Documenti di Didattica
Documenti di Professioni
Documenti di Cultura
27 - Amines, Amides and Amino Acids
Caricato da
Abbas HaiderCopyright
Formati disponibili
Condividi questo documento
Condividi o incorpora il documento
Hai trovato utile questo documento?
Questo contenuto è inappropriato?
Segnala questo documentoCopyright:
Formati disponibili
27 - Amines, Amides and Amino Acids
Caricato da
Abbas HaiderCopyright:
Formati disponibili
27 Amines, amides and amino acids
Topic summary
Amines are weak organic bases, reacting with acids to form salts, and dissolving in water to give
alkaline solutions.
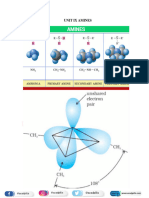
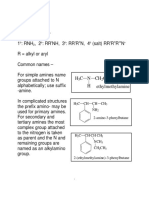
There are three types of amine primary, RNH2, secondary, R2NH, and tertiary, R3N.
Aryl amines react with nitric(III) acid (nitrous acid) to form diazonium salts, from which many
useful azo dyes are manufactured.
Amino acids contain the NH2 and CO2H functional groups adjacent to each other. In solution
and in the solid they exist as zwitterions, +NH3CHRCO2.
Most amino acids are chiral. Those isolated from natural proteins have the l configuration.
Electrophoresis can be used to separate amino acids and peptides.
Synthetic polyamides such as nylon are made by condensing diamines with dicarboxylic acids.
Key reactions you should know
(R = alkyl or aryl unless otherwise stated)
Amines:
Alkylation:
RNH2 + CH3Br RNHCH3 + HBr
Acylation:
RNH2 + CH3COCl RNHCOCH3 + HCl
With nitrous acid (nitric(III) acid):
Amides:
Hydrolysis:
Reduction:
Polymerisation:
Potrebbero piacerti anche
- Chapter 9 AminesDocumento35 pagineChapter 9 AminesHanna AnneNessuna valutazione finora
- Nitrogen CompoundsDocumento129 pagineNitrogen CompoundsSherey FathimathNessuna valutazione finora
- Amines: Chemistry 20Documento48 pagineAmines: Chemistry 20David AloNessuna valutazione finora
- AminesDocumento23 pagineAminesIqbal YeahNessuna valutazione finora
- AMINESDocumento2 pagineAMINESgiftNessuna valutazione finora
- Organic Chemistry Chapter 19: AminesDocumento40 pagineOrganic Chemistry Chapter 19: Aminesmelg16Nessuna valutazione finora
- Amines ppt2 PDFDocumento29 pagineAmines ppt2 PDFKareem MckenzieNessuna valutazione finora
- 15 - Amines (New) PDFDocumento25 pagine15 - Amines (New) PDFthinkiitNessuna valutazione finora
- Chapter 16 - Amines and Amides: N, N-DimethylanilineDocumento6 pagineChapter 16 - Amines and Amides: N, N-DimethylanilineStephen BrooksNessuna valutazione finora
- Chapter 16 - Amines and Amides: N, N-DimethylanilineDocumento6 pagineChapter 16 - Amines and Amides: N, N-DimethylanilineStephen BrooksNessuna valutazione finora
- Amine 2Documento43 pagineAmine 2MaryNessuna valutazione finora
- Amines 2021 LectureDocumento36 pagineAmines 2021 LectureMichael AttehNessuna valutazione finora
- 6.Amina-Amida KulDocumento25 pagine6.Amina-Amida KulFelicia GunawanNessuna valutazione finora
- Nitrogen Containing Compuonds-01-TheoryDocumento20 pagineNitrogen Containing Compuonds-01-TheoryRaju SinghNessuna valutazione finora
- Organic Chemistry II Amides: Structure, Nomenclature, Preparation and ReactionsDocumento25 pagineOrganic Chemistry II Amides: Structure, Nomenclature, Preparation and Reactionsshahera rosdiNessuna valutazione finora
- NotesDocumento8 pagineNotesVanisha RaghavendraNessuna valutazione finora
- 2aminesmm Lec.5Documento22 pagine2aminesmm Lec.5ghlafhlyNessuna valutazione finora
- 3.3 AminesDocumento81 pagine3.3 Aminessaadzubair0307Nessuna valutazione finora
- Amines Ic19770Documento6 pagineAmines Ic19770Satendra KumarNessuna valutazione finora
- Bahan Ajar AminaDocumento44 pagineBahan Ajar AminaAnindya Putri KurniasariNessuna valutazione finora
- A MineDocumento8 pagineA MineilencikNessuna valutazione finora
- Sri Arunodaya Degree & P.G College Amino AcidsDocumento12 pagineSri Arunodaya Degree & P.G College Amino AcidsrajnagpNessuna valutazione finora
- C9 AmineDocumento61 pagineC9 AmineNURHANNANI BINTI MOHD FAISALNessuna valutazione finora
- Actinide SeparationDocumento35 pagineActinide SeparationZain MSDNessuna valutazione finora
- AminaDocumento19 pagineAminaFachry GatesNessuna valutazione finora
- Organic 2 Chapter 1&2Documento94 pagineOrganic 2 Chapter 1&2bahru demekeNessuna valutazione finora
- Acids and BasesDocumento29 pagineAcids and BasesSara MolinaroNessuna valutazione finora
- Amines and Heterocycles Synthesis ReactionsDocumento37 pagineAmines and Heterocycles Synthesis ReactionsTiffany YehNessuna valutazione finora
- CHAPTER 8 EditedDocumento18 pagineCHAPTER 8 EditedSyafiqah SuhaimiNessuna valutazione finora
- Nitrocompounds - Amines. Diazo - and Azocompounds.Documento90 pagineNitrocompounds - Amines. Diazo - and Azocompounds.P RamakrishnaNessuna valutazione finora
- Hydrocarbon DerivativesDocumento10 pagineHydrocarbon DerivativesDee Olivar CamaongayNessuna valutazione finora
- Amine IDocumento13 pagineAmine IjohnsmithprayNessuna valutazione finora
- 12 Chemistry Notes ch13 Amines-1Documento8 pagine12 Chemistry Notes ch13 Amines-1mv7602456Nessuna valutazione finora
- Amines: Classification, Properties and ReactionsDocumento12 pagineAmines: Classification, Properties and ReactionsNavya NitashNessuna valutazione finora
- Chapter 1amine Student Hand OutDocumento67 pagineChapter 1amine Student Hand OuthazimNessuna valutazione finora
- Chemical Properties of Amino AcidsDocumento5 pagineChemical Properties of Amino AcidsLERMA, Cheenee B.Nessuna valutazione finora
- Amines & Amides: Grade 12 ChemistryDocumento45 pagineAmines & Amides: Grade 12 ChemistryfhdlakNessuna valutazione finora
- AminesDocumento13 pagineAminesSohamNessuna valutazione finora
- Reactions of AmidesDocumento4 pagineReactions of AmidesNdiemfor Shanel SirriNessuna valutazione finora
- Module 5 - XII NEET - ChemistryDocumento128 pagineModule 5 - XII NEET - ChemistryGhanshyam MatlaneNessuna valutazione finora
- Properties and Reactions of Carboxylic Acid DerivativesDocumento32 pagineProperties and Reactions of Carboxylic Acid DerivativesAdi Kurniawan EffendiNessuna valutazione finora
- Andi Ria Indahsari - 1913442004 Paper AmineDocumento12 pagineAndi Ria Indahsari - 1913442004 Paper AmineAndi RiaNessuna valutazione finora
- Chemistry R&D (Notes)Documento11 pagineChemistry R&D (Notes)Low Kit Ying100% (1)
- Lecture 7-ProteinsDocumento70 pagineLecture 7-ProteinsRoxanne SalvageNessuna valutazione finora
- Amines: H C N H CH CH EthylmethylamineDocumento19 pagineAmines: H C N H CH CH EthylmethylaminetrangNessuna valutazione finora
- Metal HydridesDocumento22 pagineMetal HydridesPranay Poloju100% (1)
- General Chemistry I M2W4Documento5 pagineGeneral Chemistry I M2W4Warley JabelNessuna valutazione finora
- Carboxylic Acid Derivatives Experiment (Organic ChemistryDocumento9 pagineCarboxylic Acid Derivatives Experiment (Organic ChemistryJashan LigNessuna valutazione finora
- Class - 12 Chemistry - AminesDocumento34 pagineClass - 12 Chemistry - AminesAnonymous RuslwNZZlNessuna valutazione finora
- Hsslive XII Chemistry Amines NoteDocumento4 pagineHsslive XII Chemistry Amines Notetrendzz youtuberNessuna valutazione finora
- Amines: + HCL RC O N R' H R'NH + RC O CLDocumento7 pagineAmines: + HCL RC O N R' H R'NH + RC O CLCamille AdleNessuna valutazione finora
- Local Anesthetics SarDocumento15 pagineLocal Anesthetics SarSomnath MondalNessuna valutazione finora
- Unit-Ii: Aromatic AminesDocumento17 pagineUnit-Ii: Aromatic Aminesvarunn3110Nessuna valutazione finora
- 23 AminesDocumento52 pagine23 AminesGoka Agbesi GokaNessuna valutazione finora
- Amides: Classification, Nomenclature, Properties and ApplicationsDocumento21 pagineAmides: Classification, Nomenclature, Properties and ApplicationsSheeza ChaudaryNessuna valutazione finora
- Properties of Acids and BasesDocumento5 pagineProperties of Acids and BasesSmrita SinghNessuna valutazione finora
- Chapter 2 Acids, Bases and SaltsDocumento5 pagineChapter 2 Acids, Bases and SaltsDileep Singh ParmarNessuna valutazione finora
- L7 Amines and Amino AcidsDocumento16 pagineL7 Amines and Amino AcidsCheng FuNessuna valutazione finora
- Schaum's Easy Outline of Organic Chemistry, Second EditionDa EverandSchaum's Easy Outline of Organic Chemistry, Second EditionValutazione: 3.5 su 5 stelle3.5/5 (2)
- The Organometallic Chemistry of N-heterocyclic CarbenesDa EverandThe Organometallic Chemistry of N-heterocyclic CarbenesNessuna valutazione finora
- Things You Should Know For: Design, Analysis and Planning: VariablesDocumento7 pagineThings You Should Know For: Design, Analysis and Planning: VariablesAbbas HaiderNessuna valutazione finora
- Physics TipsDocumento19 paginePhysics TipsAbbas HaiderNessuna valutazione finora
- Maths TipsDocumento2 pagineMaths TipsAbbas HaiderNessuna valutazione finora
- AS Level Chemistry Practical Paper 3: TitrationDocumento8 pagineAS Level Chemistry Practical Paper 3: TitrationNabindra RuwaliNessuna valutazione finora
- 20 - Further Energy ChangesDocumento1 pagina20 - Further Energy ChangesAbbas HaiderNessuna valutazione finora
- Addition and condensation polymers: key reactions and structuresDocumento1 paginaAddition and condensation polymers: key reactions and structuresAbbas HaiderNessuna valutazione finora
- 30 - Organic Synthesis and AnalysisDocumento1 pagina30 - Organic Synthesis and AnalysisAbbas HaiderNessuna valutazione finora
- Studying Tips: You Can Download My Notes HereDocumento7 pagineStudying Tips: You Can Download My Notes HereCh'ng Lee KeeNessuna valutazione finora
- 9701 Chemistry Paper 5 NotesDocumento4 pagine9701 Chemistry Paper 5 NotesTanvir Ahmed Mazumder75% (4)
- Sr. No. Reaction Reagent Condition Mechanism Example NoteDocumento3 pagineSr. No. Reaction Reagent Condition Mechanism Example NoteAbbas HaiderNessuna valutazione finora
- 25 - Arenes and PhenolsDocumento2 pagine25 - Arenes and PhenolsAbbas HaiderNessuna valutazione finora
- Carboxylic Acid Derivatives: Acyl Chlorides and PolyestersDocumento1 paginaCarboxylic Acid Derivatives: Acyl Chlorides and PolyestersAbbas HaiderNessuna valutazione finora
- 23 - ElectrochemistryDocumento1 pagina23 - ElectrochemistryAbbas HaiderNessuna valutazione finora
- 29 Techniques for Analyzing CompoundsDocumento1 pagina29 Techniques for Analyzing CompoundsAbbas HaiderNessuna valutazione finora
- 22 - Quantitative EquilibriaDocumento1 pagina22 - Quantitative EquilibriaAbbas HaiderNessuna valutazione finora
- 21 - Quantitative KineticsDocumento1 pagina21 - Quantitative KineticsAbbas HaiderNessuna valutazione finora
- 4 - DynamicsDocumento2 pagine4 - DynamicsAbbas HaiderNessuna valutazione finora
- The 3d Block Elements: Properties and Complex Ion FormationDocumento1 paginaThe 3d Block Elements: Properties and Complex Ion FormationAbbas HaiderNessuna valutazione finora
- 1 - Physical Quantities and UnitsDocumento2 pagine1 - Physical Quantities and UnitsAbbas HaiderNessuna valutazione finora
- h2 Physics DefinitionsDocumento7 pagineh2 Physics DefinitionsSyed Osama HussainNessuna valutazione finora
- Measurement Techniques and Their AccuracyDocumento1 paginaMeasurement Techniques and Their AccuracyAbbas HaiderNessuna valutazione finora
- 3 - KinematicsDocumento1 pagina3 - KinematicsAbbas HaiderNessuna valutazione finora
- Physics Practical Tips PDFDocumento4 paginePhysics Practical Tips PDFAbbas HaiderNessuna valutazione finora
- Physics Equations GuideDocumento15 paginePhysics Equations GuidesourceofnotesNessuna valutazione finora
- 1.4.3 The Processor's Instruction SetDocumento8 pagine1.4.3 The Processor's Instruction SetAbbas HaiderNessuna valutazione finora
- 1.3.1 Logic GatesDocumento8 pagine1.3.1 Logic GatesismaelNessuna valutazione finora
- DDDocumento21 pagineDDSyed HaiderNessuna valutazione finora
- P3 Revision SummariesDocumento15 pagineP3 Revision SummariesAbbas HaiderNessuna valutazione finora
- 1.4.4 Assembly LanguageDocumento6 pagine1.4.4 Assembly LanguageAbbas Haider100% (1)