Documenti di Didattica
Documenti di Professioni
Documenti di Cultura
Mcmurry Oc8e Ev Ch09
Caricato da
MúslimÄhIslamCopyright
Formati disponibili
Condividi questo documento
Condividi o incorpora il documento
Hai trovato utile questo documento?
Questo contenuto è inappropriato?
Segnala questo documentoCopyright:
Formati disponibili
Mcmurry Oc8e Ev Ch09
Caricato da
MúslimÄhIslamCopyright:
Formati disponibili
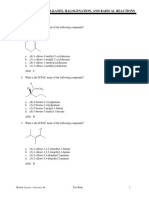
Chapter 9Alkynes: An Introduction to Organic Synthesis
SHORT ANSWER
Drawing Instructions: Draw structures corresponding to each of the given names.
1.
Draw: ethynylcyclopropane
ANS:
2.
Draw: 3,10-dimethyl-6-sec-butylcyclodecyne
ANS:
3.
Draw: 4-bromo-3,3-dimethyl-1-hexen-5-yne
ANS:
4.
Draw: acetylene
ANS:
IUPAC Naming Instructions: Provide proper IUPAC names.
5.
Name:
ANS:
4-methyl-2-heptyne
Alkynes: An Introduction to Organic Synthesis
6.
Name:
ANS:
1-ethynyl-2-methylcyclopentane
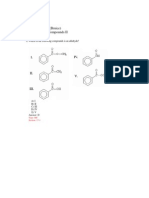
Exhibit 9-1
The compound below has been isolated from the safflower plant. Consider its structure to answer the
following question(s).
7.
Refer to Exhibit 9-1. What is the molecular formula for this natural product?
ANS:
C13H10
8.
Refer to Exhibit 9-1. What is the degree of unsaturation for this compound?
ANS:
We can arrive at the degree of unsaturation for a structure in two ways. Since we know that the degree of
unsaturation is the number of rings and/or multiple bonds in a compound, we can simply count them.
There are three double bonds (3 degrees) and three triple bonds (six degrees), so the degree of
unsaturation is 9.
We can verify this by using the molecular formula, C13H10, to calculate a degree of unsaturation. The
saturated 13-carbon compound should have the base formula C 13H28, so (28 10) 2 = 18 2 = 9.
Chapter 9
9.
Refer to Exhibit 9-1. Assign E or Z configuration to each of the double bonds in the compound.
ANS:
10.
Refer to Exhibit 9-1. Provide the name for this unusual natural product.
ANS:
(3E, 11E)-1,3,11-tridecatrien-5,7,9-triyne or (3E,11E)-trideca-1,3,11-trien-5,7,9-triyne
Exhibit 9-2
To answer the following question(s), consider the information below:
The heat of hydrogenation of 1,4-pentadiene is 254.4 kJ/mol. The heat of hydrogenation of 1-pentyne is
approximately 292.9 kJ/mol.
11.
Refer to Exhibit 9-2. Which structure is more stable, 1,4-pentadiene or 1-pentyne? Briefly explain
your answer.
ANS:
1,4-pentadiene
The heat of hydration is the amount of energy released when hydrogen adds to the multiple carbon-tocarbon bonds in a compound and converts it to the corresponding saturated compound. The larger the
value, the more energy that is released during the hydrogenation. Both of these substances, end up as
pentane upon complete hydrogenation. That is, they end up at the same final energy level. Less energy is
released by 1,4-pentadiene, therefore, this reactant has less energy to start with or is more stable than 1pentyne.
Alkynes: An Introduction to Organic Synthesis
12.
Refer to Exhibit 9-2. Show the energy differences between the hydrogenation of 1,4-pentadiene and
1-pentyne on a reaction energy diagram.
ANS:
Exhibit 9-3
Consider an unknown with the molecular formula C 4H6.
13.
Refer to Exhibit 9-3. How many degrees of unsaturation are present?
ANS:
A saturated four carbon compound has the formula C 4H10. Therefore this compound has (10 6) 2 = 2
degrees of unsaturation.
14.
ANS:
Refer to Exhibit 9-3. Draw six of the nine possible structures with this formula.
Chapter 9
Exhibit 9-4
Predict the product of each reaction below. Be sure to indicate stereochemistry when appropriate.
15.
ANS:
16.
ANS:
17.
ANS:
18.
ANS:
Alkynes: An Introduction to Organic Synthesis
19.
ANS:
20.
ANS:
21.
ANS:
Exhibit 9-5
To answer the following question(s) consider this reaction:
22.
Refer to Exhibit 8-5. On the structures provided, draw arrows showing the electron flow for the
reaction mechanism for the electrophilic addition of hydrogen bromide to 1-hexyne.
Chapter 9
ANS:
23.
Refer to Exhibit 8-5. The key intermediate in the electrophilic addition reaction shown above is
called:
an acetylenic carbocation
a vinylic bromide
a secondary carbocation
a vinylic carbocation
ANS:
d
Exhibit 9-6
Select the best reagent or sequence of reagents from the list provided which would best accomplish each
transformation below. Place the letter corresponding to the reagent(s) in the blank to the left of each
reaction. Each transformation requires only one answer.
H2SO4, H2O, HgSO4
H2, Lindlar
BH3, THF
H2O2
NaNH2, NH3
CH3CH2I
24.
Br2, CCl4
2 NaNH2, NH3
HCl
NaNH2, NH3
Li/NH3
NaNH2, NH3
CH3CH2CH2I
_____
ANS:
g
Alkynes: An Introduction to Organic Synthesis
25.
_____
ANS:
a
26.
_____
ANS:
h
27.
_____
ANS:
e
Exhibit 9-7
Show all reagents and intermediates necessary to carry out the following conversions.
28.
ANS:
Chapter 9
29.
ANS:
Exhibit 9-8
Using acetylene and any alkyl halides as starting materials, synthesize the following compounds. More
than one step may be required. Show all reagents and all intermediate compounds in your synthetic
scheme.
30.
ANS:
Alkynes: An Introduction to Organic Synthesis
31.
ANS:
32.
ANS:
33.
ANS:
10
Chapter 9
34.
ANS:
35.
Draw the structure(s) of the product(s) formed when the following substance is treated with
NaNH2/NH3 and 1-bromo-3-methylhexane.
ANS:
No reaction occurs since this species is an internal alkyne. A terminal alkyne is needed to react under the
given conditions.
36.
Consider the three structures shown below.
Explain why Structure C is unstable
11
Alkynes: An Introduction to Organic Synthesis
ANS:
The hybridization on the carbon atoms of the triple bond is sp and produces a bond angle of 180. This
dictates a linear geometry about both carbon atoms of the triple bond. In Structure C the internal bond
angles between the sp hybridized carbon atoms and the adjacent sp3 carbon atoms of the ring is much less
than 180 (approximately 120). This compression of the bond angle produces too much strain for the
ring to be stable. Puckering of the ring cannot relieve the strain to the degree that is does for Structures A
and B. The linear geometry is required to allow for the appropriate orbital overlap to form the sigma
bonds between the sp carbon atoms and the sp3 carbon atoms.
37.
ANS:
12
Draw the skeletal formula for the reactant and product that correspond to the enol formed in a
hydroboration/oxidation reaction. Atoms other than carbon and hydrogen are labeled.
Chapter 9
MULTIPLE CHOICE
1.
Specify the hybridization on the carbons shown in the following structure.
1: sp3 2: sp2
1: sp2 2: sp
1: sp3 2: sp
1: sp2 2: sp
ANS: C
2.
Consider the following compound.
This compound
is weakly acidic.
could produce a single carboxylic acid upon oxidation.
would produce a high yield of product upon oxidative cleavage.
yields an alkene upon treatment with hydrogen in the presence of a Lindlar catalyst.
None of the above characterize this compound
ANS: D
13
Alkynes: An Introduction to Organic Synthesis
3.
What is the term given to the following species?
carbene
carbanion
acetylide anion
carbocation
ANS: C
4.
The following species
formed when ethyne is treated with a strong base.
is the conjugate base of acetylene.
could react with bromoethane to form 1-butyne.
could react with bromocyclopentane to form an internal alkyne.
a and b
a, b, and c
a, b, and d
all of the above
ANS: F
5.
The term retrosynthesis refers to syntheses developed:
starting with simple molecules.
devised by examining the product.
working forward and backward from intermediates.
beginning by examining the reactant available.
ANS: B
6.
An acetylide anion is more stable than either a vinylic or alkyl anion due to
the stabilization of the negative charge in orbitals with higher s character.
the greater distance of the negative charge from the nucleus of the carbon atom.
the greater stability of an sp hybrid orbital.
the larger number of electrons.
ANS: A
14
Chapter 9
7.
What is the skeletal formula for the product of the reaction when the following is treated with BH 3
in THF followed by H2O2?
ANS: D
8.
Which of the following alkynes will produce a single product upon mercury(II)-catalyzed
hydration?
2-methyl-5-ethyl-3-heptyne
3,3-dimethyl-1-heptyne
3-hexyne
2-hexyne
Both 3,3-dimethyl-1-heptyne and 3-hexyne
ANS: C
9.
When the following substance is treated with excess HBr,
15
Alkynes: An Introduction to Organic Synthesis
The product of the reaction is
A mixture of a and b would be produced.
A mixture of a, b, and c would be produced.
ANS: C
10.
When the following substance is treated with 1 equivalent of Br 2,
The product of the reaction is
16
Chapter 9
A mixture of a and b would be produced.
ANS: A
17
Potrebbero piacerti anche
- TBA Chapter9Documento23 pagineTBA Chapter9Ha Vi100% (1)
- Chapter 11: Radical Reactions: Multiple ChoiceDocumento24 pagineChapter 11: Radical Reactions: Multiple Choicelp_blackout50% (2)
- Stereochem Test BankDocumento19 pagineStereochem Test BankCarmela Liria100% (15)
- Test Bank For Organic Chemistry 9Th Edition Wade Test Bank For Organic Chemistry 9Th Edition WadeDocumento23 pagineTest Bank For Organic Chemistry 9Th Edition Wade Test Bank For Organic Chemistry 9Th Edition WadeAshleyNessuna valutazione finora
- Full Download Ebook PDF Organic Chemistry 6th Edition by Janice Smith PDFDocumento41 pagineFull Download Ebook PDF Organic Chemistry 6th Edition by Janice Smith PDFjohn.french68797% (33)
- Chapter 08 MergedDocumento38 pagineChapter 08 MergedreemNessuna valutazione finora
- 1 Alkene Practice Problems MOC PDFDocumento8 pagine1 Alkene Practice Problems MOC PDFsamkarthik47Nessuna valutazione finora
- Chapter FifteenDocumento43 pagineChapter Fifteenwhatsup_11798100% (2)
- Aromaticity TutorialDocumento15 pagineAromaticity TutorialAlex-Mihai Ciubara100% (2)
- Fall 2008 Old - Exam - 4Documento12 pagineFall 2008 Old - Exam - 4alfredNessuna valutazione finora
- Test Bank For Organic Chemistry 7th Edition by BrownDocumento23 pagineTest Bank For Organic Chemistry 7th Edition by BrownandielanaNessuna valutazione finora
- Welcome To Chem 206: Fall Term, 2005, David A. EvansDocumento22 pagineWelcome To Chem 206: Fall Term, 2005, David A. EvanseraborNessuna valutazione finora
- Chapter 7Documento56 pagineChapter 7itsjc0% (1)
- CH 8 Test BankDocumento14 pagineCH 8 Test BankVanessa James100% (2)
- ACS Review 9 AlkynesDocumento9 pagineACS Review 9 AlkynesMohamad HabbabaNessuna valutazione finora
- CH203 Fall 2014 Exam Two Practice Test With AnswersDocumento10 pagineCH203 Fall 2014 Exam Two Practice Test With AnswersBUCH203Nessuna valutazione finora
- Homework ChemDocumento26 pagineHomework ChemChristine De GuzmanNessuna valutazione finora
- Qoii0708 CO 17 TIFDocumento34 pagineQoii0708 CO 17 TIFLovely Joysweet100% (2)
- CHM 2210 Practice Exam 1Documento12 pagineCHM 2210 Practice Exam 1Shaima MossamatNessuna valutazione finora
- Study Guide 2Documento4 pagineStudy Guide 2Orçun AtasevenNessuna valutazione finora
- ACS Review 15 Alcohols Diols and ThiolsDocumento10 pagineACS Review 15 Alcohols Diols and ThiolsJana BazziNessuna valutazione finora
- Exam Three Practice TestDocumento13 pagineExam Three Practice TestBUCH203100% (1)
- Chapter 19Documento69 pagineChapter 19Rebecca Campbell71% (7)
- Organic Chemistry Practice MidtermDocumento7 pagineOrganic Chemistry Practice MidtermAmy HanNessuna valutazione finora
- Quiz 3-Practice questions (1) نسخةDocumento8 pagineQuiz 3-Practice questions (1) نسخةSabaa AbuzaidNessuna valutazione finora
- Reviewer Organic Chemistry LectureDocumento9 pagineReviewer Organic Chemistry LectureAlyanna Elisse Vergara100% (1)
- ACS Review 24 PhenolsDocumento10 pagineACS Review 24 PhenolsJana BazziNessuna valutazione finora
- Chapter-7 Key AnswersDocumento40 pagineChapter-7 Key AnswersJesseth AlotaNessuna valutazione finora
- Chapter 5: Structure and Preparation of Alkenes - Elimination ReactionsDocumento13 pagineChapter 5: Structure and Preparation of Alkenes - Elimination ReactionsRahma AshrafNessuna valutazione finora
- 235practice Exam 2 AnswerDocumento9 pagine235practice Exam 2 Answernbobs7Nessuna valutazione finora
- Chapter 7Documento71 pagineChapter 7cjn999982% (11)
- Practice CH 22 AnsDocumento33 paginePractice CH 22 AnsDante Ramoth75% (4)
- Oxidation and Reduction Reactions in Organic ChemistryDocumento9 pagineOxidation and Reduction Reactions in Organic ChemistryTarun Lfc Gerrard100% (1)
- Practice Test 1 CHM2210C CH 1-3 PDFDocumento13 paginePractice Test 1 CHM2210C CH 1-3 PDFkara lane100% (1)
- ACS Review 12 Reactions of Arenes - Electrophilic Aromatic SDocumento12 pagineACS Review 12 Reactions of Arenes - Electrophilic Aromatic SMohamad HabbabaNessuna valutazione finora
- PMR Spectroscopy: Solved Problems Volume : IIDa EverandPMR Spectroscopy: Solved Problems Volume : IIValutazione: 5 su 5 stelle5/5 (3)
- Alcohols IIT PACEDocumento19 pagineAlcohols IIT PACEDushyant GuptaNessuna valutazione finora
- Catalysis in Petrochemical ProcessesDocumento211 pagineCatalysis in Petrochemical ProcessesDavid LunaNessuna valutazione finora
- Chapter 10 Alkenes - SmithDocumento14 pagineChapter 10 Alkenes - SmithRen Liew Jia Qing75% (4)
- Lab Report Chemist Chapter 7Documento7 pagineLab Report Chemist Chapter 7SPMUSER9A60% (10)
- Carboxylic Acid & NitrilesDocumento19 pagineCarboxylic Acid & NitrilesDante Luis SilvaNessuna valutazione finora
- Chapter 17Documento47 pagineChapter 17Luke Dhillon100% (1)
- Chapter 9 Organic Chemistry SolomonDocumento6 pagineChapter 9 Organic Chemistry SolomonSukhi Sohal0% (1)
- Chapter 12: Reactions of Arenes - Electrophilic Aromatic SubstitutionDocumento29 pagineChapter 12: Reactions of Arenes - Electrophilic Aromatic SubstitutionAnonymous Ngsu7C4aNessuna valutazione finora
- Alkenes SeatworkDocumento5 pagineAlkenes SeatworkJhefNessuna valutazione finora
- Chapter 6: Reactions of Alkenes - Addition Reactions: Trans-1,2-Dimethylcyclopentane Cis-1,2-DimethylcyclopentaneDocumento21 pagineChapter 6: Reactions of Alkenes - Addition Reactions: Trans-1,2-Dimethylcyclopentane Cis-1,2-DimethylcyclopentaneRahma AshrafNessuna valutazione finora
- Chapter 12: Reactions of Arenes - Electrophilic Aromatic SubstitutionDocumento29 pagineChapter 12: Reactions of Arenes - Electrophilic Aromatic SubstitutionRahma AshrafNessuna valutazione finora
- Chapter 8 Nucleophilic Substitution: Answers Prof. Sivaguru JayaramanDocumento16 pagineChapter 8 Nucleophilic Substitution: Answers Prof. Sivaguru JayaramanRahma AshrafNessuna valutazione finora
- Organic Chemistry 2 Practice Exam 1Documento15 pagineOrganic Chemistry 2 Practice Exam 1KaybidoNessuna valutazione finora
- Chapter 7 TEST BANK Chapter 7 TEST BANKDocumento61 pagineChapter 7 TEST BANK Chapter 7 TEST BANKangelineNessuna valutazione finora
- Oc ch17Documento34 pagineOc ch17xavier8491Nessuna valutazione finora
- Chapter 4Documento38 pagineChapter 4Rebecca Campbell100% (1)
- Chapter 21 II PDFDocumento23 pagineChapter 21 II PDFadelNessuna valutazione finora
- Organic Chem 4Documento22 pagineOrganic Chem 4tyron9520100% (1)
- CH 07Documento61 pagineCH 07Simranjit Kaur75% (4)
- Organic Chem Practice Exam by Solomon CH 1-4Documento12 pagineOrganic Chem Practice Exam by Solomon CH 1-4Natasha Moo100% (1)
- Aromatic Hydrocarbon (Q.B.) (MSC)Documento14 pagineAromatic Hydrocarbon (Q.B.) (MSC)Raj ModiNessuna valutazione finora
- Mcmurry Foc7e Ch03Documento12 pagineMcmurry Foc7e Ch03bebsybiswezNessuna valutazione finora
- Ch08-Testbank PDFDocumento30 pagineCh08-Testbank PDFAdrienne Chelsea GabayNessuna valutazione finora
- Model Answer: The Following Questions Answer Choose The Correct Answer: (20Documento4 pagineModel Answer: The Following Questions Answer Choose The Correct Answer: (20Khalid AbeedNessuna valutazione finora
- Practices Exam - Organic Chemistry To 2nd PartialDocumento10 paginePractices Exam - Organic Chemistry To 2nd PartialShary MosqueraNessuna valutazione finora
- Organic Chemistry 231 Final ExamDocumento19 pagineOrganic Chemistry 231 Final ExamAlex Rose100% (1)
- Aromatic Cmpds AnskeyDocumento6 pagineAromatic Cmpds AnskeyAaron LeeNessuna valutazione finora
- CH 17Documento117 pagineCH 17Kathy YellaNessuna valutazione finora
- Nurbio Act 6Documento5 pagineNurbio Act 6Cake ManNessuna valutazione finora
- Chemical Engineering: ReactionDocumento70 pagineChemical Engineering: ReactionKaunaini ChusnaNessuna valutazione finora
- Exam 4 KEYDocumento12 pagineExam 4 KEYcwodNessuna valutazione finora
- x2 BenzophenoneDocumento3 paginex2 Benzophenoneachmad_128612997Nessuna valutazione finora
- Cuaderno Trabajo 2019-1Documento36 pagineCuaderno Trabajo 2019-1Isaac Farfan CondorNessuna valutazione finora
- Case Based Question Haloalkanes HaloarenesDocumento3 pagineCase Based Question Haloalkanes HaloarenesFake GamerNessuna valutazione finora
- Halogen Dance Reactions - Schnürch, M. & Spina M.Documento12 pagineHalogen Dance Reactions - Schnürch, M. & Spina M.Anuar HernandezNessuna valutazione finora
- Racemization Mandelic AcidDocumento23 pagineRacemization Mandelic Acidanel_galoisNessuna valutazione finora
- Phosphorus, Sulfur, and SiliconDocumento6 paginePhosphorus, Sulfur, and SiliconDrBonny PatelNessuna valutazione finora
- Dibenzalaseton Article 19-2-7Documento8 pagineDibenzalaseton Article 19-2-7Fitriani TanraNessuna valutazione finora
- Rajah 2.1 Menunjukkan Dua Tong Gas Yang Mengandungi Dua Jenis Hidrokarbon Yang Mempunyai Tiga Atom Karbon Per MolekulDocumento6 pagineRajah 2.1 Menunjukkan Dua Tong Gas Yang Mengandungi Dua Jenis Hidrokarbon Yang Mempunyai Tiga Atom Karbon Per MolekulTai ZikingNessuna valutazione finora
- Science of SynthesisDocumento186 pagineScience of Synthesisohjaja100% (4)
- Conjugate AdditionDocumento15 pagineConjugate Additionsally gomaaNessuna valutazione finora
- Substitution Reaction of Alkanes - Lam PhucDocumento6 pagineSubstitution Reaction of Alkanes - Lam PhucNguyen Trang NhungNessuna valutazione finora
- McMurry ReactionDocumento4 pagineMcMurry ReactionMonii Das0% (1)
- IR ProcedureDocumento5 pagineIR ProcedurePuvaneswary LoganathanNessuna valutazione finora
- Alkaloids IntroductionDocumento4 pagineAlkaloids IntroductionPawan KumarNessuna valutazione finora
- Klang High Trial STPM 2019 P3Documento13 pagineKlang High Trial STPM 2019 P3Khang Ni 康妮 FooNessuna valutazione finora
- 2814 01jan08t51626Documento20 pagine2814 01jan08t51626Philip_8300% (1)
- 4.12 F. Y. B. Sc. ChemistryDocumento18 pagine4.12 F. Y. B. Sc. ChemistryJonnyJamesNessuna valutazione finora
- Biomacromolecules (Carbohydrate, Protein, Lipids, Minerals, Nucleic Acid)Documento42 pagineBiomacromolecules (Carbohydrate, Protein, Lipids, Minerals, Nucleic Acid)Ram Kewal Tripathi100% (1)
- Cm-jc-exm-009-V1 JC Chem - Topical Revision - Reaction Kinetics (2020 v2019 LT)Documento72 pagineCm-jc-exm-009-V1 JC Chem - Topical Revision - Reaction Kinetics (2020 v2019 LT)George ChooNessuna valutazione finora
- Chem113 - Week 3 - Lab CarbohydratesDocumento2 pagineChem113 - Week 3 - Lab CarbohydratesFormosa G.Nessuna valutazione finora
- Associated With HO: H H H H HDocumento1 paginaAssociated With HO: H H H H HKendra ShresthaNessuna valutazione finora
- GOC-jeemain GuruDocumento108 pagineGOC-jeemain GuruncomdpNessuna valutazione finora