Documenti di Didattica
Documenti di Professioni
Documenti di Cultura
Eureka Math Grade 5 Module 2 Tips For Parents
Caricato da
api-3274226470 valutazioniIl 0% ha trovato utile questo documento (0 voti)
154 visualizzazioni2 pagineTitolo originale
eureka math grade 5 module 2 tips for parents
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Formati disponibili
PDF, TXT o leggi online da Scribd
Condividi questo documento
Condividi o incorpora il documento
Hai trovato utile questo documento?
Questo contenuto è inappropriato?
Segnala questo documentoCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Formati disponibili
Scarica in formato PDF, TXT o leggi online su Scribd
0 valutazioniIl 0% ha trovato utile questo documento (0 voti)
154 visualizzazioni2 pagineEureka Math Grade 5 Module 2 Tips For Parents
Caricato da
api-327422647Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Formati disponibili
Scarica in formato PDF, TXT o leggi online su Scribd
Sei sulla pagina 1di 2
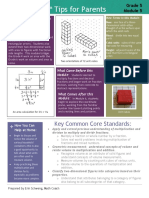
Eureka Math Tips for Parents
Multiplying and
Dividing Whole
Numbers and Decimals
Thinking mathematically is
hard but important work!
Estimate: Approximation of
the value of a quantity or
number
What Came Before this
Module: We worked very hard
What Comes After this
Module: We will begin work
with the base-10 place value
system
Become familiar with
the area model, a
different method of
multiplying than you
may have learned
Continue to review the
place value system with
your student
Discuss mathematical
patterns, such as 5 x 9,
5 x 90, 50 x 90, 50 x
900, etc.
Decimal: A fraction whose
denominator is a power of ten
Equation: A statement that
the values of two expressions
are equal
to understand the values of
numbers on the place value
chart.
you can
+ How
help at home:
Key Words to Know
Decimal Fraction: A proper
fraction whose denominator is
a power of ten
In this module, we will be
building up our knowledge of
first multiplication and then
division. We will start with
whole numbers and then move to
decimals as we practice different
ways to model these operations.
Sample area model of
multiplication for 64 x 73:
Grade 5
Module 2
Product: The result of a
multiplication
Quotient: The result of
dividing one quantity by
another
Remainder: The number left
over when one integer is divided
by another
Unit Form: Place value
counting, e.g., 34 is stated as
3 tens 4 ones
Key Common Core Standards:
Write and interpret numerical expressions, e.g., Add
8 and 7, then multiply by 2 is represented as 2 x (8 +
7)
Perform operations with multi-digit whole numbers
and with decimals to the hundredths, e.g., 46 x 72, 3.1
x 33
Convert like measurement units within a given
measurement system, e.g., 5 cm is 0.05 m
Prepared by Erin Schweng, Math Coach
Eureka Math, A Story of Units
Grade 5
Module 2
Spotlight on Math
Models:
Tape Diagrams
You will often see
this mathematical
representation in
A Story of Units.
A Story of Units has several key mathematical models
that will be used throughout a students elementary years.
The tape diagram is a powerful model that students can use to solve various kinds
of problems. In second grade, you will often see this model as an aid to addition and
subtraction problems. Tape diagrams are also called bar models and consist of a
simple bar drawing that students make and adjust to fit a word problem. They then
use the drawing to discuss and solve the problem.
As students move through the grades, tape diagrams provide an essential bridge to
algebra. Below is a sample word problem from Module 2 solved using a tape diagram
to show the parts of the problem.
Sample Problem from Module 2:
(Example taken from Lesson 3, Module 2)
Robin is 11 years old. Her mother,
Gwen, is 2 years more than 3
times Robins age. How old is
Gwen?
For more information visit commoncore.org
Potrebbero piacerti anche
- A Model Unit For Grade 3: Attracting and Repelling: Connecting with Canadians, Forces That Attract and RepelDa EverandA Model Unit For Grade 3: Attracting and Repelling: Connecting with Canadians, Forces That Attract and RepelNessuna valutazione finora
- Eureka Math Grade 5 Module 3 Parent Tip Sheet 1Documento2 pagineEureka Math Grade 5 Module 3 Parent Tip Sheet 1api-326893495Nessuna valutazione finora
- Eureka Math Grade 5 Module 5 Parent Tip SheetDocumento2 pagineEureka Math Grade 5 Module 5 Parent Tip Sheetapi-326893495Nessuna valutazione finora
- Eureka Math Grade 5 Module 6 Parent Tip SheetDocumento2 pagineEureka Math Grade 5 Module 6 Parent Tip Sheetapi-326893495100% (1)
- Eureka Math Grade 5 Module 4 Parent Tip SheetDocumento2 pagineEureka Math Grade 5 Module 4 Parent Tip Sheetapi-326893495Nessuna valutazione finora
- Eureka Math Grade 7: Teacher EditionDocumento232 pagineEureka Math Grade 7: Teacher EditionMICHAEL USTARENessuna valutazione finora
- As TRC1 AB U2 FlashcardsDocumento6 pagineAs TRC1 AB U2 Flashcardsalitasaavedra23Nessuna valutazione finora
- Little GorillaDocumento6 pagineLittle GorillaGiovanna Mariel PirisNessuna valutazione finora
- Vocabulary Ladders - Grade 6 - Showing InterestDocumento6 pagineVocabulary Ladders - Grade 6 - Showing InterestfairfurNessuna valutazione finora
- Assessments and Inventories WTWDocumento5 pagineAssessments and Inventories WTWapi-259640817Nessuna valutazione finora
- Bar Model JuniorDocumento59 pagineBar Model JuniorptbestariNessuna valutazione finora
- ACT 数学难题集标题Documento205 pagineACT 数学难题集标题o100% (1)
- FantasticPhonics Book 39Documento6 pagineFantasticPhonics Book 39BelmaKNessuna valutazione finora
- Numeracy Professional Development ProjectsDocumento57 pagineNumeracy Professional Development ProjectsS TANCREDNessuna valutazione finora
- Group 7 J Phonics Decodable Reading Cards - Group 7Documento11 pagineGroup 7 J Phonics Decodable Reading Cards - Group 7Prabuddh VermaNessuna valutazione finora
- Developing Number Sense and Early Number Concepts: Edn 322 HoDocumento12 pagineDeveloping Number Sense and Early Number Concepts: Edn 322 HoAnonymous GpBfdWD9Nessuna valutazione finora
- Lesson 4 Adjectives - OnealDocumento2 pagineLesson 4 Adjectives - Onealapi-122378129Nessuna valutazione finora
- Phonics Activity Mat 2 Resource Pack English Ver 5Documento12 paginePhonics Activity Mat 2 Resource Pack English Ver 5GuenNessuna valutazione finora
- 10 Things To Do With A Book - Primary Learning ResourceDocumento13 pagine10 Things To Do With A Book - Primary Learning ResourceElena FragkakiNessuna valutazione finora
- Math Word Problems Extension 31 16Documento2 pagineMath Word Problems Extension 31 16woof1800Nessuna valutazione finora
- 6+1 Traits Grading RubricDocumento1 pagina6+1 Traits Grading RubricKorey BradleyNessuna valutazione finora
- Eureka Math™ Homework Helper 2015-2016 Grade 5 Module 2 (PDFDrive)Documento56 pagineEureka Math™ Homework Helper 2015-2016 Grade 5 Module 2 (PDFDrive)Băng Tâm NgôNessuna valutazione finora
- 5 2 Simplifying FractionsDocumento1 pagina5 2 Simplifying Fractionsapi-325053822Nessuna valutazione finora
- Big Number Crunch Addition: Step 1Documento5 pagineBig Number Crunch Addition: Step 1kevintconlonNessuna valutazione finora
- Math g6 m1 Topic A Lesson 1 Student PDFDocumento4 pagineMath g6 m1 Topic A Lesson 1 Student PDFChong Xue ErNessuna valutazione finora
- AustralianationalcurriculumDocumento56 pagineAustralianationalcurriculumapi-355090152Nessuna valutazione finora
- Words Their Way Middle School Collaborative Group Agenda 2fnotes 2016-2017Documento61 pagineWords Their Way Middle School Collaborative Group Agenda 2fnotes 2016-2017api-371911756Nessuna valutazione finora
- Math Crossword PuzzleDocumento1 paginaMath Crossword PuzzleNour HlwaniNessuna valutazione finora
- Regrouping ConceptDocumento11 pagineRegrouping ConceptVishalakshi RajendranNessuna valutazione finora
- Math 4 Unit 1 Unit 1 Interim Assessment and Practice ResourcesDocumento6 pagineMath 4 Unit 1 Unit 1 Interim Assessment and Practice ResourcesVân Nguyễn0% (1)
- English Planning Template-D Cherry-Cabramurrah PSDocumento1 paginaEnglish Planning Template-D Cherry-Cabramurrah PSS TANCRED100% (1)
- The Ultimate Guide to Data CleaningDocumento66 pagineThe Ultimate Guide to Data CleaningAntares Orion100% (1)
- Use The Chart To The Right To Answer Each Question. Show Your Work. Item PointsDocumento4 pagineUse The Chart To The Right To Answer Each Question. Show Your Work. Item PointsririNessuna valutazione finora
- Syllabication TipsDocumento3 pagineSyllabication TipsVimal NairNessuna valutazione finora
- PDF Ebooks - Org Ku 11027Documento10 paginePDF Ebooks - Org Ku 11027linguistAiaa100% (1)
- NACA 2612 Airfoil Thin TheoryDocumento2 pagineNACA 2612 Airfoil Thin TheorybatmanbittuNessuna valutazione finora
- Hiebert Pearson Taylor Richardson Paris 1998 Every Child A ReaderDocumento57 pagineHiebert Pearson Taylor Richardson Paris 1998 Every Child A ReaderDiane RodrigoNessuna valutazione finora
- Study On Vocabulary GapDocumento7 pagineStudy On Vocabulary GapMuhamad FirdausNessuna valutazione finora
- AP Statistics Textbook ListsDocumento1 paginaAP Statistics Textbook ListskunichiwaNessuna valutazione finora
- Composite Writing MatrixDocumento11 pagineComposite Writing MatrixmrkballNessuna valutazione finora
- PBL CH 9Documento2 paginePBL CH 9api-267917250Nessuna valutazione finora
- Homeless Bird, Lesson 1Documento3 pagineHomeless Bird, Lesson 1sarah100% (1)
- Workbook Level 3 Week 10Documento16 pagineWorkbook Level 3 Week 10Maryna PolishchukNessuna valutazione finora
- Fraction FactsDocumento2 pagineFraction FactsSanjay Kumar100% (1)
- Six Traits of Writing HandoutDocumento14 pagineSix Traits of Writing HandoutCheryl Dick100% (4)
- Refresh Pack: Year 2Documento56 pagineRefresh Pack: Year 2Meliza Jane Sabido-NanoNessuna valutazione finora
- Two Digit Fact FamiliesDocumento14 pagineTwo Digit Fact Familiesapi-345837027Nessuna valutazione finora
- What Does Not Belong 2Documento2 pagineWhat Does Not Belong 2Dusan TrbojevicNessuna valutazione finora
- FractionsDocumento11 pagineFractionsapi-294491980Nessuna valutazione finora
- Cuisenaire Rod Blog PPDocumento42 pagineCuisenaire Rod Blog PPisabell2booNessuna valutazione finora
- Pumpkin CircleDocumento9 paginePumpkin Circleapi-378725731Nessuna valutazione finora
- Kindergarten Spelling S SDocumento6 pagineKindergarten Spelling S Sapi-305461058Nessuna valutazione finora
- Find Perimeter WKSHTDocumento1 paginaFind Perimeter WKSHTMonica HenryNessuna valutazione finora
- WS Cornell NotesDocumento2 pagineWS Cornell NotesPaulNessuna valutazione finora
- Multiplication Problems ArraysDocumento4 pagineMultiplication Problems Arraysapi-395353190Nessuna valutazione finora
- Grade 4 Math MapDocumento1 paginaGrade 4 Math Mapapi-294862378Nessuna valutazione finora
- 8255a 3rd Grade Math Quiz 1 I Partial 2021Documento5 pagine8255a 3rd Grade Math Quiz 1 I Partial 2021Luatany NolascoNessuna valutazione finora
- Common Core Literacy for ELA, History/Social Studies, and the Humanities: Strategies to Deepen Content Knowledge (Grades 6-12)Da EverandCommon Core Literacy for ELA, History/Social Studies, and the Humanities: Strategies to Deepen Content Knowledge (Grades 6-12)Nessuna valutazione finora
- 20132014parentguide Ela 5092013Documento6 pagine20132014parentguide Ela 5092013api-327422647Nessuna valutazione finora
- Grade 5 Module 6 Family LetterDocumento2 pagineGrade 5 Module 6 Family Letterapi-327422647Nessuna valutazione finora
- Eureka Mathtips For Parentsgrade 5 Module 4Documento2 pagineEureka Mathtips For Parentsgrade 5 Module 4api-327422647Nessuna valutazione finora
- Eureka Mathtips For Parentsgrade 5 Module 3Documento2 pagineEureka Mathtips For Parentsgrade 5 Module 3api-327422647Nessuna valutazione finora
- Math VocabularyDocumento3 pagineMath Vocabularyapi-263277852Nessuna valutazione finora
- Lesson Plan 2Documento41 pagineLesson Plan 2Fika Atina RizqianaNessuna valutazione finora
- (The Language of Literature) Roger Fowler (Auth.) - The Language of George Orwell-Macmillan Education UK (1995) PDFDocumento260 pagine(The Language of Literature) Roger Fowler (Auth.) - The Language of George Orwell-Macmillan Education UK (1995) PDFPetr Škaroupka100% (2)
- UNIT 9 - LESSON 1 - PART 2 - GrammarDocumento5 pagineUNIT 9 - LESSON 1 - PART 2 - GrammarponyoNessuna valutazione finora
- Error Analysis of Newman To Solve The Geometry Problem in Terms of Cognitive StyleDocumento4 pagineError Analysis of Newman To Solve The Geometry Problem in Terms of Cognitive Styledhanicore11Nessuna valutazione finora
- Gold Exp B1P U8 Skills Test ADocumento3 pagineGold Exp B1P U8 Skills Test APaulo NuñezNessuna valutazione finora
- Teacher S Resource Book Wonder 6 PDFDocumento129 pagineTeacher S Resource Book Wonder 6 PDFToñi García Hernández50% (2)
- 2018 Annual Report - Legal Council For Health JusticeDocumento30 pagine2018 Annual Report - Legal Council For Health JusticeLegal CouncilNessuna valutazione finora
- The Cultural Web: Mapping and Re-Mapping Organisational Culture: A Local Government ExampleDocumento12 pagineThe Cultural Web: Mapping and Re-Mapping Organisational Culture: A Local Government ExampleQuang Truong100% (1)
- 1 我的专业是土木工程Documento18 pagine1 我的专业是土木工程JasmineNessuna valutazione finora
- Psychosexual Service BookletDocumento28 paginePsychosexual Service Bookletgrtbags2302Nessuna valutazione finora
- Roxas EpotfolioDocumento47 pagineRoxas EpotfolioBSED-3A- John Rael RoxasNessuna valutazione finora
- ACT Nomination Guidelines January 2022 Canberra ResidentDocumento22 pagineACT Nomination Guidelines January 2022 Canberra ResidentRajeshNessuna valutazione finora
- Reputation Magazine 29, Michaelmas 2020Documento12 pagineReputation Magazine 29, Michaelmas 2020Sara MazzarellaNessuna valutazione finora
- Grammar Reference: Page 174-Lifestyle English For Work Socializing and TravelDocumento5 pagineGrammar Reference: Page 174-Lifestyle English For Work Socializing and TravelSamahNessuna valutazione finora
- Neela - NIPER GuwahatiDocumento19 pagineNeela - NIPER GuwahatiPalanisamy SelvamaniNessuna valutazione finora
- PQ June 2017Documento40 paginePQ June 2017MISODZI CHIBAKWENessuna valutazione finora
- CPM 1 - Fundamental Elements of Project ManagementDocumento22 pagineCPM 1 - Fundamental Elements of Project ManagementlukeNessuna valutazione finora
- A Psychosocial Approach to DesignDocumento96 pagineA Psychosocial Approach to DesignGanesan SolomonNessuna valutazione finora
- Opportunities and Obstacles1Documento24 pagineOpportunities and Obstacles1Mhing's Printing ServicesNessuna valutazione finora
- Medical Foods From Natural SourcesDocumento223 pagineMedical Foods From Natural Sourcestemp011Nessuna valutazione finora
- Essay 1Documento4 pagineEssay 1Andreita GonzalezNessuna valutazione finora
- The Enormous Crocodile: Alternative EndingsDocumento2 pagineThe Enormous Crocodile: Alternative EndingsRania FarranNessuna valutazione finora
- English graphic stimuli and writing guidelinesDocumento3 pagineEnglish graphic stimuli and writing guidelinesalvina_sumping0% (1)
- J218EMPLOYDocumento3 pagineJ218EMPLOYsyed saleh nasirNessuna valutazione finora
- Syllabus - Middle School WritingDocumento11 pagineSyllabus - Middle School Writingmrspercuoco100% (2)
- Cover Letter CitiDocumento11 pagineCover Letter CitiTheBusinessInsider100% (3)
- Activities Binder Assignment 1Documento3 pagineActivities Binder Assignment 1api-659087537Nessuna valutazione finora
- 03 - Billy Bunters Barring-OutDocumento103 pagine03 - Billy Bunters Barring-Outkalram420Nessuna valutazione finora
- Introduction To BQ2Documento10 pagineIntroduction To BQ2Emir KandemirNessuna valutazione finora
- District Health Management Information Systems (D-HMIS) - Tanzania - IICDDocumento4 pagineDistrict Health Management Information Systems (D-HMIS) - Tanzania - IICDAbebe BelachewNessuna valutazione finora