Documenti di Didattica
Documenti di Professioni
Documenti di Cultura
Photorespiration: Bundle Sheath Cells
Caricato da
api-296833859Titolo originale
Copyright
Formati disponibili
Condividi questo documento
Condividi o incorpora il documento
Hai trovato utile questo documento?
Questo contenuto è inappropriato?
Segnala questo documentoCopyright:
Formati disponibili
Photorespiration: Bundle Sheath Cells
Caricato da
api-296833859Copyright:
Formati disponibili
C4 Plants: The Exception
Photorespiration: It is an unwanted process during which rubisco catalyses the reaction between
RuBP and oxygen instead of RuBP and carbon dioxide. This is more likely to happen at high
temperatures and high light intensities.
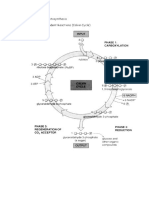
- The difference between C3 and C4 plants:
In C3 plants, in the first step of the light independent reactions, an unstable 6C organic
compound forms and breaks down into two 3C organic compounds (glycerate 3-phosphate).
In 4C plants, in the first step of the light independent reactions, a 4C compound is formed
(oxaloacetate).
- Adaptations against photorespiration
4C plants, such as maize, sugarcane, and other tropical plants have adaptations against
photorespiration.
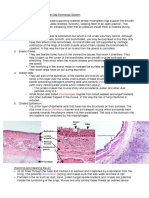
- The enzymes for the Calvin cycle (e.g. rubisco) are kept in special bundle sheath cells
surrounding the vascular bundle, where they are not in contact with air/oxygen.
1. The mesophyll cells around the bundle sheath cells are in contact with oxygen. The light
dependent reactions take place in these mesophyll cells.
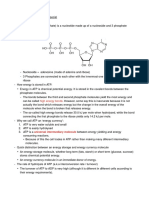
2. Then, carbon dioxide is fixed by PEP carboxylase (phosphoenol pyruvate carboxylase)
and combined with PEP, a 3C molecule, to form oxaloacetate.
3. Oxaloacetate is converted into malate.
4. Malate is transferred to the bundle sheath cells.
5. Malate is broken down into pyruvate and carbon dioxide.
6. The carbon dioxide takes part in the Calvin cycle as usual and the pyruvate returns to
the mesophyll cells in order to reform PEP.
- The enzyme PEP carboxylase has a higher optimum temperature in plants from tropical/
hot regions (45 degrees) compared to the same enzyme in other plants (30 degrees).
Potrebbero piacerti anche
- PhotosynthesisDocumento20 paginePhotosynthesisVinch Samuel AchacosoNessuna valutazione finora
- PhotorespirationDocumento16 paginePhotorespirationMoa ArmyNessuna valutazione finora
- Hatch and Slack CycleDocumento30 pagineHatch and Slack CycleKalyani SreejithNessuna valutazione finora
- Outline Electron Transport Chain in PhotosynthesisDocumento2 pagineOutline Electron Transport Chain in PhotosynthesisspenzercadienteeNessuna valutazione finora
- Photosynthesis Study Material C4 Cycle OnwardsDocumento6 paginePhotosynthesis Study Material C4 Cycle OnwardsmoonyNessuna valutazione finora
- CRPSCI 1100-Module5Documento14 pagineCRPSCI 1100-Module5carbonel.carlaNessuna valutazione finora
- Chapter-4 Photosynthesis in Higher Plants: Very Short Answers QuestionsDocumento10 pagineChapter-4 Photosynthesis in Higher Plants: Very Short Answers QuestionsPraveen KumarNessuna valutazione finora
- Content Paper For C3 and C4 PlantsDocumento3 pagineContent Paper For C3 and C4 PlantsHazel Love AlforqueNessuna valutazione finora
- Biology Chapter 13 PhotosynthesisDocumento8 pagineBiology Chapter 13 PhotosynthesisSokuntheary SrunNessuna valutazione finora
- Day 5 Cam, C3, C4Documento50 pagineDay 5 Cam, C3, C4Bruh MomentNessuna valutazione finora
- Photosynth EsisDocumento14 paginePhotosynth Esiscleahveil badanNessuna valutazione finora
- Cuestionario Fisiotecnia en InglésDocumento4 pagineCuestionario Fisiotecnia en InglésMokr Guerrero EsperanzaNessuna valutazione finora
- Revision Chapter 6 Photosynthesis (Calvin Cycle)Documento6 pagineRevision Chapter 6 Photosynthesis (Calvin Cycle)MOHAMAD SAHIMI BIN MAHAT MoeNessuna valutazione finora
- Photosynthetic Pathways 9Documento8 paginePhotosynthetic Pathways 9Nathaly Mendoza MorenoNessuna valutazione finora
- PHOTOSYNTHESIS PATHWAYS - rePORTDocumento22 paginePHOTOSYNTHESIS PATHWAYS - rePORTGarry Michael Tarroma SarmientoNessuna valutazione finora
- Biosynthetic Pathway Dark ReactionDocumento5 pagineBiosynthetic Pathway Dark ReactionspenzercadienteeNessuna valutazione finora
- C4 PhotosynthesisDocumento15 pagineC4 PhotosynthesisArtwell ChiboworaNessuna valutazione finora
- Comparing and Contrasting C3, C4, CAM - AP BiologyDocumento1 paginaComparing and Contrasting C3, C4, CAM - AP BiologyFVCproductionsNessuna valutazione finora
- Photosynthesis PDFDocumento4 paginePhotosynthesis PDFbluemonkeymei4921100% (1)
- Types of PhotosyntheseDocumento6 pagineTypes of PhotosyntheseZain ul abdin QureshiNessuna valutazione finora
- Photosynthesis (KEY)Documento6 paginePhotosynthesis (KEY)kylevNessuna valutazione finora
- C4 Plants: Features To Avoid PhotorespirationDocumento6 pagineC4 Plants: Features To Avoid PhotorespirationNathuAndrewsNessuna valutazione finora
- Photosynthetic Adaptations: C Cycle and CAM: Prepared By: Group 7 (Cabatingan, Ocaya, Cardente, Guillermo, and Andamon)Documento8 paginePhotosynthetic Adaptations: C Cycle and CAM: Prepared By: Group 7 (Cabatingan, Ocaya, Cardente, Guillermo, and Andamon)Una Kaya CabatinganNessuna valutazione finora
- Coping With Environmental Variation: EnergyDocumento4 pagineCoping With Environmental Variation: EnergyKim CaelianNessuna valutazione finora
- Carbon Fixation Activity SheetDocumento2 pagineCarbon Fixation Activity SheetLesley BoultonNessuna valutazione finora
- Week - 3 - Lectures 1-1Documento74 pagineWeek - 3 - Lectures 1-1Benjamin SamaniNessuna valutazione finora
- Raven, P. H. Et Al. 1992Documento73 pagineRaven, P. H. Et Al. 1992Teflon SlimNessuna valutazione finora
- 1 Photosyn General Info 4Documento42 pagine1 Photosyn General Info 4Ruperto VidalNessuna valutazione finora
- Plant Life ProcessesDocumento53 paginePlant Life ProcessesGel Mi AmorNessuna valutazione finora
- Photosynthesis Light Reaction, Dark Reaction (Calvin Cycle) and c3 Plant, c4 Plant, and Cam PlantDocumento6 paginePhotosynthesis Light Reaction, Dark Reaction (Calvin Cycle) and c3 Plant, c4 Plant, and Cam Plantwahyunipbiologi100% (1)
- Bio2 PhotosynthesisDocumento24 pagineBio2 Photosynthesisjvvuvuuv lopezNessuna valutazione finora
- Advantages and Disadvantages of C4 Plant PhotosynthesisDocumento5 pagineAdvantages and Disadvantages of C4 Plant PhotosynthesisAhsan Raza100% (1)
- PhotosynthesisDocumento5 paginePhotosynthesisbluemonkeymei4921100% (1)
- Photosynthesis in C4 PlantsDocumento5 paginePhotosynthesis in C4 PlantsErvin Ade PrasetyoNessuna valutazione finora
- Plant Physiology EvaluationsDocumento13 paginePlant Physiology Evaluationslisanames.23Nessuna valutazione finora
- C4 PlantsDocumento4 pagineC4 PlantsIsidro ChanNessuna valutazione finora
- Ch. 8 SlidesDocumento65 pagineCh. 8 SlidesKayla BrezenskiNessuna valutazione finora
- Calvin Cycle (Dark Reactions / Light Independent Reaction)Documento47 pagineCalvin Cycle (Dark Reactions / Light Independent Reaction)L'ya Lieslotte100% (2)
- The Calvin CycleDocumento8 pagineThe Calvin CycleVaan ChinNessuna valutazione finora
- Chapter 7: Photosynthesis: Light Independent Reactions: How Is Chemical Energy Stored in Glucose MoleculesDocumento18 pagineChapter 7: Photosynthesis: Light Independent Reactions: How Is Chemical Energy Stored in Glucose MoleculesJonard PedrosaNessuna valutazione finora
- C2 C3 C4 & Cam Variations On The Theme of PhotosynthesisDocumento20 pagineC2 C3 C4 & Cam Variations On The Theme of PhotosynthesisKoons KoonsNessuna valutazione finora
- Lecture No: 12: Photosynthetic Pathways (C3, C4 and Cam)Documento22 pagineLecture No: 12: Photosynthetic Pathways (C3, C4 and Cam)AnandKuttiyanNessuna valutazione finora
- Function of PhotosynthesisDocumento58 pagineFunction of PhotosynthesisJulian ChristopherNessuna valutazione finora
- Hatch and Slack PathwayDocumento8 pagineHatch and Slack Pathwayvijend0% (1)
- Energy Variations PracticeDocumento3 pagineEnergy Variations Practiceapi-522847737Nessuna valutazione finora
- Wa0009Documento9 pagineWa0009law fullNessuna valutazione finora
- 18 PhotorespirationDocumento21 pagine18 Photorespiration黄心怡Nessuna valutazione finora
- Carbon Fixation - WikipediaDocumento64 pagineCarbon Fixation - WikipediaBashiir NuurNessuna valutazione finora
- Finals Gen Physio Lab ExamDocumento3 pagineFinals Gen Physio Lab ExamShaira CogollodoNessuna valutazione finora
- Discussion of C3, C4, and CAM PhotosynthesisDocumento2 pagineDiscussion of C3, C4, and CAM Photosynthesiswaqas bhatti00Nessuna valutazione finora
- Crop Ecology - Productivity and Management in Agricultural Systems - (2011) Queensland Recomendation-275-295Documento21 pagineCrop Ecology - Productivity and Management in Agricultural Systems - (2011) Queensland Recomendation-275-295CarolinaNessuna valutazione finora
- Chapter 8: Photosynthesis: Inquiry Into Life, Thirteenth EditionDocumento2 pagineChapter 8: Photosynthesis: Inquiry Into Life, Thirteenth Editionmisst23Nessuna valutazione finora
- 8.4.1 Plant MetabolismDocumento15 pagine8.4.1 Plant Metabolismnersyanhariri71Nessuna valutazione finora
- Alternative Carbon FixationDocumento18 pagineAlternative Carbon Fixationlady ann apple colipanoNessuna valutazione finora
- Chapter 7 Reading QuestionsDocumento2 pagineChapter 7 Reading QuestionsDefault AccountNessuna valutazione finora
- Photorespiration: The Assignment Submitted by Mumtahin Ul KousarDocumento11 paginePhotorespiration: The Assignment Submitted by Mumtahin Ul KousarJunaid MushtaqNessuna valutazione finora
- Photosynthesis C4 CAMDocumento17 paginePhotosynthesis C4 CAMDeborah EckhardtNessuna valutazione finora
- PhotosynthesisDocumento4 paginePhotosynthesissteven7 IsaacsNessuna valutazione finora
- Chapter 7 Reading Questions-1-1Documento2 pagineChapter 7 Reading Questions-1-1Default AccountNessuna valutazione finora
- Selective Advantage Natural Selection Selection Pressure: Speciation SpeciesDocumento2 pagineSelective Advantage Natural Selection Selection Pressure: Speciation Speciesapi-296833859Nessuna valutazione finora
- TranscriptoneDocumento2 pagineTranscriptoneapi-296833859Nessuna valutazione finora
- Negative Effects of Growing Herbicide Resistant Crops IncludeDocumento3 pagineNegative Effects of Growing Herbicide Resistant Crops Includeapi-296833859Nessuna valutazione finora
- Selection PressuresDocumento1 paginaSelection Pressuresapi-296833859Nessuna valutazione finora
- Selective AdvantagesDocumento2 pagineSelective Advantagesapi-296833859Nessuna valutazione finora
- Background Genes Progeny TestingDocumento1 paginaBackground Genes Progeny Testingapi-296833859Nessuna valutazione finora
- Inbreeding Interbreeding Outbreeding Inbreeding DepressionDocumento1 paginaInbreeding Interbreeding Outbreeding Inbreeding Depressionapi-296833859Nessuna valutazione finora
- Photophosphorylation:: PhotoactivationDocumento1 paginaPhotophosphorylation:: Photoactivationapi-296833859Nessuna valutazione finora
- The Founder Effect: Genetic DriftDocumento1 paginaThe Founder Effect: Genetic Driftapi-296833859Nessuna valutazione finora
- Limiting FactorDocumento2 pagineLimiting Factorapi-296833859Nessuna valutazione finora
- Energy DensityDocumento1 paginaEnergy Densityapi-296833859Nessuna valutazione finora
- Absorbance Spectrum Action SpectrumDocumento2 pagineAbsorbance Spectrum Action Spectrumapi-296833859Nessuna valutazione finora
- Coevolution Fitness Natural Selection: Discontinuous VariationDocumento2 pagineCoevolution Fitness Natural Selection: Discontinuous Variationapi-296833859Nessuna valutazione finora
- PhotolysisDocumento1 paginaPhotolysisapi-296833859Nessuna valutazione finora
- Organic Molecule Respiration Potential Energy Chemical Potential EnergyDocumento1 paginaOrganic Molecule Respiration Potential Energy Chemical Potential Energyapi-296833859Nessuna valutazione finora
- GahhDocumento1 paginaGahhapi-296833859Nessuna valutazione finora
- High Energy Bonds: Universal Intermediary MoleculeDocumento2 pagineHigh Energy Bonds: Universal Intermediary Moleculeapi-296833859Nessuna valutazione finora
- Anaerobic Respiration (In The: CytoplasmDocumento1 paginaAnaerobic Respiration (In The: Cytoplasmapi-296833859Nessuna valutazione finora
- Overcrowded Substandard Housing Low ImmunityDocumento2 pagineOvercrowded Substandard Housing Low Immunityapi-296833859Nessuna valutazione finora
- Cytoplasm: GlycolysisDocumento4 pagineCytoplasm: Glycolysisapi-296833859Nessuna valutazione finora
- Cardiac Cycle: PacemakerDocumento3 pagineCardiac Cycle: Pacemakerapi-296833859Nessuna valutazione finora
- CholeraDocumento1 paginaCholeraapi-296833859Nessuna valutazione finora
- Gas Exchange: One (1.8 CM) Yes Yes Yes Yes No YesDocumento2 pagineGas Exchange: One (1.8 CM) Yes Yes Yes Yes No Yesapi-296833859Nessuna valutazione finora
- Passive Smoking: CarcinogensDocumento3 paginePassive Smoking: Carcinogensapi-296833859Nessuna valutazione finora
- AntibioticsDocumento2 pagineAntibioticsapi-296833859Nessuna valutazione finora
- Cardiac Muscle: MyogenicDocumento2 pagineCardiac Muscle: Myogenicapi-296833859Nessuna valutazione finora
- Glycoproteins Called Mucin: DesiccationDocumento2 pagineGlycoproteins Called Mucin: Desiccationapi-296833859Nessuna valutazione finora
- The Molecule of More: How a Single Chemical in Your Brain Drives Love, Sex, and Creativity--and Will Determine the Fate of the Human RaceDa EverandThe Molecule of More: How a Single Chemical in Your Brain Drives Love, Sex, and Creativity--and Will Determine the Fate of the Human RaceValutazione: 4.5 su 5 stelle4.5/5 (517)
- Gut: the new and revised Sunday Times bestsellerDa EverandGut: the new and revised Sunday Times bestsellerValutazione: 4 su 5 stelle4/5 (393)
- Why We Die: The New Science of Aging and the Quest for ImmortalityDa EverandWhy We Die: The New Science of Aging and the Quest for ImmortalityValutazione: 4 su 5 stelle4/5 (5)
- All That Remains: A Renowned Forensic Scientist on Death, Mortality, and Solving CrimesDa EverandAll That Remains: A Renowned Forensic Scientist on Death, Mortality, and Solving CrimesValutazione: 4.5 su 5 stelle4.5/5 (397)
- Tales from Both Sides of the Brain: A Life in NeuroscienceDa EverandTales from Both Sides of the Brain: A Life in NeuroscienceValutazione: 3 su 5 stelle3/5 (18)
- A Brief History of Intelligence: Evolution, AI, and the Five Breakthroughs That Made Our BrainsDa EverandA Brief History of Intelligence: Evolution, AI, and the Five Breakthroughs That Made Our BrainsValutazione: 4.5 su 5 stelle4.5/5 (6)
- When the Body Says No by Gabor Maté: Key Takeaways, Summary & AnalysisDa EverandWhen the Body Says No by Gabor Maté: Key Takeaways, Summary & AnalysisValutazione: 3.5 su 5 stelle3.5/5 (2)
- Return of the God Hypothesis: Three Scientific Discoveries That Reveal the Mind Behind the UniverseDa EverandReturn of the God Hypothesis: Three Scientific Discoveries That Reveal the Mind Behind the UniverseValutazione: 4.5 su 5 stelle4.5/5 (52)
- The Ancestor's Tale: A Pilgrimage to the Dawn of EvolutionDa EverandThe Ancestor's Tale: A Pilgrimage to the Dawn of EvolutionValutazione: 4 su 5 stelle4/5 (812)
- Gut: The Inside Story of Our Body's Most Underrated Organ (Revised Edition)Da EverandGut: The Inside Story of Our Body's Most Underrated Organ (Revised Edition)Valutazione: 4 su 5 stelle4/5 (411)
- 10% Human: How Your Body's Microbes Hold the Key to Health and HappinessDa Everand10% Human: How Your Body's Microbes Hold the Key to Health and HappinessValutazione: 4 su 5 stelle4/5 (33)
- Masterminds: Genius, DNA, and the Quest to Rewrite LifeDa EverandMasterminds: Genius, DNA, and the Quest to Rewrite LifeNessuna valutazione finora
- The Other Side of Normal: How Biology Is Providing the Clues to Unlock the Secrets of Normal and Abnormal BehaviorDa EverandThe Other Side of Normal: How Biology Is Providing the Clues to Unlock the Secrets of Normal and Abnormal BehaviorNessuna valutazione finora
- Who's in Charge?: Free Will and the Science of the BrainDa EverandWho's in Charge?: Free Will and the Science of the BrainValutazione: 4 su 5 stelle4/5 (65)
- Seven and a Half Lessons About the BrainDa EverandSeven and a Half Lessons About the BrainValutazione: 4 su 5 stelle4/5 (110)
- Buddha's Brain: The Practical Neuroscience of Happiness, Love & WisdomDa EverandBuddha's Brain: The Practical Neuroscience of Happiness, Love & WisdomValutazione: 4 su 5 stelle4/5 (216)
- Fast Asleep: Improve Brain Function, Lose Weight, Boost Your Mood, Reduce Stress, and Become a Better SleeperDa EverandFast Asleep: Improve Brain Function, Lose Weight, Boost Your Mood, Reduce Stress, and Become a Better SleeperValutazione: 4.5 su 5 stelle4.5/5 (16)
- Good Without God: What a Billion Nonreligious People Do BelieveDa EverandGood Without God: What a Billion Nonreligious People Do BelieveValutazione: 4 su 5 stelle4/5 (66)
- Human: The Science Behind What Makes Your Brain UniqueDa EverandHuman: The Science Behind What Makes Your Brain UniqueValutazione: 3.5 su 5 stelle3.5/5 (38)
- Undeniable: How Biology Confirms Our Intuition That Life Is DesignedDa EverandUndeniable: How Biology Confirms Our Intuition That Life Is DesignedValutazione: 4 su 5 stelle4/5 (11)
- The Lives of Bees: The Untold Story of the Honey Bee in the WildDa EverandThe Lives of Bees: The Untold Story of the Honey Bee in the WildValutazione: 4.5 su 5 stelle4.5/5 (44)
- The Rise and Fall of the Dinosaurs: A New History of a Lost WorldDa EverandThe Rise and Fall of the Dinosaurs: A New History of a Lost WorldValutazione: 4 su 5 stelle4/5 (596)
- Moral Tribes: Emotion, Reason, and the Gap Between Us and ThemDa EverandMoral Tribes: Emotion, Reason, and the Gap Between Us and ThemValutazione: 4.5 su 5 stelle4.5/5 (115)
- A Series of Fortunate Events: Chance and the Making of the Planet, Life, and YouDa EverandA Series of Fortunate Events: Chance and the Making of the Planet, Life, and YouValutazione: 4.5 su 5 stelle4.5/5 (62)
- The Consciousness Instinct: Unraveling the Mystery of How the Brain Makes the MindDa EverandThe Consciousness Instinct: Unraveling the Mystery of How the Brain Makes the MindValutazione: 4.5 su 5 stelle4.5/5 (93)