Documenti di Didattica
Documenti di Professioni
Documenti di Cultura
Math Toolbox
Caricato da
KurtisCopyright
Formati disponibili
Condividi questo documento
Condividi o incorpora il documento
Hai trovato utile questo documento?
Questo contenuto è inappropriato?
Segnala questo documentoCopyright:
Formati disponibili
Math Toolbox
Caricato da
KurtisCopyright:
Formati disponibili
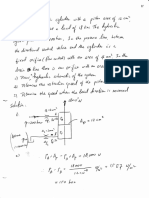
Mathematical Toolbox
1. Solution of quadratic equations
For an equation: ax 2 + bx + c = 0
There are two solutions given by: x =
b b 2 4ac
2a
2. Geometry
1. The internal angles of a triangle add up to 1800.
+ + = 1800
2. The external angle equals the sum of the angles facing the other two
sides.
= +
3. Trigonometry
1. For a right angled triangle having sides a,b,c, with the hypotenuse the
side c opposite the right angle, and a the angle opposite side a etc.
sina = a/c
cosa =b/c
tana = a/b = sina
/ cosa
sin is an odd function hence sin(-) = -sin()
cos in an even function hence cos(-) = cos()
Hence tan is an odd function with tan (-a ) = -tan(a )
sin(900 - ) = cos ()
Pythagoras (applies to right angled triangle) a2 + b2 = c2
Cosine rule (applies to any triangle)
a2 = b2 + c2 2bc cosa
2. The identity
sin2 + cos2 = 1
4. Expansions
1. binomial theorem: x + y
=
k =0
FG n IJ x
H kK
nk
y k where
and factorial m is denoted m! = 1 2 3.......m; 0! = 1
FG n IJ = n!
H k K (n k )! k !
e.g
b x yg
b x yg
= x 2 2 xy + y 2
= x 3 3x 2 y + 3xy 2 y 3
if x2 < 1 then the following can be used:
b1 + xg
= 1 + nx +
b g
b gb g
n n 1 2 n n 1 n 2 3
x +
x +L
2!
3!
2. expansions of trigonometric functions
sin =
tan = +
3
3!
3
3
5
5!
7
7!
cos = 1
+K
FG
H
2 5 17 7
2
+
+K 2 <
15
315
4
IJ
K
3. expansion of exponentials and logarithms
x2 x3
ex = 1 x + + L
2 ! 3!
x2 x3 x4
ln(1 + x ) = x + + L x 2 < 1
2
3 4
5. Areas and Volumes
1. Circle
Circumference = 2r
Area = r2
2. Sphere
Area = 4r2
Volume = 4r3/3
3. Cylinder
height h, radius r
Volume = r2h
4. Triangle
area = base x height
6. Derivatives and Integrals
1.
Product Rule:
if u and v are functions of x
b g
d
dv
du
uv = u + v
dx
dx
dx
if u is a function of y and y in turn is a function of x:
2. Chain Rule:
du du dy
=
dx dy dx
3. Integration by parts
2
2
2!
4
4!
6
6!
+K
dv
du
dx = uv v dx
dx
dx
4. Two integrals:
r =a
1
a
r =b r dr = loge b
u
r =a
r =b
1 1
dr =
b a
5. General rules
m
x dx =
x m +1
m +1
cos d = sin[ f ] sin[ i ]
i
7. Vectors
In a Cartesian coordinate system, with three mutually perpendicular linear coordinates in
variables x, y and z denoted by the unit vectors i , j and k .
Dot product ii = jj = kk = 1
ij = jk = ki = 0
Vector product i i = j j = k k = 0
i j= k j k = i k i = j
Order of vector product
j i = - k k j = -i i k = -j
For any arbitrary vector a = ax i + ay j +az k, when operated on by other arbitrary
vectors b and c defined in a similar way,
a (b + c) = a b + a c
sa b = a sb = s(a b)
where s is a scalar
Scalar (dot) product of two vectors
ab = ba = axbx + ayby + azbz = ab cos
where is the acute angle between a and b
and a,b are the magnitudes (size) of a and b.
Vector ( cross) product of two vectors
ab=-ba=
ax
ay
az
bx
by
bz
= (aybz-azby)i (axbz -azbx)j + (axby-aybx)k
= ab sin
3
Potrebbero piacerti anche
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeDa EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeValutazione: 4 su 5 stelle4/5 (5794)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreDa EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreValutazione: 4 su 5 stelle4/5 (1090)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItDa EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItValutazione: 4.5 su 5 stelle4.5/5 (838)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceDa EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceValutazione: 4 su 5 stelle4/5 (895)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceDa EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceValutazione: 4 su 5 stelle4/5 (588)
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeDa EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeValutazione: 4.5 su 5 stelle4.5/5 (537)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersDa EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersValutazione: 4.5 su 5 stelle4.5/5 (344)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureDa EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureValutazione: 4.5 su 5 stelle4.5/5 (474)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesDa EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesValutazione: 4 su 5 stelle4/5 (821)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Da EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Valutazione: 4.5 su 5 stelle4.5/5 (120)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerDa EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerValutazione: 4.5 su 5 stelle4.5/5 (271)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingDa EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingValutazione: 3.5 su 5 stelle3.5/5 (399)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyDa EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyValutazione: 3.5 su 5 stelle3.5/5 (2259)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Da EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Valutazione: 4 su 5 stelle4/5 (98)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaDa EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaValutazione: 4.5 su 5 stelle4.5/5 (266)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryDa EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryValutazione: 3.5 su 5 stelle3.5/5 (231)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnDa EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnValutazione: 4.5 su 5 stelle4.5/5 (234)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealDa EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealValutazione: 4 su 5 stelle4/5 (73)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaDa EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaValutazione: 4 su 5 stelle4/5 (45)
- HTL - JL: C RL L - CL: ° "" ,/ I'""Documento3 pagineHTL - JL: C RL L - CL: ° "" ,/ I'""KurtisNessuna valutazione finora
- Course Outline MECH 4003 F16 - Final PDFDocumento2 pagineCourse Outline MECH 4003 F16 - Final PDFKurtisNessuna valutazione finora
- Course Outline MECH 4003 F16 - FinalDocumento2 pagineCourse Outline MECH 4003 F16 - FinalKurtis100% (1)
- Project Outline MECH 4003 F16Documento2 pagineProject Outline MECH 4003 F16KurtisNessuna valutazione finora
- OutlineDocumento5 pagineOutlineKurtisNessuna valutazione finora
- Final Paper GuidelinesDocumento1 paginaFinal Paper GuidelinesKurtisNessuna valutazione finora
- ASA Citation GuideDocumento27 pagineASA Citation GuideKurtisNessuna valutazione finora
- Single Page Integral Table PDFDocumento2 pagineSingle Page Integral Table PDFMehmet Helva100% (2)
- Herat Transfer A3Q5Documento4 pagineHerat Transfer A3Q5KurtisNessuna valutazione finora
- Stats PDFDocumento2 pagineStats PDFHarish KumarNessuna valutazione finora
- Stats PDFDocumento2 pagineStats PDFHarish KumarNessuna valutazione finora
- DocDocumento1 paginaDocKurtisNessuna valutazione finora
- Single Page Integral Table PDFDocumento2 pagineSingle Page Integral Table PDFMehmet Helva100% (2)
- Single Page Integral Table PDFDocumento2 pagineSingle Page Integral Table PDFMehmet Helva100% (2)
- CombinedBendingTensionTest PDFDocumento2 pagineCombinedBendingTensionTest PDFKurtisNessuna valutazione finora
- Angle Facts Powerpoint ExcellentDocumento10 pagineAngle Facts Powerpoint ExcellentNina100% (1)
- Cutting WatermelonDocumento5 pagineCutting WatermelonlizbethsingsNessuna valutazione finora
- ContinuityDocumento9 pagineContinuityarjunsaiNessuna valutazione finora
- Finland School Education MethodsDocumento3 pagineFinland School Education MethodsArvind RanganathanNessuna valutazione finora
- District 205 Personnel Agenda November 2023Documento4 pagineDistrict 205 Personnel Agenda November 2023WGIL RadioNessuna valutazione finora
- Trigonometric Functions - by TrockersDocumento122 pagineTrigonometric Functions - by TrockersGracious ChiweraNessuna valutazione finora
- Lesson 2-09 Areas Under A Standard Normal CurveDocumento12 pagineLesson 2-09 Areas Under A Standard Normal CurveJamiefel PungtilanNessuna valutazione finora
- 5 3 Yr9 Linear Equations TestDocumento7 pagine5 3 Yr9 Linear Equations Testapi-374589174100% (1)
- Probability and Statistics Advanced (Second Edition)Documento359 pagineProbability and Statistics Advanced (Second Edition)Juiced-IN it100% (1)
- 3.pair of Linear Equations Top 25 QuestionsDocumento3 pagine3.pair of Linear Equations Top 25 QuestionsNitin KhajuriaNessuna valutazione finora
- Smops 2018Documento13 pagineSmops 2018Marilyn Citadel0% (1)
- Polyhedral TessellationDocumento81 paginePolyhedral TessellationSiti Hajar RahimNessuna valutazione finora
- Emma Baugher Resume Portfolio Copy 2019Documento2 pagineEmma Baugher Resume Portfolio Copy 2019api-315323061Nessuna valutazione finora
- Airdomes Sport in EnglandDocumento3 pagineAirdomes Sport in EnglandRudi EnosNessuna valutazione finora
- EducationDocumento2 pagineEducationFlora BartalosovaNessuna valutazione finora
- Triangle Congruence Theorems Applications of ITT and CITTDocumento15 pagineTriangle Congruence Theorems Applications of ITT and CITTcj2zabalaNessuna valutazione finora
- Handbook DGEDocumento47 pagineHandbook DGEAadhu AdhavanNessuna valutazione finora
- Rebecca Cooper ResumeDocumento2 pagineRebecca Cooper Resumeapi-242983452Nessuna valutazione finora
- Barnett Who Goes and Why It MattersDocumento16 pagineBarnett Who Goes and Why It MattersEducation JusticeNessuna valutazione finora
- 08 Practice Tests Set 17 - Paper 2H-3H Mark SchemeDocumento15 pagine08 Practice Tests Set 17 - Paper 2H-3H Mark SchemeKenneth SorraNessuna valutazione finora
- Chapter 33Documento9 pagineChapter 33narasimhaNessuna valutazione finora
- FormulasDocumento6 pagineFormulasram poisonNessuna valutazione finora
- 6-Introduction To PolygonsDocumento4 pagine6-Introduction To PolygonsAymenNessuna valutazione finora
- P.5 MTC NotesDocumento137 pagineP.5 MTC NotesSamuel OloyaNessuna valutazione finora
- MODULE 7-The Straight LinesDocumento18 pagineMODULE 7-The Straight Linesidaman2905Nessuna valutazione finora
- June HigherDocumento28 pagineJune Highernaz2you100% (3)
- Laura Seay ResumeDocumento1 paginaLaura Seay Resumeapi-338265572Nessuna valutazione finora
- Maths CH-12 Special Product and ExpansionDocumento6 pagineMaths CH-12 Special Product and ExpansionfmzirkNessuna valutazione finora
- My ProfileDocumento2 pagineMy Profileapi-459074614Nessuna valutazione finora
- Annual Examation (March-2007) : General InstructionsDocumento3 pagineAnnual Examation (March-2007) : General InstructionsMidhun Bhuvanesh.B 7ANessuna valutazione finora