Documenti di Didattica
Documenti di Professioni
Documenti di Cultura
7.2.2.4 Packet Tracer Configuring Basic EIGRP With IPv4 Instructions
Caricato da
Daniel OsorioCopyright
Formati disponibili
Condividi questo documento
Condividi o incorpora il documento
Hai trovato utile questo documento?
Questo contenuto è inappropriato?
Segnala questo documentoCopyright:
Formati disponibili
7.2.2.4 Packet Tracer Configuring Basic EIGRP With IPv4 Instructions
Caricato da
Daniel OsorioCopyright:
Formati disponibili
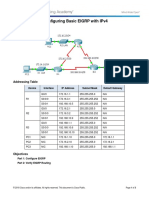
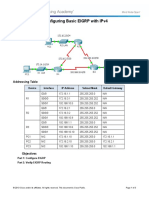
Packet Tracer Configuring Basic EIGRP with IPv4
Topology
Addressing Table
Device
Interface
IP Address
Subnet Mask
Default Gateway
G0/0
172.16.1.1
255.255.255.0
N/A
S0/0/0
172.16.3.1
255.255.255.252
N/A
S0/0/1
192.168.10.5
255.255.255.252
N/A
G0/0
172.16.2.1
255.255.255.0
N/A
S0/0/0
172.16.3.2
255.255.255.252
N/A
S0/0/1
192.168.10.9
255.255.255.252
N/A
G0/0
192.168.1.1
255.255.255.0
N/A
S0/0/0
192.168.10.6
255.255.255.252
N/A
S0/0/1
192.168.10.10
255.255.255.252
N/A
PC1
NIC
172.16.1.10
255.255.255.0
172.16.1.1
PC2
NIC
172.16.2.10
255.255.255.0
172.16.2.1
PC3
NIC
192.168.1.10
255.255.255.0
192.168.1.1
R1
R2
R3
Objectives
Part 1: Configure EIGRP
Part 2: Verify EIGRP Routing
Background
In this activity, you will implement basic EIGRP configurations including network commands, passive interfaces
and disabling automatic summarization. You will then verify your EIGRP configuration using a variety of show
commands and testing end-to-end connectivity.
2013 Cisco and/or its affiliates. All rights reserved. This document is Cisco Public.
Page 1 of 3
Packet Tracer Configuring Basic EIGRP with IPv4
Part 1: Configure EIGRP
Step 1: Enable the EIGRP routing process.
Enable the EIGRP routing process on each router using AS number 1. The configuration for R1 is shown.
R1(config)# router eigrp 1
What is the range of numbers that can be used for AS numbers? __R1(config)# router eigrp 1_
Note: Packet Tracer currently does not support the configuration of an EIGRP router ID.
Step 2: Advertise directly connected networks.
a. Use the show ip route command to display the directly connected networks on each router.
How can you tell the difference between subnet addresses and interface addresses?
____the diferent area advertising EIGRP__
b. On each router, configure EIGRP to advertise the specific directly connected subnets. The configuration
for R1 is shown.
R1(config-router)# network 172.16.1.0 0.0.0.255
R1(config-router)# network 172.16.3.0 0.0.0.3
R1(config-router)# network 192.168.10.4 0.0.0.3
Step 3: Configure passive interfaces.
Configure the LAN interfaces to not advertise EIGRP updates. The configuration for R1 is shown.
R1(config-router)# passive-interface g0/0
Step 4: Disable automatic summarization.
The topology contains discontiguous networks. Therefore, disable automatic summarization on each router.
The configuration for R1 is shown.
R1(config-router)# no auto-summary
Note: Prior to IOS 15 auto-summary had to be manually disabled.
Step 5: Save the configurations.
Part 2: Verify EIGRP Routing
Step 1: Examine neighbor adjacencies.
a. Which command displays the neighbors discovered by EIGRP? _Shoe ip eigrp neighbord_
b. All three routers should have two neighbors listed. The output for R1 should look similar to the following:
IP-EIGRP neighbors for process 1
H
Address
Interface
0
1
172.16.3.2
192.168.10.6
Se0/0/0
Se0/0/1
Hold Uptime
(sec)
14
00:25:05
12
00:13:29
2013 Cisco and/or its affiliates. All rights reserved. This document is Cisco Public.
SRTT
(ms)
40
40
RTO
Q
Cnt
1000 0
1000 0
Seq
Num
28
31
Page 2 of 3
Packet Tracer Configuring Basic EIGRP with IPv4
Step 2: Display the EIGRP routing protocol parameters.
a. What command displays the parameters and other information about the current state of any active IPv4
routing protocol processes configured on the router? ___ospf __
b. On R2, enter the command you listed for 2a and answer the following questions:
How many routers are sharing routing information with R2? _R1 R2
Where is this information located under? _not information__
What is the maximum hop count? __ 00:25:05 40 __
Step 3: Verify end-to-end connectivity
PC1, PC2 and PC3 should now be able to ping each other. If not, troubleshoot your EIGRP configurations.
Suggested Scoring Rubric
Activity Section
Part 1: Configure EIGRP
Question
Location
Possible
Points
Step 1
Step 2a
Part 1 Total
Part 2: Verify EIGRP
Routing
Step 1a
Step 2a
Step 2b
Part 2 Total
16
Packet Tracer Score
80
Total Score
100
2013 Cisco and/or its affiliates. All rights reserved. This document is Cisco Public.
Earned
Points
Page 3 of 3
Potrebbero piacerti anche
- 7.2.2.4 Packet Tracer - Configuring Basic EIGRP With IPv4 InstructionsDocumento3 pagine7.2.2.4 Packet Tracer - Configuring Basic EIGRP With IPv4 InstructionsNicky Villa50% (2)
- 2.2.1 Packet Tracer - Configure Basic EIGRP With IPv4Documento3 pagine2.2.1 Packet Tracer - Configure Basic EIGRP With IPv4venkteshmmoger13Nessuna valutazione finora
- 2.2.1 Packet Tracer - Configure Basic EIGRP With IPv4 - ITExamAnswersDocumento4 pagine2.2.1 Packet Tracer - Configure Basic EIGRP With IPv4 - ITExamAnswersIwanNessuna valutazione finora
- 7.2.2.4 Packet Tracer - Configuring Basic EIGRP With IPv4 Instructions IGDocumento5 pagine7.2.2.4 Packet Tracer - Configuring Basic EIGRP With IPv4 Instructions IGkarenNessuna valutazione finora
- 6.2.2.4 Packet Tracer - Configuring Basic EIGRP With IPv4 InstructionsDocumento3 pagine6.2.2.4 Packet Tracer - Configuring Basic EIGRP With IPv4 InstructionsJessica Gregory100% (1)
- 6.2.2.4 Packet Tracer - Configuring Basic EIGRP With IPv4 InstructionsDocumento3 pagine6.2.2.4 Packet Tracer - Configuring Basic EIGRP With IPv4 InstructionsMiguel AngelNessuna valutazione finora
- Configuring EIGRP: BSCI Module 2-2 - Implementing and Verifying EIGRPDocumento24 pagineConfiguring EIGRP: BSCI Module 2-2 - Implementing and Verifying EIGRPHerlander FaloNessuna valutazione finora
- 8.1.5.5 Lab Configuring Advanced EIGRP For IPv4 FeaturesDocumento11 pagine8.1.5.5 Lab Configuring Advanced EIGRP For IPv4 FeaturesDaniel OsorioNessuna valutazione finora
- 7.2.2.4 Packet Tracer - Configuring Basic EIGRP With IPv4 InstructionsDocumento3 pagine7.2.2.4 Packet Tracer - Configuring Basic EIGRP With IPv4 InstructionsArfian HaryonoNessuna valutazione finora
- 02-Implementing and Verifying EIGRPDocumento24 pagine02-Implementing and Verifying EIGRPPablo MotaNessuna valutazione finora
- 6.2.3.8 Lab - Configuring Multiarea OSPFv2 FinalDocumento13 pagine6.2.3.8 Lab - Configuring Multiarea OSPFv2 FinalJoseph Ryan WolfNessuna valutazione finora
- 6.2.2.5 Lab - Configuring Basic EIGRP For IPv4Documento10 pagine6.2.2.5 Lab - Configuring Basic EIGRP For IPv4Ana DianaNessuna valutazione finora
- 6.2.2.4 Packet Tracer - Configuring Basic EIGRP With IPv4 InstructionsDocumento3 pagine6.2.2.4 Packet Tracer - Configuring Basic EIGRP With IPv4 Instructionsyair cedillo jaramillo0% (1)
- 7.1.3.6 Lab Configuring Advanced EIGRP For IPv4 Features 1Documento9 pagine7.1.3.6 Lab Configuring Advanced EIGRP For IPv4 Features 1белимNessuna valutazione finora
- Lab 2 - Configuring Basic EIGRP For IPv4Documento9 pagineLab 2 - Configuring Basic EIGRP For IPv4Shrey AnchalwarNessuna valutazione finora
- Lab - Configuring Advanced EIGRP For IPv4 Features - ILMDocumento22 pagineLab - Configuring Advanced EIGRP For IPv4 Features - ILMEl ProfaNessuna valutazione finora
- 6.2.7 Lab - Configure Automated Security FeaturesDocumento11 pagine6.2.7 Lab - Configure Automated Security FeaturesHani GoytomNessuna valutazione finora
- CCNA Certification EIGRP Configuration Lab SimulationDocumento8 pagineCCNA Certification EIGRP Configuration Lab Simulationergu vfuko fghuiNessuna valutazione finora
- 6.2.7 Lab - Configure Automated Security FeaturesDocumento11 pagine6.2.7 Lab - Configure Automated Security FeaturesntutaNessuna valutazione finora
- 6.2.7 Lab Configure Automated Security FeaturesDocumento11 pagine6.2.7 Lab Configure Automated Security FeaturesCesar Lazo DiazNessuna valutazione finora
- 6.3.6 Lab - Basic Device Configuration and OSPF AuthenticationDocumento7 pagine6.3.6 Lab - Basic Device Configuration and OSPF AuthenticationGISTSalehuddinNessuna valutazione finora
- 12.1.2 Lab - Implement BGP Path Manipulation - ITExamAnswersDocumento22 pagine12.1.2 Lab - Implement BGP Path Manipulation - ITExamAnswersiqmalkuaciNessuna valutazione finora
- Packet Tracer - Configuring Basic Eigrp With Ipv4: ObjectivesDocumento2 paginePacket Tracer - Configuring Basic Eigrp With Ipv4: ObjectivesMehdi SultaniNessuna valutazione finora
- 6.4.3.3 Packet Tracer - Connect A Router To A LANDocumento5 pagine6.4.3.3 Packet Tracer - Connect A Router To A LANAzeemuddin MohammedNessuna valutazione finora
- 6.4.3.3 Packet Tracer - Connect A Router To A LANDocumento5 pagine6.4.3.3 Packet Tracer - Connect A Router To A LANSergio MonteNessuna valutazione finora
- 02-Implementing and Verifying EIGRPDocumento24 pagine02-Implementing and Verifying EIGRPTeslevel LevelNessuna valutazione finora
- 2.6.6-Packet-Tracer - 19030313Documento8 pagine2.6.6-Packet-Tracer - 19030313Dante CamachoNessuna valutazione finora
- 4.4.7 Lab - Configure Secure Administrative AccessDocumento11 pagine4.4.7 Lab - Configure Secure Administrative AccessJesús EnriqueNessuna valutazione finora
- Packet Tracer - Connect A Router To A LAN: TopologyDocumento5 paginePacket Tracer - Connect A Router To A LAN: TopologyShulav PoudelNessuna valutazione finora
- 4.4.7 Lab Configure Secure Administrative AccessDocumento10 pagine4.4.7 Lab Configure Secure Administrative AccessHector De Jesus Tapia GorgonioNessuna valutazione finora
- 6.3.6 Lab - Basic Device Configuration and OSPF Authentication - ILMDocumento11 pagine6.3.6 Lab - Basic Device Configuration and OSPF Authentication - ILMRony Schäfer JaraNessuna valutazione finora
- 8.3.2.7 Lab - Testing Network Connectivity With Ping and TracerouteDocumento15 pagine8.3.2.7 Lab - Testing Network Connectivity With Ping and TracerouteasdfjklNessuna valutazione finora
- 1Documento26 pagine1Ifeakor Young KosisochukwuNessuna valutazione finora
- 13.1.2 Lab - Implement BGP Communities PDFDocumento15 pagine13.1.2 Lab - Implement BGP Communities PDFTrần Hoàng ThôngNessuna valutazione finora
- 7.3.2.7 Lab - Testing Network Connectivity With Ping and TracerouteDocumento16 pagine7.3.2.7 Lab - Testing Network Connectivity With Ping and TracerouteRaja Dang Jalernpan100% (6)
- 8.2.2.7 Cisco Packet TracerDocumento3 pagine8.2.2.7 Cisco Packet Tracerjstring69Nessuna valutazione finora
- 11.1.3 Lab - Implement MP-BGP - ITExamAnswersDocumento22 pagine11.1.3 Lab - Implement MP-BGP - ITExamAnswersiqmalkuaciNessuna valutazione finora
- Chapter 2 Lab 2-3, EIGRP For IPv6Documento31 pagineChapter 2 Lab 2-3, EIGRP For IPv6leoNessuna valutazione finora
- Day 11 EIGRPDocumento13 pagineDay 11 EIGRPGorvam SaddarNessuna valutazione finora
- 2.6.1.2 Lab - Securing The Router For Administrative Access PDFDocumento38 pagine2.6.1.2 Lab - Securing The Router For Administrative Access PDFAAANessuna valutazione finora
- Lab - Securing The Router For Administrative Access: IntegrantesDocumento59 pagineLab - Securing The Router For Administrative Access: IntegrantesAlex Fernando GarcesNessuna valutazione finora
- Activity-6 Routing Informatio Protocol (RIP)Documento6 pagineActivity-6 Routing Informatio Protocol (RIP)raffy arranguezNessuna valutazione finora
- Laporan Configuring Basic Eigrp For Ipv4Documento18 pagineLaporan Configuring Basic Eigrp For Ipv4sumar tiniNessuna valutazione finora
- 4.4.1.2 Lab - Configuring Zone-Based Policy Firewalls-ALDO PUGLIESEDocumento21 pagine4.4.1.2 Lab - Configuring Zone-Based Policy Firewalls-ALDO PUGLIESEsheckie jarabaNessuna valutazione finora
- 2.6.1.2 Lab - Securing The Router For Administrative Access (Filled)Documento38 pagine2.6.1.2 Lab - Securing The Router For Administrative Access (Filled)true0soul80% (5)
- 2.6.1.2 Lab - Securing The Router For Administrative AccessDocumento54 pagine2.6.1.2 Lab - Securing The Router For Administrative AccessDaniel Ergicho100% (1)
- 4.4.3.5 Lab - Configuring Basic EIGRP For IPv6 PDFDocumento9 pagine4.4.3.5 Lab - Configuring Basic EIGRP For IPv6 PDFGabo NuñezNessuna valutazione finora
- 6.4.3.3 - ZachDocumento5 pagine6.4.3.3 - ZachZack ShoreNessuna valutazione finora
- 2.6.1.2 Lab - Securing The Router For Administrative Access - UnlockedDocumento44 pagine2.6.1.2 Lab - Securing The Router For Administrative Access - UnlockedAlonso Chi CitukNessuna valutazione finora
- Lab 4 - Static RoutingDocumento5 pagineLab 4 - Static RoutingdaveNessuna valutazione finora
- Ccnpv6 Route Lab2-1 Eigrp Config StudentDocumento13 pagineCcnpv6 Route Lab2-1 Eigrp Config Studentadncl2Nessuna valutazione finora
- Lab 01 - Securing The Router For Administrative AccessDocumento39 pagineLab 01 - Securing The Router For Administrative AccessespolieeeNessuna valutazione finora
- 7.4.3.5 Lab - Configuring Basic EIGRP For IPv6 - ILM PDFDocumento17 pagine7.4.3.5 Lab - Configuring Basic EIGRP For IPv6 - ILM PDFMaksim Korsakov97% (31)
- 6.3.7 Packet Tracer - Configure OSPF AuthenticationDocumento2 pagine6.3.7 Packet Tracer - Configure OSPF AuthenticationJose TapiaNessuna valutazione finora
- BGP Lab 4 - Implement BGP CommunitiesDocumento17 pagineBGP Lab 4 - Implement BGP CommunitiesSam A. SalmanNessuna valutazione finora
- 10.3.12 Lab - Configure ZPFsDocumento12 pagine10.3.12 Lab - Configure ZPFsJesús EnriqueNessuna valutazione finora
- CISCO PACKET TRACER LABS: Best practice of configuring or troubleshooting NetworkDa EverandCISCO PACKET TRACER LABS: Best practice of configuring or troubleshooting NetworkNessuna valutazione finora
- Advanced Raspberry Pi: Raspbian Linux and GPIO IntegrationDa EverandAdvanced Raspberry Pi: Raspbian Linux and GPIO IntegrationNessuna valutazione finora
- Network with Practical Labs Configuration: Step by Step configuration of Router and Switch configurationDa EverandNetwork with Practical Labs Configuration: Step by Step configuration of Router and Switch configurationNessuna valutazione finora
- DASAN V5816 DataSheet ENDocumento15 pagineDASAN V5816 DataSheet ENRafal ZNessuna valutazione finora
- IEEE11Documento52 pagineIEEE11api-3703205Nessuna valutazione finora
- BG ADAMO 4K PBDocumento2 pagineBG ADAMO 4K PBzsawnNessuna valutazione finora
- Ficha Técnica Teldat Atlas 840Documento4 pagineFicha Técnica Teldat Atlas 840diazpomalayajoseNessuna valutazione finora
- Huawei AR 46 SeriesDocumento6 pagineHuawei AR 46 SeriesYeboua Yao Angoua StephaneNessuna valutazione finora
- 9500 MPR R6 1 0 Release NoticeDocumento76 pagine9500 MPR R6 1 0 Release NoticeddNessuna valutazione finora
- 3.1.1.1 Video - Creating PDUs in Simulation ModeDocumento2 pagine3.1.1.1 Video - Creating PDUs in Simulation ModeT1T0 3L3KNessuna valutazione finora
- Sar 7705Documento2.170 pagineSar 7705arjantonio6118Nessuna valutazione finora
- Cisco IOS XR Getting Started Guide For The Cisco CRS Router, Release 4.1Documento222 pagineCisco IOS XR Getting Started Guide For The Cisco CRS Router, Release 4.1PazNessuna valutazione finora
- UA5000Documento59 pagineUA5000pipiredNessuna valutazione finora
- Internet Settings PDFDocumento6 pagineInternet Settings PDFRudy Nikoi AddoNessuna valutazione finora
- Itcertnotes - Manipulating Routing UpdatesDocumento11 pagineItcertnotes - Manipulating Routing Updateskim tehaNessuna valutazione finora
- ABC of ViptelaDocumento45 pagineABC of ViptelaOSCAR100% (1)
- As-B - SmartStruxure SolutionDocumento12 pagineAs-B - SmartStruxure SolutionJoão Carlos AlmeidaNessuna valutazione finora
- Library Switch IP: 192.168.254.74 ConfigurationDocumento11 pagineLibrary Switch IP: 192.168.254.74 ConfigurationkingfairgodNessuna valutazione finora
- Netcat Sohaib 3008Documento2 pagineNetcat Sohaib 3008sohaibchNessuna valutazione finora
- JNCIS-SP Voucher AssessmentDocumento16 pagineJNCIS-SP Voucher Assessmentromeo821100% (5)
- Stop and Wait ProtocolDocumento3 pagineStop and Wait Protocoldevarum40% (5)
- Final BGP Project - v1.1Documento24 pagineFinal BGP Project - v1.1vincentNessuna valutazione finora
- Networking Notes by Anand Sir CODEITUPDocumento186 pagineNetworking Notes by Anand Sir CODEITUPmukeshNessuna valutazione finora
- Switch Ports MerakiDocumento10 pagineSwitch Ports MerakiCarlos Torres MoranNessuna valutazione finora
- Tcp/Ip Model: Application LayerDocumento3 pagineTcp/Ip Model: Application LayerVikas SharmaNessuna valutazione finora
- OS6450 AOS 6.6.3 R01 Network Configuration GuideDocumento932 pagineOS6450 AOS 6.6.3 R01 Network Configuration GuideMuhammadNessuna valutazione finora
- What Is TCP/IP?: Transmission Control Protocol, or TCPDocumento17 pagineWhat Is TCP/IP?: Transmission Control Protocol, or TCPShubham GuptaNessuna valutazione finora
- Huawei Ont Product DatatsheetDocumento41 pagineHuawei Ont Product Datatsheetasram fauziNessuna valutazione finora
- Network Sizes and IEEE 802.X StandardsDocumento28 pagineNetwork Sizes and IEEE 802.X StandardsVim SamNessuna valutazione finora
- CCNA 3 All ModulesDocumento48 pagineCCNA 3 All ModulesFi3ta100% (1)
- VPN GateDocumento14 pagineVPN GateEAKANSH GUPTANessuna valutazione finora
- Wiser For KNX - LSS100100Documento2 pagineWiser For KNX - LSS100100Thiago FelipeNessuna valutazione finora
- CMD and Port NumberDocumento15 pagineCMD and Port Numberyami adiNessuna valutazione finora