Documenti di Didattica
Documenti di Professioni
Documenti di Cultura
The Difference Between NMOS
Caricato da
Rey TiburonCopyright
Formati disponibili
Condividi questo documento
Condividi o incorpora il documento
Hai trovato utile questo documento?
Questo contenuto è inappropriato?
Segnala questo documentoCopyright:
Formati disponibili
The Difference Between NMOS
Caricato da
Rey TiburonCopyright:
Formati disponibili
The Difference Between NMOS, PMOS and CMOS transistors
NMOS:
NMOS is built with n-type source and drain and a p-type substrate,
In a NMOS, carriers are electrons
When a high voltage is applied to the gate, NMOS will conduct
When a low voltage is applied in the gate, NMOS will not conduct
NMOS are considered to be faster than PMOS, since the carriers in NMOS, which
are electrons, travel twice as fast as holes.
NMOS ICs would be smaller than PMOS ICs
NMOS can provide one-half of the impedance provided by a PMOS
NMOS represents N type MOS transistor.
PMOS:
PMOS is built with p-type source and drain and a n-type substrate.
PMOS, carriers are holes.
When a high voltage is applied to the gate, PMOS will not conduct
When a low voltage is applied in the gate, PMOS will conduct
Which are the carriers in PMOS.
PMOS devices are more immune to noise than NMOS devices.
PMOS represents P type MOS transistor.
CMOS:
CMOS means Complementary Metal-Oxide-Semiconductor Transistor. CMOS
circuit contains PMOS transistor and NMOS transistor.
CMOS is more of a process technology term.
Written 15 Feb View Upvotes
Related QuestionsMore Answers Below
What exactly Trigate Transistor Technology is and how is it differ with
ordinary transistor?
What is the difference between a process and a transistor model?
What is the fabrication process of NMOS transistor?
What does it mean to complete a CMOS circuit with transistor
complements?
What is the difference between CMOS and MOS circuits?
Amitabh Songara (Electroker), I am an Electronics and Communication Engineer.
22.3k Views Amitabh has 30+ answers in Engineering
NMOS - N-type metal-oxide-semiconductor logic uses n-type field effect
transistors (MOSFETs) to implement logic gates and other digital circuits. These
nMOS transistors operate by creating an inversion layer in a p-type transistor body.
This inversion layer, called the n-channel, can conduct electrons between n-type
"source" and "drain" terminals. The n-channel is created by applying voltage to the
third terminal, called the gate. Like other MOSFETs, nMOS transistors have four
modes of operation: cut-off (or sub-threshold), triode, saturation (sometimes called
active), and velocity saturation.
NMOS logic
PMOS - P-type metal-oxide-semiconductor logic uses p-channel metal-oxidesemiconductor field effect transistors (MOSFETs) to implement logic gates and
other digital circuits. PMOS transistors operate by creating an inversion layer in an
n-type transistor body. This inversion layer, called the p-channel, can conduct holes
between p-type "source" and "drain" terminals.
The p-channel is created by applying voltage to the third terminal, called the gate.
Like other MOSFETs, PMOS transistors have four modes of operation: cut-off (or
subthreshold), triode, saturation (sometimes called active), and velocity saturation.
PMOS logic
CMOS - Complementary metaloxidesemiconductor (CMOS) is a technology for
constructing integrated circuits. CMOS technology is used in microprocessors,
microcontrollers, static RAM, and other digital logic circuits. CMOS technology is
also used for several analog circuits such as image sensors (CMOS sensor), data
converters, and highly integrated transceivers for many types of communication. In
1963, while working for Fairchild Semiconductor, Frank Wanlass patented CMOS
CMOS
H2H (Happy 2 Help)
Written 4 Feb View Upvotes
Pravin Parmar
24.2k Views
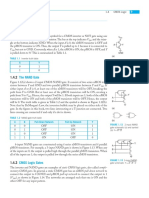
NMOS:Four terminals: gate, source, drain, body
Gate oxide body stack looks like a capacitor
Gate and body are conductors
SiO2 (oxide) is a very good insulator
Called metal oxide semiconductor (MOS) capacitor
Body is usually tied to ground (0 V)
When the gate is at a low voltage:
P-type body is at low voltage
Source-body and drain-body diodes are OFF
No current flows, transistor is OFF
When the gate is at a high voltage:
Positive charge on gate of MOS capacitor
Negative charge attracted to body
Inverts a channel under gate to n-type
Now current can flow through n-type silicon from source through
channel to drain, transistor is ON
PMOS:Similar, but doping and voltages reversed
Body tied to high voltage (VDD)
Gate low: transistor ON
Gate high: transistor OFF
Bubble indicates inverted behavior
CMOS:Typically use p-type substrate for nMOS transistors
Requires n-well for body of pMOS transistors
Potrebbero piacerti anche
- v2 Led LCD Screen Panel Repair MIRKODocumento213 paginev2 Led LCD Screen Panel Repair MIRKOErRobert Ch96% (25)
- Beck ZapperDocumento6 pagineBeck ZapperAR RmsNessuna valutazione finora
- Electronic Circuit Laboratory MANUAL PDFDocumento94 pagineElectronic Circuit Laboratory MANUAL PDFAbel KalavadakkenNessuna valutazione finora
- Artificial Intelligence VOLUME II (AI Course Book 2)Documento352 pagineArtificial Intelligence VOLUME II (AI Course Book 2)Rey TiburonNessuna valutazione finora
- Dynamic Logic Circuits: Kang and Leblebicic, Chapter 9Documento34 pagineDynamic Logic Circuits: Kang and Leblebicic, Chapter 9Lovey SalujaNessuna valutazione finora
- IIR FilterDocumento26 pagineIIR FilterKyax Ginaheeq100% (1)
- Matlab Code For MtechDocumento47 pagineMatlab Code For MtechSangha MithraNessuna valutazione finora
- Unit 2 - CMOS Logic, Fabrication and LayoutDocumento34 pagineUnit 2 - CMOS Logic, Fabrication and LayoutphillipNessuna valutazione finora
- Dcom-Pam - PPM - PWM Scientech 2110Documento43 pagineDcom-Pam - PPM - PWM Scientech 2110Shivangi Pandey100% (1)
- Applications of 8051 MicrocontrollersDocumento23 pagineApplications of 8051 MicrocontrollersUsama Spiffy100% (1)
- Uniform Plane Waves SolutionsDocumento52 pagineUniform Plane Waves SolutionsmboillaNessuna valutazione finora
- Network Analysis and Synthesis PDFDocumento2 pagineNetwork Analysis and Synthesis PDFLakum Hitesh100% (3)
- Proyectos Divertidos para Estudiantes de ElectronicaDocumento191 pagineProyectos Divertidos para Estudiantes de Electronica2006electro3392Nessuna valutazione finora
- Static Cmos DesignDocumento7 pagineStatic Cmos Designtechspaceofatul100% (3)
- PhotodiodesDocumento20 paginePhotodiodesRavindra Kumar100% (1)
- Planos Router CNC-1Documento112 paginePlanos Router CNC-1Rey TiburonNessuna valutazione finora
- Ee8451 Lic NotesDocumento224 pagineEe8451 Lic NotesUma100% (1)
- CMOS VLSI DESIGN NOTES Made by Barun Dhiman From Various Books Like Kamran Neil E WasteDocumento226 pagineCMOS VLSI DESIGN NOTES Made by Barun Dhiman From Various Books Like Kamran Neil E WasteBarun DhimanNessuna valutazione finora
- Expt 6 - Colpitts Oscillator (2020)Documento4 pagineExpt 6 - Colpitts Oscillator (2020)samarthNessuna valutazione finora
- EDC Lecture NotesDocumento187 pagineEDC Lecture NotesKARTHIKAMANI RNessuna valutazione finora
- Dynamic CMOS DesignDocumento30 pagineDynamic CMOS DesignAllwyn Anand SNessuna valutazione finora
- Chapter 5-Metal Semiconductor FET (MESFET)Documento26 pagineChapter 5-Metal Semiconductor FET (MESFET)mdhuNessuna valutazione finora
- Eca Lab-Min PDFDocumento87 pagineEca Lab-Min PDFAkashita SharmaNessuna valutazione finora
- VLSI Design Subsystem Design and Architectural IssuesDocumento26 pagineVLSI Design Subsystem Design and Architectural IssuesSanjana M PNessuna valutazione finora
- A Research Proposal On Mimo Wireless System Technology1Documento22 pagineA Research Proposal On Mimo Wireless System Technology1Deepraj BhujelNessuna valutazione finora
- Solid State Device Modeling 1Documento199 pagineSolid State Device Modeling 1DarwinNessuna valutazione finora
- OFDM Complete Block DiagramDocumento2 pagineOFDM Complete Block Diagramgaurav22decNessuna valutazione finora
- Module 6 Temperature SensorsDocumento20 pagineModule 6 Temperature SensorsJyothi SamanthulaNessuna valutazione finora
- MEMS Micro-electromechanical Systems OverviewDocumento10 pagineMEMS Micro-electromechanical Systems Overviewabhi shekNessuna valutazione finora
- Class 1-20Documento149 pagineClass 1-20SaurabhBisht100% (1)
- DC Characteristics of A MOS TransistorDocumento17 pagineDC Characteristics of A MOS TransistorAbdo SalamonNessuna valutazione finora
- Delay Optimization TechniquesDocumento38 pagineDelay Optimization TechniquesiknowiamanidiotNessuna valutazione finora
- Optical Communication Viva QuestionDocumento2 pagineOptical Communication Viva Questiondivya1717Nessuna valutazione finora
- EC8004 - Wireless Networks Exam GuideDocumento2 pagineEC8004 - Wireless Networks Exam GuideBoopathi Sambandha MoorthiNessuna valutazione finora
- Dataflow Modeling in Verilog Lab ExplainedDocumento22 pagineDataflow Modeling in Verilog Lab ExplainedWaqas Ahmed0% (1)
- Gunn DiodeDocumento80 pagineGunn DiodeBindu Narayanan Nampoothiri100% (2)
- Cmos Fabrication: N - Well ProcessDocumento42 pagineCmos Fabrication: N - Well ProcessArun GopinathNessuna valutazione finora
- Digital Communication Lab Manual ExperimentsDocumento50 pagineDigital Communication Lab Manual ExperimentsAniket BhowmikNessuna valutazione finora
- Unit-1 PPT-Concepts in VHDLDocumento58 pagineUnit-1 PPT-Concepts in VHDLSUMASRI MNessuna valutazione finora
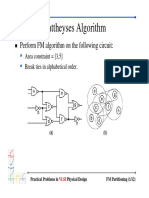
- Fiduccia-Mattheyses Algorithm: Perform FM Algorithm On The Following CircuitDocumento12 pagineFiduccia-Mattheyses Algorithm: Perform FM Algorithm On The Following CircuitiiitsainiNessuna valutazione finora
- Digital To Analog Converter Using R 2R Ladder Network and 741 Op AmpDocumento3 pagineDigital To Analog Converter Using R 2R Ladder Network and 741 Op AmpPuneeth Siddappa100% (1)
- A-Law and U-Law CompandingDocumento4 pagineA-Law and U-Law CompandingAchyut Dev50% (2)
- Analog Electronic Circuits Lab ManualDocumento86 pagineAnalog Electronic Circuits Lab ManualsanjuNessuna valutazione finora
- MOSFET CapacitancesDocumento26 pagineMOSFET CapacitancesModyKing99Nessuna valutazione finora
- Special Purpose DevicesDocumento57 pagineSpecial Purpose DevicesBHARGAVA REDDYNessuna valutazione finora
- Ece III Network Analysis (10es34) NotesDocumento94 pagineEce III Network Analysis (10es34) NotesNandu NaikNessuna valutazione finora
- Arduino Base Over Voltage and Under Voltage Protection Circuit LITERATURE REVIEWDocumento23 pagineArduino Base Over Voltage and Under Voltage Protection Circuit LITERATURE REVIEWOlasupo IyaboNessuna valutazione finora
- UNIT 4 PN Junction Diode Complete Notes BEEDocumento12 pagineUNIT 4 PN Junction Diode Complete Notes BEESomesh Singh RathoreNessuna valutazione finora
- Communication EngineeringDocumento2 pagineCommunication EngineeringalokanitaNessuna valutazione finora
- Linear Circuit Analysis Lab ManualsDocumento97 pagineLinear Circuit Analysis Lab ManualsAbdul Saboor KhanNessuna valutazione finora
- Communication SystemDocumento13 pagineCommunication SystemSyieda ZamryNessuna valutazione finora
- Layout & Lambda Design RuleDocumento1 paginaLayout & Lambda Design RuleNihar PandaNessuna valutazione finora
- Adder Cum SubtractorDocumento4 pagineAdder Cum SubtractorCHERISMA100% (2)
- Delay Time Estimation in Digital DesignDocumento12 pagineDelay Time Estimation in Digital DesignSandeep PaulNessuna valutazione finora
- MosfetDocumento15 pagineMosfetAnkita BanerjeeNessuna valutazione finora
- Chapter 2 Wave GuidesDocumento150 pagineChapter 2 Wave GuidesMohdIhsanNessuna valutazione finora
- Antennas and Microwave Engineering LaboratoryDocumento190 pagineAntennas and Microwave Engineering LaboratorySRNessuna valutazione finora
- Experiment No. 1: Aim: Study of Tanner Tools THEORY: Tanner ToolsDocumento24 pagineExperiment No. 1: Aim: Study of Tanner Tools THEORY: Tanner ToolsVarun GargNessuna valutazione finora
- CMOS Processing TechnologyDocumento35 pagineCMOS Processing Technologysneha rNessuna valutazione finora
- K-Map Method for Logic MinimizationDocumento57 pagineK-Map Method for Logic MinimizationHugh100% (1)
- Technical Details: Complementary Metal-Oxide-Semiconductor (CMOS) (PronouncedDocumento7 pagineTechnical Details: Complementary Metal-Oxide-Semiconductor (CMOS) (PronouncedAbderrezzaq ZianeNessuna valutazione finora
- CMOSDocumento6 pagineCMOSالمؤسس عثمان بن ارطغرلNessuna valutazione finora
- Technical Details: Complementary Metal-Oxide-Semiconductor (CMOS) (Documento9 pagineTechnical Details: Complementary Metal-Oxide-Semiconductor (CMOS) (RailyNessuna valutazione finora
- CMOS (Disambiguation) : For Other Uses, SeeDocumento6 pagineCMOS (Disambiguation) : For Other Uses, SeeManas NagNessuna valutazione finora
- Complementary Metal-Oxide-Semiconductor (CMOS) (PronouncedDocumento7 pagineComplementary Metal-Oxide-Semiconductor (CMOS) (PronouncedArchana SadanandanNessuna valutazione finora
- Transformer Less Power Supplies Resistive and CapacitiveDocumento14 pagineTransformer Less Power Supplies Resistive and Capacitivechatmar-thailand-3038Nessuna valutazione finora
- 10W Per Channel Stereo AmplifierDocumento6 pagine10W Per Channel Stereo AmplifierRey TiburonNessuna valutazione finora
- MOSFET TutorialDocumento39 pagineMOSFET Tutorialnoor_dcetNessuna valutazione finora
- Amplifier Clase DDocumento12 pagineAmplifier Clase DRey TiburonNessuna valutazione finora
- 555 Datasheet Revb1 PDFDocumento8 pagine555 Datasheet Revb1 PDFRey TiburonNessuna valutazione finora
- Arduinobasedintelligentgreenhouse 140523094327 Phpapp02Documento51 pagineArduinobasedintelligentgreenhouse 140523094327 Phpapp02Rey TiburonNessuna valutazione finora
- Make It Right: Micro + MACRO MIR Floating HouseDocumento2 pagineMake It Right: Micro + MACRO MIR Floating HousePimpinela GrooveNessuna valutazione finora
- Panasonic SA-AK750GCPDocumento106 paginePanasonic SA-AK750GCPvasilemil100% (1)
- ELECTRONIC PROJECTS FOR MUSICIANS by Craig Anderton PDFDocumento219 pagineELECTRONIC PROJECTS FOR MUSICIANS by Craig Anderton PDFRey TiburonNessuna valutazione finora
- Coil TestDocumento1 paginaCoil TestIwan BerlianNessuna valutazione finora
- Presentationonehvtransmissionlines 141216031423 Conversion Gate01 PDFDocumento151 paginePresentationonehvtransmissionlines 141216031423 Conversion Gate01 PDFRey TiburonNessuna valutazione finora
- Telwin Tecnica 144-164 Welding-Inverter SMDocumento21 pagineTelwin Tecnica 144-164 Welding-Inverter SMAndreea TudoseNessuna valutazione finora
- HANDBOOK FOR DIGITAL PROJECTS:A Management Toolfor Preservation AndaccessDocumento182 pagineHANDBOOK FOR DIGITAL PROJECTS:A Management Toolfor Preservation AndaccessDalia GuerreiroNessuna valutazione finora
- Ai ML Demystified Mwux2017 Final 171016011705Documento66 pagineAi ML Demystified Mwux2017 Final 171016011705maroro11Nessuna valutazione finora
- Easy Stereo Amplifier Circuit IC TDA 2003Documento1 paginaEasy Stereo Amplifier Circuit IC TDA 2003Rey TiburonNessuna valutazione finora
- MicroSolutions January February 2018Documento22 pagineMicroSolutions January February 2018Rey Tiburon100% (1)
- Maheshpicarmavr 130912012611 Phpapp01Documento113 pagineMaheshpicarmavr 130912012611 Phpapp01Rey TiburonNessuna valutazione finora
- Basic Electronic ComponentsDocumento28 pagineBasic Electronic ComponentsJafar ShaikhNessuna valutazione finora
- Coil Less AM Receiver PDFDocumento1 paginaCoil Less AM Receiver PDFRey TiburonNessuna valutazione finora
- Constructional and technical info on Sinclair Project 80 modular hi-fi amplifier systemDocumento32 pagineConstructional and technical info on Sinclair Project 80 modular hi-fi amplifier systemRey TiburonNessuna valutazione finora
- ADocumento842 pagineARey TiburonNessuna valutazione finora
- Maquina CNC Con Todas Sus MedidasDocumento54 pagineMaquina CNC Con Todas Sus MedidasUlisses FabianoNessuna valutazione finora
- Wirelessrfmoduleabhi 120911035259 Phpapp01Documento43 pagineWirelessrfmoduleabhi 120911035259 Phpapp01Rey TiburonNessuna valutazione finora
- Ac Motor Controls and Vfds WhitepaperDocumento7 pagineAc Motor Controls and Vfds WhitepaperRey TiburonNessuna valutazione finora
- NPN Plastic Transistor 2SC1923 Technical DataDocumento1 paginaNPN Plastic Transistor 2SC1923 Technical DataRey TiburonNessuna valutazione finora
- CMOS Logic: The InverterDocumento1 paginaCMOS Logic: The InverterCarlos SaavedraNessuna valutazione finora
- A Comparative Performance Analysis of Various CMOS Design Techniques For XOR and XNOR CircuitsDocumento10 pagineA Comparative Performance Analysis of Various CMOS Design Techniques For XOR and XNOR CircuitsGarima PantNessuna valutazione finora
- Circuitikzmanual PDFDocumento172 pagineCircuitikzmanual PDFahmed357Nessuna valutazione finora
- Static Logigates 12Documento19 pagineStatic Logigates 12api-3750190Nessuna valutazione finora
- Hawkins CH 3Documento35 pagineHawkins CH 3Rinat EzerNessuna valutazione finora
- Exp No 1Documento6 pagineExp No 1Jeevitha ECENessuna valutazione finora
- DC Transfer Characteristics of CMOS Gates and Pass TransistorsDocumento6 pagineDC Transfer Characteristics of CMOS Gates and Pass Transistorswajid aliNessuna valutazione finora
- Design of CMOS Inverter Using Different Aspect Ratios: Key Words: CMOS Parameters, Threshold Voltage, W/LDocumento6 pagineDesign of CMOS Inverter Using Different Aspect Ratios: Key Words: CMOS Parameters, Threshold Voltage, W/LArshi DhimanNessuna valutazione finora
- Comparator Slides v1 - 0Documento44 pagineComparator Slides v1 - 0Preeti BobdeNessuna valutazione finora
- Getting Started Manuel Cadence 2017-18Documento32 pagineGetting Started Manuel Cadence 2017-18陳景裕Nessuna valutazione finora
- Advanced VLSI Design Lab (EC17203) Experiment No. 9Documento4 pagineAdvanced VLSI Design Lab (EC17203) Experiment No. 9Huzaifa AhmedNessuna valutazione finora
- CMOS Fabrication Steps - Best VLSI Training - VLSI FOR ALL-5Documento5 pagineCMOS Fabrication Steps - Best VLSI Training - VLSI FOR ALL-5ESWAR TERLINessuna valutazione finora
- Introduction to CMOS logic and gate designDocumento45 pagineIntroduction to CMOS logic and gate designNishanth Nish0% (1)
- Logic Family Introduction and OverviewDocumento96 pagineLogic Family Introduction and OverviewNikhil DattaNessuna valutazione finora
- NAND NOR GatesDocumento17 pagineNAND NOR GatesFelan Carlo GarciaNessuna valutazione finora
- 1998-Electrostatic Discharge (ESD) Protection For CMOS Output Buffers in Scaled-Down VLSI TechnologyDocumento21 pagine1998-Electrostatic Discharge (ESD) Protection For CMOS Output Buffers in Scaled-Down VLSI TechnologyNeha TripathiNessuna valutazione finora
- Chapter Outline: Basic Concept of A CMOS Inverter Power DissipationDocumento26 pagineChapter Outline: Basic Concept of A CMOS Inverter Power DissipationAnkur PatelNessuna valutazione finora
- Transconductance and output resistance of a stageDocumento22 pagineTransconductance and output resistance of a stageMohsin Abbas ZafarNessuna valutazione finora
- Circuit Layout EulerDocumento72 pagineCircuit Layout Eulerជើងកាង ភូមិNessuna valutazione finora
- Comparative Study of Various Latch-Type Sense AmplifiersDocumento5 pagineComparative Study of Various Latch-Type Sense AmplifiersShreevatsa BhatNessuna valutazione finora
- Niraj K. Jha, Sandip Kundu (Auth.) Testing and Reliable Design of CMOS Circuits 1990Documento238 pagineNiraj K. Jha, Sandip Kundu (Auth.) Testing and Reliable Design of CMOS Circuits 1990jjnNessuna valutazione finora
- ECE 164 Lecture 1 - IC TechnologyDocumento25 pagineECE 164 Lecture 1 - IC TechnologyJackieNessuna valutazione finora
- Exam 1 ECE 410 Fall 2002Documento5 pagineExam 1 ECE 410 Fall 2002Bereket LemmaNessuna valutazione finora
- Designing and Characterization of 60nm p-well MOSFETDocumento4 pagineDesigning and Characterization of 60nm p-well MOSFETKathleen Zipora RahuellahNessuna valutazione finora
- MOSFET Biasing TechniquesDocumento33 pagineMOSFET Biasing TechniquesKesani Venkat Narsimha ReddyNessuna valutazione finora
- 1167 Etp4333Documento5 pagine1167 Etp4333Navjot KaurNessuna valutazione finora
- Implement Logic Using Cmos GatesDocumento51 pagineImplement Logic Using Cmos GatesPranav DarganNessuna valutazione finora
- High-Speed Hybrid-Logic Full Adder Using High-Performance 10-T - CellDocumento10 pagineHigh-Speed Hybrid-Logic Full Adder Using High-Performance 10-T - CellAnu SinghNessuna valutazione finora
- Srikanth Reddy Paramaiahgari 1206321047 Project Part2Documento15 pagineSrikanth Reddy Paramaiahgari 1206321047 Project Part2Srikanth Reddy ParamaiahgariNessuna valutazione finora
- Infineon 2EDS9265H DataSheet v02 - 08 ENDocumento38 pagineInfineon 2EDS9265H DataSheet v02 - 08 ENshirazNessuna valutazione finora