Documenti di Didattica
Documenti di Professioni
Documenti di Cultura
Merge Sort
Caricato da
Varun SharmaCopyright
Formati disponibili
Condividi questo documento
Condividi o incorpora il documento
Hai trovato utile questo documento?
Questo contenuto è inappropriato?
Segnala questo documentoCopyright:
Formati disponibili
Merge Sort
Caricato da
Varun SharmaCopyright:
Formati disponibili
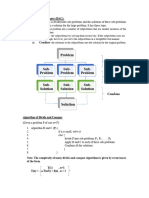
MERGE SORT
ALGORITHM:
1. Divide the unsorted list into two sublists of about half the size
2. Sort each of the two sublists
3. Merge the two sorted sublists back into one sorted list
CODE:
void MergeSort(int low, int high)
// a[low : high] is a global array to be sorted.
// Small(P) is true if there is only one element to
// sort. In this case the list is already sorted.
{
if (low < high) { // If there are more than one element
// Divide P into subproblems.
// Find where to split the set.
int mid = (low + high)/2;
// Solve the subproblems.
MergeSort(low, mid);
MergeSort(mid + 1, high);
// Combine the solutions.
Merge(low, mid, high);
}
}
void Merge(int low, int mid, int high)
// a[low:high] is a global array containing two sorted
// subsets in a[low:mid] and in a[mid+1:high]. The goal
// is to merge these two sets into a single set residing
// in a[low:high]. b[] is an auxiliary global array.
{
int h = low, i = low, j = mid+1, k;
while ((h <= mid) && (j <= high)) {
if (a[h] <= a[j]) { b[i] = a[h]; h++; }
else { b[i] = a[j]; j++; } i++;
}
if (h > mid) for (k=j; k<=high; k++) {
b[i] = a[k]; i++;
}
else for (k=h; k<=mid; k++) {
b[i] = a[k]; i++;
}
for (k=low; k<=high; k++) a[k] = b[k];
}
Advantages :
1. conceptually simple
2. suited to sorting linked lists of elements because merge traverses each
linked list
3. suited to sorting external files; divides data into smaller files until can be
stored in array in memory
4. stable performance
Potrebbero piacerti anche
- Srs For Attendance Management SystemDocumento10 pagineSrs For Attendance Management SystemVarun Sharma89% (19)
- MergeDocumento1 paginaMergeYashwanth SomisettyNessuna valutazione finora
- Brief Summary of Insertion SortDocumento5 pagineBrief Summary of Insertion SortYi Lin LimNessuna valutazione finora
- 4.2 Two Way Merge Sort, Quick Sort, Selection SortDocumento8 pagine4.2 Two Way Merge Sort, Quick Sort, Selection SortAkash SharmaNessuna valutazione finora
- Merge SortDocumento10 pagineMerge Sort6178.shrutimishraNessuna valutazione finora
- 04 Divide and ConquerDocumento2 pagine04 Divide and Conquersol recién salidoNessuna valutazione finora
- Sample Experiment DAADocumento3 pagineSample Experiment DAAMamata swainNessuna valutazione finora
- Merge Sor1Documento5 pagineMerge Sor1RamanjaneyarajuGantasalaNessuna valutazione finora
- Merge SortDocumento8 pagineMerge SortCHRISTIAN GERALDNessuna valutazione finora
- Department of Computer Science and Engineering: CS41 - Design and Analysis of Algorithm Assignment Questions Unit - IIDocumento8 pagineDepartment of Computer Science and Engineering: CS41 - Design and Analysis of Algorithm Assignment Questions Unit - IIPooja SinhaNessuna valutazione finora
- Codes PDFDocumento6 pagineCodes PDFSaja AbdelmailkNessuna valutazione finora
- Daa R20 Unit 2Documento19 pagineDaa R20 Unit 2A Raghava Chowdary maddipatiNessuna valutazione finora
- Presentation On Merge SortDocumento10 paginePresentation On Merge SortSaraswati SharmaNessuna valutazione finora
- Lab Experiment-1 AIMDocumento21 pagineLab Experiment-1 AIMvishalsingh20112003Nessuna valutazione finora
- Data Structure Module 5Documento22 pagineData Structure Module 5ssreeram1312.tempNessuna valutazione finora
- Chapter Two Int 2 AlgorithmDocumento12 pagineChapter Two Int 2 AlgorithmKirubel MulugetaNessuna valutazione finora
- DS Data Structures PPT-module-7Documento13 pagineDS Data Structures PPT-module-7ravikumar03508Nessuna valutazione finora
- Divide and ConquerDocumento9 pagineDivide and Conquersayansmith420Nessuna valutazione finora
- Ms 2019 BitDocumento15 pagineMs 2019 BitSudharshanNessuna valutazione finora
- Quicksort On Singly Linked List 14. Iterative Quick Sort 15. Merge Sort For Linked ListDocumento21 pagineQuicksort On Singly Linked List 14. Iterative Quick Sort 15. Merge Sort For Linked ListPRE-GAMERS INC.Nessuna valutazione finora
- Practical File DaaDocumento84 paginePractical File Daa828Nitish KumarNessuna valutazione finora
- Heap Sort Algorithm: Relationship Between Array Indexes and Tree ElementsDocumento15 pagineHeap Sort Algorithm: Relationship Between Array Indexes and Tree ElementsMudit ChoudharyNessuna valutazione finora
- 2 NDDocumento3 pagine2 NDPratik KakaniNessuna valutazione finora
- Data Structures and Algorithms Lab Lab 2Documento7 pagineData Structures and Algorithms Lab Lab 2Safi HussainNessuna valutazione finora
- SortingDocumento2 pagineSortingSandip DasNessuna valutazione finora
- CH 3Documento47 pagineCH 3menberNessuna valutazione finora
- DS Surprise TestDocumento9 pagineDS Surprise Testaditya polNessuna valutazione finora
- Binary Search PDFDocumento5 pagineBinary Search PDFGaurav TomarNessuna valutazione finora
- SortingDocumento20 pagineSortingshenbagaraman cseNessuna valutazione finora
- Dsoop (Co 221) - 2Documento36 pagineDsoop (Co 221) - 2rakesh dasNessuna valutazione finora
- Data Structures: Merge SortDocumento4 pagineData Structures: Merge Sortakash raviNessuna valutazione finora
- DAA-Important QNA'sDocumento18 pagineDAA-Important QNA'sMIKHAIEL gamingNessuna valutazione finora
- ALG Part1 ASSIGNMENTDocumento28 pagineALG Part1 ASSIGNMENThdsasdadNessuna valutazione finora
- Merge Sort: SCJ2013 Data Structure & AlgorithmsDocumento16 pagineMerge Sort: SCJ2013 Data Structure & AlgorithmsSaimo MghaseNessuna valutazione finora
- Divide and ConquerDocumento9 pagineDivide and ConquertrhdtyjdNessuna valutazione finora
- SLR26 (A ONLY) - Algorithms (A4 Scaffolded)Documento13 pagineSLR26 (A ONLY) - Algorithms (A4 Scaffolded)moran14tomNessuna valutazione finora
- Arrays Merge Sort AlgorithmDocumento3 pagineArrays Merge Sort AlgorithmChiradip BasuNessuna valutazione finora
- Shell Sort AlgorithmDocumento3 pagineShell Sort AlgorithmrenugaNessuna valutazione finora
- ITEC2150 SortDocumento57 pagineITEC2150 Sortadam bellNessuna valutazione finora
- Sorting Algorithm In-Place Comparison Sort O Insertion SortDocumento13 pagineSorting Algorithm In-Place Comparison Sort O Insertion Sorts4ndzNessuna valutazione finora
- Sorting, Searching, and The ComplexityDocumento41 pagineSorting, Searching, and The ComplexityEva UliaNessuna valutazione finora
- Merge SortDocumento6 pagineMerge SortLovely BeatsNessuna valutazione finora
- Binary Search AlgorithmDocumento1 paginaBinary Search AlgorithmHamza SajidNessuna valutazione finora
- DAA Lab-ManualDocumento38 pagineDAA Lab-Manualraviy3083Nessuna valutazione finora
- Merge SortDocumento4 pagineMerge SortyouhavemyuseridNessuna valutazione finora
- CHAPTER-04 (Searching&sorting) 1Documento32 pagineCHAPTER-04 (Searching&sorting) 1xx69dd69xxNessuna valutazione finora
- Divide and Conquer 2Documento6 pagineDivide and Conquer 2John WebbNessuna valutazione finora
- CheatsheetDocumento6 pagineCheatsheetHữu HoàngNessuna valutazione finora
- Heap Sort Min-Heap or Max-HeapDocumento11 pagineHeap Sort Min-Heap or Max-HeapRehan PathanNessuna valutazione finora
- Discrete Structures Practice ProblemDocumento6 pagineDiscrete Structures Practice ProblemAyesha A. RahmanNessuna valutazione finora
- Data Structure ExamDocumento6 pagineData Structure ExamAyesha A. RahmanNessuna valutazione finora
- Binary Search: Private Boolean Int Int IntDocumento1 paginaBinary Search: Private Boolean Int Int Int:v jejejejejeNessuna valutazione finora
- Lab04 ArraysDocumento6 pagineLab04 ArraysHồ NamNessuna valutazione finora
- Merge Sort - Quick Sort - Exercises: Unit 28 1Documento13 pagineMerge Sort - Quick Sort - Exercises: Unit 28 1Jhay Em100% (1)
- Sorting AnalysisDocumento24 pagineSorting Analysisapi-254089610Nessuna valutazione finora
- Week13 Lecture 38Documento11 pagineWeek13 Lecture 38wardabibi69Nessuna valutazione finora
- Analysis & Design of Algorithms (3466) 2Documento9 pagineAnalysis & Design of Algorithms (3466) 2Tooba Hassan 364-FSS/BSIAA/F19Nessuna valutazione finora
- Binary Search i-WPS OfficeDocumento9 pagineBinary Search i-WPS OfficeYohan JamesNessuna valutazione finora
- 05 Lab2 Solution-NewDocumento6 pagine05 Lab2 Solution-NewLê NgHuânNessuna valutazione finora
- 50 most powerful Excel Functions and FormulasDa Everand50 most powerful Excel Functions and FormulasValutazione: 4 su 5 stelle4/5 (1)
- MS Excel Bible, Save Your Time With MS Excel!: 8 Quality Excel Books in 1 PackageDa EverandMS Excel Bible, Save Your Time With MS Excel!: 8 Quality Excel Books in 1 PackageNessuna valutazione finora
- Brief History of Acquiring CompanyDocumento13 pagineBrief History of Acquiring CompanyVarun SharmaNessuna valutazione finora
- Cisco Strategy: Concentrating On Software Platform Leadership Aggressive Acquisition TacticsDocumento5 pagineCisco Strategy: Concentrating On Software Platform Leadership Aggressive Acquisition TacticsVarun SharmaNessuna valutazione finora
- Price JustificationDocumento1 paginaPrice JustificationVarun SharmaNessuna valutazione finora
- AigDocumento31 pagineAigVarun SharmaNessuna valutazione finora
- Subprime Crisis 2008 Housing Bubble: USADocumento59 pagineSubprime Crisis 2008 Housing Bubble: USAVarun SharmaNessuna valutazione finora
- Causes of Subprime CrisisDocumento4 pagineCauses of Subprime CrisisVarun SharmaNessuna valutazione finora
- Robot Programming: by 143-Akash Sanghvi 144-Varun Sharma 145-Gopesh Raval 146-Nitesh DawaniDocumento10 pagineRobot Programming: by 143-Akash Sanghvi 144-Varun Sharma 145-Gopesh Raval 146-Nitesh DawaniVarun SharmaNessuna valutazione finora
- Job Sequencing With Deadline (Greedy Algorithm)Documento1 paginaJob Sequencing With Deadline (Greedy Algorithm)Varun SharmaNessuna valutazione finora
- Project Quality ManagementDocumento13 pagineProject Quality ManagementVarun SharmaNessuna valutazione finora
- Research On How Demographic Factors Affect The EquityDocumento13 pagineResearch On How Demographic Factors Affect The EquityVarun SharmaNessuna valutazione finora