Documenti di Didattica
Documenti di Professioni
Documenti di Cultura
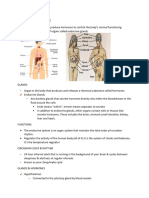
Endocrine Glands The Producers of Chemical Messengers
Caricato da
ahmedTitolo originale
Copyright
Formati disponibili
Condividi questo documento
Condividi o incorpora il documento
Hai trovato utile questo documento?
Questo contenuto è inappropriato?
Segnala questo documentoCopyright:
Formati disponibili
Endocrine Glands The Producers of Chemical Messengers
Caricato da
ahmedCopyright:
Formati disponibili
BIOLOGY ENDOCRINE GLANDS THE PRODUCERS OF CHEMICAL MESSENGERS
Endocrine Glands
The Producers of Chemical Messengers
Multicellular organisms communicate with and control their various activities by means of two major
systemsthe nervous system and the endocrine system.
Hormonal Control
Affects bodily activities by releasing
chemical messengers called hormones
into the blood stream.
Action is slow.
Effects can be short-term or long lasting.
Can affect growth.
Brings about specific chemical changes,
thus regulating metabolism.
Nervous Control
Controls and maintains the internal
environment of the body by sending
impulses to neurons.
Action is immediate.
Effects are brief.
Does not affect growth.
Does not influence chemical changes and
hence cannot regulate metabolism.
Hormones
A hormone is a secretion from some glandular part of the body, which is poured into the blood and which
acts on the target organs or cells of the same individual.
Most hormones are secreted by special glands called endocrine glands.
General Properties of Hormones
1.
2.
3.
4.
Hormones are secreted by the endocrine glands directly into the blood.
Produced in very small quantities.
Biologically very active.
Act on target organs or cells usually away from the source.
www.topperlearning.com
BIOLOGY ENDOCRINE GLANDS THE PRODUCERS OF CHEMICAL MESSENGERS
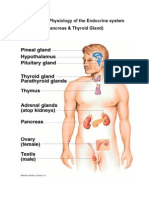
Endocrine System
The endocrine system is made of endocrine glands and tissues.
Adrenal
Glands
Gonads
Pancreas
Endocrine Glands
Thyroid
Gland
Thymus
Parathyroid
Gland
Pituitary
Gland
Adrenal Glands
The human body has two adrenal glands located on top of the kidneys; hence, they are also known as
suprarenal glands.
Adrenal Gland
www.topperlearning.com
BIOLOGY ENDOCRINE GLANDS THE PRODUCERS OF CHEMICAL MESSENGERS
Adrenal Cortex
Adrenal Medulla
Adrenaline
(prepares the body
for the fight and
flight mechanism)
Mineralocorticoids
(Regulate mineral
metabolism)
Glucocorticoids
(Regulate
carbohydrate,
protein and fat
metabolism)
Response to Adrenaline
Body Part
Effects of Adrenaline
Heart
Beats faster and blood
pressure increases
Muscles of body
Tenses muscles
Liver
Conversion of
glycogen to glucose
Biological Advantage
Sends more glucose and
oxygen to the muscles
Ready for immediate action
Glucose available in blood
for energy production
Effect or Sensation
Thumping heart
Tense feeling,
shivering
No sensation
Adrenaline also causes dilation of the pupil of the eyes, stimulates uterine contraction during child
delivery and increases the clotting capacity of blood.
Abnormal Secretions of Adrenal Glands
Hyposecretion of the adrenal cortex causes Addisons Disease.
Hypersecretion of the adrenal cortex causes Cushing Syndrome.
Pancreas
Pancreas
www.topperlearning.com
BIOLOGY ENDOCRINE GLANDS THE PRODUCERS OF CHEMICAL MESSENGERS
The pancreas is exocrine as well as an endocrine gland.
The exocrine part pours its secretionpancreatic juiceinto the duodenum through the pancreatic duct.
The endocrine part is made up of a special group of cells known as islets of Langerhans.
Three kinds of cells found in the islets of Langerhans and their secretions are
Alpha Cells
Secrete glucagon
Glucagon stimulates the
breakdown of glycogen
into glucose in the liver
Beta Cells
Secrete insulin
Insulin maintains the rise
of the blood sugar level
Delta Cells
Secrete somatostatin
Somatostatin controls the
secretion of glucagon and
insulin
Abnormal Secretions of Insulin
Insufficient Secretion of Insulin
Oversecretion of Insulin
Causes diabetes mellitus
Symptoms:
High concentration of sugar in blood
(hyperglycemia).
Excretes a large amount of urine
containing more concentration of sugar.
Treatment: It cannot be cured, but sugar
levels can be maintained by the
administration of insulin.
The sugar level in the blood is lowered,
i.e. hypoglycemia.
If the level becomes too low, then the
brain may enter a state of coma for a few
minutes.
A patient may become unconscious due to
an overdose of insulin. This is called insulin
shock.
Thyroid Gland
The thyroid gland is a bilobed, butterfly-shaped gland.
The two lobes are joined by a narrow mass of tissues called isthmus.
Thyroid Gland - Front View and Back View
www.topperlearning.com
BIOLOGY ENDOCRINE GLANDS THE PRODUCERS OF CHEMICAL MESSENGERS
Secretion of Thyroid
Gland
Thyroxine
(Regulates basal
metabolsim)
Calcitonin
(Regulates calcium
and phosphate
levels in the blood)
Disorders of
the Thyroid
Gland
Hypothyroidism
Simple Goitre
(Enlargement
of the thyroid
gland)
Cretinism
(Dwarfism,
mental
retardation)
Hyperthyroidism
Myxoedema
(Swelling on
the face and
hands)
Exophthalmic
Goitre
(Enlargement
of the glands,
eyes protrude)
Pituitary Gland
It is a small gland about the size of a pea.
The pituitary controls the secretions of all the other endocrine glands; therefore, it is also called the
master gland.
The pituitary gland is divided into three lobes. The secretions from these lobes are as follows:
www.topperlearning.com
BIOLOGY ENDOCRINE GLANDS THE PRODUCERS OF CHEMICAL MESSENGERS
Pituitary
Glands
Anterior
Pituitary
Intermediate
Lobe
Posterior
Pituitary
Growth
Hormone
Anti-diuretic
Hormone
Thyroid
Stimulating
Hormone
Oxytocin
FSH/LH
ACTH
Anterior Pituitary
Growth Hormone:
o Essential for normal growth.
o Deficiency of growth hormone causes dwarfism.
o Oversecretion causes gigantism and acromegaly.
Thyroid Stimulating Hormone (TSH):
o Controls the activities of the thyroid gland.
Gonadotropins (FSH/LH):
o Regulate the activities of testes and ovaries.
Adrenocorticotropic Hormone (ACTH):
o Regulates the activity of the adrenal cortex.
Intermediate Lobe of the Pituitary Gland: Regulates the activity of the adrenal cortex.
Posterior Pituitary
Anti-diuretic Hormone (Vasopressin):
o Regulates the amount of water excreted in the urine.
o Deficiency of ADH causes diabetes insipidus.
Oxytocin:
o Stimulates contraction of uterine muscles during childbirth.
www.topperlearning.com
BIOLOGY ENDOCRINE GLANDS THE PRODUCERS OF CHEMICAL MESSENGERS
Feedback Mechanism
Negative Feedback Mechanism
The body has mechanisms to maintain a normal state.
Whenever there is a change in the normal state, the messages are sent to increase secretions if there
is a fall below normal or to decrease secretions if there is a rise above normal to restore the normal
body state. Such a mechanism is called a Negative Feedback Mechanism.
Gonads
1. Testes
Found in males.
Lie in scrotum.
Interstitial cells of testes secrete testosterone.
Testosterone is responsible for the maturation of sperms.
Stimulates the growth and development of the male reproductive system.
www.topperlearning.com
BIOLOGY ENDOCRINE GLANDS THE PRODUCERS OF CHEMICAL MESSENGERS
2. Ovaries
They are the female gonads.
Found in females.
They secrete oestrogen, progesterone and relaxin.
Oestrogen is responsible for the development of ovarian follicles.
Progesterone is responsible for the development of corpus luteum and placenta.
Relaxin dilates the cervix towards the end of pregnancy.
Parathyroid Glands
Parathyroid Glands
Two pairs of parathyroid glands are located on the posterior surface of the thyroid gland.
These glands secrete parathormone (PTH).
PTH controls calcium metabolism and maintains blood calcium at a constant level.
Its hyposecretion causes tetany, while its hypersecretion results in demineralisation of bones.
www.topperlearning.com
BIOLOGY ENDOCRINE GLANDS THE PRODUCERS OF CHEMICAL MESSENGERS
Thymus Gland
It is a bilobed gland which is present between the lungs.
This gland produces different hormones such as thymic protein, thymosin etc.
Functions:
o Controls the maturation and distribution of lymphocytes.
o Stimulates antibody production.
www.topperlearning.com
10
Potrebbero piacerti anche
- Powermatic 58480438-Millrite-Mvn-Manual PDFDocumento54 paginePowermatic 58480438-Millrite-Mvn-Manual PDFJason Willis75% (4)
- Nursing Care Plan ConstipationDocumento3 pagineNursing Care Plan Constipationbmrose3783% (12)
- A Module On Human Body: Lesson V: The Endocrine SystemDocumento8 pagineA Module On Human Body: Lesson V: The Endocrine Systemapi-3731377Nessuna valutazione finora
- Pa Tho Physiology of SepsisDocumento5 paginePa Tho Physiology of SepsisMikee Ann ValdezNessuna valutazione finora
- Endocrine System PresentationDocumento29 pagineEndocrine System PresentationTanayNessuna valutazione finora
- Ky 9 KZ OCt YO96 LBRL 0 HH DDocumento22 pagineKy 9 KZ OCt YO96 LBRL 0 HH DVenu GopalNessuna valutazione finora
- Endocrineglands 140817003157 Phpapp01Documento61 pagineEndocrineglands 140817003157 Phpapp01Musfira KhalidNessuna valutazione finora
- BioSci LO#2Documento16 pagineBioSci LO#2AudzkieNessuna valutazione finora
- Psychology - Endocrine Glands (SEM - 2 - CC-6)Documento7 paginePsychology - Endocrine Glands (SEM - 2 - CC-6)Srinivasu ChintalaNessuna valutazione finora
- Sistem Endokrin: Oleh: Dr. Siska Anggreni Lubis, SPKKDocumento25 pagineSistem Endokrin: Oleh: Dr. Siska Anggreni Lubis, SPKKRichas Interisti SumatraNessuna valutazione finora
- The Endocrine System: Exocrine GlandsDocumento5 pagineThe Endocrine System: Exocrine GlandsahmedfikryNessuna valutazione finora
- Endocrine GlandsDocumento4 pagineEndocrine GlandsEzeh PrincessNessuna valutazione finora
- Endocrine System: Image Courtesy of - ContactDocumento8 pagineEndocrine System: Image Courtesy of - ContactShri VkNessuna valutazione finora
- Endocrine SystemDocumento24 pagineEndocrine Systempromisefo65Nessuna valutazione finora
- 10 Endocrine SystemDocumento35 pagine10 Endocrine SystemALICIA GOMEZNessuna valutazione finora
- Here You Will Get Following Materials:-: All Study Materials in Free of CostDocumento24 pagineHere You Will Get Following Materials:-: All Study Materials in Free of CostBha nu Sin ghNessuna valutazione finora
- Here You Will Get Following Materials:-: All Study Materials in Free of CostDocumento24 pagineHere You Will Get Following Materials:-: All Study Materials in Free of CostBha nu Sin ghNessuna valutazione finora
- Endocrine System Anatomy and Physiology - NurseslabsDocumento29 pagineEndocrine System Anatomy and Physiology - NurseslabsAlyssum Marie50% (2)
- Endocrine SystemDocumento9 pagineEndocrine Systemkevin maheshNessuna valutazione finora
- How Are Endocrine Glands Designed To Perform TheirDocumento23 pagineHow Are Endocrine Glands Designed To Perform TheirEA CatalanNessuna valutazione finora
- The Endocrine SystemDocumento8 pagineThe Endocrine SystemVictoria VintuNessuna valutazione finora
- Endocrine SystemDocumento19 pagineEndocrine Systemethel roseNessuna valutazione finora
- Endocrine System OutlineDocumento17 pagineEndocrine System OutlineEsthermae PanadenNessuna valutazione finora
- 3-Coordination in AnimalsDocumento23 pagine3-Coordination in AnimalsDerrick MNessuna valutazione finora
- Chapter 2Documento8 pagineChapter 2melanielampera17Nessuna valutazione finora
- Anatomy & Physiology of The Endocrine System (Pancreas & Thyroid Gland)Documento5 pagineAnatomy & Physiology of The Endocrine System (Pancreas & Thyroid Gland)Joanna DuapaNessuna valutazione finora
- Chemical Coordination and IntegrationDocumento6 pagineChemical Coordination and IntegrationRonaldNessuna valutazione finora
- 34-2 PowerPointDocumento24 pagine34-2 PowerPointLeo HellawellNessuna valutazione finora
- TOPIC 3 - The Endocrine SystemDocumento34 pagineTOPIC 3 - The Endocrine SystemKaren Pearl TagleNessuna valutazione finora
- The Endocrine System Overview/ Introduction: Nur112: Anatomy and Physiology ISU Echague - College of NursingDocumento6 pagineThe Endocrine System Overview/ Introduction: Nur112: Anatomy and Physiology ISU Echague - College of NursingWai KikiNessuna valutazione finora
- Endocrine System (Vertebrate) : HomeostasisDocumento7 pagineEndocrine System (Vertebrate) : HomeostasisKaleem UllahNessuna valutazione finora
- What Does The Endocrine System Do?Documento10 pagineWhat Does The Endocrine System Do?hadiqa azizNessuna valutazione finora
- Endocrine Organ System Body Function Hormones PDFDocumento5 pagineEndocrine Organ System Body Function Hormones PDFworldfindings.comNessuna valutazione finora
- A.S.Harenee: Biology ProjectDocumento16 pagineA.S.Harenee: Biology ProjectHema SubramaniNessuna valutazione finora
- Endocrine SystemDocumento27 pagineEndocrine SystemJessica CulangoNessuna valutazione finora
- The Endocrine System Study Guide 101 PDFDocumento17 pagineThe Endocrine System Study Guide 101 PDFStephanie Kate PelenioNessuna valutazione finora
- Endocrine SystemDocumento46 pagineEndocrine Systemespinajeff07Nessuna valutazione finora
- Adrenal GlandDocumento47 pagineAdrenal GlandsuthaNessuna valutazione finora
- CBSE Quick Revision Notes (Class-11 Biology) Chapter-22 Chemical Coordination and IntegrationDocumento3 pagineCBSE Quick Revision Notes (Class-11 Biology) Chapter-22 Chemical Coordination and IntegrationNANDAKUMAR BABUNessuna valutazione finora
- CBSE Quick Revision Notes (Class-11 Biology) Chapter-22 Chemical Coordination and IntegrationDocumento3 pagineCBSE Quick Revision Notes (Class-11 Biology) Chapter-22 Chemical Coordination and IntegrationNANDAKUMAR BABUNessuna valutazione finora
- Endocrine SystemDocumento20 pagineEndocrine SystemJamie BagundolNessuna valutazione finora
- M3 Endocrine System. UpdatedDocumento33 pagineM3 Endocrine System. Updatedlalarela.cindyNessuna valutazione finora
- Endocrine System - Part 2Documento31 pagineEndocrine System - Part 2Maryem NabawiNessuna valutazione finora
- Endocrine System and Hormones 1Documento41 pagineEndocrine System and Hormones 1Jizaille Audrey Ho QuirongNessuna valutazione finora
- Lesson Plan For Anatomy and PhysiologyDocumento7 pagineLesson Plan For Anatomy and PhysiologyJamie Bagundol100% (1)
- Chapter VI EndocrineDocumento8 pagineChapter VI EndocrineTitoMacoyTVNessuna valutazione finora
- GROUP 9 Edocrine System ReportDocumento52 pagineGROUP 9 Edocrine System Reportroyeth montezaNessuna valutazione finora
- Natural EndocrineDocumento121 pagineNatural EndocrinetanasedanielaNessuna valutazione finora
- ICSE-X Biology Chap-11 (Endocrine System)Documento14 pagineICSE-X Biology Chap-11 (Endocrine System)TAHMEENA ZAFARNessuna valutazione finora
- 2.the Endocrine SystemDocumento24 pagine2.the Endocrine SystemranzNessuna valutazione finora
- Endocrine SystemDocumento11 pagineEndocrine SystemSarthak AgarwalNessuna valutazione finora
- CLASS:10 Subject:Biology Chapter:Control and CoordinationDocumento14 pagineCLASS:10 Subject:Biology Chapter:Control and Coordinationkhushi guptaNessuna valutazione finora
- Endocrine System Anatomy and PhysiologyDocumento17 pagineEndocrine System Anatomy and PhysiologyKBD0% (1)
- Endocrine SystemDocumento9 pagineEndocrine System•Svbrinv29•Nessuna valutazione finora
- Endocrine Glands - Definition Examples Function Biology DictionaryDocumento7 pagineEndocrine Glands - Definition Examples Function Biology Dictionaryrania khanNessuna valutazione finora
- 11 Biology Notes ch22 Chemical Coordination and Integration PDFDocumento6 pagine11 Biology Notes ch22 Chemical Coordination and Integration PDFAarav VarshneyNessuna valutazione finora
- Hormones in The BodyDocumento9 pagineHormones in The BodySherry SinghNessuna valutazione finora
- Endocrine SystemDocumento35 pagineEndocrine SystemLinkNessuna valutazione finora
- Psychology AssignmentDocumento6 paginePsychology Assignmentbijina AnnNessuna valutazione finora
- Grade VIII Biology Synopsis Theme 4: Unit 1 Name of The Chapter: Human Body-Endocrine System Date: 20-10-2021 No. of Pages: 6Documento6 pagineGrade VIII Biology Synopsis Theme 4: Unit 1 Name of The Chapter: Human Body-Endocrine System Date: 20-10-2021 No. of Pages: 6shashwatthegamerytNessuna valutazione finora
- Module 9 The Endocrine SystemDocumento15 pagineModule 9 The Endocrine SystemMisha WilliamsNessuna valutazione finora
- Adrenal Fatigue: Understanding the Symptoms: How Malfunctioning Adrenal Glands Negatively Affect the BodyDa EverandAdrenal Fatigue: Understanding the Symptoms: How Malfunctioning Adrenal Glands Negatively Affect the BodyNessuna valutazione finora
- BITSAT ArchivesDocumento3 pagineBITSAT ArchivesahmedNessuna valutazione finora
- What It Takes To Manage An EV FleetDocumento7 pagineWhat It Takes To Manage An EV FleetahmedNessuna valutazione finora
- Scooter Rentals Give New Spin To Asset-Light Model - The Economic TimesDocumento3 pagineScooter Rentals Give New Spin To Asset-Light Model - The Economic TimesahmedNessuna valutazione finora
- Geography Text Book PDFDocumento126 pagineGeography Text Book PDFahmedNessuna valutazione finora
- הרצאה- אנמיה וטרומבוציטופניהDocumento87 pagineהרצאה- אנמיה וטרומבוציטופניהliatfurmanNessuna valutazione finora
- DefibrillatorDocumento2 pagineDefibrillatorVasanth VasanthNessuna valutazione finora
- GASESDocumento55 pagineGASESja_QuinineNessuna valutazione finora
- 30356-Article Text-56848-1-10-20210201Documento14 pagine30356-Article Text-56848-1-10-20210201Mel FaithNessuna valutazione finora
- All Vaccinees Are Requested To Bring Certificate of Dose-II From COWIN Portal Alongwith Registered Mobile Number Before Proceeding For VaccinationDocumento7 pagineAll Vaccinees Are Requested To Bring Certificate of Dose-II From COWIN Portal Alongwith Registered Mobile Number Before Proceeding For VaccinationRakesh KumarNessuna valutazione finora
- Stats Review CH 1-6Documento15 pagineStats Review CH 1-6Megha BanerjeeNessuna valutazione finora
- O OP PE ER RA Attiin NG G Iin NS STTR RU UC Cttiio ON NS S: UF 755 G UF 455 GDocumento14 pagineO OP PE ER RA Attiin NG G Iin NS STTR RU UC Cttiio ON NS S: UF 755 G UF 455 GHomeroPerezNessuna valutazione finora
- Clipsal RCD Tester 486D PDFDocumento4 pagineClipsal RCD Tester 486D PDF322399mk7086Nessuna valutazione finora
- Difference Between Gram Positive and GramDocumento3 pagineDifference Between Gram Positive and Grambaraa aburassNessuna valutazione finora
- HIPULSE U 80kVA 500kVA-Manual - V1.1Documento157 pagineHIPULSE U 80kVA 500kVA-Manual - V1.1joseph mendezNessuna valutazione finora
- Msla Business FeesDocumento1 paginaMsla Business FeesNBC MontanaNessuna valutazione finora
- WWW - Devicemanuals.eu: GardenaDocumento6 pagineWWW - Devicemanuals.eu: GardenapotoculNessuna valutazione finora
- Dolor Postoperatorio y Efectos Secundarios de La Uvulo Palstia Con Radiofrecuencia en Roncopatia Primaria.Documento5 pagineDolor Postoperatorio y Efectos Secundarios de La Uvulo Palstia Con Radiofrecuencia en Roncopatia Primaria.Alejandro RuizNessuna valutazione finora
- Pelatihan Olahan Pangan Ukm LamselDocumento6 paginePelatihan Olahan Pangan Ukm LamselCalista manda WidyapalastriNessuna valutazione finora
- Jis C 8156-2017, EngDocumento32 pagineJis C 8156-2017, Eng7620383tlNessuna valutazione finora
- EC Type-Examination Certificate: Reg.-No.: 01/205/5192.02/18Documento11 pagineEC Type-Examination Certificate: Reg.-No.: 01/205/5192.02/18Orlando Ortiz VillegasNessuna valutazione finora
- Development of Elevator Ropes: Tech Tip 15Documento2 pagineDevelopment of Elevator Ropes: Tech Tip 15أحمد دعبسNessuna valutazione finora
- Dearcán Ó Donnghaile: ProfileDocumento2 pagineDearcán Ó Donnghaile: Profileapi-602752895Nessuna valutazione finora
- Afico Pipe InsulaionDocumento4 pagineAfico Pipe InsulaionProcurement AlamcoNessuna valutazione finora
- Implementing Self-Administration of Insulin in Hospital: A Journey of Discovery and Innovation. Part 1: Culture and StorageDocumento4 pagineImplementing Self-Administration of Insulin in Hospital: A Journey of Discovery and Innovation. Part 1: Culture and Storagesunrise755Nessuna valutazione finora
- Nfpa Training - Nfpa 72Documento107 pagineNfpa Training - Nfpa 72yusuf.ahmediutNessuna valutazione finora
- TG Chap. 10Documento7 pagineTG Chap. 10Gissele AbolucionNessuna valutazione finora
- Naming Alcohols, Aldehydes. EtcDocumento1 paginaNaming Alcohols, Aldehydes. Etcim_mikezNessuna valutazione finora
- C 08 S 09Documento8 pagineC 08 S 09Marnel Roy MayorNessuna valutazione finora
- Man Wah Ranked As Top 10 Furniture Sources For U.S. MarketDocumento2 pagineMan Wah Ranked As Top 10 Furniture Sources For U.S. MarketWeR1 Consultants Pte LtdNessuna valutazione finora
- DS Flow SwitchesDocumento51 pagineDS Flow SwitchesAnonymous Xnaj1g8Y3100% (1)
- Tool 10 Template Working Papers Cover SheetDocumento4 pagineTool 10 Template Working Papers Cover Sheet14. Đỗ Kiến Minh 6/5Nessuna valutazione finora
- Schengen Certificate ExampleDocumento2 pagineSchengen Certificate ExampleGabriel Republi CanoNessuna valutazione finora