Documenti di Didattica
Documenti di Professioni
Documenti di Cultura
04 Accel Incline TN
Caricato da
Eric S. ParkCopyright
Formati disponibili
Condividi questo documento
Condividi o incorpora il documento
Hai trovato utile questo documento?
Questo contenuto è inappropriato?
Segnala questo documentoCopyright:
Formati disponibili
04 Accel Incline TN
Caricato da
Eric S. ParkCopyright:
Formati disponibili
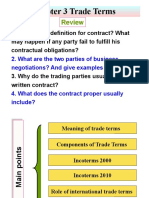
Activity 4
Teacher Notes: Acceleration on an Inclined Track
PS-2826
Teacher Notes Activity 4: Acceleration on an Inclined Track
Time Estimates
Preparation: 15 min
Activity: 30 min
Objectives
Students will be able to
use a Motion Sensor to measure the motion of a cart as it moves up and down an inclined track.
use the Xplorer GLX to record and display the motion of the cart.
analyze the graphs of position and velocity versus time for the motion of the accelerating cart.
compare the slope of velocity versus time to the mean value of acceleration versus time.
Notes
Pushing the cart up the incline so that it does not get too close to the sensor may take some
practice before data collection is done.
It is important that students understand the following graphical representations:
Identification of the measurement and units of the vertical or y-axis.
Identification of the measurement and units of the horizontal or x-axis.
Meaning of the slope on the velocity-time graph: The physical representation of the slope can be
found by looking at the units of the vertical axis divided by the units of the horizontal axis. The units
are meters per second per second the units of acceleration.
Be certain that the motion sensor is set on the near (cart) setting. In
addition, the sensor must be aimed such that it points directly at its
target.
If the cart comes closer than 15 cm to the front of the Motion Sensor,
the sensor wont record accurate data.
Motion Sensor Setting
When students examine the Graph screen for velocity, they may
probably need to Scale and Move the axes before they select Linear Fit to find the slope.
When students examine the Graph screen for acceleration, they may need to Scale and Move the
axes. Challenge them to re-scale the y-axis so the maximum and minimum values are
approximately the same as shown in the Sample Data section below.
Introductory Physics with the Xplorer GLX
2006 PASCO
p. 13
Activity 4
Teacher Notes: Acceleration on an Inclined Track
PS-2826
Sample Data
The screenshots show the plots of position, velocity, and acceleration versus time for the cart
moving up and down the inclined track. The second screenshot shows the slope of the velocity
versus time (from the Linear Fit). The last screenshot shows the mean value of the selected
region of the acceleration.
Fig. 1: Position graph
Fig. 2: Velocity graph
Fig. 3 Acceleration graph
Introductory Physics with the Xplorer GLX
2006 PASCO
p. 14
Activity 4
Teacher Notes: Acceleration on an Inclined Track
PS-2826
Lab Report - Activity 4: Acceleration on an Inclined Track
Answers and Sample Data
Data
Sketch your graph of data from the Motion Sensor for position versus time and for velocity
versus time for the cart up and down the incline. Include labels and units for your y-axes and xaxes. (See the Sample Data screenshots.)
Introductory Physics with the Xplorer GLX
2006 PASCO
p. 15
Activity 4
Teacher Notes: Acceleration on an Inclined Track
PS-2826
Data Table
Item
Value
Acceleration (slope)
0.444 m/s2
Acceleration (mean)
0.4 m/s2
Questions
1.
Describe the position versus time plot of the Graph screen. Why does the distance begin at
a maximum and decrease as the cart moves up the inclined plane?
The position plot is parabolic and is a mirror image of the plot of position for an object that is
thrown upward and then falls downward. The distance begins at a maximum and then decreases
because the cart is decreasing its distance from the Motion Sensor as it goes up the inclined
plane. The Motion Sensor measures motion toward it as negative (decreasing distance).
2.
Describe the velocity versus time plot.
In the region that corresponds to the motion of the cart after it is pushed and before it stops at
the bottom, the velocity plot is linear with a positive slope.
3.
Describe the acceleration versus time plot of the Graph display.
In the region that corresponds to the motion of the cart after it is pushed and before it stops at
the bottom, the acceleration plot appears to be linear with almost zero slope.
4.
How does the acceleration determined in the plot of velocity compare to the mean value of
acceleration from the plot of acceleration?
Answers will vary. In the example, the acceleration determined in the plot of velocity (0.444
m/s2) is nearly the same as the mean value of acceleration from the plot of acceleration (0.4
m/s2).
Introductory Physics with the Xplorer GLX
2006 PASCO
p. 16
Potrebbero piacerti anche
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeDa EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeValutazione: 4 su 5 stelle4/5 (5784)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingDa EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingValutazione: 3.5 su 5 stelle3.5/5 (399)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceDa EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceValutazione: 4 su 5 stelle4/5 (890)
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeDa EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeValutazione: 4.5 su 5 stelle4.5/5 (537)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceDa EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceValutazione: 4 su 5 stelle4/5 (587)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureDa EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureValutazione: 4.5 su 5 stelle4.5/5 (474)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Da EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Valutazione: 4 su 5 stelle4/5 (98)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnDa EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnValutazione: 4.5 su 5 stelle4.5/5 (234)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItDa EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItValutazione: 4.5 su 5 stelle4.5/5 (838)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerDa EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerValutazione: 4.5 su 5 stelle4.5/5 (271)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryDa EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryValutazione: 3.5 su 5 stelle3.5/5 (231)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaDa EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaValutazione: 4.5 su 5 stelle4.5/5 (265)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersDa EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersValutazione: 4.5 su 5 stelle4.5/5 (344)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealDa EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealValutazione: 4 su 5 stelle4/5 (72)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyDa EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyValutazione: 3.5 su 5 stelle3.5/5 (2219)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaDa EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaValutazione: 4 su 5 stelle4/5 (45)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreDa EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreValutazione: 4 su 5 stelle4/5 (1090)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Da EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Valutazione: 4.5 su 5 stelle4.5/5 (119)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesDa EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesValutazione: 4 su 5 stelle4/5 (821)
- Group analyzes Sunsilk brand auditDocumento49 pagineGroup analyzes Sunsilk brand auditinkLLL0% (1)
- Strict Liability - ProjectDocumento7 pagineStrict Liability - ProjectRushabh Lalan100% (1)
- 02 Takaful CREDIT & DEBIT CARD AUTOPAY Authorization Form V1.0 2018Documento2 pagine02 Takaful CREDIT & DEBIT CARD AUTOPAY Authorization Form V1.0 2018UstazFaizalAriffinOriginalNessuna valutazione finora
- Commissioner of Internal Revenue V CaDocumento3 pagineCommissioner of Internal Revenue V CaJimenez LorenzNessuna valutazione finora
- Service Level ManagementDocumento8 pagineService Level Managementrashmib1980Nessuna valutazione finora
- 3G Ardzyka Raka R 1910631030065 Assignment 8Documento3 pagine3G Ardzyka Raka R 1910631030065 Assignment 8Raka RamadhanNessuna valutazione finora
- 0 Proposal Form Top Up SUBMITTED BY Markandeya Raju PDFDocumento3 pagine0 Proposal Form Top Up SUBMITTED BY Markandeya Raju PDFHOD (MVGR Civil)Nessuna valutazione finora
- Chapter 3 Views in ASP - NET CoreDocumento23 pagineChapter 3 Views in ASP - NET Coremohammadabusaleh628Nessuna valutazione finora
- 2021-2022 Reopening Plan 2.0Documento22 pagine2021-2022 Reopening Plan 2.0Dan LehrNessuna valutazione finora
- Business Process Reengineering and Performance Improvement in The BankDocumento12 pagineBusiness Process Reengineering and Performance Improvement in The BankYakut Rumani SultanNessuna valutazione finora
- Breadtalk AR 2011Documento158 pagineBreadtalk AR 2011Wong ZieNessuna valutazione finora
- Introduction To Global Business 2nd Edition Gaspar Test BankDocumento26 pagineIntroduction To Global Business 2nd Edition Gaspar Test BankJerryGarrettmwsi100% (56)
- Company Profile 2016 PDFDocumento81 pagineCompany Profile 2016 PDFabioduncityNessuna valutazione finora
- Practice Ch3Documento108 paginePractice Ch3Agang Nicole BakwenaNessuna valutazione finora
- Chapter 10Documento28 pagineChapter 10ahmedNessuna valutazione finora
- Dokumen - Tips Md110-ForumDocumento317 pagineDokumen - Tips Md110-ForumMiguel Ángel CoriaNessuna valutazione finora
- Pulau Besar Island Off Malacca CoastDocumento5 paginePulau Besar Island Off Malacca CoastLucy TyasNessuna valutazione finora
- Industrial Tour Report (JEWEL - MANAGEMENT-CU)Documento37 pagineIndustrial Tour Report (JEWEL - MANAGEMENT-CU)Mohammad Jewel100% (2)
- TOT Calendar Oct Dec. 2018 1Documento7 pagineTOT Calendar Oct Dec. 2018 1Annamneedi PrasadNessuna valutazione finora
- 2011 Ringgold County Fair EditionDocumento16 pagine2011 Ringgold County Fair EditionMountAyrRecordNewsNessuna valutazione finora
- Competition Patriotism and Collaboratio PDFDocumento22 pagineCompetition Patriotism and Collaboratio PDFAngga PrianggaraNessuna valutazione finora
- Frias Lindsay Iste Stds Self AssessmentDocumento4 pagineFrias Lindsay Iste Stds Self Assessmentapi-572977540Nessuna valutazione finora
- United States v. James Lonzo Turner and Kevin Orlando Moore, 120 F.3d 271, 10th Cir. (1997)Documento4 pagineUnited States v. James Lonzo Turner and Kevin Orlando Moore, 120 F.3d 271, 10th Cir. (1997)Scribd Government DocsNessuna valutazione finora
- Detection of Phising Websites Using Machine Learning ApproachesDocumento9 pagineDetection of Phising Websites Using Machine Learning Approachesshresthabishal721Nessuna valutazione finora
- Only PandasDocumento8 pagineOnly PandasJyotirmay SahuNessuna valutazione finora
- ReleaseDocumento36 pagineReleasebassamrajehNessuna valutazione finora
- Masonry Design and DetailingDocumento21 pagineMasonry Design and DetailingKIMBERLY ARGEÑALNessuna valutazione finora
- Applying problem solving techniques to routine computer issuesDocumento2 pagineApplying problem solving techniques to routine computer issuesBirhanu Atnafu0% (1)
- Προσχέδιο Έκθεσης Γ.Γ. ΟΗΕ για Καλές ΥπηρεσίεςDocumento20 pagineΠροσχέδιο Έκθεσης Γ.Γ. ΟΗΕ για Καλές ΥπηρεσίεςARISTEIDIS VIKETOSNessuna valutazione finora
- Soft ListDocumento21 pagineSoft Listgicox89Nessuna valutazione finora