid Ahmed AliNessuna valutazione finora
- Superposition and Norton TheoremDocumento24 pagineSuperposition and Norton TheoremMahmudul AlamNessuna valutazione finora
- Ohm'S Law: ResistanceDocumento27 pagineOhm'S Law: Resistancedaniel gelawNessuna valutazione finora
- Mesh AnalysisDocumento12 pagineMesh AnalysisshihabNessuna valutazione finora
- CIRCUIT1 Lec03 Methods of AnalysisDocumento35 pagineCIRCUIT1 Lec03 Methods of AnalysisChristian JavierNessuna valutazione finora
- BEE Mesh Analysis PresentationDocumento8 pagineBEE Mesh Analysis Presentation230301120111Nessuna valutazione finora
- Week 4 - 5 (ULO 1a)Documento26 pagineWeek 4 - 5 (ULO 1a)sammy greyNessuna valutazione finora
- L1Documento52 pagineL1KENEDY MWALUKASANessuna valutazione finora
- Mod 2 - 3 - 4 - 5Documento26 pagineMod 2 - 3 - 4 - 5Georji kairuNessuna valutazione finora
- Mod 2 - 3 - 4Documento17 pagineMod 2 - 3 - 4Georji kairuNessuna valutazione finora
- Chap 2 - Circuit AnalysisDocumento22 pagineChap 2 - Circuit AnalysisYang Yew RenNessuna valutazione finora
- Electrical Analogues of Pin-Jointed Systems: International Series of Monographs on Electronics and InstrumentationDa EverandElectrical Analogues of Pin-Jointed Systems: International Series of Monographs on Electronics and InstrumentationNessuna valutazione finora
- Market Manipulation Rules and IPO Underpricing: Huu - Duong@monash - EduDocumento54 pagineMarket Manipulation Rules and IPO Underpricing: Huu - Duong@monash - EduTI Logic ?? sobayedNessuna valutazione finora
- False: True True True TrueDocumento2 pagineFalse: True True True TrueSuubi brianNessuna valutazione finora
- Nuxeo BookDocumento335 pagineNuxeo Bookdannao4Nessuna valutazione finora
- 16 Astral - Pool Heating 2008Documento38 pagine16 Astral - Pool Heating 2008drožmanićNessuna valutazione finora
- Chapter 2 Approaches To Software DesignDocumento25 pagineChapter 2 Approaches To Software DesigntarunkakkarNessuna valutazione finora
- FAR21x7 28x7 Operator's Manual P 4-8-11Documento312 pagineFAR21x7 28x7 Operator's Manual P 4-8-11Miguel PerezNessuna valutazione finora
- Bind Second Valve OverviewDocumento27 pagineBind Second Valve OverviewNitin AggarwalNessuna valutazione finora
- A Generic Circular BufferDocumento3 pagineA Generic Circular BufferSatish KumarNessuna valutazione finora
- SPE15010Documento11 pagineSPE15010Leandro NavarroNessuna valutazione finora
- Proview TutorialDocumento12 pagineProview TutorialManoel NascimentoNessuna valutazione finora
- Chapter Test 2nd Quarter.Documento5 pagineChapter Test 2nd Quarter.Roziel MontalbanNessuna valutazione finora
- 2 - EE - Intro - Electronics Pg. 28-41 Op Amp-Merged PDFDocumento402 pagine2 - EE - Intro - Electronics Pg. 28-41 Op Amp-Merged PDFAdelin IonutNessuna valutazione finora
- Calculation of Altitude CorrectionDocumento3 pagineCalculation of Altitude CorrectionMikami TeruNessuna valutazione finora
- Komposisi Jenis Dan Struktur Vegetasi Hutan GambutDocumento13 pagineKomposisi Jenis Dan Struktur Vegetasi Hutan GambutI2O42OO54 IRFAN FAUZINessuna valutazione finora
- Regcm 4.3 Training Session Ii Regcm4.3-Rc OutputDocumento8 pagineRegcm 4.3 Training Session Ii Regcm4.3-Rc OutputShane Marie VisagaNessuna valutazione finora
- Chapter6b-Combinational Logic Design PracticesDocumento38 pagineChapter6b-Combinational Logic Design PracticesZulkarnineNessuna valutazione finora
- 2210 w18 Ms 12Documento12 pagine2210 w18 Ms 12Fiyazul HaqueNessuna valutazione finora
- High Performance Liquid Chromatographic Technique and Validation For Determination of Favipiravir in Bulk and Tablet FormulationDocumento7 pagineHigh Performance Liquid Chromatographic Technique and Validation For Determination of Favipiravir in Bulk and Tablet FormulationEditor IJTSRDNessuna valutazione finora
- Automotive Solutions: Setting The Pace For InnovationDocumento36 pagineAutomotive Solutions: Setting The Pace For InnovationAda TopanNessuna valutazione finora
- Manual AvicadDocumento676 pagineManual AvicadOlivia BlanaruNessuna valutazione finora
- Aksa Ajd170Documento5 pagineAksa Ajd170mhmmd14Nessuna valutazione finora
- BM2 24H+Installation+InstructionsDocumento7 pagineBM2 24H+Installation+InstructionsremediospereiraNessuna valutazione finora
- Unit 7 Motion Review Sheet AnswersDocumento3 pagineUnit 7 Motion Review Sheet AnswersFlorie Fe Rosario Ortega100% (1)
- Topic: Partnership: Do Not Distribute - Highly Confidential 1Documento7 pagineTopic: Partnership: Do Not Distribute - Highly Confidential 1Tharun NaniNessuna valutazione finora