Documenti di Didattica
Documenti di Professioni
Documenti di Cultura
Memb243 Mom Final Semi 15-16
Caricato da
Malik IsmailCopyright
Formati disponibili
Condividi questo documento
Condividi o incorpora il documento
Hai trovato utile questo documento?
Questo contenuto è inappropriato?
Segnala questo documentoCopyright:
Formati disponibili
Memb243 Mom Final Semi 15-16
Caricato da
Malik IsmailCopyright:
Formati disponibili
COLLEGE OF ENGINEERING
PUTRAJAYA CAMPUS
FINAL EXAMINATION
SEMESTER 1 2015 / 2016
PROGRAMME
: Bachelor of Mechanical Engineering (Honours).
SUBJECT CODE
: MEMB243.
SUBJECT
: Mechanics of Materials.
DATE
: September 2015.
TIME
: (3 hours).
INSTRUCTIONS TO CANDIDATES:
1.
This paper contains FIVE (5) questions in SEVEN (7) pages.
2.
Answer ALL questions.
3.
Write ALL answers in the answer booklet provided.
4.
Write answer to each question on a new page.
THIS QUESTION PAPER CONSISTS OF 7 PRINTED PAGES INCLUDING THIS COVER
PAGE.
Page 1 of 7
MEMB243, Semester I 2015/2016
QUESTION 1 [20 marks].
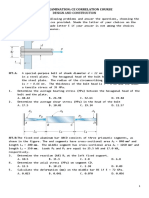
(a) Figure 1a shows an angle bracket ABC which is attached to a control rod AD of diameter,
d1 = 15mm supported two loads P1 = 40kN and P2 =30kN. Given that all pin diameter, d2 = 25mm
and the thickness of each support bracket is 5 mm.
(i)
Draw the free body diagram of bracket ABC and determine all support
reactions;
(ii)
[5 marks]
Determine the normal stresses in the rod AD, shear stress at pin B and the
bearing stress in the support bracket at B.
[7 marks]
Figure 1a
(b) The solid cylinder A and hollow cylinder B were under torque loadings as shown in
Figure 1b. Determine,
(i) the maximum shearing stress for the 75 mm diameter solid cylinder A.
[3 marks]
(ii) the inner diameter of the hollow cylinder B, if maximum shear stress is same as solid
cylinder A. Given that the outer diameter for the cylinder B is 100mm.
Figure 1b
Page 2 of 7
[5 marks]
MEMB243, Semester I 2015/2016
QUESTION 2 [20 marks].
Figure 2 shows a rigid member CD is supported by links A and B, with a load P = 150 kN at D
and temperature changes of 100 C are applied to the pin-connected structure. Link A is made of
aluminum alloy and link B is made of steel. The coefficients of thermal expansion for aluminum
alloy, A = 22 x 10-6 /C and steel, B = 12 x 10-6 /C respectively; Ealuminium = 75 GPa and
Esteel = 200 GPa. Determine,
(a)
the support reaction at link A and B.
[12 marks]
(b)
the normal stresses in links A and B.
[4 marks]
(c)
the vertical deflection at point D.
[4 marks]
Figure 2
Page 3 of 7
MEMB243, Semester I 2015/2016
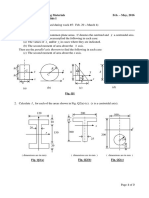
QUESTION 3 [20 marks]
An aluminum beam AB of span 4 m and a square cross section of 150 mm wide by 150 mm depth,
is to support load P = 50 kN as shown in Figure 3. The bearing at C and B exert only vertical
reactions on the beam.
(a)
Draw the shear and bending moment diagrams for the entire beam and determine the
location and magnitude of the largest bending moment;
[8 marks]
(b)
Verify by calculation whether the beam design is safe if the allowable bending stress
for aluminum is allow = 160 MPa and allowable shear stress of allow = 3.6 MPa
respectively. If the answer is no, suggest the changes in term of design aspect.
[12 marks]
Figure 3
Page 4 of 7
MEMB243, Semester I 2015/2016
QUESTION 4 [20 marks]
A beam is made from three wooden strips that are glue together as shown in Figure 4. The bearing
support at A and B exert only vertical reactions on the beam.
(a) Draw the shear diagrams for the loaded beam. Ignore the mass of the beam.
[6 marks]
(b) Determine the maximum load, P that can be applied without causing the glue to lose its
load if the allowable shear stress of allow = 70 kPa.
[8 marks]
(c) Hence, sketch the variation of shear stress along the depth of beam section.
[6 marks]
Figure 4
Page 5 of 7
MEMB243, Semester I 2015/2016
QUESTION 5 [20 MARKS]
(a) A cantilever beam AB in Figure 5a is subjected to a load P. Determine the equation of
elastic curve of beam AB. Take EI as constant.
[10 marks]
Figure 5a
(b) Determine the maximum force P that can be applied to the handle so that steel rod AB does
not buckle. The rod AB has a diameter of 30 mm. Assume that all support at end of the rod
are pin connected as shown in Figure 5b. Given Esteel = 200 GPa.
[10 marks]
Figure 5b
-END OF QUESTION PAPERPage 6 of 7
MEMB243, Semester I 2015/2016
Appendix:
F
;
A
Fundamental Equations
Bending Equation:
Torsion Equation:
Poisson' s ratio,
M E
;
I
y R
Lateral strain y z
Linear strain x x
For square or rectangular section, I G
BD 3
12
T G
J r
L
For solid circular shaft, J
d 4
32
and for hollow circular shaft, J
Shear Stress Due to Transverse Loading: xy
Equation of The Elastic Curve: E I
d2y
dx 2
VQ
and Q A y
Ib
M( x )
Parallel Axis Theorem: I I G A h 2
Coordinate of Centroid: x
A x
A
&
A y
A
Table of Moment of Inertia
Page 7 of 7
( D4 d 4 )
32
Potrebbero piacerti anche
- Structural Steel Design to Eurocode 3 and AISC SpecificationsDa EverandStructural Steel Design to Eurocode 3 and AISC SpecificationsNessuna valutazione finora
- MEMB123 Final Examination Paper Sem 2-09-10 FinalDocumento6 pagineMEMB123 Final Examination Paper Sem 2-09-10 FinalMei QiiNessuna valutazione finora
- The Fracture of Brittle Materials: Testing and AnalysisDa EverandThe Fracture of Brittle Materials: Testing and AnalysisNessuna valutazione finora
- Structural Analysis Exam PapersDocumento3 pagineStructural Analysis Exam Papersfesada1100% (1)
- Composite Structures of Steel and Concrete: Beams, Slabs, Columns and Frames for BuildingsDa EverandComposite Structures of Steel and Concrete: Beams, Slabs, Columns and Frames for BuildingsNessuna valutazione finora
- Advanced Design of Steel StructuresDocumento3 pagineAdvanced Design of Steel StructuresManish Shashikant DharekNessuna valutazione finora
- Bhm1123-Mechanics of Materials 11415Documento7 pagineBhm1123-Mechanics of Materials 11415MysteryNessuna valutazione finora
- Stress in ASME Pressure Vessels, Boilers, and Nuclear ComponentsDa EverandStress in ASME Pressure Vessels, Boilers, and Nuclear ComponentsNessuna valutazione finora
- College of Engineering Putrajaya Campus Final Examination SEMESTER 1 2013 / 2014Documento8 pagineCollege of Engineering Putrajaya Campus Final Examination SEMESTER 1 2013 / 2014Muhd Aidil ZuhairNessuna valutazione finora
- Mace 60035Documento7 pagineMace 60035eng_ayman_H_MNessuna valutazione finora
- UTM Final Exam - Mechanics Sab 2223 Sem 1 2012-13Documento10 pagineUTM Final Exam - Mechanics Sab 2223 Sem 1 2012-13Nurhafizah AhmadNessuna valutazione finora
- Gujarat Technological University: InstructionsDocumento3 pagineGujarat Technological University: InstructionsBhavesh PipaliyaNessuna valutazione finora
- College of Engineering Putrajaya Campus Final Examination SEMESTER 1 2014 / 2015Documento8 pagineCollege of Engineering Putrajaya Campus Final Examination SEMESTER 1 2014 / 2015Muhd Aidil ZuhairNessuna valutazione finora
- BFC 20903Documento10 pagineBFC 20903Priyaah KarunakaranNessuna valutazione finora
- BAA 3223 Steel & Timber Design Final Exam PaperDocumento11 pagineBAA 3223 Steel & Timber Design Final Exam PaperAzil14100% (4)
- 1213sem2 Ce5611Documento11 pagine1213sem2 Ce5611Yu Tian LiNessuna valutazione finora
- CVEN3302 Final Exam S2 2012Documento5 pagineCVEN3302 Final Exam S2 2012Avinash SinghNessuna valutazione finora
- Tutorial Sheets SOMDocumento20 pagineTutorial Sheets SOMPriyanshu Sharma100% (1)
- Steel Plate 2Documento32 pagineSteel Plate 2Rollen de LeonNessuna valutazione finora
- Mechanical Engineering Design 1 EBME1021 January 2015 Semester Final ExaminationDocumento8 pagineMechanical Engineering Design 1 EBME1021 January 2015 Semester Final ExaminationAnonymous 5YMOxVQNessuna valutazione finora
- Ce-221 Solid Mechanics End-Sem Exam 07/11/16 Paper Code: DDocumento7 pagineCe-221 Solid Mechanics End-Sem Exam 07/11/16 Paper Code: DAshutosh AnandNessuna valutazione finora
- CVEN3302 - Final Examination 2008Documento5 pagineCVEN3302 - Final Examination 2008fflegendsNessuna valutazione finora
- Assignment Stress Strain 19202Documento4 pagineAssignment Stress Strain 19202Jarul ZahariNessuna valutazione finora
- Define Factor of SafetyDocumento3 pagineDefine Factor of SafetySunil AdhikariNessuna valutazione finora
- TCW1101200904 Engineering Mechanics I StaticsDocumento6 pagineTCW1101200904 Engineering Mechanics I StaticsTanaka MurekachiroNessuna valutazione finora
- Soalan Final Analisis Struktur UTHMDocumento13 pagineSoalan Final Analisis Struktur UTHMliyana2030Nessuna valutazione finora
- BTCE - 501 Roll No. - B.Tech. (Civil) End Semesterexamination-V Sem DEC-JAN2015 Structure Analysis IiDocumento4 pagineBTCE - 501 Roll No. - B.Tech. (Civil) End Semesterexamination-V Sem DEC-JAN2015 Structure Analysis IisdfghNessuna valutazione finora
- College of Engineering Putrajaya Campus Final Examination SEMESTER 2 2010 / 2011Documento5 pagineCollege of Engineering Putrajaya Campus Final Examination SEMESTER 2 2010 / 2011Mei QiiNessuna valutazione finora
- Kolej Yayasan Pelajaran Johor Assignment 3 Sesi Ogos/September 2021Documento8 pagineKolej Yayasan Pelajaran Johor Assignment 3 Sesi Ogos/September 2021koko sampNessuna valutazione finora
- Advanced Structural AnalysisDocumento3 pagineAdvanced Structural AnalysisAmit ThoriyaNessuna valutazione finora
- 9A01301 Mechanics of SolidsDocumento4 pagine9A01301 Mechanics of SolidssivabharathamurthyNessuna valutazione finora
- (2012) Eas152 - Strength of Materials June PDFDocumento21 pagine(2012) Eas152 - Strength of Materials June PDFSteven KuaNessuna valutazione finora
- TutorialDocumento4 pagineTutorialvarjith007Nessuna valutazione finora
- Section: R Assignment No. Date of Assignment - /9/2015 Date of Submission - /9/2015Documento3 pagineSection: R Assignment No. Date of Assignment - /9/2015 Date of Submission - /9/2015Bharat SharmaNessuna valutazione finora
- Theory of Structure 1Documento10 pagineTheory of Structure 1Anil Thapa100% (1)
- Mech Sol - 2020 - Compre Part A&bDocumento4 pagineMech Sol - 2020 - Compre Part A&brohit BindNessuna valutazione finora
- Final-20192020 1Documento12 pagineFinal-20192020 1Zul HafizzNessuna valutazione finora
- Design 1qsy1718 QuestionsDocumento9 pagineDesign 1qsy1718 QuestionsRachel Delos ReyesNessuna valutazione finora
- Tut1 Part30Documento1 paginaTut1 Part30AnmolNessuna valutazione finora
- Sab 3233Documento13 pagineSab 3233xperia30Nessuna valutazione finora
- r05322102 Aerospace Vehicle Structures IIDocumento12 paginer05322102 Aerospace Vehicle Structures IISRINIVASA RAO GANTA100% (2)
- Assignment 4Documento2 pagineAssignment 4Emmanuel ConstantinidisNessuna valutazione finora
- Final Exam Question StaticDocumento13 pagineFinal Exam Question StaticAsmadi Yussuf100% (1)
- Sab 4333 Set ADocumento8 pagineSab 4333 Set AUsama EL AlaouiNessuna valutazione finora
- Engineering Mechanic Sem 1 Session 1112Documento9 pagineEngineering Mechanic Sem 1 Session 1112Amirul AizatNessuna valutazione finora
- Department of Civil Engineering CIVL2201 Structural MechanicsDocumento8 pagineDepartment of Civil Engineering CIVL2201 Structural Mechanicssky willaNessuna valutazione finora
- Last Year Papaer 20112012Documento14 pagineLast Year Papaer 20112012Farah Hani TENessuna valutazione finora
- AE December 2016 98 Civ A2Documento3 pagineAE December 2016 98 Civ A2NikhilBennyNessuna valutazione finora
- Baa3223 - Steel & Timber DesignDocumento6 pagineBaa3223 - Steel & Timber DesignTing Wee KietNessuna valutazione finora
- Tutorial Sheet 3Documento3 pagineTutorial Sheet 3Ayush KumarNessuna valutazione finora
- Final ExamSOMFinal 2016 FinalDocumento11 pagineFinal ExamSOMFinal 2016 Finalkhalil alhatabNessuna valutazione finora
- L-2/T-2/WRE Date: 06/07/2013Documento18 pagineL-2/T-2/WRE Date: 06/07/2013MuradNessuna valutazione finora
- CE2021 ME2010 2016 Tute 05 PDFDocumento3 pagineCE2021 ME2010 2016 Tute 05 PDFAAKIL AHAMEDNessuna valutazione finora
- Prob SheetDocumento20 pagineProb SheetAditya ShuklaNessuna valutazione finora
- rr320102 Structural Analysis IIDocumento9 paginerr320102 Structural Analysis IISRINIVASA RAO GANTANessuna valutazione finora
- Universiti Tun Hussein Onn Malaysia Final Examination Semester I SESSION 2009/2010Documento15 pagineUniversiti Tun Hussein Onn Malaysia Final Examination Semester I SESSION 2009/2010Muhammad AzriNessuna valutazione finora
- R5 210304 Mechanics of SolidsDocumento2 pagineR5 210304 Mechanics of SolidssivabharathamurthyNessuna valutazione finora
- 507 39 Solutions-Instructor-manual Ch7 DRCSDocumento13 pagine507 39 Solutions-Instructor-manual Ch7 DRCSArun GoyalNessuna valutazione finora
- TOS I Schem Model Answer PaperDocumento6 pagineTOS I Schem Model Answer Paperirshadmirza753Nessuna valutazione finora
- 1415 Sem 2 Modelling and Analysis of Dynamic SystemsDocumento9 pagine1415 Sem 2 Modelling and Analysis of Dynamic SystemsMalik IsmailNessuna valutazione finora
- 1314 Sem 2 Modelling and Analysis of Dynamic SystemsDocumento10 pagine1314 Sem 2 Modelling and Analysis of Dynamic SystemsMalik IsmailNessuna valutazione finora
- V Belt ReportDocumento13 pagineV Belt ReportMalik Ismail100% (1)
- Memb263 Theory of MachinesDocumento6 pagineMemb263 Theory of MachinesMalik IsmailNessuna valutazione finora
- Final Exam (Sem 2 1415)Documento6 pagineFinal Exam (Sem 2 1415)Malik IsmailNessuna valutazione finora
- Midterm Test Sem 1-10-11 (Ans)Documento9 pagineMidterm Test Sem 1-10-11 (Ans)Malik IsmailNessuna valutazione finora
- Mechanics of Fluids Sem 1 1112Documento11 pagineMechanics of Fluids Sem 1 1112Malik IsmailNessuna valutazione finora
- Memb243 S1 14 15Documento7 pagineMemb243 S1 14 15Malik IsmailNessuna valutazione finora
- Eeeb113 Sem S 2013 - Test 2Documento9 pagineEeeb113 Sem S 2013 - Test 2Malik IsmailNessuna valutazione finora
- MEHB213 1314S2 Final Exam QuestionDocumento4 pagineMEHB213 1314S2 Final Exam QuestionMalik IsmailNessuna valutazione finora
- EEEB113 - Final Sem 2 13-14 v5Documento9 pagineEEEB113 - Final Sem 2 13-14 v5Malik IsmailNessuna valutazione finora
- Chapter 3 MFG IIDocumento145 pagineChapter 3 MFG IITiliksew Wudie Assabe100% (1)
- Objective: Find The Displacement and Stress Fields. Problem Definition: Consider An Ideal Flow of Air Around A Cylinder, As Shown in Figure. TheDocumento1 paginaObjective: Find The Displacement and Stress Fields. Problem Definition: Consider An Ideal Flow of Air Around A Cylinder, As Shown in Figure. ThepmagrawalNessuna valutazione finora
- Borehole Stability PresentationDocumento28 pagineBorehole Stability PresentationTimmyPRC100% (1)
- Material CR460LA - Wlasciwosci I Inne OznaczeniaDocumento1 paginaMaterial CR460LA - Wlasciwosci I Inne OznaczeniaAdam WoźniakNessuna valutazione finora
- Light Guage Silo Hopper Design PDFDocumento27 pagineLight Guage Silo Hopper Design PDFPaul RuckNessuna valutazione finora
- Collapse PDFDocumento98 pagineCollapse PDFSuresh nathanNessuna valutazione finora
- SDP - 15 To 17Documento58 pagineSDP - 15 To 17Swapna BharaliNessuna valutazione finora
- By Hamid R. Lotfi and P. Benson Shing, 2 Members, ASCE AbstractDocumento18 pagineBy Hamid R. Lotfi and P. Benson Shing, 2 Members, ASCE AbstractafuhcivNessuna valutazione finora
- Petrophysics MSC Course Notes - Chapter 4 - Fluid Saturation and Capillary PressureDocumento23 paginePetrophysics MSC Course Notes - Chapter 4 - Fluid Saturation and Capillary PressureVandear GoalcantaraNessuna valutazione finora
- Normalized Carbon Steel 230M07Documento12 pagineNormalized Carbon Steel 230M07Mohamad AhmadNessuna valutazione finora
- Plate No.6 - Autor, Joy LauriaDocumento12 paginePlate No.6 - Autor, Joy LauriaJoy lauriaNessuna valutazione finora
- Asphalt Techno Road Engineering Ebook FrEdDocumento61 pagineAsphalt Techno Road Engineering Ebook FrEdvynaNessuna valutazione finora
- Unit 4 Sandwich Composite Materials and StructuresDocumento43 pagineUnit 4 Sandwich Composite Materials and StructuresprsnthNessuna valutazione finora
- ME 141B: The MEMS Class Introduction To MEMS and MEMS DesignDocumento48 pagineME 141B: The MEMS Class Introduction To MEMS and MEMS DesignFarheenNessuna valutazione finora
- Strength Consideration in Product Design, Shiva, DeepakDocumento8 pagineStrength Consideration in Product Design, Shiva, DeepakShivaprasad.P100% (1)
- The Performance of Epoxy-Coated Shear Reinforcement: Aci Structural Journal Technical PaperDocumento7 pagineThe Performance of Epoxy-Coated Shear Reinforcement: Aci Structural Journal Technical PaperpicottNessuna valutazione finora
- Strength of Materials by S K MondalDocumento429 pagineStrength of Materials by S K MondalSaajal Sharma88% (26)
- Engineering Materials Lab ManualDocumento14 pagineEngineering Materials Lab ManualHarood Nishat100% (1)
- Momentum Transfer: Lecture 3: Equations of Change For Isothermal SystemsDocumento31 pagineMomentum Transfer: Lecture 3: Equations of Change For Isothermal SystemsLisajanelollyNessuna valutazione finora
- MonorailDocumento3 pagineMonorailHelard AlvarezNessuna valutazione finora
- Asme Sec Viii D1 Nma App ADocumento8 pagineAsme Sec Viii D1 Nma App AADRIANNessuna valutazione finora
- Polipropileno Hostacom Xm2 v05Documento2 paginePolipropileno Hostacom Xm2 v05LucasNessuna valutazione finora
- Thermo Coupled Stress Analysis of Exhaust Manifold Assemblage Using ABAQUSDocumento6 pagineThermo Coupled Stress Analysis of Exhaust Manifold Assemblage Using ABAQUSInfogain publicationNessuna valutazione finora
- Timber GradingDocumento16 pagineTimber GradingDevansh MehtaNessuna valutazione finora
- En GJS 600 3Documento2 pagineEn GJS 600 3abhiNessuna valutazione finora
- Glass Transition Temperature-Agglomeration, Sticky PointDocumento9 pagineGlass Transition Temperature-Agglomeration, Sticky Pointgalu348Nessuna valutazione finora
- Introduction To MaterialsDocumento23 pagineIntroduction To MaterialsManuel Tutacha ™Nessuna valutazione finora
- Thermal Properties of GlassDocumento4 pagineThermal Properties of Glasssewwan7653Nessuna valutazione finora
- Carpentry Made Easy - The Science and Art of Framing - With Specific Instructions for Building Balloon Frames, Barn Frames, Mill Frames, Warehouses, Church SpiresDa EverandCarpentry Made Easy - The Science and Art of Framing - With Specific Instructions for Building Balloon Frames, Barn Frames, Mill Frames, Warehouses, Church SpiresValutazione: 1 su 5 stelle1/5 (2)
- ChatGPT Money Machine 2024 - The Ultimate Chatbot Cheat Sheet to Go From Clueless Noob to Prompt Prodigy Fast! Complete AI Beginner’s Course to Catch the GPT Gold Rush Before It Leaves You BehindDa EverandChatGPT Money Machine 2024 - The Ultimate Chatbot Cheat Sheet to Go From Clueless Noob to Prompt Prodigy Fast! Complete AI Beginner’s Course to Catch the GPT Gold Rush Before It Leaves You BehindNessuna valutazione finora
- A Welder’s Handbook to Robotic ProgrammingDa EverandA Welder’s Handbook to Robotic ProgrammingValutazione: 5 su 5 stelle5/5 (3)
- Advanced Modelling Techniques in Structural DesignDa EverandAdvanced Modelling Techniques in Structural DesignValutazione: 5 su 5 stelle5/5 (3)
- To Engineer Is Human: The Role of Failure in Successful DesignDa EverandTo Engineer Is Human: The Role of Failure in Successful DesignValutazione: 4 su 5 stelle4/5 (137)
- Structural Steel Design to Eurocode 3 and AISC SpecificationsDa EverandStructural Steel Design to Eurocode 3 and AISC SpecificationsNessuna valutazione finora
- Arduino: The complete guide to Arduino for beginners, including projects, tips, tricks, and programming!Da EverandArduino: The complete guide to Arduino for beginners, including projects, tips, tricks, and programming!Valutazione: 4 su 5 stelle4/5 (3)
- Marine Structural Design CalculationsDa EverandMarine Structural Design CalculationsValutazione: 4.5 su 5 stelle4.5/5 (13)
- Artificial Intelligence: From Medieval Robots to Neural NetworksDa EverandArtificial Intelligence: From Medieval Robots to Neural NetworksValutazione: 4 su 5 stelle4/5 (3)
- Artificial Intelligence Revolution: How AI Will Change our Society, Economy, and CultureDa EverandArtificial Intelligence Revolution: How AI Will Change our Society, Economy, and CultureValutazione: 4.5 su 5 stelle4.5/5 (2)
- Pocket Guide to Flanges, Fittings, and Piping DataDa EverandPocket Guide to Flanges, Fittings, and Piping DataValutazione: 3.5 su 5 stelle3.5/5 (22)
- Structural Cross Sections: Analysis and DesignDa EverandStructural Cross Sections: Analysis and DesignValutazione: 4.5 su 5 stelle4.5/5 (19)
- Green Roofs, Facades, and Vegetative Systems: Safety Aspects in the StandardsDa EverandGreen Roofs, Facades, and Vegetative Systems: Safety Aspects in the StandardsNessuna valutazione finora
- Artificial Intelligence: The Complete Beginner’s Guide to the Future of A.I.Da EverandArtificial Intelligence: The Complete Beginner’s Guide to the Future of A.I.Valutazione: 4 su 5 stelle4/5 (5)
- The Heart and the Chip: Our Bright Future with RobotsDa EverandThe Heart and the Chip: Our Bright Future with RobotsNessuna valutazione finora
- Dark Aeon: Transhumanism and the War Against HumanityDa EverandDark Aeon: Transhumanism and the War Against HumanityValutazione: 5 su 5 stelle5/5 (1)
- Artificial Intelligence: Learning about Chatbots, Robotics, and Other Business ApplicationsDa EverandArtificial Intelligence: Learning about Chatbots, Robotics, and Other Business ApplicationsValutazione: 5 su 5 stelle5/5 (3)
- Pile Design and Construction Rules of ThumbDa EverandPile Design and Construction Rules of ThumbValutazione: 4.5 su 5 stelle4.5/5 (15)