Documenti di Didattica
Documenti di Professioni
Documenti di Cultura
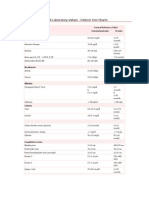
Laboratory and Diagnostic Worksheet For Clinical
Caricato da
Tee WoodTitolo originale
Copyright
Formati disponibili
Condividi questo documento
Condividi o incorpora il documento
Hai trovato utile questo documento?
Questo contenuto è inappropriato?
Segnala questo documentoCopyright:
Formati disponibili
Laboratory and Diagnostic Worksheet For Clinical
Caricato da
Tee WoodCopyright:
Formati disponibili
Laboratory and Diagnostic Worksheet
Test
Normal
Adult Range
Clients
Range
List all possible causes for abnormal values
White Blood Cell:
WBC- Primary effector cell against
Infection and tissue damage
Red Blood Cell:
RBC Primary function
Is to carry 02
Hemoglobin:
Hgb Iron containing pigment
Or RBC which carries 02 from lungs
Hematocrit:
Hct: Volume of RBCs in a given
Volume of blood
5,000-10,000
n/a
Infection, leukemic cancer, bone marrow failure
Male: 4.7-6.1
Female: 4.25.4
n/a
COPD, anemia, heart disease, hemorrhage
Male: 14-18
Female: 12-16
L 9.0
COPD, dehydration, heart disease
Male: 42%52%
Female: 37%47%
150,000400,000
L 29%
COPD, anemia, heart disease, hemorrhage
Prothrombin time:
(PT) time it takes for clotting to occur
After thromboplastin and calcium
Are added to the blood (extrinsic pathway)
Checks blood clotting: regularly checked on
people taking anticoagulants, such as
Coumadin
PTT (Partial throboplastin time)
Evaluates intrinsic pathway in
Coagulation. blood test that looks at how
long it takes for blood to clot. It can help
tell if you have a bleeding problem or if
your blood does not clot properly.
INR:
International normalized ratio
System of standardization of PT
>1.5-2.0 times
the control
40-130 U/L
H130
High- blood too thin
Low- blood too thick
1.5-2.5
n/a
Deficiency of blood clotting factors
0.8-1.2
1.2
BUN: Blood area, nitrogen
Nitrogen in blood in the form of urea
(a by- product of protein metabolism
Indirect measurement of kidney function
Creatinine:
End product of metabolism
Sensitive indicator of renal function
Used to diagnose impaired kidney function
Glucose:
Primary energy source
within most cells
Sodium:
10-20 mg/dL
H 55
Effectiveness of warfarin therapy. INR, patients
taking 2-3.5 The therapeutic range for INR is 2-3.5,
although specific ranges vary warfarin sodium based
on diagnosis
High- low blood volume, shock, kidney disease, drug
toxicity to the kidney
Low: liver failure, overhydration, nephrotic(kidney)
syndrome
Male: 0.6-1.2
mg/dL
Female: 0.51.1 mg/dL
0.8
High- kidney disease
Low- debilitation, decreased muscle mass
70-105
94
High: diabetes, stress response
Low: - too much insulin production, hypothyroidism,
insulin overdose
136-145
140
High- increased dietary intake, Cushing's syndrome
Platelet Count:
# of circulating platelets
Checks blood's ability to clot
Rheumatoid arthritis, cancer therapy, HighMalignant disorders, infection
Na: most abundant
cation in extracellular fluid
evaluates and monitors fluid and electrolyte
status
Potassium:
K: principal cation
meq/L
Low: decreased dietary intake, Addison's disease,
excessive oral water intake
3.5-5.0
4.7
High- excessive dietary intake, kidney disease or
failure, Addison's disease
Low: Deficient dietary intake, use of diuretics,
Cushing's Syndrome
Calcium- measures the level of calcium in
the blood.
8.5-10.8
8.6
Bone cancer, prolonged bed rest, kidney failure,
liver disease, hyperparathyroidism, tuberculosis,
Albumin- Albumin is a protein made by the
liver. A serum albumin test can help
determine if a patient has liver disease or
kidney disease, or if the body is not
absorbing enough protein.
CO2- The CO2 test is most often done as
part of an electrolyte or basic metabolic
panel. Changes in your CO2 level may
suggest that you are losing or retaining
fluid. This may cause an imbalance in your
body's electrolytes.
Phosp- Phosphate, or phosphorous, is
similar to calcium, as it is found in your
teeth and bones. Like calcium, you need
vitamin D in order to absorb phosphate
properly.
Chloride- one of the most important
electrolytes in the blood. It helps keep the
amount of fluid inside and outside of your
cells in balance. It also helps maintain
proper blood volume, blood pressure, and
pH of your body fluids
Anion Gap- This test looks at electrically
charged particles in your blood. This
helps your health care provider diagnose
acid-base problems
3.5-5.5 g/dL
2.3
Kidney or liver disease
23-29
32
Lower than normal may indicate: diarrhea, kidney
disease, aspirin overdose, Addison's disease
Higher than normal may indicate: breathing
disorders, vomiting, Cushing's disease
2.5-4.6
2.4
the most common cause of increased phosphate
levels (or hyperphosphatemia) is the kidney's
inability to get rid of phosphate.
Kidney failure, thyroid problems, muscle damage
96-106
105
Hyperchloremia is an electrolyte imbalance and is
indicated by a high level of chloride in
the blood. . Chloride is an important electrolyte and
works to ensure that your body's metabolism is
working correctly. Your kidneys control the levels
of chloride in your blood.
8-16
Your body makes too much acid
You lose too much bicarbonate. This can happen
if you have diarrhea
The body doesn't get rid of enough acid in your
urine because of problems with your kidneys.
BNP-test measures the amount of
100-300
pg/mL sugges
t heart failure
is present.
4136
BNP levels above 300 pg/mL indicate mild heart failure.
BNP levels above600 pg/mL indicate moderate heart
failure. BNP levels above 900 pg/mL indicate severe heart
failure.
in intracellular fluid
evaluates and monitors fluid and
electrolyte status: provides information
on heart function
the BNP hormone in your blood. BNP is
made by your heart and tells how well
your heart is
Test
Normal
Adult Range
Clients
Range
List all possible causes for abnormal values
BNP/100300
4136
Indicates heart failure
Risk Score16
18 or less
indicates
skin
breakdow
n
Other Laboratory Tests
Cardiac Labs
Sputum Cultures
Microbiology Cultures for C-diff, Staph,
MRSA
Other Diagnostic Tests
X-Ray
CT Scan
Pulmonary Function Tests
EKG
Endoscopy Procedures
Diagnostic Surgery
Skin Integrity
Potrebbero piacerti anche
- Lab Values Cheat SheetDocumento3 pagineLab Values Cheat Sheetmadison61404Nessuna valutazione finora
- Alert Medical Series: Emergency Medicine Alert IIIDa EverandAlert Medical Series: Emergency Medicine Alert IIINessuna valutazione finora
- ThrombocytopeniaDocumento1 paginaThrombocytopeniaanum786110Nessuna valutazione finora
- OncologyDocumento38 pagineOncologyNidhi PalNessuna valutazione finora
- Med SurgDocumento9 pagineMed SurgCharlie Gemarino LumasagNessuna valutazione finora
- Vital signs and medication reference tableDocumento1 paginaVital signs and medication reference tablejhenssineNessuna valutazione finora
- Waiters Pulmonary Embolism Form PDFDocumento1 paginaWaiters Pulmonary Embolism Form PDFmp17570% (1)
- Pharm Drugs ListDocumento14 paginePharm Drugs ListHumbe Oshun100% (1)
- SBARQ FormDocumento1 paginaSBARQ FormTracy100% (5)
- Charting Examples For Physical AssessmentDocumento16 pagineCharting Examples For Physical Assessmentim3in1Nessuna valutazione finora
- Patient AssessmentDocumento3 paginePatient AssessmentYemaya84100% (1)
- Philosophy of NursingDocumento8 paginePhilosophy of Nursingapi-430575435Nessuna valutazione finora
- vSim CLINICAL REPLACEMENT PACKETDocumento14 paginevSim CLINICAL REPLACEMENT PACKETBhargav DaveNessuna valutazione finora
- 1538 Exam 4 Cell Reg & GriefDocumento35 pagine1538 Exam 4 Cell Reg & GriefJade EdanoNessuna valutazione finora
- Head To Toe Physical Assessment: College of NursingDocumento4 pagineHead To Toe Physical Assessment: College of NursingMaicah ShaneNessuna valutazione finora
- Blood Pressure Regulation-2Documento40 pagineBlood Pressure Regulation-2Juliza FelicianoNessuna valutazione finora
- Preparation Worksheets For NUR 345 Heart Failure SimDocumento14 paginePreparation Worksheets For NUR 345 Heart Failure SimclarimerNessuna valutazione finora
- Medicine1 Grand PE ScriptDocumento10 pagineMedicine1 Grand PE ScriptCarmeline Santi BeronillaNessuna valutazione finora
- EndocrineDocumento23 pagineEndocrinensvickneswaranNessuna valutazione finora
- Downtime Daily Nursing Assessment & Care Plan: 1 of 5 Date: TimeDocumento5 pagineDowntime Daily Nursing Assessment & Care Plan: 1 of 5 Date: TimerupaliNessuna valutazione finora
- POC and Concepts Maps Week 12Documento23 paginePOC and Concepts Maps Week 12Michelle CollinsNessuna valutazione finora
- Grading edema levels and vital signs chartDocumento3 pagineGrading edema levels and vital signs chartKristina EitelNessuna valutazione finora
- Nursing Assessment Form: A. Demographic DataDocumento5 pagineNursing Assessment Form: A. Demographic Datacat_w0m4nNessuna valutazione finora
- StatementDocumento5 pagineStatementtrinity_brannonNessuna valutazione finora
- Chamberlain College of Nursing: Name: DateDocumento6 pagineChamberlain College of Nursing: Name: DategabrielNessuna valutazione finora
- Pneumonia Cheat Sheet: by ViaDocumento3 paginePneumonia Cheat Sheet: by ViaGayle MarieNessuna valutazione finora
- References: NCSBN's Review For The NCLEX-PN ExaminationDocumento5 pagineReferences: NCSBN's Review For The NCLEX-PN Examinationbapimirab6540% (1)
- Family Medicine M3 Clerkship: Hypertensive Disorders GuideDocumento35 pagineFamily Medicine M3 Clerkship: Hypertensive Disorders GuideJT ThomasNessuna valutazione finora
- E.N.T Assessment Format - 023053Documento2 pagineE.N.T Assessment Format - 023053Shubhrima KhanNessuna valutazione finora
- Mnemonics PDFDocumento15 pagineMnemonics PDFbeingfiredNessuna valutazione finora
- Patient Education for Ileal Conduit CareDocumento11 paginePatient Education for Ileal Conduit CareICa MarlinaNessuna valutazione finora
- Client's Chart: PathophysiologyDocumento1 paginaClient's Chart: PathophysiologyTrisha VergaraNessuna valutazione finora
- Medication List and InformationDocumento9 pagineMedication List and InformationHealthAndFitnessGuyNessuna valutazione finora
- Cardiovascular AssessmentDocumento21 pagineCardiovascular AssessmentRhitzle AnnNessuna valutazione finora
- Pharmacology Section on Antibiotics, Antivirals and AntifungalsDocumento5 paginePharmacology Section on Antibiotics, Antivirals and AntifungalsPathalee ThalpavilaNessuna valutazione finora
- Pre Hos TraumaDocumento11 paginePre Hos TraumaGel OmugtongNessuna valutazione finora
- Disorders of Acid Base BalanceDocumento1 paginaDisorders of Acid Base BalanceLyn Domingo EllaquezNessuna valutazione finora
- Anti-Infectives Course #25Documento18 pagineAnti-Infectives Course #25Gina Giammalvo100% (2)
- Medical Surgical Nursing PinoyDocumento85 pagineMedical Surgical Nursing PinoyrosebaseNessuna valutazione finora
- Hypertension Potassium: DO NOT Delegate What You Can EAT! E - Evaluate A - Assess T - TeachDocumento35 pagineHypertension Potassium: DO NOT Delegate What You Can EAT! E - Evaluate A - Assess T - TeachEsterly Puracan AmparoNessuna valutazione finora
- Interactive Quiz: Deal or No DealDocumento7 pagineInteractive Quiz: Deal or No DealShaira Jean GeminaNessuna valutazione finora
- Emergency Guidelines for Medical EmergenciesDocumento72 pagineEmergency Guidelines for Medical EmergenciesRumana Ali100% (2)
- Normal Laboratory Values - Patient Test Reference RangesDocumento10 pagineNormal Laboratory Values - Patient Test Reference RangesGita Elisa Berlina GintingNessuna valutazione finora
- Case 36 AscitesDocumento4 pagineCase 36 AscitesMichaelNessuna valutazione finora
- Pre-Op Medication Reference SheetDocumento3 paginePre-Op Medication Reference Sheetsabbo morsNessuna valutazione finora
- Potential Complications Signs and SymptomsDocumento2 paginePotential Complications Signs and SymptomsJessica GomezNessuna valutazione finora
- Ineffective Coping - Nursing Diagnosis & Care Plan - NurseslabsDocumento13 pagineIneffective Coping - Nursing Diagnosis & Care Plan - NurseslabsLester MooreNessuna valutazione finora
- Medical AbbreviationsDocumento8 pagineMedical AbbreviationsSofia LozanoNessuna valutazione finora
- Hopkins History Taking ArtDocumento5 pagineHopkins History Taking ArtAnastasia TjanNessuna valutazione finora
- Ir-026 Fluid and Electrolytes - 1Documento4 pagineIr-026 Fluid and Electrolytes - 1Muhammad ShakeelNessuna valutazione finora
- Family Names of DrugsDocumento1 paginaFamily Names of DrugsangelNessuna valutazione finora
- CVDocumento4 pagineCVapi-312365364Nessuna valutazione finora
- Directional Terms WSDocumento2 pagineDirectional Terms WSLisa PNessuna valutazione finora
- ACLS Primary Survey Guide for Respiratory ArrestDocumento34 pagineACLS Primary Survey Guide for Respiratory Arrest강기연100% (1)
- Stroke - RN YoutubeDocumento10 pagineStroke - RN YoutubeMarina Wasem NetzlaffNessuna valutazione finora
- Vancomycin Dosing and Monitoring in AdultsDocumento1 paginaVancomycin Dosing and Monitoring in AdultsjulialeoNessuna valutazione finora
- NURSING CARE OF ADULTS II: Passbooks Study GuideDa EverandNURSING CARE OF ADULTS II: Passbooks Study GuideNessuna valutazione finora
- 14 Fun Facts About Your Heart: Educational VersionDa Everand14 Fun Facts About Your Heart: Educational VersionNessuna valutazione finora
- SyllabusDocumento14 pagineSyllabusTee WoodNessuna valutazione finora
- Chapter 35Documento41 pagineChapter 35Tee WoodNessuna valutazione finora
- ATI CompDocumento9 pagineATI CompTee Wood100% (1)
- Musculoskeletal Disorders Part I FinalDocumento77 pagineMusculoskeletal Disorders Part I FinalTee WoodNessuna valutazione finora
- DocDocumento17 pagineDocTee WoodNessuna valutazione finora
- PN Pharmacology Online Practice 2014 BDocumento5 paginePN Pharmacology Online Practice 2014 BTee Wood67% (3)
- Chapter 27 & 28 Student VersionDocumento52 pagineChapter 27 & 28 Student VersionTee WoodNessuna valutazione finora
- ATI Mental Health ReviewDocumento30 pagineATI Mental Health ReviewTee Wood100% (10)
- Suanders ReviewDocumento10 pagineSuanders ReviewTee WoodNessuna valutazione finora
- Mental Health Analysis Movie Paper Woodward Tonya MDocumento8 pagineMental Health Analysis Movie Paper Woodward Tonya MTee WoodNessuna valutazione finora
- ATI Assignment # 6Documento9 pagineATI Assignment # 6Tee Wood0% (2)
- Postpartum Hemorrhage Scenario Assignment Woodward, Tonya 1Documento4 paginePostpartum Hemorrhage Scenario Assignment Woodward, Tonya 1Tee WoodNessuna valutazione finora
- TonicityDocumento3 pagineTonicityTee WoodNessuna valutazione finora
- DKA Simlab FinalDocumento3 pagineDKA Simlab FinalTee WoodNessuna valutazione finora
- Patho Phys Diabetic Keto AcidosisDocumento6 paginePatho Phys Diabetic Keto AcidosisTee WoodNessuna valutazione finora
- Nursing Care Plan For HematuriaDocumento2 pagineNursing Care Plan For HematuriaTee Wood63% (8)
- Abstract 1Documento7 pagineAbstract 1Tee WoodNessuna valutazione finora
- Reproduction and Embryonic DevelopmentDocumento56 pagineReproduction and Embryonic DevelopmentTee WoodNessuna valutazione finora
- Chapter 41-444 NursingDocumento14 pagineChapter 41-444 NursingTee WoodNessuna valutazione finora
- Chapter 56 CompleteDocumento10 pagineChapter 56 CompleteTee WoodNessuna valutazione finora
- Chapter 50 Principles of PharmacologyDocumento47 pagineChapter 50 Principles of PharmacologyTee WoodNessuna valutazione finora
- Nursing Dosage Calculation Practice Problems and SolutionsDocumento10 pagineNursing Dosage Calculation Practice Problems and SolutionssamaghnaimNessuna valutazione finora
- Inserting An Indwelling Urinary Catheter Check OffDocumento2 pagineInserting An Indwelling Urinary Catheter Check OffTee Wood100% (1)
- Miracles Study Guide For Chapter 34Documento3 pagineMiracles Study Guide For Chapter 34Tee WoodNessuna valutazione finora
- Nursing Basics Vital SignsDocumento22 pagineNursing Basics Vital SignsTee WoodNessuna valutazione finora
- Nursing MathDocumento74 pagineNursing MathJakeys1100% (1)
- HeparinDocumento2 pagineHeparinTee WoodNessuna valutazione finora
- Lovenox: Anticoagulant for DVT Prevention and TreatmentDocumento1 paginaLovenox: Anticoagulant for DVT Prevention and TreatmentTee WoodNessuna valutazione finora
- Eye Ear AssessDocumento37 pagineEye Ear AssessEfraem SamonteNessuna valutazione finora
- Paediatric Drug Calculations For Third Year Medical StudentsDocumento17 paginePaediatric Drug Calculations For Third Year Medical StudentsFret Ramirez Coronia RNNessuna valutazione finora
- Elias, Adikwu, Et Al. 2014Documento15 pagineElias, Adikwu, Et Al. 2014priya panaleNessuna valutazione finora
- End - Stage Renal Disease-PresentationDocumento28 pagineEnd - Stage Renal Disease-PresentationjamchanNessuna valutazione finora
- Multitask Learning and Benchmarking With Clinical Time Series DataDocumento18 pagineMultitask Learning and Benchmarking With Clinical Time Series DataJiancheng ZhangNessuna valutazione finora
- Presentation Prof Mtioui CSDocumento15 paginePresentation Prof Mtioui CSNaoufalMtiouiChkairiNessuna valutazione finora
- FINAL PPT of Grand Case Presentation About CKDDocumento66 pagineFINAL PPT of Grand Case Presentation About CKDmaria erika94% (16)
- ProteinuriaDocumento1 paginaProteinuriamutiara nurzaniNessuna valutazione finora
- Clinical Chemistry I: Tests, Disorders & Lab TechniquesDocumento34 pagineClinical Chemistry I: Tests, Disorders & Lab TechniquesCoțovanu IulianNessuna valutazione finora
- Acute: Renal Failure Management in The NeonateDocumento8 pagineAcute: Renal Failure Management in The NeonatejahangirealamNessuna valutazione finora
- Excretion and Osmoregulation-2Documento120 pagineExcretion and Osmoregulation-2S SNessuna valutazione finora
- OU SumberDocumento5 pagineOU SumberAnggaNessuna valutazione finora
- Thyroid Hormone Profile in Chronic Kidney DiseaseDocumento6 pagineThyroid Hormone Profile in Chronic Kidney DiseaserefaNessuna valutazione finora
- Horizon Academic Research Journal Vol. 2 No. 2Documento398 pagineHorizon Academic Research Journal Vol. 2 No. 2Horizon AcademicNessuna valutazione finora
- NP 3Documento21 pagineNP 3Adriano Odysseus Jon O.Nessuna valutazione finora
- Predisposing Factors: Precipitating Factors: - Stagnant, Clean - Dirty, Dark, Cold - ImmuneDocumento5 paginePredisposing Factors: Precipitating Factors: - Stagnant, Clean - Dirty, Dark, Cold - ImmuneJohn Kevin GianganNessuna valutazione finora
- MS Lec Review FinalsDocumento2 pagineMS Lec Review FinalsMaricar RosasNessuna valutazione finora
- Acute Pyelonephritis - Correlation of Clinical Parameter With Radiological Imaging AbnormalitiesDocumento7 pagineAcute Pyelonephritis - Correlation of Clinical Parameter With Radiological Imaging AbnormalitiesKhristine Caye FernandezNessuna valutazione finora
- Effect of Dialysis On Bleeding Time in Chronic Renal FailureDocumento5 pagineEffect of Dialysis On Bleeding Time in Chronic Renal FailureAhsan Tanio DaulayNessuna valutazione finora
- Chronic Renal FailureDocumento54 pagineChronic Renal FailureAkia Cayasan BayaNessuna valutazione finora
- High Yield Plab TopicsDocumento20 pagineHigh Yield Plab TopicsBeaulah HunidzariraNessuna valutazione finora
- Pedia Notes Compilation MKDoseDocumento18 paginePedia Notes Compilation MKDosemefav7778520Nessuna valutazione finora
- Aan Midad - Ginjal & Dentral Management FinalDocumento32 pagineAan Midad - Ginjal & Dentral Management FinalAan Mi'dadNessuna valutazione finora
- Drug Induced NephrotoxicityDocumento13 pagineDrug Induced NephrotoxicityAgnes BastonNessuna valutazione finora
- Krok English PathologyDocumento10 pagineKrok English PathologyJothivanan KettavanNessuna valutazione finora
- Nephrology PDFDocumento74 pagineNephrology PDFthejbond100% (1)
- Red Flags in Pedia NephrDocumento46 pagineRed Flags in Pedia NephrDoaa YoussefNessuna valutazione finora
- Medical CVDocumento100 pagineMedical CVhoyasaxonNessuna valutazione finora
- 216093371Documento48 pagine216093371khuzaima933% (15)
- Nutritional Support for Critically Ill PatientsDocumento122 pagineNutritional Support for Critically Ill Patientssams_popNessuna valutazione finora
- APSGNDocumento3 pagineAPSGNmadimadi11Nessuna valutazione finora
- Primer On Nephrology 2022Documento1.713 paginePrimer On Nephrology 2022Maievp53100% (1)