Documenti di Didattica
Documenti di Professioni
Documenti di Cultura
Lecture 3 - Vector Operations PDF
Caricato da
AyeeSerrano0 valutazioniIl 0% ha trovato utile questo documento (0 voti)
467 visualizzazioni26 pagineThe document discusses vector operations including the scalar product, vector product, and mixed triple product of vectors. It defines each operation, provides properties and examples. The scalar product (dot product) of two vectors results in a scalar and is used to determine the angle between vectors. The vector product (cross product) of two vectors results in a third vector perpendicular to the plane of the first two vectors. It is used to find projections of vectors. The mixed triple product of three vectors results in a scalar equal to the volume of the parallelepiped formed by the vectors.
Descrizione originale:
Titolo originale
Lecture 3 - Vector Operations.pdf
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Formati disponibili
PDF, TXT o leggi online da Scribd
Condividi questo documento
Condividi o incorpora il documento
Hai trovato utile questo documento?
Questo contenuto è inappropriato?
Segnala questo documentoThe document discusses vector operations including the scalar product, vector product, and mixed triple product of vectors. It defines each operation, provides properties and examples. The scalar product (dot product) of two vectors results in a scalar and is used to determine the angle between vectors. The vector product (cross product) of two vectors results in a third vector perpendicular to the plane of the first two vectors. It is used to find projections of vectors. The mixed triple product of three vectors results in a scalar equal to the volume of the parallelepiped formed by the vectors.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Formati disponibili
Scarica in formato PDF, TXT o leggi online su Scribd
0 valutazioniIl 0% ha trovato utile questo documento (0 voti)
467 visualizzazioni26 pagineLecture 3 - Vector Operations PDF
Caricato da
AyeeSerranoThe document discusses vector operations including the scalar product, vector product, and mixed triple product of vectors. It defines each operation, provides properties and examples. The scalar product (dot product) of two vectors results in a scalar and is used to determine the angle between vectors. The vector product (cross product) of two vectors results in a third vector perpendicular to the plane of the first two vectors. It is used to find projections of vectors. The mixed triple product of three vectors results in a scalar equal to the volume of the parallelepiped formed by the vectors.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Formati disponibili
Scarica in formato PDF, TXT o leggi online su Scribd
Sei sulla pagina 1di 26
VECTOR OPERATIONS
ES 11 Statics of Rigid Bodies
Lecture 3
SCALAR PRODUCT OF TWO VECTORS
(DOT PRODUCT)
The scalar product of two vectors P and Q is defined as the
product of the magnitudes of P and Q and of the cosine of
the angle formed by P and Q.
The result of the above expression is a scalar (scalar
product).
SCALAR PRODUCT OF TWO VECTORS
(DOT PRODUCT)
PROPERTIES OF THE SCALAR PRODUCT:
APPLICATIONS OF SCALAR PRODUCT
ANGLE FORMED BY 2 GIVEN VECTORS
To obtain an equation for the angle in terms of the
components of the vectors,
APPLICATIONS OF SCALAR PRODUCT
ANGLE FORMED BY 2 GIVEN VECTORS
EXAMPLE:
Given vector A with magnitude of 15 and line of action that
passes through points (2, 3, 5) and (1, 0, -4), and vector B
<-9, 1, 2>. Determine the angle between vectors A and B.
APPLICATIONS OF SCALAR PRODUCT
ANGLE FORMED BY 2 GIVEN VECTORS
APPLICATIONS OF SCALAR PRODUCT
PROJECTION OF A VECTOR ON A GIVEN AXIS
Consider a vector Q directed along OL and of the same
sense as OL. The projection of vector P along axis OL is
given by
APPLICATIONS OF SCALAR PRODUCT
PROJECTION OF A VECTOR ON A GIVEN AXIS
EXAMPLE
P=ij+k
Q = i 2j 3k
R = -2i + sj k
1. What is the value of s if R is perpendicular to P?
2. Find the component of Q parallel to P.
APPLICATIONS OF SCALAR PRODUCT
PROJECTION OF A VECTOR ON A GIVEN AXIS
VECTOR PRODUCT OF TWO VECTORS
(CROSS PRODUCT)
The vector product of two vectors P and Q is defined as the
vector V which satisfies the following conditions:
1. The line of action of V is perpendicular to the plane
containing P and Q.
VECTOR PRODUCT OF TWO VECTORS
(CROSS PRODUCT)
2. The magnitude of V is the product of the magnitude of P
and Q and of the sine of the angle formed by P and Q
(the measure of which will always be 1800 or less).
V = PQ sin
VECTOR PRODUCT OF TWO VECTORS
(CROSS PRODUCT)
3. Direction of V is obtained from the right-hand rule.
Close your right hand and hold it so that your fingers are
curled in the same sense as the rotation through which
brings the vector P in line with the vector Q; your thumb will
then indicate the direction of the vector V.
VECTOR PRODUCT OF TWO VECTORS
(CROSS PRODUCT)
PROPERTIES OF THE VECTOR PRODUCT:
VECTOR PRODUCT IN TERMS OF
COMPONENTS
To obtain an equation for the cross product of two vectors
in terms of their components, we must determine the
cross products formed from the unit vectors i, j, and k. For
example:
Where e is a unit vector perpendicular
to i and j. Either e = k or e = -k.
To determine which of the two is
the vector product, use the righthand rule.
VECTOR PRODUCT IN TERMS OF
COMPONENTS
These results can be remembered
easily by arranging the unit vectors in a
circle.
Cross product is third vector. + if
same direction of arrows, otherwise -
VECTOR PRODUCT IN TERMS OF
COMPONENTS
The cross product of two vectors P and Q expressed in
terms of their component is
VECTOR PRODUCT IN TERMS OF
COMPONENTS
The result can be compactly written as the determinant:
VECTOR PRODUCT IN TERMS OF
COMPONENTS
A 3x3 determinant can be evaluated by repeating its first
two columns and evaluating the products of the terms
along the six diagonal lines.
VECTOR PRODUCT IN TERMS OF
COMPONENTS
EXAMPLE:
Determine the cross product of the vectors U = (-2i + j) and
V = (3i -4k).
VECTOR PRODUCT IN TERMS OF
COMPONENTS
EXAMPLE:
Line L passes through
point A and is
perpendicular to the
plane formed by
points A, B, and C.
Find the projection of
force F = 200 N,
which passes through
points D and E, on
line L.
VECTOR PRODUCT IN TERMS OF
COMPONENTS
Mixed Triple Product of 3
Vectors
The mixed triple product of the three vectors P, Q, and
R is given by
In terms of components of the vectors
Mixed Triple Product of 3
Vectors
In determinant form,
Note: Interchanging any two of the vectors in the mixed
triple product changes the sign but not the absolute
value of the result.
Mixed Triple Product of 3
Vectors
The mixed triple product is the volume of the
parallelepiped bounded by the three vectors.
Note:
Mixed Triple Product of 3
Vectors
EXAMPLE:
Knowing that the volume
of the parallelepiped
shown is 21 cubic units,
and that the origin is a
vertex of the solid, find
the value of a.
Mixed Triple Product of 3
Vectors
Potrebbero piacerti anche
- Bab 3 Vectors r2 r3 PDFDocumento41 pagineBab 3 Vectors r2 r3 PDFLailatul MaghfirohNessuna valutazione finora
- The Dot and Cross ProductDocumento9 pagineThe Dot and Cross ProductVikash SharmaNessuna valutazione finora
- The Breaking of Bread 1 Corinthians 11.23-29 PDFDocumento5 pagineThe Breaking of Bread 1 Corinthians 11.23-29 PDFMicahhackettNessuna valutazione finora
- Heart of DavidDocumento9 pagineHeart of DavidTawanda MhuriNessuna valutazione finora
- Vectors and TensorsDocumento12 pagineVectors and TensorsAndrei CioroianuNessuna valutazione finora
- Lesson+5 +bibleDocumento62 pagineLesson+5 +bibleMegan Parcasio (rosie)Nessuna valutazione finora
- Convergence Rates On Root Finding: Com S 477/577 Oct 5, 2004Documento5 pagineConvergence Rates On Root Finding: Com S 477/577 Oct 5, 2004Mich LadycanNessuna valutazione finora
- ElectrostaticsDocumento39 pagineElectrostaticsFatehNessuna valutazione finora
- The Uniqueness of Jesus Christ Among The Various ReligionsDocumento8 pagineThe Uniqueness of Jesus Christ Among The Various ReligionsAjay JosephNessuna valutazione finora
- EC Signals and SystemsDocumento48 pagineEC Signals and SystemsJeeva KeshavNessuna valutazione finora
- Chapter5pp043 051 PDFDocumento9 pagineChapter5pp043 051 PDFInderMaheshNessuna valutazione finora
- Numerical AnalysisDocumento63 pagineNumerical AnalysisMohammad AhmedNessuna valutazione finora
- Questions On Time-Domain Analysis of CT SystemsDocumento20 pagineQuestions On Time-Domain Analysis of CT Systemskibrom atsbhaNessuna valutazione finora
- Book of PrayerDocumento50 pagineBook of PrayermsmthameezNessuna valutazione finora
- Introduction To VectorsDocumento8 pagineIntroduction To VectorsCynthia PlazaNessuna valutazione finora
- ThessaloniansDocumento89 pagineThessalonianslaleye_olumideNessuna valutazione finora
- Numerical Analysis Solution HomeworkDocumento2 pagineNumerical Analysis Solution HomeworkJadTahhanNessuna valutazione finora
- HSC 11 Scalars and Vectors Ch2Documento5 pagineHSC 11 Scalars and Vectors Ch2Snehal PanchalNessuna valutazione finora
- First Term Ss2 Further Mathematics 1Documento3 pagineFirst Term Ss2 Further Mathematics 1stefala2005Nessuna valutazione finora
- Quest Electrostatics 4 KeyDocumento5 pagineQuest Electrostatics 4 KeyCarlos OrtizNessuna valutazione finora
- Survey of Calculus and Its Applications IIDocumento3 pagineSurvey of Calculus and Its Applications IITaiwo OgunmolaNessuna valutazione finora
- POE Formula Sheet Rev 3 - 24 - 12 PDFDocumento6 paginePOE Formula Sheet Rev 3 - 24 - 12 PDFstuart ashrafNessuna valutazione finora
- Simple Harmonic Motion and ElasticityDocumento15 pagineSimple Harmonic Motion and ElasticitySubho BhattacharyaNessuna valutazione finora
- Physics For Scientists and EngineersDocumento46 paginePhysics For Scientists and EngineersloloAG100% (1)
- MATH 320 Numerical Analysis NotesDocumento70 pagineMATH 320 Numerical Analysis NotesWinnie Mutuku100% (1)
- Ratios, Proportions, and Percents AnswersDocumento4 pagineRatios, Proportions, and Percents AnswersharshiniNessuna valutazione finora
- Equilibrium Statics ProblemsDocumento10 pagineEquilibrium Statics ProblemsTheAznNessuna valutazione finora
- ECE 3500 Signals and Systems Quiz Solutions Quiz 1Documento2 pagineECE 3500 Signals and Systems Quiz Solutions Quiz 1skybosgNessuna valutazione finora
- Biomechanics-Inter-segmental Forces and Joint Stability, NotesDocumento60 pagineBiomechanics-Inter-segmental Forces and Joint Stability, NotesmanishpaliNessuna valutazione finora
- Unit 1: MechanicsDocumento51 pagineUnit 1: MechanicsMaria BhaijiNessuna valutazione finora
- Roject Management: by Naveen KumarDocumento22 pagineRoject Management: by Naveen Kumarbharathselvam.1Nessuna valutazione finora
- SPH3U: Delivery! Position - Time Graphs: QuestionsDocumento12 pagineSPH3U: Delivery! Position - Time Graphs: Questionsمنیر ساداتNessuna valutazione finora
- F. Rotation, Reflection, Translation and EnlargementDocumento33 pagineF. Rotation, Reflection, Translation and Enlargementthi tar lwinNessuna valutazione finora
- Tertullian's Letter On PatienceDocumento14 pagineTertullian's Letter On PatienceSelvaArockiamNessuna valutazione finora
- AutomataDocumento106 pagineAutomataJay Kant Yadav100% (1)
- Dot Product: Algebraic DefinitionDocumento6 pagineDot Product: Algebraic DefinitionNurul AbrarNessuna valutazione finora
- Sta 121Documento10 pagineSta 121Abraham BanjoNessuna valutazione finora
- Trigonometry QuestionsDocumento2 pagineTrigonometry Questionsitope84Nessuna valutazione finora
- Alevel Math 2 Mock 2023Documento5 pagineAlevel Math 2 Mock 2023Namiiro ShamimNessuna valutazione finora
- Engineering Dynamics Lecture 3Documento30 pagineEngineering Dynamics Lecture 3Anokha LadlaNessuna valutazione finora
- Physics Exam CheatsheetDocumento2 paginePhysics Exam CheatsheetCindy NguyenNessuna valutazione finora
- Equilibrium of Particle Systems (2D) : 440:221 Intro To Engineering Mechanics: StaticsDocumento20 pagineEquilibrium of Particle Systems (2D) : 440:221 Intro To Engineering Mechanics: StaticsVatsal PandyaNessuna valutazione finora
- Homework #15 (Phy 112) SolutionsDocumento23 pagineHomework #15 (Phy 112) SolutionsKvn4N6100% (1)
- Fundamentals of MeasurementDocumento27 pagineFundamentals of MeasurementBakaali HuzaifaNessuna valutazione finora
- Intersection of Line and PlaneDocumento2 pagineIntersection of Line and PlaneAljon AbriamNessuna valutazione finora
- Maxwell, The 21 Irrefutable Laws of Leadership (1998) Chapter 2Documento5 pagineMaxwell, The 21 Irrefutable Laws of Leadership (1998) Chapter 2Jon Brewer100% (1)
- 13.5 Curl and DivergenceDocumento11 pagine13.5 Curl and DivergenceDaniel Gaytan-JenkinsNessuna valutazione finora
- 02 Components of A VectorDocumento29 pagine02 Components of A VectorMiNessuna valutazione finora
- Assignment 3 SolutionDocumento9 pagineAssignment 3 SolutionMurat BayrakNessuna valutazione finora
- Ch34 ISM 070623Documento56 pagineCh34 ISM 070623Ian GravesNessuna valutazione finora
- Bitsat Paper 03Documento21 pagineBitsat Paper 03Arnab SenNessuna valutazione finora
- Incorrect Proofs and Mathematical InductionDocumento34 pagineIncorrect Proofs and Mathematical InductionDKNessuna valutazione finora
- Wk5 - Solution of Algebraic and Transcendental EquationsDocumento14 pagineWk5 - Solution of Algebraic and Transcendental EquationsFazelah YakubNessuna valutazione finora
- Chapter5 VectorsDocumento23 pagineChapter5 VectorsFaiz RusliNessuna valutazione finora
- Motion 2d AakashDocumento10 pagineMotion 2d AakashNavin RaiNessuna valutazione finora
- VectorsDocumento48 pagineVectorsUltra Gamer (sishant)Nessuna valutazione finora
- And Electric Field: Equal ToDocumento5 pagineAnd Electric Field: Equal ToAli HassenNessuna valutazione finora
- 1 - Mohsin EM Lecture 3,4Documento69 pagine1 - Mohsin EM Lecture 3,4UsamaNessuna valutazione finora
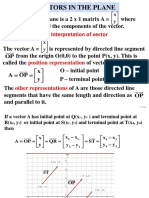
- 1.1 Vectors in The Plane (2-D)Documento24 pagine1.1 Vectors in The Plane (2-D)M Venter KheeNessuna valutazione finora
- Introduction to Vectorial and Matricial CalculusDa EverandIntroduction to Vectorial and Matricial CalculusNessuna valutazione finora
- BD Bessel Functions PDFDocumento10 pagineBD Bessel Functions PDFAndang Dwi PrasetyoNessuna valutazione finora
- Lesson Plan DisciminantDocumento4 pagineLesson Plan DisciminantGrethel Ann Chico100% (7)
- Engineering Maths I - SyllabusDocumento3 pagineEngineering Maths I - SyllabusTawanda MakombeNessuna valutazione finora
- 57F0DDocumento10 pagine57F0DHassaan AhmedNessuna valutazione finora
- Transmission LinDocumento41 pagineTransmission Linrupa kumar dhanavathNessuna valutazione finora
- Aq Ah: On A Theorem of Liouville Concerning Integrable Problems of DynamicsDocumento5 pagineAq Ah: On A Theorem of Liouville Concerning Integrable Problems of DynamicsForgeLionNessuna valutazione finora
- Mangoosh Guide For Math Formula PDFDocumento20 pagineMangoosh Guide For Math Formula PDFNarayana KumarNessuna valutazione finora
- Deriving Using Product and Quotient Rules: Michael Turner Alex BarboloviciDocumento31 pagineDeriving Using Product and Quotient Rules: Michael Turner Alex BarboloviciAlex BarboloviciNessuna valutazione finora
- Multivariable Calculus With Applications - LaxDocumento488 pagineMultivariable Calculus With Applications - Laxedison94% (18)
- AL E B A: Teaching School Mathematics: Pre-AlgebraDocumento407 pagineAL E B A: Teaching School Mathematics: Pre-AlgebraBob CrossNessuna valutazione finora
- Equations Transformable Into Quadratic Equations: Module in Mathematics 9Documento24 pagineEquations Transformable Into Quadratic Equations: Module in Mathematics 9Dee En Martinez100% (1)
- Year 6 Algebra AssignmentDocumento3 pagineYear 6 Algebra AssignmentJoel OkohNessuna valutazione finora
- M 111 RevDocumento13 pagineM 111 RevDexter BordajeNessuna valutazione finora
- Solving Equations: Direct and Inverse ProcessesDocumento17 pagineSolving Equations: Direct and Inverse ProcessesshivamSRINessuna valutazione finora
- CaseletsDocumento11 pagineCaseletsapi-26456455Nessuna valutazione finora
- Dorf App GDF GeDocumento10 pagineDorf App GDF GerafaelkiNessuna valutazione finora
- PMC Number TheoryDocumento19 paginePMC Number TheoryNaseeb AliiNessuna valutazione finora
- Advanced Functions and Introductory Calculus v2Documento480 pagineAdvanced Functions and Introductory Calculus v2Karen Feng100% (3)
- Algebra Task 2Documento3 pagineAlgebra Task 2Xaviour MugariNessuna valutazione finora
- SbammDocumento6 pagineSbammDeepak Rajaram100% (1)
- QuestionsDocumento3 pagineQuestionssukanya dasguptaNessuna valutazione finora
- Cycloides Field-Serge LangDocumento264 pagineCycloides Field-Serge Langcharlyshaka1100% (2)
- 04 CSMATH2 - Vectors in The PlaneDocumento33 pagine04 CSMATH2 - Vectors in The PlaneFrancis ObinaNessuna valutazione finora
- Project in Calculus IiDocumento14 pagineProject in Calculus IiBunny DummyNessuna valutazione finora
- Word Problem Involving FactoringDocumento5 pagineWord Problem Involving Factoringmcheche12Nessuna valutazione finora
- Geometric Algebra ThesisDocumento6 pagineGeometric Algebra ThesisJill Brown100% (2)
- Commutative Algebra - BourbakiDocumento324 pagineCommutative Algebra - Bourbakishd_strkh100% (4)
- Important Notes of 10th Class Math Exercise 2.4Documento2 pagineImportant Notes of 10th Class Math Exercise 2.4Tayyabah ShahNessuna valutazione finora
- Advanced Mathematic S.6 Learner's Book2 PDFDocumento518 pagineAdvanced Mathematic S.6 Learner's Book2 PDFFelicia Yva Nyirahabimana94% (16)
- Literal EquationsDocumento4 pagineLiteral Equationsapi-348347219Nessuna valutazione finora