Documenti di Didattica
Documenti di Professioni
Documenti di Cultura
Acetic Acid
Caricato da
Haxiba ArxhadCopyright
Formati disponibili
Condividi questo documento
Condividi o incorpora il documento
Hai trovato utile questo documento?
Questo contenuto è inappropriato?
Segnala questo documentoCopyright:
Formati disponibili
Acetic Acid
Caricato da
Haxiba ArxhadCopyright:
Formati disponibili
Acetic Acid
Acetic acid is known as ethanoic acid and methane carboxylic acid is a colorless liquid
that has a strong and distinct pungent and sour smell. Its chemical formula is C2H4O2. It
has two carbon (C) atoms, four hydrogen (H) atoms and two oxygen (O) atoms. Because
it has a carbon in its chemical formula, it is an organic compound. Vinegar is a household
essential often used for cooking. What chemical substance makes vinegar smell the way
it does? Vinegar is actually a solution that is made of 4-8% of acetic acid that is
dissolved in water and other substances that give vinegar its flavor depending on its type.
Acetic acid is one of the simplest carboxylic acid. The chemical structure of carboxylic
acid is:
The global demand of acetic acid is around 6.5 million tonnes per year (mt/a).Pure acetic
acid is very useful because it acts as a hygroscopic liquid. The acetic acid freezes below
16.7C,melting point is 16.7C.Boiling point is 118C, flash point is 40C and Explosion
limits is 4 to 16%. Acetic acid is weak acid having Pka value of 4.8.The acetic acid has a
moderate dielectric constant of 6.2 as it is protic solvent like ethanol and water. We most
commonly know that acetic acid is used in vinegar, it is used for so much more, and it is a
very important chemical used in many industrial processes. Let's take a look at the
various uses of acetic acid. A majority of the acetic acid that is produced is used to
produce vinyl acetate monomer, or VAM and other major application is production of
acetic anhydride. It is used to produce the synthetic fibers and fabrics, it is also used for
photographic film. Chemically all acetates is soluble in water except of chromium (2)
acetate It is highly corrosive with metals like iron and zinc but is is non corrosive in
presence of stainless steel. The acetic acid is very useful as industrial point of view so
the acetic acid is produced by three methods and these methods are:
1) Oxidation of acetaldehyde (old method)
2) N-butane Oxidation
3) Methanol Carbonylation
Production of Acetic acid
N-butane Oxidation:
Acetic acid is produced by cobalt-catalyzed oxidation of n-butane at temperature of
110C-120C and pressure of 60 atm. Butane reacts with oxygen, contains gas in the
presences s of a soluble cobalt compound at a concentration of 0.5 to about 20% by
weight cobalt based upon a lower fatty acid in reaction composition at a temperature of
93-100C. The process operates while maintaining a high partial pressure of oxygen
throughout the reaction zone and a high cobalt catalyst concentration to obtain a high
reaction rate. Constant temperature may also be maintained in the reaction zone. The
liquid phase oxidation of butane yields acetic acid, ketones and eaters n-butane ideally
yields two moles of acetic acid .The lBO process produces 500 lb millions of acetic acid.
In the process, n-butane add air is feed to the reactor where oxidation takes place The
product mixtures is passed through coolers and then through separators such as decanter
(separation on the basis of density) and flash tank (separation on the boiling point
/relative volatility) The initial reaction involves formation of butane n-hydro peroxide
further oxidation and decomposition of resultant radicals produce acetic acid:
C4H10 + 2 1/2O2
2CH3COOH + H2
Before methanol carbonylation become commercialized in 1989, butane oxidation was
major source of acetic acid. Now produces up to 10% of acetic acid annually. The process
diagram is :
Potrebbero piacerti anche
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryDa EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryValutazione: 3.5 su 5 stelle3.5/5 (231)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Da EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Valutazione: 4.5 su 5 stelle4.5/5 (121)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceDa EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceValutazione: 4 su 5 stelle4/5 (588)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaDa EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaValutazione: 4.5 su 5 stelle4.5/5 (266)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingDa EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingValutazione: 3.5 su 5 stelle3.5/5 (400)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItDa EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItValutazione: 4.5 su 5 stelle4.5/5 (838)
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeDa EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeValutazione: 4.5 su 5 stelle4.5/5 (537)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerDa EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerValutazione: 4.5 su 5 stelle4.5/5 (271)
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeDa EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeValutazione: 4 su 5 stelle4/5 (5794)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyDa EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyValutazione: 3.5 su 5 stelle3.5/5 (2259)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersDa EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersValutazione: 4.5 su 5 stelle4.5/5 (344)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnDa EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnValutazione: 4.5 su 5 stelle4.5/5 (234)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreDa EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreValutazione: 4 su 5 stelle4/5 (1090)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceDa EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceValutazione: 4 su 5 stelle4/5 (895)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesDa EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesValutazione: 4 su 5 stelle4/5 (821)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureDa EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureValutazione: 4.5 su 5 stelle4.5/5 (474)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaDa EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaValutazione: 4 su 5 stelle4/5 (45)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Da EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Valutazione: 4 su 5 stelle4/5 (98)
- WPS FormatDocumento2 pagineWPS FormatAmit SarkarNessuna valutazione finora
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealDa EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealValutazione: 4 su 5 stelle4/5 (73)
- IBR Design Calculations - FinalDocumento6 pagineIBR Design Calculations - Finalshazan100% (1)
- Historical Steelwork HandbookDocumento80 pagineHistorical Steelwork HandbookÉmilie Riverin100% (1)
- ASTMDocumento46 pagineASTMJuliana100% (1)
- TD ManualDocumento31 pagineTD Manualramlalmittal100% (1)
- STP 550-1986Documento58 pagineSTP 550-1986Anonymous pSozzNFcNessuna valutazione finora
- Promax - Property Packages Selection GuideDocumento2 paginePromax - Property Packages Selection GuidedumpmejunkmailsNessuna valutazione finora
- Turflow Heat Exchanger High Efficiency Heat Transfer Solution-Sales BrochureDocumento8 pagineTurflow Heat Exchanger High Efficiency Heat Transfer Solution-Sales BrochurePablo Angel ToiaNessuna valutazione finora
- Group A Rawat Lab Presentation FinalDocumento96 pagineGroup A Rawat Lab Presentation Finalumair100% (3)
- Fabr Pneumatic 033009Documento28 pagineFabr Pneumatic 033009daniper89Nessuna valutazione finora
- Example 9.2 1Documento3 pagineExample 9.2 1jthaaschNessuna valutazione finora
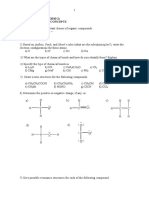
- CHM3201 Tutorial 1 Basic ConceptsDocumento3 pagineCHM3201 Tutorial 1 Basic ConceptsAkmalZharifAbdullahNessuna valutazione finora
- Module 4 HIgh Cycle and Low Cycle FatigueDocumento21 pagineModule 4 HIgh Cycle and Low Cycle FatiguerohanNessuna valutazione finora
- Heat Energy RubricDocumento1 paginaHeat Energy Rubricapi-391225671Nessuna valutazione finora
- Lab 3heatengine PhysicDocumento3 pagineLab 3heatengine Physicapi-263500375Nessuna valutazione finora
- Sekine Et Al 2011 EPSLDocumento10 pagineSekine Et Al 2011 EPSLpleasure masangoNessuna valutazione finora
- Wear in ChutesDocumento17 pagineWear in ChutesJDNessuna valutazione finora
- Semiconductor - Experiment PDFDocumento116 pagineSemiconductor - Experiment PDFMuthu KumarNessuna valutazione finora
- PG 462-486 PDFDocumento25 paginePG 462-486 PDFfilkeNessuna valutazione finora
- Science Magazine April 07 2006 PDFDocumento144 pagineScience Magazine April 07 2006 PDFAndrés FrankowNessuna valutazione finora
- Digestive SystemDocumento102 pagineDigestive Systemkavya nandhiNessuna valutazione finora
- (59-68) Monitoring and Modeling of Fayoum Distribution Networks According To Tri Halo Me Thanes FormationDocumento11 pagine(59-68) Monitoring and Modeling of Fayoum Distribution Networks According To Tri Halo Me Thanes FormationAlexander DeckerNessuna valutazione finora
- Nov1994 Paper3 ChemistryDocumento11 pagineNov1994 Paper3 ChemistrydhsNessuna valutazione finora
- ESB 2018 Abstract Proceedings 4Documento1.099 pagineESB 2018 Abstract Proceedings 4Alan PolancoNessuna valutazione finora
- Growth Kinetic Models For Microalgae Cultivation A ReviewDocumento16 pagineGrowth Kinetic Models For Microalgae Cultivation A ReviewJesús Eduardo De la CruzNessuna valutazione finora
- Duragyp 13mm AA - VOC Emission Report - Indoor Air Comfort GoldDocumento20 pagineDuragyp 13mm AA - VOC Emission Report - Indoor Air Comfort GoldDimitris KousoulasNessuna valutazione finora
- An Overview of Brake Noise and Vibration ProblemsDocumento7 pagineAn Overview of Brake Noise and Vibration ProblemsChangbum YuNessuna valutazione finora
- Assignment Booklet: BTME ProgrammeDocumento20 pagineAssignment Booklet: BTME ProgrammeSarvanKumarNessuna valutazione finora
- Aluminium Etching MicroChemicals PDFDocumento3 pagineAluminium Etching MicroChemicals PDFDaniela Silva MolinaNessuna valutazione finora
- Analytica Chimica Acta: Jacopo La Nasa, Francesca Modugno, Matteo Aloisi, Anna Lluveras-Tenorio, Ilaria BonaduceDocumento8 pagineAnalytica Chimica Acta: Jacopo La Nasa, Francesca Modugno, Matteo Aloisi, Anna Lluveras-Tenorio, Ilaria Bonaducejuanda.scienceNessuna valutazione finora