Documenti di Didattica
Documenti di Professioni
Documenti di Cultura
DHCP Security Using A DHCP Proxy Agent (En)
Caricato da
779482688Titolo originale
Copyright
Formati disponibili
Condividi questo documento
Condividi o incorpora il documento
Hai trovato utile questo documento?
Questo contenuto è inappropriato?
Segnala questo documentoCopyright:
Formati disponibili
DHCP Security Using A DHCP Proxy Agent (En)
Caricato da
779482688Copyright:
Formati disponibili
NETMANIAS
TECH-BLOG
Please visit www.netmanias.com to view more posts
DHCP Security Using a DHCP Proxy Agent
October 1, 2013 | By Chris (tech@netmanias.com) | Netmanias Tech-Blog | www.netmanias.com
Last time when we introduced a DHCP proxy agent through our previous blog post dated in September 1. 2013,
we mentioned that this DHCP proxy agent can offer the benefits of enhanced security. So, we will look into
these security-related functions in more detail today.
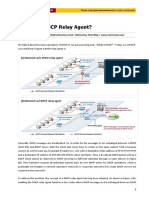
As shown in the figure below, if there is a DHCP proxy agent in a network, all DHCP messages (used in IP
address allocation, IP address renewal and IP address release procedures) pass through (i.e. are forwarded to)
the DHCP proxy agent. Due to such scheme, the DHCP proxy agent is able to block any traffic coming from
users who do not have an IP address allocated through DHCP, but have a static IP address. The proxy agent
can do so by using one of the following two methods:
First, this DHCP proxy agent function is generally enabled in the default gateway router of a DHCP client (i.e.
the first one the client connects). Then, when the client needs to send any Internet traffic via the DHCP proxy
agent (which is the default gateway router), it sends an ARP Request packet, to the default gateway router
(DHCP proxy agent) to get the MAC address of the default gateway router.
At this time, the DHCP proxy agent responds only to the ARP Request packets with an IP address allocated
through DHCP procedure, and not to the ones with a non-DHCP IP address (i.e. static IP address), as illustrated
in the following figure. This function comes standard in most routers.
Second, despite the foregoing function, it only takes the MAC address of a default gateway router for a static
IP user (malicious user) to threaten the network security. So, for more enhanced security, the DHCP proxy
agent needs to examine the IP address of all user data traffic as well as ARP packets. Then it can either permit
the packets with a DHCP IP address or deny ones with a non-DHCP IP address (i.e. static IP address). However,
such implementation is practically impossible with most of regular network equipment, and only Broadband
Remote Access Server (BRAS), capable of managing users, can support such implementation.
DHCP Server
Authorized User
User Traffic
DHCP Client
DHCP Proxy
Agent
Unauthorized User
Internet
User Traffic
Static IP illegally
A DHCP proxy agent:
Refers to the IP-to-MAC binding table
Discards all ARP Request packets sent by a user who has not acquired its
IP address through DHCP
Prevents such users from accessing the Internet
Some of such routers introduced by KT (Korea Telecom) include Juniper E320 and Redback (acquired by
Ericsson) SE800. Just so you know, BRAS can process user traffic on data plane (the layers over which user data
flows), and thus it is possible to support different QoS policies per user (e.g. bandwidth control)". That
explains why it is so expensive compared to other routers.
Netmanias Tech-Blog: DHCP Security Using a DHCP Proxy Agent
Please note we only cover the DHCP proxy agent function today, and will revisit BRAS next time. The figure
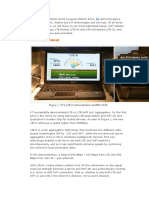
below illustrates the security functions mentioned above in more detail.
In the figure, when PC1 obtains an IP address (1.1.1.0) through a normal DHCP procedure, the DHCP proxy
agent creates an IP-to-MAC binding table on the control plane (where no user traffic is delivered, and
routers are controlled through functions, such as routing protocol, ARP, DHCP proxy agent, etc.). This table
contains a MAC address of a user who received an IP address through a DHCP process, IP address, the
interface number of the DHCP proxy agent that the user PC connects to, DHCP lease time and expired time.
The expired time is initially set same as the IP lease time, and thereafter decreases by one (1) every second.
Then, when it eventually reaches 0, its relevant entry is deleted from the IP-to-MAC binding table.
When PC1 with an allocated IP address sends an ARP Request packet to the default gateway router (DHCP
proxy agent) which receives the packet checks whether or not both the Sender MAC address (m1) and IP
address (1.1.1.10) in the packet are registered in the IP-to-MAC binding table. If they are, the proxy agent
returns its MAC address to the user PC through an ARP Reply message.
However, if PC2 with a static IP address (1.1.1.20) sends an ARP Request packet to the default gateway router
(DHCP proxy agent), the DHCP proxy agent does not send any ARP Reply packet since no information (MAC
address (m2) and IP address (1.1.1.20)) about the client is found in the IP-to-MAC binding table. So, PC2
cannot have access to the Internet.
PC MAC=m1
L2 Network
PC1
MAC=m10
IP=1.1.1.254 Proxy
DHCP
DHCP Discover/Reqeust
DHCP Discover/Reqeust
DHCP Offer/Ack
DHCP Offer/Ack
DHCP Payload {Your IP=1.1.1.10, Client MAC=m1}
1.1.1.254 !
ARP Request Please let us know your MAC address !
Who has 1.1.1.254? Tell 1.1.1.10/m1
Ge1/1
IP-to-MAC Binding Table
MAC IP Address Interface Lease Time Expired Time
m1
1.1.1.10
Ge1/1
3600 sec
3000 sec
ARP Reply
My MAC address is m10
1.1.1.254 is at m10
Ge1/1
1 Matched
Internet Access
SIP=1.1.1.10
Ge1/1
Internet
PC MAC=m2
PC2
Configure IP address=1.1.1.20 at PC illegally
1.1.1.254 !
ARP Request Please let us know your MAC address !
IP-to-MAC Binding Table
Who has 1.1.1.254? Tell 1.1.1.20/m2
I need the MAC address of default
gateway (1.1.1.254) to access the
Internet
Whats taking so long?
MAC IP Address Interface Lease Time Expired Time
m1
1.1.1.10
Ge1/1
3600 sec
3000 sec
Ge1/1
2 Not Matched
So, Ignore(Discard) ARP Request packet
Netmanias Research and Consulting Scope
99
00
01
02
03
04
05
06
07
08
09
10
11
12
13
eMBMS/Mobile IPTV
CDN/Mobile CDN
Transparent Caching
BSS/OSS
Services
Cable TPS
Voice/Video Quality
IMS
Policy Control/PCRF
IPTV/TPS
LTE
Mobile
Network
Mobile WiMAX
Carrier WiFi
LTE Backaul
Data Center Migration
Carrier Ethernet
FTTH
Wireline
Network
Data Center
Metro Ethernet
MPLS
IP Routing
CDN
Transparent
Caching
Analysis
Networks
eMBMS
LTE
IMS
Infrastructure Services
Analyze trends, technologies and market
Report
Technical documents
Blog
One-Shot gallery
Concept Design
DRM
POC
Training
Wi-Fi
We design the future
protocols
IP/MPLS
We design the future
Carrier Ethernet
We design the future
Consulting
Visit http://www.netmanias.com to view and download more technical documents.
Future
About NMC Consulting Group (www.netmanias.com)
NMC Consulting Group is an advanced and professional network consulting company, specializing in IP network areas (e.g., FTTH, Metro Ethernet and IP/MPLS), service
areas (e.g., IPTV, IMS and CDN), and wireless network areas (e.g., Mobile WiMAX, LTE and Wi-Fi) since 2002.
Copyright 2002-2013 NMC Consulting Group. All rights reserved.
Potrebbero piacerti anche
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeDa EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeValutazione: 4 su 5 stelle4/5 (5794)
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeDa EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeValutazione: 4.5 su 5 stelle4.5/5 (537)
- DHCP Message FormatDocumento4 pagineDHCP Message Format779482688Nessuna valutazione finora
- DHCP Detailed Operation (En)Documento13 pagineDHCP Detailed Operation (En)779482688Nessuna valutazione finora
- What Is A DHCP Relay Agent (En)Documento3 pagineWhat Is A DHCP Relay Agent (En)779482688Nessuna valutazione finora
- What Is A DHCP Proxy Agent (En)Documento3 pagineWhat Is A DHCP Proxy Agent (En)779482688Nessuna valutazione finora
- What Is DHCP (En)Documento4 pagineWhat Is DHCP (En)779482688100% (1)
- DHCP Basic Operation (En)Documento16 pagineDHCP Basic Operation (En)779482688100% (1)
- CoMP (2) .CoMP Coordination Areas Defined in 7 Different 3GPP ScenariosDocumento5 pagineCoMP (2) .CoMP Coordination Areas Defined in 7 Different 3GPP Scenarios779482688Nessuna valutazione finora
- Demonstrations of LTE-H and LTE-UDocumento7 pagineDemonstrations of LTE-H and LTE-U779482688Nessuna valutazione finora
- What Are Minimum IP Network Bandwidths Required For Watching 4K UHD IPTVDocumento5 pagineWhat Are Minimum IP Network Bandwidths Required For Watching 4K UHD IPTV779482688Nessuna valutazione finora
- Captive Portal-Based User Authentication in KT, SK Telecom and LG U+'s Wi-Fi HotspotsDocumento6 pagineCaptive Portal-Based User Authentication in KT, SK Telecom and LG U+'s Wi-Fi Hotspots779482688Nessuna valutazione finora
- Things You Should Know About Enterprise WLANDocumento5 pagineThings You Should Know About Enterprise WLAN779482688100% (1)
- RFC 5630Documento56 pagineRFC 5630779482688Nessuna valutazione finora
- Demonstrations of LTE-H and LTE-UDocumento7 pagineDemonstrations of LTE-H and LTE-U779482688Nessuna valutazione finora
- Debates On LTE-unlicensed and WiFi (KT, SK Telecom, Qualcomm)Documento7 pagineDebates On LTE-unlicensed and WiFi (KT, SK Telecom, Qualcomm)779482688Nessuna valutazione finora
- 5G and Network Slicing - enDocumento8 pagine5G and Network Slicing - en779482688Nessuna valutazione finora
- CoMP (1) - CoMP Types - CS, CB, JT and DPSDocumento9 pagineCoMP (1) - CoMP Types - CS, CB, JT and DPS779482688Nessuna valutazione finora
- CoMP (2) .CoMP Coordination Areas Defined in 7 Different 3GPP ScenariosDocumento5 pagineCoMP (2) .CoMP Coordination Areas Defined in 7 Different 3GPP Scenarios779482688Nessuna valutazione finora
- Key Parameters For 5G Mobile Communications (ITU-R WP 5D Standardization Status)Documento5 pagineKey Parameters For 5G Mobile Communications (ITU-R WP 5D Standardization Status)779482688Nessuna valutazione finora
- Mobile Network Architecture For 5G Era - New C-RAN Architecture and Distributed 5G CoreDocumento6 pagineMobile Network Architecture For 5G Era - New C-RAN Architecture and Distributed 5G Core779482688Nessuna valutazione finora
- KT 5G Network ArchitectureDocumento1 paginaKT 5G Network Architecture779482688Nessuna valutazione finora
- Lte HeNB GatewayDocumento16 pagineLte HeNB Gateway779482688100% (1)
- Analysis of KT's 5G Network ArchitectureDocumento7 pagineAnalysis of KT's 5G Network Architecture779482688Nessuna valutazione finora
- Concept and Characteristics of 5G Mobile Communication SystemsDocumento6 pagineConcept and Characteristics of 5G Mobile Communication Systems779482688Nessuna valutazione finora
- C-RAN and BHFH ArchitectureDocumento5 pagineC-RAN and BHFH Architecture779482688Nessuna valutazione finora
- RFC 5621Documento19 pagineRFC 5621779482688Nessuna valutazione finora
- RFC 5366Documento13 pagineRFC 5366779482688Nessuna valutazione finora
- RFC 3761Documento18 pagineRFC 3761779482688Nessuna valutazione finora
- RFC 3264Documento25 pagineRFC 3264779482688Nessuna valutazione finora
- RFC 3311Documento13 pagineRFC 3311Vikash SinghNessuna valutazione finora
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Da EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Valutazione: 4 su 5 stelle4/5 (98)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceDa EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceValutazione: 4 su 5 stelle4/5 (895)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersDa EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersValutazione: 4.5 su 5 stelle4.5/5 (344)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingDa EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingValutazione: 3.5 su 5 stelle3.5/5 (399)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceDa EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceValutazione: 4 su 5 stelle4/5 (588)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerDa EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerValutazione: 4.5 su 5 stelle4.5/5 (271)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaDa EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaValutazione: 4.5 su 5 stelle4.5/5 (266)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItDa EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItValutazione: 4.5 su 5 stelle4.5/5 (838)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryDa EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryValutazione: 3.5 su 5 stelle3.5/5 (231)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealDa EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealValutazione: 4 su 5 stelle4/5 (73)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureDa EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureValutazione: 4.5 su 5 stelle4.5/5 (474)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnDa EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnValutazione: 4.5 su 5 stelle4.5/5 (234)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyDa EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyValutazione: 3.5 su 5 stelle3.5/5 (2259)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaDa EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaValutazione: 4 su 5 stelle4/5 (45)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreDa EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreValutazione: 4 su 5 stelle4/5 (1090)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Da EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Valutazione: 4.5 su 5 stelle4.5/5 (120)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesDa EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesValutazione: 4 su 5 stelle4/5 (821)
- Router R2Documento8 pagineRouter R2Santiago LuceroNessuna valutazione finora
- Zyxel P-793HDocumento2 pagineZyxel P-793HneylaxNessuna valutazione finora
- Lab 6.3.1 Configuring and Propagating An OSPF Default RouteDocumento5 pagineLab 6.3.1 Configuring and Propagating An OSPF Default Routemohammad_shahzad_iiuiNessuna valutazione finora
- Vlan-Rutas EstaticasDocumento5 pagineVlan-Rutas EstaticasJuan CarlosNessuna valutazione finora
- BGP Maximum PrefixDocumento7 pagineBGP Maximum PrefixEryk Al QarniNessuna valutazione finora
- CNv6 instructorPPT Chapter6Documento44 pagineCNv6 instructorPPT Chapter6mohammedqundiNessuna valutazione finora
- 4.3RISE PCE CAA Connectivity - Options - Wave4Documento17 pagine4.3RISE PCE CAA Connectivity - Options - Wave4Islam El SemmaryNessuna valutazione finora
- 4 Ways To Crack A Facebook Password - Software - Intel ExchangeDocumento9 pagine4 Ways To Crack A Facebook Password - Software - Intel ExchangePedroSimõesNessuna valutazione finora
- How Do I Adjust Eth-Trunk Configurations When Eth-Trunk Load Balancing Is UnevenDocumento17 pagineHow Do I Adjust Eth-Trunk Configurations When Eth-Trunk Load Balancing Is Unevenchristyan leonNessuna valutazione finora
- EXFO White Paper038 Understanding Ethernet OAM enDocumento6 pagineEXFO White Paper038 Understanding Ethernet OAM enDerrick SenyoNessuna valutazione finora
- DocxDocumento5 pagineDocxjikjikNessuna valutazione finora
- Name: Saad Kabir Uddin Matric No: A19EC4056 Section: 08: Task 1: IP AddressingDocumento14 pagineName: Saad Kabir Uddin Matric No: A19EC4056 Section: 08: Task 1: IP AddressingSaad Kabir ProttoyNessuna valutazione finora
- Network Design Scheme For XX Telecom Pilot Office (LLD & DD)Documento86 pagineNetwork Design Scheme For XX Telecom Pilot Office (LLD & DD)Tariq EhsanNessuna valutazione finora
- Alcatel 7302/7330 ISAM: 3FL 00276 AAAA WBZZA Ed 02 1 © 2006 Alcatel Bell N.V., All Rights ReservedDocumento79 pagineAlcatel 7302/7330 ISAM: 3FL 00276 AAAA WBZZA Ed 02 1 © 2006 Alcatel Bell N.V., All Rights ReservedKien TranNessuna valutazione finora
- C1000Z 802.11n VDSL2 Wireless Gateway: BenefitsDocumento2 pagineC1000Z 802.11n VDSL2 Wireless Gateway: BenefitsTorrey PinesNessuna valutazione finora
- Sample Configuration of EtherChannel - Link Aggregation Control Protocol...Documento8 pagineSample Configuration of EtherChannel - Link Aggregation Control Protocol...JaffarNessuna valutazione finora
- Address Mapping in Data CommunicationDocumento16 pagineAddress Mapping in Data CommunicationYELCHURI VENKATA NAGASAI RAVI TEJANessuna valutazione finora
- Ipcop Con RoadwarriorDocumento17 pagineIpcop Con Roadwarriorelbillyto100% (1)
- CCNP Routing Switching SyllabusDocumento8 pagineCCNP Routing Switching Syllabuskrishna100% (1)
- Legal EthicalDocumento36 pagineLegal EthicalJane MaralitNessuna valutazione finora
- ZXR10-B-En-QinQ Principle and Configuration (ZXR10 2900 Switch QinQ Principle and Configuration-2 20110324 18Documento18 pagineZXR10-B-En-QinQ Principle and Configuration (ZXR10 2900 Switch QinQ Principle and Configuration-2 20110324 18Omingo KingiNessuna valutazione finora
- Subnetting Cheat SheetDocumento2 pagineSubnetting Cheat SheetSantanuNessuna valutazione finora
- How To Create VLANs Within A Virtual Switch in VMware ESXiDocumento10 pagineHow To Create VLANs Within A Virtual Switch in VMware ESXimyfarlockNessuna valutazione finora
- PCNE WorkbookDocumento83 paginePCNE WorkbookDaniel N Sherine FooNessuna valutazione finora
- 1-3 C320 (V2.0.0) System StructureDocumento20 pagine1-3 C320 (V2.0.0) System StructureErnestoLopezGonzalezNessuna valutazione finora
- Manual-balanceo-De-carga PCC Router Neutro 3 ADSLDocumento3 pagineManual-balanceo-De-carga PCC Router Neutro 3 ADSLDiego PirelaNessuna valutazione finora
- Basic VoIPDocumento134 pagineBasic VoIPDamián MarésNessuna valutazione finora
- PC Hardware & Networking Syllabus PDFDocumento2 paginePC Hardware & Networking Syllabus PDFAvik GharaNessuna valutazione finora
- USB Type-C Cable CertificationsDocumento33 pagineUSB Type-C Cable CertificationsAnonymous F1xtU2RNessuna valutazione finora