Documenti di Didattica
Documenti di Professioni
Documenti di Cultura
Functions: One-to-One, Onto, Both
Caricato da
Deby BermudezTitolo originale
Copyright
Formati disponibili
Condividi questo documento
Condividi o incorpora il documento
Hai trovato utile questo documento?
Questo contenuto è inappropriato?
Segnala questo documentoCopyright:
Formati disponibili
Functions: One-to-One, Onto, Both
Caricato da
Deby BermudezCopyright:
Formati disponibili
One-to-one and Onto Functions
Remember that a function is a set of ordered pairs in which no two ordered
pairs that have the same first component have different second
components. This means that given any x, there is only one y that can be
paired with that x.
Onto Function
A function f from A to B is called onto if for all b in B there is
an a in Asuch that f (a) = b. All elements in B are used.
Such functions are referred to as surjective.
"Onto"
NOT "Onto"
(all elements in B are used)
(the 8 and 1 in Set B are not used)
By definition, to determine if a function is ONTO, you need to know
information about both set A and B.
When working in the coordinate plane, the sets A and B may both become the Real numbers, stat
as
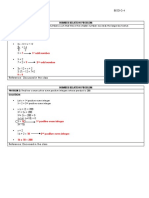
XAMPLE 1: Is f (x) = 3x - 4 onto where
?
This function (a straight line)
isONTO.
As you progress along the line,
every possible y-value is used.
In addition, this straight line also possesses the
property that each x-value has one uniqueyvalue that is not used by any other x-element.
This characteristic is referred to as being oneto-one.
EXAMPLE 2: Is g (x) = x - 2 onto where
This function (a parabola) is
NOT ONTO.
Values less than -2 on the y-axis are never
used. Since possible y-values belong to the
set of ALL Real numbers, not ALL
possibley-values are used.
In addition, this parabola also has y-values
that are paired with more than one x-value,
such as (3, 7) and (-3, 7).
This function will not be one-to-one.
EXAMPLE 3: Is g (x) = x - 2 onto where
?
If set B is redefined to be
, ALL of the possible y-values are now used, and
function g (x) (under these conditions) is ONTO.
One-to-One Function
A function f from A to B is called one-to-one (or 1-1) if whenever
f (a) = f (b) then a = b. No element of B is the image of more
than one element in A.
In a one-to-one function, given any y there is only one x that can be paired with the
given y. Such functions are referred to as injective.
"One-to-One"
NOT "One-to-One"
EXAMPLE 1: Is f (x) = x one-to-one where
?
This function is One-to-One.
This cubic function possesses the property that
each x-value has one unique y-value that is not used
by any other x-element. This characteristic is
referred to as being 1-1.
Also, in this function, as you progress along the
graph, every possible y-value is used, making the
function onto.
EXAMPLE 2: Is g (x) = | x - 2 | one-to-one where
This function is
NOT One-to-One.
This absolute value function has y-values that
are paired with more than one x-value, such
as (4, 2) and (0, 2).
This function is not one-to-one.
In addition, values less than 0 on the y-axis
are never used, making the function NOT
onto.
EXAMPLE 3: Is g (x) = | x - 2 | one-to-one where
With set B redefined to be
, function g (x) will still be NOT one-to-one, but it will now be ON
BOTH
Functions can be both one-to-one and onto.
Such functions are called bijective.
Bijections are functions that are both injective and surjective.
"Both"
NOT "Both" - not Onto
Examples of functions that are BOTH onto and one-to-one
can be seen in each of the categories above.
Potrebbero piacerti anche
- MATH147 Calculus Integration Substitution TechniquesDocumento9 pagineMATH147 Calculus Integration Substitution TechniquesKotori100% (1)
- Set TheoryDocumento114 pagineSet TheoryNeri Sangalang0% (1)
- Algebraic SubstitutionDocumento6 pagineAlgebraic SubstitutionIchiroue Whan GNessuna valutazione finora
- Elliptic Geometry Concepts and TheoremsDocumento5 pagineElliptic Geometry Concepts and Theoremsrenzy3polaron3baylosNessuna valutazione finora
- Differential EquationsDocumento180 pagineDifferential EquationsTrishaNessuna valutazione finora
- L4 - Application of Indefinite IntegralDocumento7 pagineL4 - Application of Indefinite IntegralJOHN RafaelNessuna valutazione finora
- Write An Equation To Represent The Function From The Following Table of ValuesDocumento10 pagineWrite An Equation To Represent The Function From The Following Table of ValuesErnie Caracas LahaylahayNessuna valutazione finora
- Math 101 Unit 1 Lesson 1Documento29 pagineMath 101 Unit 1 Lesson 1Paul John PanganibanNessuna valutazione finora
- CALCULUS 2 - MODULE 1 - Lessons 1 4Documento10 pagineCALCULUS 2 - MODULE 1 - Lessons 1 4Kim Opena100% (1)
- Chapter TestDocumento22 pagineChapter TestSheila Mae AsuelaNessuna valutazione finora
- r2 - Lecture - CO2 - Math 21-1Documento38 paginer2 - Lecture - CO2 - Math 21-1Benmar N. OcolNessuna valutazione finora
- Mathematical Language and SymbolsDocumento18 pagineMathematical Language and SymbolsMaricel CarreonNessuna valutazione finora
- Number Theory Chapter: Integers, Divisors, and Linear CombinationsDocumento23 pagineNumber Theory Chapter: Integers, Divisors, and Linear CombinationsMyla Velasco100% (1)
- Logic 2Documento39 pagineLogic 2Kim Abigelle GarciaNessuna valutazione finora
- 9.4 Integration With Trigonometric FunctionsDocumento17 pagine9.4 Integration With Trigonometric FunctionsHin Wa LeungNessuna valutazione finora
- Functions & Limits ConceptsDocumento23 pagineFunctions & Limits ConceptsJeriza AquinoNessuna valutazione finora
- Modern Geometry Chapter IVDocumento19 pagineModern Geometry Chapter IVEdelmar BenosaNessuna valutazione finora
- 2.4 Integrands Involving Quadratic ExpressionsDocumento2 pagine2.4 Integrands Involving Quadratic Expressionscory kurdapyaNessuna valutazione finora
- Finite Geometry of YoungDocumento11 pagineFinite Geometry of YoungLEIZEL MANAGATNessuna valutazione finora
- Integration by PartsDocumento12 pagineIntegration by PartsAlbert AwoponeNessuna valutazione finora
- Integration RulesDocumento3 pagineIntegration Rulesamitdeo99Nessuna valutazione finora
- Module 1 Lesson 6Documento18 pagineModule 1 Lesson 6alex medina100% (1)
- BSEE Calculus ReviewDocumento13 pagineBSEE Calculus ReviewRonalyn ManzanoNessuna valutazione finora
- Actual and Approximate TimeDocumento2 pagineActual and Approximate TimeAriane Malou GorreonNessuna valutazione finora
- Number RelationDocumento5 pagineNumber RelationFreshDianne Mhilkie SilvosaNessuna valutazione finora
- SYSTEM OF NON LINEAR EQUATION Grade 11Documento6 pagineSYSTEM OF NON LINEAR EQUATION Grade 11ha hakdogNessuna valutazione finora
- Circular Functions PDFDocumento10 pagineCircular Functions PDFMaze GomezNessuna valutazione finora
- Elimination of Arbitrary ConstantsDocumento4 pagineElimination of Arbitrary ConstantsShirsendu Mondol100% (1)
- Trigonometric IntegralsDocumento14 pagineTrigonometric IntegralsStevenzel Eala EstellaNessuna valutazione finora
- Math111 Limits and ContinuityDocumento23 pagineMath111 Limits and ContinuityAbdul Halil AbdullahNessuna valutazione finora
- Calculus I: Assignment Problems Applications of DerivativesDocumento37 pagineCalculus I: Assignment Problems Applications of DerivativesИРадојичићNessuna valutazione finora
- PUP Quezon Math Language Sets Logic AssignmentDocumento3 paginePUP Quezon Math Language Sets Logic Assignmentacurvz2005100% (2)
- Lesson 2.3 Standard Normal Curve and Z ScoresDocumento18 pagineLesson 2.3 Standard Normal Curve and Z ScoresKlarence Timothy Pineda BundangNessuna valutazione finora
- Lesson 5:: GI - Example Case 1Documento5 pagineLesson 5:: GI - Example Case 1Keith Syrell AzucenaNessuna valutazione finora
- Learn the Fundamentals of Geometry's Axiomatic SystemDocumento7 pagineLearn the Fundamentals of Geometry's Axiomatic SystemRovelyn PiamonteNessuna valutazione finora
- Module 8 - Truth TablesDocumento8 pagineModule 8 - Truth TablesAngelica CardañoNessuna valutazione finora
- Measures of Central Tendency (Finals)Documento18 pagineMeasures of Central Tendency (Finals)Edesa JarabejoNessuna valutazione finora
- (MOD) 02 Vectors and ScalarsDocumento11 pagine(MOD) 02 Vectors and ScalarsShydene SalvadorNessuna valutazione finora
- Statistical Notations and OperationsDocumento9 pagineStatistical Notations and OperationsKrizell Jane Ojarliza Acha100% (1)
- The Earliest Concepts On Mathematics That That GainedDocumento5 pagineThe Earliest Concepts On Mathematics That That GainedRodelNessuna valutazione finora
- Operations With FunctionsDocumento6 pagineOperations With FunctionsKez MaxNessuna valutazione finora
- Mode For Grouped DataDocumento37 pagineMode For Grouped DataTheKnow04Nessuna valutazione finora
- Integration by Miscellaneous SubstitutionDocumento8 pagineIntegration by Miscellaneous SubstitutionAlwin Palma jrNessuna valutazione finora
- FINITE GEOMETRIES OF FANO, YOUNG, PAPPUS AND DESARGUESDocumento15 pagineFINITE GEOMETRIES OF FANO, YOUNG, PAPPUS AND DESARGUESAndrie Dagta ConsultaNessuna valutazione finora
- Detailed Lesson PlanDocumento11 pagineDetailed Lesson PlanAyesha TrinidadNessuna valutazione finora
- GEC05 MODULE 1 Lesson 1&2Documento14 pagineGEC05 MODULE 1 Lesson 1&2Arohalism PHNessuna valutazione finora
- Preliminary Exam in College AlgebraDocumento1 paginaPreliminary Exam in College AlgebraAllan Victoriano Baritua100% (1)
- Section 13 Homomorphisms: HomomorphismDocumento8 pagineSection 13 Homomorphisms: HomomorphismErica CanonNessuna valutazione finora
- Lesson 3 Continuity of FunctionsDocumento6 pagineLesson 3 Continuity of FunctionsLarisha Jan PomboNessuna valutazione finora
- Lesson 13 - Logic Statements and Quantifiers PDFDocumento2 pagineLesson 13 - Logic Statements and Quantifiers PDFPeter EcleviaNessuna valutazione finora
- MATHENG4 Differential EquationsDocumento66 pagineMATHENG4 Differential EquationsJed Guzarem YbañezNessuna valutazione finora
- Abstract AlgebraDocumento47 pagineAbstract AlgebraMedardo BombitaNessuna valutazione finora
- Logic 4Documento24 pagineLogic 4Kim Abigelle GarciaNessuna valutazione finora
- Sets, Functions, and Binary Operations PDFDocumento23 pagineSets, Functions, and Binary Operations PDF구해본Nessuna valutazione finora
- Solid Geometry: Certc - DavaoDocumento68 pagineSolid Geometry: Certc - DavaochristineNessuna valutazione finora
- Math - Grade 9 - Q2 - WEEK 4 - Module5.SIMPLIFIES EXPRESSIONS WITH Rational Expression RATIONALEX and Vice VerDocumento15 pagineMath - Grade 9 - Q2 - WEEK 4 - Module5.SIMPLIFIES EXPRESSIONS WITH Rational Expression RATIONALEX and Vice VerJonathan OlegarioNessuna valutazione finora
- Engineering Mathematics I FunctionDocumento10 pagineEngineering Mathematics I FunctionRavi RanjanNessuna valutazione finora
- Differential Calculus Guide: Limits, Derivatives, Maxima & MinimaDocumento85 pagineDifferential Calculus Guide: Limits, Derivatives, Maxima & MinimaParminder singh parmarNessuna valutazione finora
- Post Class Reading Week+3Documento11 paginePost Class Reading Week+3Shaheen Ali YarNessuna valutazione finora
- RA Tut 1 (Edited) - 2022-23Documento4 pagineRA Tut 1 (Edited) - 2022-23Priyajit DebnathNessuna valutazione finora
- Mathematical Foundation of Computer Science Exam QuestionsDocumento5 pagineMathematical Foundation of Computer Science Exam Questionssathiya rajNessuna valutazione finora
- Mappings and Functions BestDocumento22 pagineMappings and Functions BestBalogun AbimbolaNessuna valutazione finora
- School of Mathematical Sciences MAT 3044 Discrete MathematicsDocumento20 pagineSchool of Mathematical Sciences MAT 3044 Discrete MathematicsThalika RuchaiaNessuna valutazione finora
- Functions As RelationsDocumento4 pagineFunctions As RelationsAlaz FofanaNessuna valutazione finora
- Logica Matematica Parte 1Documento360 pagineLogica Matematica Parte 1vandars100% (3)
- Design Method For Knowledge Base Systems in Education Using COKB-ONTDocumento7 pagineDesign Method For Knowledge Base Systems in Education Using COKB-ONTSam NamNessuna valutazione finora
- (Graduate Texts in Mathematics 12) Richard Beals (Auth.)-Advanced Mathematical Analysis_ Periodic Functions and Distributions, Complex Analysis, Laplace Transform and Applications-Springer-Verlag NewDocumento241 pagine(Graduate Texts in Mathematics 12) Richard Beals (Auth.)-Advanced Mathematical Analysis_ Periodic Functions and Distributions, Complex Analysis, Laplace Transform and Applications-Springer-Verlag NewClaudio Ramón Rodriguez Mondragón100% (1)
- ASSIGNMENT # A Functions Enthuse Student Copy 230426 091240Documento7 pagineASSIGNMENT # A Functions Enthuse Student Copy 230426 091240priyanshu rawatNessuna valutazione finora
- Functional Equations in Mathematical Olympiads (2017 - 2018) Problems and Solutions (Vol. I PDFDocumento175 pagineFunctional Equations in Mathematical Olympiads (2017 - 2018) Problems and Solutions (Vol. I PDFbooby fischer100% (4)
- MC0082 - Theory of Computer ScienceDocumento235 pagineMC0082 - Theory of Computer SciencePurushottam KumarNessuna valutazione finora
- Linear Transformations and Matrix RepresentationsDocumento4 pagineLinear Transformations and Matrix RepresentationsCarlo KaramNessuna valutazione finora
- Abstract Algebra Problem Set SolutionsDocumento4 pagineAbstract Algebra Problem Set SolutionsOutworld DevourerNessuna valutazione finora
- Invit To Real Analysis PDFDocumento318 pagineInvit To Real Analysis PDFcarolina100% (3)
- Lecture Note 2033 Full VersionDocumento43 pagineLecture Note 2033 Full VersionWeilung TinNessuna valutazione finora
- Probabilty Notes at IITDocumento154 pagineProbabilty Notes at IITrapsjadeNessuna valutazione finora
- Introduction To Mathematical AnalysisDocumento141 pagineIntroduction To Mathematical AnalysisDuende6850% (4)
- The Function of Composition and InverseDocumento20 pagineThe Function of Composition and InversenormasulasaNessuna valutazione finora
- Lie Groups and Lie Algebras NotesDocumento150 pagineLie Groups and Lie Algebras NotesAlejandro GastonNessuna valutazione finora
- Synopsis - Grade 12 Math Part I: Chapter 1: Relations and FunctionsDocumento24 pagineSynopsis - Grade 12 Math Part I: Chapter 1: Relations and FunctionsDayallini WinxNessuna valutazione finora
- Functions - Group 2Documento26 pagineFunctions - Group 2Annjanah AsilomNessuna valutazione finora
- Wa0010.Documento192 pagineWa0010.IbinNessuna valutazione finora
- Lecturenote 418728295text Book of Transformation GeometryDocumento233 pagineLecturenote 418728295text Book of Transformation GeometryAbenezer EndaleNessuna valutazione finora
- Assignment CLO 1: Relation, Function, and Recurrence: Discrete Mathematics (CII1G3)Documento10 pagineAssignment CLO 1: Relation, Function, and Recurrence: Discrete Mathematics (CII1G3)maulanbach riburaneNessuna valutazione finora
- UCF Computer Science Foundation Exam Study PlanDocumento17 pagineUCF Computer Science Foundation Exam Study Planmagicmindman100% (1)
- Introduction To CalculusDocumento22 pagineIntroduction To CalculusPeter HajduNessuna valutazione finora
- MATH 220 homework bijection proofsDocumento5 pagineMATH 220 homework bijection proofsOscar Alarcon CelyNessuna valutazione finora
- Lecture NoteDocumento135 pagineLecture NoteLoh Jun XianNessuna valutazione finora