Documenti di Didattica
Documenti di Professioni
Documenti di Cultura
Bab 7
Caricato da
Afiqah AbdullahCopyright
Formati disponibili
Condividi questo documento
Condividi o incorpora il documento
Hai trovato utile questo documento?
Questo contenuto è inappropriato?
Segnala questo documentoCopyright:
Formati disponibili
Bab 7
Caricato da
Afiqah AbdullahCopyright:
Formati disponibili
Sains Tingkatan 3 Bab 7 Keelektrikan
Nama:
Kelas:
Tarikh:
BAB
Keelektrikan
Electricity
PETA KONSEP
KEELEKTRIKAN
ELECTRICITY
Elektrostatik
Cas statik
Properties
Fenomena
Phenomena
Langkah
keselamatan
Safety measures
Magnetism
Measuring electricity
Medan magnet
Alat pengukuran
Statik charge
Sifat-sifat
Kemagnetan
Pengukuran keelektrikan
Electrostatics
Magnetic field
Instruments
Arus, voltan, dan rintangan
Current, voltage and resistance
Aliran arus dan
elektron
Flow of current and
electrons
Hubungan
Relationship
Hukum Ohm
Ohms law
Litar selari dan litar bersiri
Parallel and series circuits
Arus, voltan, dan
rintangan
Current, voltage and
resistance
Persamaan dan
perbezaan
Similarities and
differences
Kebaikan dan
kelemahan
Advantages and
disadvantages
K ATA K U N C I
Litar lengkap Complete circuit
Arus Current
Keelektromagnetan Electromagnetism
Rintangan Resistance
Voltan Voltage
Berapa jauhkah elektrik
bergerak per saat?
How far does electricity
travel per second?
Garisan daya
magnet
Magnetic field lines
Kompas
Compass
Keelektromagnetan
Electromagnetism
Elektromagnet
Electromagnet
Sains Tingkatan 3 Bab 7 Keelektrikan
Nama:
Kelas:
Objektif Pembelajaran
EKSPERIMEN
Inkuiri
Tarikh:
7.1 Memahami elektrostatik
Penghasilan dan Pengesanan Cas Elektrik Statik
7.1
Production and Detection of Static Electrical Charges
Penemuan Inkuiri
Tujuan
Menghasilkan dan mengesan cas elektrik statik dengan elektroskop
Bahan
Rod selulosa asetat, rod ebonit, rod kaca, dan kain flanel
Radas
Elektroskop / Electroscope
To produce and detect static electrical charges with an electroscope
Cellulose acetate rod, ebonite rod, glass rod and flannel cloth
Prosedur
Semua radas mesti bersih dan kering, termasuklah tangan anda. Air ialah konduktor
elektrik yang lemah dan akan mempengaruhi keputusan aktiviti ini.
All apparatus used must be clean and dry. Your hands must be dry. Water is a weak electrical conductor and
will affect the results of this activity.
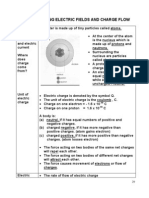
1. Dekatkan rod selulosa asetat yang neutral ke ceper logam
elektroskop seperti yang ditunjukkan dalam rajah. Perhatikan
kerajang emas.
Bring a neutral cellulose acetate rod near the metal cap of an electroscope
as shown in the diagram. Observe the gold leaf.
Rod selulosa
asetat
Cellulose
acetate rod
Ceper logam
Metal cap
2. Gosokkan rod selulosa asetat dengan kuat dengan menggunakan
kain flanel.
Elektroskop
Electroscope
Rub the cellulose acetate rod vigorously with a flannel cloth.
3. Dekatkan rod selulosa asetat yang telah digosok ke ceper logam
elektroskop. Perhatikan kerajang emas.
Bring the rubbed cellulose acetate rod near the metal cap of the electroscope. Observe the gold leaf.
4. Ulang langkah 1 hingga 3 dengan menggunakan rod ebonit dan rod kaca.
5. Rekodkan semua pemerhatian anda. / Record all your observation.
Repeat steps 1 to 3 with the ebonite rod and glass rod.
Pemerhatian
Pencapahan kerajang emas / Divergence of gold leaf
Bahan
Material
Sebelum digosok/ Before rubbing
Selepas digosok / After rubbing
Rod selulosa asetat
Tidak mencapah
Mencapah
Rod ebonit
Tidak mencapah
Mencapah
Rod kaca
Tidak mencapah
Mencapah
Cellulose acetate rod
No divergence
Ebonite rod
Diverged
No divergence
Glass rod
Diverged
No divergence
Diverged
Nyatakan definisi bagi elektrostatik. / State the definition of electrostatic.
Perbincangan 1.
Elektrostatik ialah kajian tentang cas elektrik statik.
Electrostatic is the study of static electrical charges.
2. Apakah fungsi elektroskop dalam aktiviti ini?
What is the function of the electroscope in this activity?
Mengesan cas-cas
elektrik statik
/ To detect
electrostatic
charges
HASIL PEMBELAJARAN
Memerihalkan maksud elektrostatik
Memerihalkan bagaimana cas elektrik statik dihasilkan dalam bahan tertentu
Memerihalkan cara mengesan cas elektrik statik
105
Sains Tingkatan 3 Bab 7 Keelektrikan
3. Bagaimanakah cas-cas elektrik statik dihasilkan? / How were electrostatic charges produced?
dengan kuat dengan kain
Rod selulosa asetat, rod ebonit, dan rod kaca
digosok
flanel.
rubbed
The cellulose acetate, ebonite and glass rods were
vigorously with a flannel cloth.
4. Adakah keputusan yang sama diperoleh sekiranya kain flanel yang basah digunakan?
Mengapa?
Would you get the same results if a damp flannel cloth was used? Why?
Tidak
. Hal ini kerana air pada kain akan
elektrik statik terkumpul pada rod.
mengalirkan
No
. This is because the water in the cloth will
cas. Tiada cas
conduct
the charges. No
electrostatic charges will be collected on the rods.
5. Apakah yang akan terjadi apabila objek bercas positif didekatkan ke ceper logam elektroskop?
What happens when a positively charged object is brought near the metal cap of an electroscope?
positif
Objek bercas positif akan mengaruh cas
pada batang logam dan kerajang
emas. Cas yang sama menyebabkan kerajang emas
positive
The positively charged object induces
charges causes the gold leaf to
mencapah
charges on the metal plate and gold leaf. The same
.
diverge
6. (a) Bagaimanakah anda menyahcas elektroskop? / How do you discharge an electroscope?
Sentuh ceper logam elektroskop dengan jari yang
Touch the metal cap of the charged electroscope with a
kering
finger
dry
(b) Tulis pemerhatian bagi jawapan anda di 6(a). / Write your observation for your answer in 6(a).
Kerajang emas
tidak mencapah
collapses
. / The gold leaf
(c) Berikan sebab bagi jawapan anda di 6(b). / Give a reason for your answer in 6(b).
dibumikan
Cas-cas pada elektroskop akan
The charges from the electroscope will be
KBAT
oleh jari.
by the finger.
earthed
7. Sebatang pembaris keluli digosok dengan kuat dengan kain sutera. Pembaris itu didekatkan
ke ceper logam elektroskop.
A stainless steel ruler was vigorously rubbed with a silk cloth. The ruler was brought near to the metal cap of
an electroscope.
(a) Ramalkan keadaan yang anda perhatikan. / Predict what you will observe.
Kerajang emas
tidak mencapah
. / The gold leaf
will not diverge
(b) Berikan sebab bagi jawapan anda di 7(a). / Give a reason for your answer in 7(a).
Kesimpulan
Pembaris keluli nirkarat ialah konduktor
melalui pembaris itu.
The stainless steel ruler is an
electrical
An electroscope is a device used to detect
and glass can be charged by
Menguasai
106
Belum Menguasai
rubbing
digosok
electrical
, maka cas-cas akan mengalir
conductor, so charges will flow through it.
elektrik
Elektroskop ialah alat untuk mengesan cas
ebonit, dan kaca boleh dicaskan apabila
elektrik
KBAT
. Bahan seperti selulosa asetat,
dengan kain flanel.
charges. Materials such as cellulose acetate, ebonite
them with a flannel cloth.
Tandatangan Guru: _______________________________
Sains Tingkatan 3 Bab 7 Keelektrikan
Nama:
EKSPERIMEN
Inkuiri
Tujuan
Kelas:
7.2
Sifat-sifat Cas Elektrik Statik
The Properties of Static Electrical Charges
Penemuan Inkuiri
Memerhati perubahan yang berlaku apabila dua objek bercas didekatkan antara satu sama lain
To observe what happens when two charged objects are brought near to each other
Bahan
Tali rafia, rod politena, rod selulosa asetat, dan kain bulu
Radas
Kaki retort dengan pengapit
Prosedur
Tarikh:
Band 4
Raffia string, polythene rods, cellulose acetate rods and woollen cloth
Retort stand with clamp
Semua radas mesti bersih dan kering, termasuklah tangan anda. Air ialah konduktor
elektrik yang lemah dan akan mempengaruhi keputusan aktiviti ini.
All apparatus used must be clean and dry. Your hands must be dry. Water is a weak electrical conductor and
will affect the results of this activity.
1. Ikat rod politena pada kaki retort dan gosokkan satu
hujung rod politena dengan kain bulu.
Kaki retort
Retort stand
Tie a polythene rod to a retort stand and rub one end of the polythene
rod with a woollen cloth.
Tali rafia
Raffia string
2. Gosokkan rod politena yang satu lagi dengan kain bulu
dan dekatkannya ke hujung rod yang digantung seperti
yang ditunjukkan dalam rajah. Perhatikan perubahan
yang berlaku.
Rod politena
Polythene rods
Rub another polythene rod with a woollen cloth and bring it near the
charged end of the suspended rod as shown in the diagram. Observe
what happens.
3. Ulang langkah 1 dan 2 dengan menggunakan
Repeat steps 1 and 2 by using
(a) dua rod selulosa asetat
two cellulose acetate rods
(b) satu rod politena dan satu rod selulosa asetat
one polythene rod and one cellulose acetate rod
4. Rekodkan semua pemerhatian anda.
Record all your observation.
Observation
Bahan yang digunakan
Pemerhatian
Materials used
Dua rod politena
Observation
Dua rod
Two polythene rods
Two rods
Dua rod selulosa asetat
Dua rod
menolak
repel
menolak
Two cellulose acetate rods
Two rods
Satu rod politena dan satu rod selulosa asetat
Dua rod
menarik
Two rods
attract
One polythene rod and one cellulose acetate rod
repel
antara satu sama lain.
each other.
antara satu sama lain.
each other.
antara satu sama lain.
each other.
HASIL PEMBELAJARAN
Menyatakan jenis cas elektrik statik
Menyatakan sifat cas elektrik statik
107
Sains Tingkatan 3 Bab 7 Keelektrikan
Perbincangan 1. Namakan jenis cas elektrik. / Name the types of electrical charges.
Positive
dan cas
/
Cas
positif
negatif
negative
and
charges
2. Apakah perbezaan antara cas positif dengan cas negatif?
What is the difference between positive and negative charges?
Cas positif terdiri daripada proton manakala cas negatif terdiri daripada elektron
.
.
Positive charges consist of protons while negative charges consist of electrons
3. Apakah inferens yang dapat dibuat tentang cas pada kedua-dua rod politena?
What inference can you make about the charges on both polythene rods?
sama
Cas yang
same
The
wujud pada kedua-dua rod politena.
type of charge exists on both polythene rods.
4. Apakah inferens yang dapat dibuat tentang cas pada rod politena dan rod selulosa asetat?
What inference can you make about the charges on the polythene rod and the cellulose acetate rod?
Cas yang
wujud pada dua rod yang berlainan.
berlainan
Opposite
charges are found on these two different rods.
KBAT
5. Apakah kesimpulan yang dapat dibuat tentang daya antara cas-cas?
What can you conclude about the forces between charges?
Cas yang berlainan menghasilkan daya
daya
tolakan
Unlike charges exert
. Cas yang sama menghasilkan
tarikan
.
forces. Like charges exert
attractive
repulsive
forces.
6. Adakah pemerhatian yang sama diperoleh sekiranya rod politena dipegang dengan tangan?
Mengapa? / Will you observe the same results if you hold the polythene rod in your hand? Why?
. Hal ini kerana pergerakan rod politena
Tidak
tidak dapat
. This is because the movement of the polythene rod
No
dikesan.
be detected.
cannot
7. Kilat berlaku apabila cas-cas bergerak dari satu awan bercas ke awan yang lain.
Lightning occurs when charges move from one charged cloud to another.
(a) Apakah inferens yang dapat dibuat tentang cas pada awan yang berlainan apabila kilat
berlaku? / What can you infer about the charges on different clouds when lightning occurs?
Awan yang berlainan mempunyai cas yang berlainan. Cas pada satu awan akan
menarik
cas pada awan yang berlainan, dan keadaan ini akan menghasilkan kilat.
Different clouds have different charges. The charges on one cloud will
on other clouds, resulting in lightning.
the charges
attract
(b) Bagaimanakah awan dicaskan? / How does a cloud become charged?
bergeser
dengan zarah udara.
Awan dicaskan apabila
Kesimpulan
rubs
A cloud is charged when it
against air particles.
Objek yang berlainan menghasilkan cas elektrik yang
yang berlainan
menarik
berlainan
apabila digosok. Cas
antara satu sama lain. Cas yang sama
menolak
antara satu sama lain.
Different objects produce
attract
Menguasai
108
Belum Menguasai
different
electrical charges when rubbed. Different types of charges
each other. The same type of charges
repel
each other.
Tandatangan Guru: _______________________________
Sains Tingkatan 3 Bab 7 Keelektrikan
Nama:
Kelas:
AKTIVITI
Perbincangan
Tarikh:
Fenomena yang Berkaitan dengan Cas Elektrik Statik
7.3
Phenomena Related to Electrostatic Charges
Konstruktivisme
Isi tempat kosong dengan jawapan yang betul untuk menerangkan beberapa contoh fenomena yang disebabkan
oleh cas elektrik statik.
Fill in the blanks with the correct answers to explain some examples of phenomena caused by static electrical charges.
tayar
awan
geseran
permukaan
tyres
friction
clouds
udara
mendarat
elektron
positif
logam
menyentuh
air
surface
lands
positively
metal
kilat
electrons
lightning
touch
Kilat / Lightning
Berlaku apabila
elektron
yang berkumpul di bawah awan bergerak ke
kawasan awan berdekatan yang bercas
Occurs when the
electrons
positif
accumulated at the bottom of the cloud move to the
positively
charged areas of nearby clouds.
Kilat juga berlaku apabila percikan api melompat di antara
bumi. Konduktor
permukaan
dan
awan
dipasang pada bangunan
kilat
yang tinggi supaya elektron mengalir melaluinya ke bumi.
Lightning also occurs when sparks jump between the
clouds
and the Earths
surface
conductors are installed on high buildings to make way for electrons to flow to the earth.
Lightning
Kapal terbang / Aeroplane
Cas statik berkumpul pada badan kapal terbang semasa terbang adalah disebabkan
geseran
oleh
tayar
dengan udara. Jadi, kapal terbang dipasang dengan
khas untuk mengalirkan cas ke bumi semasa
mendarat
Static charges accumulate on the body of an aeroplane flying through the air due to
with the air. So, the aeroplane is fixed with special
earth when the aeroplane
lands
tyres
friction
which conduct the charges to the
Lori tangki minyak / Oil tankers
Cas statik berkumpul semasa lori tangki minyak bergerak adalah disebabkan oleh
geseran dengan
udara
badan lori dibiarkan
menyentuh
. Rantai
logam
yang diikat pada
jalan. Cas dialirkan dari rantai logam ke bumi.
Static charges accumulate when an oil tanker moves along a road due to friction with the
The
metal
chain attached to the tankers body is allowed to
touch
air
the road. The
charges are conducted by the metal chain to the earth.
Menguasai
Belum Menguasai
Tandatangan Guru: _______________________________
HASIL PEMBELAJARAN
Memerihalkan fenomena harian yang disebabkan oleh cas elektrik statik
Menyatakan langkah keselamatan yang perlu diambil semasa pengendalian cas elektrik
109
Sains Tingkatan 3 Bab 7 Keelektrikan
Nama:
Kelas:
Objektif Pembelajaran
EKSPERIMEN
Inkuiri
Tujuan
7.4
Tarikh:
7.2 Memahami keelektrikan
Pengaliran Arus Elektrik
The Flow of Electric Current
Penemuan Inkuiri
Memerhatikan pengaliran arus elektrik dengan menggunakan penjana Van de Graaff dan
galvanometer
To observe the flow of electric current using a Van de Graaff generator and a galvanometer
Bahan
Dawai kuprum bertebat / Insulated copper wires
Radas
Penjana Van de Graaff dan galvanometer / Van de Graaff generator and galvanometer
Prosedur
1. Sambungkan kubah penjana Van de Graaff kepada terminal galvanometer dengan
menggunakan dawai kuprum bertebat.
Use an insulated copper wire to connect the dome of a Van de Graaff generator to the terminal of a galvanometer.
2. Gunakan satu dawai kuprum bertebat yang lain untuk menyambungkan terminal
galvanometer yang satu lagi ke Bumi seperti yang ditunjukkan dalam rajah.
Use another insulated copper wire to connect the other terminal of the galvanometer to earth as shown in the
diagram.
Kubah penjana
Dome
Dawai kuprum bertebat
Insulated copper wire
Galvanometer
Galvanometer
G
Penjana Van de Graaff
Van de Graaff generator
3. Hidupkan penjana Van de Graaff dan perhatikan jarum galvanometer.
4. Dekatkan kepala anda dengan rambut yang kering dan terurai ke kubah penjana. Perhatikan
perubahan yang berlaku pada rambut anda.
Switch on the Van de Graaff generator and observe the pointer of the galvanometer.
Get your head of dry, loose hair close to the dome. Observe what happens.
Nyahcas penjana Van de Graaff selepas anda mematikannya.
Discharge the Van de Graaff generator after you turn it off.
Pemerhatian
1. Apabila penjana Van de Graaff dihidupkan, jarum galvanometer
When the Van de Graaff generator is switched on, the pointer of the galvanometer
2. Apabila rambut didekatkan kepada kubah penjana, rambut
When the hair is brought close to the dome of the generator, the hair
HASIL PEMBELAJARAN
110
Memerihalkan arah arus dan pengaliran elektron dalam litar elektrik
terpesong
berdiri tegak
stands up on end
deflects
Sains Tingkatan 3 Bab 7 Keelektrikan
Perbincangan 1. Apakah fungsi penjana Van de Graaff? / What is the function of a Van de Graaff generator?
. / It produces
elektrik
Menghasilkan cas
charges.
electrical
2. Bagaimanakah cas dihasilkan oleh sebuah penjana Van de Graaff?
How does a Van de Graaff generator produce charges?
Tali sawat getah bergerak dan bergeser dengan pengguling.
sawat dengan pengguling menghasilkan cas.
friction
The belt moves and rubs against the rollers. The
antara tali
Geseran
between the moving belt and rollers
produces charges.
3. Apakah fungsi galvanometer? / What is the function of a galvanometer?
Mengesan
yang kecil. / It detects the flow of a small
arus elektrik
current
4. Buat satu inferens berdasarkan pemerhatian aktiviti ini.
Make an inference based on each observation of this activity.
(a)
mengalir dari kubah penjana Van de Graaff ke Bumi melalui
Arus elektrik
galvanometer.
electric current
An
galvanometer.
flows from the dome of the Van de Graaff generator to earth through the
(b) Rambut menerima cas
dan menolak antara satu sama lain.
positif
The strands of hair receive
charges and repel each other.
positive
(c) Nyatakan arah pengaliran arus elektrik dan elektron dalam litar elektrik.
State the direction of current and electron flow in an electric circuit.
(i) Arus elektrik: Dari terminal
positive
Current: From
negatif
negative
Electron: From
negative
terminal to
(ii) Elektron: Dari terminal
ke terminal
positif
negatif
terminal
ke terminal
positif
positive
terminal
terminal to
5. (a) Bahagian dawai kuprum bertebat yang manakah membawa cas?
Which part of the insulated copper wire carries charges?
Bahagian berlogam/kuprum di
The metal/copper part
bahan penebat
dalam
inside
the insulation
(b) Apakah nama bahagian ini? / What is the name of this part?
Konduktor / A conductor
Kesimpulan
1. Penjana Van de Graaff digunakan untuk menghasilkan
digunakan untuk mengesan pengaliran
A Van de Graaff generator is used to produce
of
electrical charges
The flow of electrical charges produces
Menguasai
Belum Menguasai
. Galvanometer
atau arus elektrik yang kecil.
cas elektrik
. A galvanometer is used to detect the flow
electrical charges
or small currents.
2. Pengaliran cas elektrik menghasilkan
cas elektrik
arus elektrik
electric current
Tandatangan Guru: _______________________________
111
Sains Tingkatan 3 Bab 7 Keelektrikan
Nama:
Kelas:
AKTIVITI
Perbincangan
Tarikh:
Tenaga Elektrik, Arus, Voltan, dan Rintangan
7.5
Electricity, Current, Voltage and Resistance
Masteri
Isi tempat kosong.
Band 2
Fill in the blanks.
tinggi
high
arus
pengaliran kuprum semakin tinggi
current
flow
copper
1. Tenaga elektrik ialah
2. Arus ialah
kadar
rate
tungsten
flow
rate
tenaga
Ohm
energy
Ohm
of electrical charges.
of flow of negative charges.
yang diperlukan untuk menggerakkan cas elektrik atau elektron dari satu
required to move electrical charges or electrons from one point to another.
energy
4. Rintangan bagi suatu bahan ialah penentangan terhadap
The resistance of a material is its opposition to the
5. Rintangan disukat dalam unit
tinggi
The materials which have
tungsten
lower
pengaliran cas negatif. / Current is the
tenaga
3. Voltan ialah
titik ke titik yang lain.
6. Bahan yang
semakin rendah
cas elektrik. / Electricity is the
pengaliran
kadar
Voltage is the
higher
arus
yang mengalir melaluinya.
flowing through it.
current
. / The resistance is measured in units of
Ohm
Ohm
rintangannya hanya membolehkan arus yang kecil mengalir melaluinya.
high
resistance allow small current to flow through it.
7. Faktor-faktor yang mempengaruhi rintangan ialah: / Factors affecting the resistance are:
(a) Jenis bahan / Type of material
mempunyai rintangan
Konduktor elektrik yang baik mempunyai rintangan yang rendah.
Kuprum
tungsten
yang lebih rendah berbanding dengan
.
tungsten
has lower resistance compared to
.
Good electric conductor has lower resistance.
Copper
(b) Panjang konduktor / Length of the conductor
semakin tinggi
Semakin panjang konduktor,
The longer the conductor, the
the resistance.
higher
(c) Tebal konduktor / Thickness of the conductor
Semakin tebal konduktor,
semakin rendah
The thicker the conductor, the
Menguasai
Tandatangan Guru: _______________________________
Kelas:
Objektif Pembelajaran
EKSPERIMEN
Inkuiri
7.6
rintangannya.
the resistance.
lower
Belum Menguasai
Nama:
rintangannya.
7.3 Mengaplikasi kefahaman cara mengukur keelektrikan
Pengukuran Arus Elektrik dan Voltan Elektrik
Measurement of Electric Current and Electrical Voltage
Penemuan Inkuiri
Tujuan
Mengukur arus elektrik dan voltan / To measure electric current and voltage
Bahan
Sel kering / Dry cells
Radas
Ammeter, voltmeter, pemegang bateri, mentol, pemegang mentol, suis, dan dawai penyambung
Ammeter, voltmeter, battery holder, bulb, bulb socket, switch and connecting wires
HASIL PEMBELAJARAN
112
Tarikh:
Menyatakan maksud keelektrikan, voltan, dan rintangan
Mengenal pasti alat pengukur arus dan voltan
Menyatakan unit arus dan voltan
Mengukur arus dan voltan dalam litar elektrik
Band 4
Sains Tingkatan 3 Bab 7 Keelektrikan
Prosedur
Ammeter
Ammeter
Mentol
Bulb
Suis
Switch
Suis
Switch
Sel kering
Dry cell
+
Voltmeter
Voltmeter
Mentol
Bulb
Sel kering / Dry cell
+
Pemegang bateri
Battery holder
(a)
(b)
Pemegang bateri
Battery holder
1. Gunakan satu sel kering dan sediakan litar seperti yang ditunjukkan dalam Rajah (a).
Use one dry cell and set up a circuit as shown in Diagram (a).
2. Hidupkan suis litar. Perhatikan mentol dan ammeter. Rekodkan bacaan anda.
3. Ulang langkah 1 dan 2 dengan dua, dan kemudian tiga sel kering.
4. Gunakan satu sel kering dan sediakan litar seperti yang ditunjukkan dalam Rajah (b).
5. Hidupkan suis litar. Perhatikan mentol dan voltmeter. Rekodkan bacaan anda.
6. Ulang langkah 4 dan 5 dengan dua, dan kemudian tiga sel kering.
Switch on the circuit. Observe the bulb and ammeter. Record your reading.
Repeat steps 1 and 2 with two and then three dry cells.
Use one dry cell and set up a circuit as shown in Diagram (b).
Switch on the circuit. Observe the bulb and voltmeter. Record your reading.
Repeat steps 4 and 5 with two and then three dry cells.
Pastikan terminal positif ammeter/voltmeter disambung ke terminal positif sel kering dan
terminal negatif ammeter/voltmeter disambung ke terminal negatif sel kering.
Make sure the positive terminal of the ammeter/voltmeter is connected to the positive terminal of the dry cell
and the negative terminal of the ammeter/voltmeter is connected to the negative terminal of the dry cell.
Keputusan
Bilangan sel
kering
Kecerahan mentol
Bacaan ammeter
(A)
Bacaan voltmeter (V)
Malap / Dim
0.25
1.5
Cerah / Bright
0.29
3.0
Sangat cerah / Very bright
0.35
4.5
Brightness of bulb
Number of dry cells
Ammeter reading (A)
Voltmeter reading (V)
Perbincangan 1. Apakah alat pengukur yang digunakan untuk mengukur arus yang mengalir melalui satu
litar lengkap?
What is the instrument used to measure the current that flows through a complete circuit?
Band 1
Ammeter / Ammeter
2. Apakah unit yang ditunjukkan pada skala ammeter?
What is the unit shown on the scale of an ammeter?
Band 1
Ampere (A) / Ampere (A)
3. Bagaimanakah ammeter disambung dalam litar? / How is an ammeter connected in a circuit?
Ammeter disambung secara
bersiri
. / The ammeter is connected in
series
113
Sains Tingkatan 3 Bab 7 Keelektrikan
4. Bagaimanakah bilangan sel kering yang digunakan dalam litar mempengaruhi
How does the number of dry cells used in a circuit affect the
(a) kecerahan mentol?
brightness of the bulb?
Kecerahan mentol
The brightness of the bulb
apabila lebih sel kering digunakan.
bertambah
when more dry cells are used.
increases
(b) bacaan ammeter?
ammeter reading?
Bacaan ammeter
bertambah
The ammeter reading
increases
apabila lebih banyak sel kering digunakan.
when more dry cells are used.
5. Apakah alat pengukur yang digunakan untuk mengukur voltan merentasi suatu komponen
Band 1
atau litar?
What is the instrument used to measure the voltage across a component or circuit?
Voltmeter / Voltmeter
6. Apakah unit yang ditunjukkan pada skala voltmeter?
Band 1
What is the unit shown on the scale of a voltmeter?
Volt (V) / Volt (V)
7. Bagaimanakah voltmeter disambung dalam litar?
How is a voltmeter connected in a circuit?
Voltmeter disambung secara
dengan komponen.
selari
The voltmeter is connected in
with the component.
parallel
8. Apakah perubahan pada bacaan voltmeter apabila bilangan sel kering bertambah?
What happens in voltmeter readings when more dry cells are used?
bertambah
Bacaan voltmeter
The voltmeter readings
Kesimpulan
Ammeter
1.
An
ampere
.
Voltmeter
volt
A
is connected in series in a circuit to measure an electric current in units of
ammeter
ampere
2.
disambungkan secara bersiri dalam litar untuk mengukur arus elektrik
dalam unit
increase
disambungkan secara selari dalam litar untuk mengukur voltan dalam unit
.
voltmeter
is connected in parallel in a circuit to measure voltage in units of
3. Penggunaan sel kering yang lebih banyak akan
menambah
volt
jumlah arus yang
mengalir dalam suatu litar dan voltan yang merentasi mentol.
Using more dry cells will
increase
the amount of current that flows in a circuit and the voltage
across the bulb.
Menguasai
114
Belum Menguasai
Tandatangan Guru: _______________________________
Sains Tingkatan 3 Bab 7 Keelektrikan
Nama:
Kelas:
Tarikh:
Objektif Pembelajaran 7.4 Mensintesis hubungan antara arus, voltan, dan rintangan
EKSPERIMEN
Tak terbimbing
Tujuan
Pernyataan
masalah
Hipotesis
7.7
Kesan Perubahan Rintangan Terhadap Arus
The Effect of Resistance on Current
Penemuan Inkuiri
Band 5
Mengkaji hubung kait antara rintangan dengan arus
To study the relationship between resistance and current
Apakah kesan perubahan rintangan terhadap arus? / What is the effect of resistance change on current?
Arus elektrik akan
Electric current will
apabila rintangan berkurang.
bertambah
increase
when resistance decreases.
Pemboleh ubah (a) Dimanipulasikan:
Rintangan / Resistance
Manipulated
(b) Bergerak balas: Bacaan ammeter/Kecerahan mentol / Ammeter reading/Brightness of bulb
Responding
(c) Dimalarkan: Nilai voltan/Jenis wayar/Tebal wayar / Voltage/Type of wire/Wire thickness
Fixed
Radas
Ammeter, mentol dan pemegangnya, suis, perintang 2 , 4 , 6 , dan 8 , dawai penyambung
dengan klip buaya, sel kering
Ammeter, bulb and bulb holder, switch, 2 , 4 , 6 and 8 resistor, connecting wires with crocodile clip, dry cells
Perancangan
eksperimen
Dengan menggunakan radas yang disediakan, rancang dan jalankan eksperimen untuk mengkaji
kesan perubahan rintangan terhadap arus seperti yang ditunjukkan dalam rajah. Senaraikan
langkah eksperimen anda dan dapatkan kebenaran daripada guru anda sebelum menjalankan
eksperimen.
Using the apparatus provided, plan and carry out an experiment to investigate the effect of change in resistance on
current as shown in the diagram. List the steps of your experiment and get your teachers approval before carry out
the experiment.
Sel kering
Dry cell
Ammeter
Ammeter
Pemegang
bateri
Battery holder
Perintang
Resistor
Kaedah
Suis
Switch
Mentol
Bulb
1. Litar disediakan dengan menggunakan perintang 2 . / The circuit was set up using the 2 resistor.
2. Suis dihidupkan dan kecerahan mentol diperhatikan.
The switch is switched on and the brightness of the bulb was observed.
3. Bacaan ammeter direkodkan. / The ammeter reading was recorded.
4. Langkah 1 hingga 3 diulang dengan menggunakan perintang 4 , 6 , dan 8 .
Steps 1 to 3 were repeated with a 4 , 6 and 8 resistor respectively.
HASIL PEMBELAJARAN
Mereka bentuk dan menjalankan eksperimen untuk mengkaji hubung kait antara rintangan dengan arus
Memerihalkan kesan perubahan rintangan ke atas arus
115
Sains Tingkatan 3 Bab 7 Keelektrikan
Pemerhatian
Rintangan ()
Resistance ()
Kecerahan mentol
Bulb brightness
Paling cerah
Cerah
Malap
Paling malap
0.9
0.7
0.5
0.3
The brightest
Bacaan ammeter (A)
Reading of ammeter (A)
Perbincangan
Bright
Dim
The most dim
1. Lukis graf arus melawan rintangan dengan menggunakan data dalam pemerhatian.
Draw a graph of current against resistance using the data in observation.
Graf arus melawan rintangan
Graph of current against resistance
1.0
0.9
0.8
Arus / Current (A)
0.7
0.6
0.5
0.4
0.3
0.2
0.1
0
3
4
5
6
7
8
Rintangan / Resistance ()
10
2. Berdasarkan graf, apakah hubung kait antara rintangan dengan arus yang mengalir di dalam
KBAT
litar?
Based on the graph, what is the relationship between resistance and the current flowing through the circuit?
Semakin besar rintangan, semakin
The greater the resistance, the
smaller
arus yang mengalir.
the current flow.
State the relationship between resistance and the ammeter reading.
Semakin besar rintangan, semakin
The greater the resistance, the
smaller
rendah
bacaan ammeter.
the ammeter reading.
KBAT
4. Nyatakan hubung kait antara rintangan dengan kecerahan mentol.
State the relationship between resistance and the brightness of the bulb.
Apabila rintangan di dalam litar bertambah, kecerahan mentol
As the resistance in the circuit increases, the brightness of the bulb
116
KBAT
3. Nyatakan hubung kait antara rintangan dengan bacaan ammeter.
rendah
decreases
berkurang
.
Sains Tingkatan 3 Bab 7 Keelektrikan
5. Berdasarkan graf, ramalkan bacaan ammeter apabila rintangannya ialah 10 .
KBAT
Based on the graph, predict the ammeter reading when the resistance is 10 .
0.1 A
6. Suatu radas disediakan dengan merendamkan gegelung pemanas di dalam air. Apabila suis
dihidupkan, arus elektrik mengalir melalui gegelung pemanas yang terdapat di dalam air.
Suatu termometer digunakan untuk mengukur suhu air. Apakah hubung kait antara masa
yang diambil dengan bacaan suhu?
KBAT
An apparatus is set up whereby a heating coil is dipped into the water. When the switch is turned on, current
flows through the heating coil in the water. A thermometer is used to measure the temperature of the water. What
is the relationship between the time taken and the temperature reading?
lama
Semakin
The
masa yang diambil, semakin
the time taken, the
longer
tinggi
bacaan suhu.
the temperature reading.
higher
7. Nyatakan definisi secara operasi bagi rintangan.
State the operational definition of resistance.
Rintangan sesuatu bahan ialah sifat yang menyebabkan mentol menyala dengan malap .
Resistance of a substance is the property that cause the bulb to
Kesimpulan
shine dimly
1. Adakah hipotesis yang dibuat dapat diterima?
Is the hypothesis made acceptable?
Ya / Yes
2. Arus elektrik
decreases
Electric current
Menguasai
Tak terbimbing
Hipotesis
Tandatangan Guru: _______________________________
Kelas:
EKSPERIMEN
Pernyataan
masalah
when resistance in the circuit increases.
Belum Menguasai
Nama:
Tujuan
apabila rintangan di dalam litar bertambah.
berkurang
7.8
Tarikh:
Kesan Perubahan Voltan Terhadap Arus
The Effect of Voltage on Current
Penemuan Inkuiri
Band 5
Mengkaji hubung kait antara voltan dengan arus
To study the relationship between voltage and current
Apakah hubung kait antara voltan dengan arus?
What is the relationship between voltage and current?
Semakin
The
tinggi
higher
voltan, semakin
the voltage, the
besar
larger
arus yang mengalir di dalam litar.
the current that flows in a circuit.
Pemboleh ubah (a) Dimanipulasikan : Bilangan sel kering (voltan) / Number of dry cells (voltage)
Manipulated
(b) Bergerak balas : Arus / Current
Responding
(c) Dimalarkan
: Rintangan / Resistance
Fixed
HASIL PEMBELAJARAN
Mereka bentuk dan menjalankan eksperimen untuk mengkaji hubung kait antara voltan dengan arus
Memerihalkan kesan perubahan voltan ke atas arus
117
Sains Tingkatan 3 Bab 7 Keelektrikan
Radas
Sel kering, pemegang bateri, mentol, pemegang mentol, ammeter, voltmeter, suis, dan dawai
penyambung
Dry cells, battery holder, bulb, bulb socket, ammeter, voltmeter, switch and connecting wires
Perancangan
eksperimen
Dengan menggunakan radas yang disediakan, rancang dan jalankan eksperimen untuk mengkaji
hubung kait antara voltan dengan arus seperti yang ditunjukkan dalam rajah. Senaraikan
langkah eksperimen anda dan dapatkan kebenaran daripada guru anda sebelum menjalankan
eksperimen.
Using the apparatus provided, plan and carry out an experiment to investigate the relationship between voltage and
current as shown in the diagram. List the steps of your experiment and get your teachers approval before carry out
the experiment.
Ammeter
Ammeter
Voltmeter
Voltmeter
Mentol / Bulb
Sel kering
Dry cell
Suis
Switch
Pemegang bateri
Battery holder
Kaedah
1. Satu sel kering digunakan untuk menyediakan litar seperti yang ditunjukkan dalam rajah.
One dry cell was used to set up the circuit as shown in the diagram.
2. Litar dihidupkan. Bacaan voltmeter dan ammeter diperhatikan. Semua keputusan
direkodkan.
The circuit was switched on. The voltmeter and ammeter readings were observed. The results were recorded.
3. Langkah 1 dan 2 diulang dengan menggunakan dua, tiga, dan kemudian empat sel kering.
Steps 1 and 2 were repeated using two, then three and finally four dry cells.
Keputusan
Bilangan sel kering
Bacaan voltmeter (V)
Bacaan ammeter (A)
1.4
0.2
3.0
0.4
4.4
0.6
6.0
0.8
Number of dry cells
118
Voltmeter reading (V)
Ammeter reading (A)
Sains Tingkatan 3 Bab 7 Keelektrikan
Perbincangan
1. Apabila bilangan sel kering dalam litar bertambah, apakah yang berlaku kepada
When the number of dry cells in a circuit increases, what happens to the
(a) bacaan voltmeter? / voltmeter reading?
.
Bacaan voltmeter
bertambah
The voltmeter reading
increases
(b) bacaan ammeter? / ammeter reading?
.
Bacaan ammeter
bertambah
The ammeter reading
increases
2. Dalam eksperimen ini, komponen yang manakah membekalkan rintangan malar?
In this experiment, which components provide constant resistance?
Mentol dan dawai / The bulb and the wires
3. Apakah yang berlaku kepada mentol apabila bilangan sel kering dalam litar bertambah?
What happens to the bulb when more dry cells are added to the circuit?
Mentol menjadi
lebih terang
. / The bulb becomes
brighter
4. Apakah hubung kait antara voltan dengan arus dalam litar?
KBAT
What is the relationship between the voltage and the current in a circuit?
Apabila voltan bertambah, arus juga
When the voltage increases, the current also
bertambah
increases
5. Plotkan graf voltan melawan arus.
Plot a graph of voltage versus current.
Voltage / Voltan (V)
Graf voltan melawan arus
Graph of voltage against current
0.2
0.4
0.6
0.8
Arus /
Current (A)
(a) Apakah jenis graf yang diperoleh?
What type of graph is obtained?
Graf garis lurus / A straight-line graph
119
Sains Tingkatan 3 Bab 7 Keelektrikan
(b) Apakah yang ditunjukkan oleh graf ini?
What does this graph show?
Arus adalah berkadar
nisbah
voltan
mewakili
rintangan
Current is
the
kepada
. Nisbah ini sentiasa malar dan
arus
dalam litar.
proportional to voltage. The gradient of the graph shows the ratio of
directly
voltage
dengan voltan. Kecerunan graf menunjukkan
terus
to
. The ratio is always constant and represents the
current
in a circuit.
resistance
(c) What law does this represent?
Apakah hukum yang diwakili?
Ohms law / Hukum Ohm
(d) Berdasarkan hukum yang dinyatakan di (c), nyatakan hubung kait antara voltan (V),
arus (I), dan rintangan (R).
Based on the law stated in (c), state the relationship between voltage (V), current (I) and resistance (R).
R =
V
I
Kesimpulan
1. Adakah hipotesis yang dibuat dapat diterima?
Is the hypothesis made acceptable?
Ya / Yes
2.
yang mengalir dalam litar bertambah apabila voltan bertambah.
Arus
The
that flows in a circuit increases when the voltage increases.
current
3. Nisbah voltan kepada arus ialah suatu
rintangan
4. Hukum Ohm menyatakan bahawa
adalah berkadar terus dengan
Ohms law states that the
voltage
Menguasai
120
Belum Menguasai
. Pemalar ini disebut sebagai
The ratio of the voltage to current is a
pemalar
current
. This constant is known as the
constant
arus
voltan
resistance
yang mengalir melalui satu konduktor
yang merentasi litar.
that flows through a conductor is directly proportional to the
across the circuit.
Tandatangan Guru: _______________________________
Sains Tingkatan 3 Bab 7 Keelektrikan
Nama:
AKTIVITI
Perbincangan
Kelas:
7.9
Tarikh:
Penyelesaian Masalah dengan Menggunakan Hukum Ohm (1)
Problem-solving Using Ohms Law (1)
Masteri
Selesaikan masalah di bawah dengan menggunakan Hukum Ohm.
Solve the problems below by using Ohms Law.
voltan / voltage (V)
Rintangan / Resistance (R) =
arus / current (I)
1. Hitung arus dalam litar ini.
Calculate the current in this circuit.
Arus / Current = ? A
Voltan / Voltage
= 24 V
Rintangan / Resistance
= 12
V
I =
R
24
=
12
=2 A
2. Dua bateri, 3 V disambungkan ke ammeter dan perintang. Jika bacaan ammeter ialah 0.5 A, hitung rintangan
perintang itu.
Two batteries, 3 V are connected to an ammeter and a resistor. If the ammeter reading is 0.5 A, calculate the resistance in the resistor.
V
R =
I
3
=
0.5
=6
3. Apakah nilai voltan pada perintang 10 apabila arus 1.5 A mengalir melaluinya?
What is the voltage across a 10 resistor when a current of 1.5 A flows through it?
V = IR
= 1.5 10
= 15 V
Menguasai
Belum Menguasai
Tandatangan Guru: _______________________________
HASIL PEMBELAJARAN
Menyatakan Hukum Ohm
121
Sains Tingkatan 3 Bab 7 Keelektrikan
Nama:
Kelas:
Objektif Pembelajaran
AKTIVITI
7.10
Projek
Tarikh:
7.5 Mensintesis konsep litar selari dan litar bersiri
Litar Bersiri dan Litar Selari
Series Circuit and Parallel Circuit
Konstruktivisme
1. Bahagikan kelas kepada beberapa kumpulan. Setiap kumpulan terdiri daripada empat orang ahli dan seorang
Band 6
ketua.
Divide class into several groups. Each group consists of four members with one leader.
2. Setiap kumpulan dikehendaki mengumpulkan maklumat tentang perkara yang berikut:
Each group is required to collect the information on the following aspects.
(a) Komponen yang diwakili oleh simbol yang berikut:
Components that are represented by the following symbols:
(b) Perbandingan antara litar bersiri dengan litar selari
Comparison between series and parallel circuits
(i) Rajah litar
Drawing of the circuit
(ii) Kelebihan dan kelemahan litar daripada segi:
Advantage and disadvantage of the circuit in terms of:
Adakah semua konponen dalam litar dikawal oleh satu suis?
Are all components in the circuit controlled by one switch?
Adakah kecerahan semua mentol dalam litar adalah sama apabila menyala?
Are all bulbs in the circuit light up with the same brightness?
Adakah sel tahan lama?
Can the cells last longer?
Apakah yang berlaku terhadap mentol yang lain apabila terdapat satu mentol terbakar?
What happens to the other bulbs if a bulb is burnt?
......
......
3. Kemudian, setiap kumpulan akan mempersembahkan hasil mereka dengan menggunakan jadual, gambar
foto, persembahan PowerPoint, atau mana-mana persembahan yang kreatif dan inovatif.
Then, each group will present their findings using table, photos, PowerPoint presentation or any other presentation that is creative and
innovative.
Menguasai
Belum Menguasai
Tandatangan Guru: _______________________________
HASIL PEMBELAJARAN
122
Mengenal pasti komponen litar elektrik dan simbolnya
Melukiskan satu gambar rajah litar yang lengkap
Membandingkan dan membezakan susunan komponen dalam litar bersiri dengan litar selari
Menerangkan kelebihan dan kelemahan litar bersiri
Menerangkan kelebihan dan kelemahan litar selari
Sains Tingkatan 3 Bab 7 Keelektrikan
Nama:
Kelas:
Objektif Pembelajaran
EKSPERIMEN
Inkuiri
Tarikh:
7.6 Menganalisis arus, voltan, dan rintangan dalam satu litar bersiri
Arus, Voltan, dan Rintangan dalam Litar Bersiri
7.11
Current, Voltage and Resistance in a Series Circuit
Penemuan Inkuiri
Band 4
Tujuan
Menganalisis arus, voltan, dan rintangan dalam litar bersiri
Radas
Ammeter, voltmeter, sel kering, pemegang bateri, dua mentol yang serupa, pemegang mentol,
suis, dan dawai penyambung
To analyse current, voltage and resistance in a series circuit
Ammeter, voltmeter, dry cells, battery holder, two identical bulbs, bulb sockets, switch and connecting wires
Prosedur
Q
A
A
V
(a) (b)
(c)
1. Sediakan litar seperti yang ditunjukkan dalam Rajah (a).
Set up a circuit as shown in Diagram (a).
2. Hidupkan suis litar. Perhatikan dan rekodkan bacaan ammeter dan voltmeter.
Switch on the circuit. Observe and record the ammeter and voltmeter readings.
3. Gunakan nilai itu untuk menghitung rintangan.
4. Matikan suis litar. Sambungkan ammeter dan voltmeter seperti yang ditunjukkan dalam
Rajah (b).
Use the values to calculate the resistance.
Switch off the circuit. Connect the ammeter and voltmeter as shown in Diagram (b).
5. Ulang langkah 2 dan 3. / Repeat steps 2 and 3.
6. Matikan suis litar. Sambungkan ammeter dan voltmeter seperti yang ditunjukkan dalam
Rajah (c).
Switch off the circuit. Connect the ammeter and voltmeter as shown in Diagram (c).
Keputusan
7. Ulang langkah 2 dan 3. / Repeat steps 2 and 3.
Mentol
V
()
I
V
Resistance, R =
I ( )
Rintangan, R =
Arus, I (A)
Voltan, V (V)
0.5
2.8
5.6
0.5
1.4
2.8
0.5
1.4
2.8
Bulb
P dan Q
P and Q
Current, I (A)
Voltage, V (V)
HASIL PEMBELAJARAN
Memerihalkan pengaliran arus melalui komponen dalam litar bersiri
Memerihalkan voltan yang merentasi komponen dalam litar bersiri
Memerihalkan rintangan dalam litar bersiri
123
Sains Tingkatan 3 Bab 7 Keelektrikan
Perbincangan
1. Arus diukur pada titik yang berlainan dalam litar bersiri. Apakah inferens yang dapat dibuat
daripada pemerhatian anda?
The current was tested at different points in the series circuit. What inference can you make from your
observation?
Arus adalah
The current is the
sama
pada semua titik dalam litar bersiri.
at all points in a series circuit.
same
2. Voltan diukur pada titik yang berlainan dalam litar bersiri. Apakah inferens yang dapat dibuat
daripada pemerhatian anda?
The voltage was tested at different points in the series circuit. What inference can you make from your
observation?
voltan yang merentasi setiap mentol.
Jumlah voltan dalam litar ialah
hasil tambah
The total voltage is the
of the voltages across each bulb.
sum
3. Voltan yang merentasi sebiji mentol dilabel sebagai V. Hitung jumlah voltan yang merentasi
tiga biji mentol yang serupa dalam litar bersiri.
The voltage across one bulb is represented by V. Calculate the total voltage across three similar bulbs connected
in series.
V + V + V = 3V
4. Apakah yang berlaku kepada jumlah rintangan dalam litar bersiri apabila lebih banyak mentol
disambungkan?
What happens to the total resistance in a series circuit when more bulbs are added?
Apabila lebih mentol disambungkan, jumlah rintangan dalam litar
When more bulbs are used, the total resistance in a circuit
bertambah
increases
5. Lima mentol disambung secara bersiri. Berapakah suis yang diperlukan untuk menghidupkan
atau mematikan kelima-lima mentol secara serentak?
Five bulbs are connected in series. How many switches are required to switch all five bulbs on or off at one go?
Satu / One
Kesimpulan
1. Dalam litar bersiri, arus pada mana-mana titik dalam litar adalah
In a series circuit, the current at any points in the circuit is
The sum of the voltages across each component is the
3. Rintangan berkesan dalam litar adalah
The effective resistance of the circuit is the
Menguasai
Belum Menguasai
total voltage
hasil tambah
sum
2. Hasil tambah voltan yang merentasi setiap komponen adalah
dibekalkan kepada litar.
124
the same
sama
jumlah voltan
yang
supplied to the circuit.
rintangan setiap mentol.
of the individual resistance of each bulb.
Tandatangan Guru: _______________________________
Sains Tingkatan 3 Bab 7 Keelektrikan
Nama:
AKTIVITI
Perbincangan
Kelas:
7.12
Tarikh:
Penyelesaian Masalah dengan Menggunakan Hukum Ohm (2)
Problem-solving Using Ohms Law (2)
Masteri
Selesaikan masalah di bawah.
Solve the problems below.
1. Hitung arus yang mengalir dalam litar.
Calculate the current that flows in the circuit.
R = R1 + R2 + R3
= (2 + 2 + 3)
=7
V
Arus / Current =
R
6
=
7
= 0.86 A
I=?
6V
2. Hitung rintangan pada perintang R2 dalam litar.
Calculate the resistance in resistor R2 in the circuit.
R1 = 1
V
R=
I
1.5
=
0.25
=6
R2 = ?
V = 1.5 V
I = 0.25 A
R = R1 + R2
6 = 1 + R2
R2 = 6 1 = 5
3. 1.0 A arus mengalir melalui suatu perintang yang bernilai 2 . Berapakah nilai voltan dalam litar bersiri ini?
1.0 A of current flows through a 2 resistor. What is the voltage in a series circuit?
V = IR
= 1.0 2
=2V
Menguasai
Belum Menguasai
Tandatangan Guru: _______________________________
HASIL PEMBELAJARAN
Menyatakan Hukum Ohm
125
Sains Tingkatan 3 Bab 7 Keelektrikan
Nama:
Kelas:
Objektif Pembelajaran
EKSPERIMEN
Inkuiri
Tarikh:
7.7 Menganalisis arus, voltan, dan rintangan dalam satu litar selari
Arus, Voltan, dan Rintangan dalam Litar Selari
7.13
Current, Voltage and Resistance in a Parallel Circuit
Penemuan Inkuiri
Band 4
Tujuan
Menganalisis arus, voltan, dan rintangan dalam litar selari
Bahan
Ammeter, voltmeter, sel kering, pemegang bateri, dua mentol yang serupa, pemegang mentol,
suis, dan dawai penyambung
Prosedur
To analyse current, voltage and resistance in a parallel circuit
Ammeter, voltmeter, dry cells, battery holder, two identical bulbs, bulb sockets, switch and connecting wires
V
P
A
P
A
(a)
(b)
(c)
1. Sediakan litar seperti yang ditunjukkan dalam Rajah (a). / Set up a circuit as shown in Diagram (a).
2. Hidupkan suis litar. Perhatikan dan rekodkan bacaan ammeter dan voltmeter.
Switch on the circuit. Observe and record the ammeter and voltmeter readings.
3. Gunakan nilai itu untuk menghitung rintangan, R dengan menggunakan Hukum Ohm
V
1
(R = ) dan kemudian nilai untuk .
I
R
V
1
Use the values to calculate the resistance, R using Ohms Law (R =
) and then the value for
4. Matikan suis litar. Sambungkan ammeter dan voltmeter seperti yang ditunjukkan dalam
Rajah (b).
Switch off the circuit. Connect the ammeter and voltmeter as shown in Diagram (b).
5. Ulang langkah 2 dan 3. / Repeat steps 2 and 3.
6. Matikan suis litar. Sambungkan ammeter dan voltmeter seperti yang ditunjukkan dalam
Rajah (c).
Switch off the circuit. Connect the ammeter and voltmeter as shown in Diagram (c).
7. Ulang langkah 2 dan 3. / Repeat steps 2 and 3.
Keputusan
Rintangan, R =
V ()
I
Mentol
Arus, I (A)
Voltan, V (V)
P dan Q / P and Q
1.5
0.5
1.5
0.5
Bulb
Current, I (A)
Voltage, V (V)
V
Resistance, R = ()
I
1
()
R
HASIL PEMBELAJARAN
126
Memerihalkan pengaliran arus melalui komponen dalam litar selari
Memerihalkan voltan yang merentasi komponen dalam litar selari
Memerihalkan rintangan dalam litar selari
Membandingkan dan membezakan antara litar bersiri dengan litar selari berdasarkan arus,
voltan, dan rintangan
Sains Tingkatan 3 Bab 7 Keelektrikan
Perbincangan
1. Arus diukur pada titik yang berlainan dalam litar selari. Apakah inferens yang dapat dibuat
daripada pemerhatian anda? / The current was measured at different points in the parallel circuit. What
inference can you make from your observation?
sama
Arus daripada sumber (bateri) dalam litar selari adalah
tambah arus dalam semua cabang.
The current from the source (battery) of a parallel circuit is
branches.
dengan hasil
as the sum of the current in all
the same
2. Voltan diukur pada titik yang berlainan dalam litar selari. Apakah inferens yang dapat dibuat
daripada pemerhatian anda? / The voltage was measured at different points in the parallel circuit. What
inference can you make from your observation?
sama
Voltan pada mana-mana titik dalam litar selari adalah
The voltage at any points in a parallel circuit is
the same
3. Jika jumlah arus ialah I dan arus merentasi mentol P dan Q ialah IP dan IQ masing-masing,
gunakan sebutan ini untuk menyatakan hubung kait antara jumlah arus yang mengalir
dalam litar dengan arus yang mengalir melalui mentol.
KBAT
If the total current is I and the current across bulbs P and Q are IP and IQ respectively, use these terms to express
a relationship between the total current flowing in the circuit and the current flowing through the bulbs.
I = IP + IQ
4. Apakah yang berlaku kepada rintangan berkesan dalam litar selari apabila lebih banyak
mentol ditambahkan?
KBAT
What happens to the effective resistance in a parallel circuit when more bulbs are added?
kurang
Rintangan berkesan dalam litar adalah
The effective resistance of the circuit is
less
daripada rintangan setiap mentol.
than the resistance of each bulb.
5. Lima mentol disambung dalam cabang selari yang berlainan. Berapakah suis yang
diperlukan untuk menghidupkan atau mematikan mentol secara berasingan?
Five bulbs are connected in separate parallel branches. How many switches are required to switch the bulbs on
or off individually?
Lima / Five
6. Bandingkan litar bersiri dengan litar selari berdasarkan arus, voltan, dan rintangan dengan
menggunakan formula yang diberikan. / Compare a series circuit and a parallel circuit in terms of
current, voltage and resistance using the formula given.
I = I1 + I2V = V1 + V2
1
1
1
= +
Rtotal
R1
R2
V = V1 = V2R = R1 + R2I = I1 = I2
Litar bersiri
Series circuit
V = V1 + V2
I = I1 = I2
R = R1 + R2
Perbezaan
Difference
Voltan
Voltage
Arus
Litar selari
Parallel circuit
V = V1 = V2
Current
I = I1 + I2
Rintangan
1
1
1
= +
Rtotal
R1
R2
Resistance
127
Sains Tingkatan 3 Bab 7 Keelektrikan
Kesimpulan
1. Dalam litar selari, arus dari sumber tenaga adalah hasil tambah arus yang mengalir melalui
setiap komponen.
In a parallel circuit, the current from the energy source is the
each component.
2. Voltan yang merentasi setiap komponen adalah
litar.
the same
The voltage across each component is
Menguasai
kurang
less
The effective resistance of the circuit is
AKTIVITI
Perbincangan
7.14
sama
dengan voltan merentasi
daripada rintangan setiap mentol.
than the resistance of each bulb.
Tandatangan Guru: _______________________________
Belum Menguasai
Nama:
of the current flowing through
as the voltage across the circuit.
3. Rintangan berkesan dalam litar adalah
sum
Kelas:
Tarikh:
Penyelesaian Masalah dengan Menggunakan Hukum Ohm (3)
Problem-solving Using Ohms Law (3)
Masteri
Selesaikan masalah di bawah.
Solve the problems below.
1. Hitung arus yang mengalir dalam litar.
Calculate the current that flows in the circuit.
=
R
1
=
R
R =
+
R1
1
+
20
12
R2
1
30
V
Arus / Current =
R
56
=
12
= 4.67 A
R2 = 30
R1 = 20
56 V
2. Hitung voltan yang dibekalkan dalam litar.
Calculate the voltage supplied in the circuit.
I = I1 + I2
= (1 + 1)A
=2A
1
=
R
1
=
R
R =
Voltan = IR
= 2 1.5
=3V
1
1
+
R1
R2
1
1
+
3
3
1.5
Menguasai
Belum Menguasai
HASIL PEMBELAJARAN
128
Menyatakan Hukum Ohm
I1 = 1 A
I2 = 1 A
Tandatangan Guru: _______________________________
Sains Tingkatan 3 Bab 7 Keelektrikan
Nama:
Kelas:
Tarikh:
Objektif Pembelajaran 7.8 Memahami kemagnetan
EKSPERIMEN
Inkuiri
7.15
Corak dan Arah Medan Magnet
The Pattern and Direction of Magnetic Field
Tujuan
Mengkaji corak dan arah medan magnet
Bahan
Magnet bar, serbuk besi, dan kadbod putih
Radas
Kompas
Penemuan Inkuiri
Band 4
To study the pattern and direction of magnetic fields
Bar magnet, iron filings and white cardboard
Prosedur
Compasses
Serbuk besi
Iron filings
Kadbod putih
White cardboard
Magnet bar
Bar magnet
(a)
Kompas
Compass
(b)
1. Letakkan sekeping kadbod putih di atas sebatang magnet bar.
2. Taburkan serbuk besi di atas kadbod putih seperti yang ditunjukkan dalam Rajah (a).
3. Tepuk tepi kadbod dengan perlahan dengan jari anda.
4. Perhatikan dan lukis corak medan magnet yang terbentuk.
5. Letakkan empat buah kompas di sekeliling magnet seperti yang ditunjukkan dalam Rajah
(b).
Place a white cardboard on top of a bar magnet.
Sprinkle iron filings all over the cardboard as shown in Diagram (a).
Gently tap the edge of the cardboard with your finger.
Observe and draw the magnetic field pattern obtained.
Place four compasses around the magnet as shown in Diagram (b).
6. Tandakan arah medan magnet dalam rajah yang telah anda lukis dalam langkah 4.
7. Ulang aktiviti ini dengan meletakkan magnet bar seperti kedudukan yang ditunjukkan dalam
Rajah (c) hingga (f).
Mark the direction of the magnetic field on the diagram that you have drawn in step 4.
Repeat the activity by placing the bar magnets in the positions shown in Diagram (c) to (f).
HASIL PEMBELAJARAN
Memerihalkan maksud medan magnet
Melukiskan medan magnet satu magnet bar
Melukiskan arah medan magnet
Menghubungkaitkan garisan medan magnet dengan kekuatan medan magnet
Menerangkan kegunaan magnet dalam kompas
129
Sains Tingkatan 3 Bab 7 Keelektrikan
Pemerhatian
Titik neutral / Neutral point
U/N
S/S
S/S
Rajah (a) / Diagram (a)
S/S
U/N
S/S
U/N
U/N
S/S
U/N
Rajah (c) / Diagram (c)
Rajah (d) / Diagram (d)
U/N
U/N
S/S
S/S
X ialah titik neutral
X is a neutral point
X ialah titik neutral
X is a neutral point
Rajah (e) / Diagram (e)
Rajah (f) / Diagram (f)
1. Apakah medan magnet?
What is a magnetic field?
Kawasan di sekeliling magnet, iaitu tempat daya
It is an area surrounding a magnet where
U/N
X
U/N
Perbincangan
S/S
S/S
magnet
dapat dikesan atau dirasai.
forces can be felt or experienced.
magnetic
2. Medan magnet tidak dapat dilihat. Bagaimanakah medan magnet dapat ditunjukkan dalam
aktiviti ini?
Magnetic field is invisible. How can the magnetic field be shown in this activity?
Garisan serbuk besi membentuk corak dari kutub
Corak ini ialah medan magnet bagi magnet bar.
Lines of iron filings forming a pattern from the
The pattern is the magnetic field of the bar magnet.
130
north
utara
ke kutub
pole to the
south
selatan
pole.
3. (a) Daripada pemerhatian anda, apakah inferens yang dapat dibuat tentang bahagian magnet
yang berlainan dengan kekuatan medan magnet?
From your observation, what can you infer about the different areas and strengths of the magnetic
field?
Medan magnet
tengah magnet.
The magnetic field is
lebih kuat
stronger
di bahagian kutub berbanding dengan bahagian
at the poles than at the centre.
Sains Tingkatan 3 Bab 7 Keelektrikan
(b) Berikan sebab bagi jawapan anda di 3(a).
Give a reason for your answer in 3(a).
serbuk besi terdapat di kedua-dua hujung magnet berbanding
Lebih banyak
dengan kawasan tengah magnet. Hal ini bermakna garis medan magnet
lebih rapat di bahagian ini
adalah
.
iron filings are found at both ends of the magnet as compared to the centre of the
More
magnet. This means that the magnetic field lines
are closely-spaced at this region
4. Bagaimanakah magnet digunakan di dalam kompas?
How is a magnet used in a compass?
Magnet digunakan sebagai penunjuk untuk menentukan arah di dalam kompas
A magnet is used as a pointer to determine direction in a compass
5. Mengapakah kompas digunakan dalam aktiviti ini?
Why is a compass used in this activity?
Menunjukkan
To show the
Kesimpulan
medan magnet
arah
direction
of the magnetic field
1. Medan magnet di kawasan kutub
magnet.
The magnetic field at the poles is
stronger
than at the centre of a bar magnet.
utara
2. Arah medan magnet adalah dari kutub
sebatang magnet bar.
The direction of a magnetic field is from the
Menguasai
Kelas:
Objektif Pembelajaran
EKSPERIMEN
Inkuiri
Tujuan
7.16
north
ke kutub
pole to the
south
selatan
bagi
pole of a bar magnet.
Tandatangan Guru: _______________________________
Belum Menguasai
Nama:
berbanding dengan kawasan tengah
lebih kuat
Tarikh:
7.9 Memahami keelektromagnetan
Medan Magnet bagi Dawai Lurus yang Membawa Arus Elektrik
The Magnetic Field of a Straight Wire Carrying Electric Current
Penemuan Inkuiri
Mengkaji medan magnet yang dihasilkan oleh dawai lurus yang membawa arus elektrik
To study the magnetic field produced by a straight wire carrying electric current
Bahan
Serbuk besi, dawai kuprum lurus, dan kadbod putih
Radas
Bekalan kuasa voltan rendah, kaki retort dengan pengapit, dan kompas
Band 4
Iron filings, straight copper wire and white cardboard
Low voltage power supply, retort stand with clamps and compasses
HASIL PEMBELAJARAN
Menghubungkaitkan arus elektrik yang mengalir melalui konduktor dengan kemagnetan
Memerihalkan maksud elektromagnet
131
Sains Tingkatan 3 Bab 7 Keelektrikan
Prosedur
Dawai kuprum
Copper wire
Serbuk besi
Iron filings
Kadbod putih
White cardboard
Kaki retort
Retort stand
Kompas
Compass
Bekalan kuasa
Power supply
1. Tepuk satu lubang di bahagian tengah kadbod putih. Apitkan kadbod putih dengan
menggunakan kaki retort.
Make a hole in the middle of a white cardboard. Clamp the white cardboard to a retort stand.
2. Masukkan dawai kuprum melalui lubang pada kadbod putih.
3. Sambungkan dawai ke bekalan kuasa voltan rendah seperti yang ditunjukkan dalam rajah.
4. Taburkan serbuk besi di atas kadbod.
5. Hidupkan suis dan tepuk tepi kadbod perlahan-lahan sehingga corak terbentuk.
6. Letakkan empat buah kompas di sekeliling dawai lurus di atas kadbod itu. Perhatikan
pergerakan jarum kompas.
Pass the copper wire through the hole of the white cardboard.
Connect the wire to the low voltage power supply as shown in the diagram.
Sprinkle iron filings all over the cardboard.
Turn on the switch and tap the edge of the cardboard gently until a pattern is formed.
Place four compasses around the straight wire on the cardboard. Observe the movement of the compass needles.
7. Matikan bekalan kuasa. Songsangkan arah arus.
8. Hidupkan bekalan kuasa sekali lagi. Perhatikan pergerakan jarum kompas.
9. Lukis arah medan magnet yang diperhatikan.
132
Switch off the power supply. Reverse the direction of current.
Switch on the power supply again. Observe the movement of the compass needles.
Draw the direction of the magnetic fields observed.
Sains Tingkatan 3 Bab 7 Keelektrikan
Pemerhatian
Arus
Current
Kadbod putih
White cardboard
Medan magnet
Magnetic field
Arus
Current
Kadbod putih
White cardboard
Perbincangan
Medan magnet
Magnetic field
1. (a) Adakah keputusan yang sama akan diperoleh jika dawai kuprum lurus yang melalui
lubang pada kadbod digantikan dengan rod besi?
Will you get the same results if the straight copper wire going through the hole on the cardboard is
replaced with an iron rod?
Ya / Yes
(b) Berikan sebab untuk jawapan anda di (a). / Give a reason for your answer in (a).
Kedua-dua dawai kuprum dan rod besi ialah
Both the copper wire and iron rod are
conductors
konduktor
2. Mengapakah serbuk besi membentuk corak di sekeliling dawai apabila arus mengalir
melaluinya?
Why do iron filings form a pattern around the wire when current flows through it?
Arus yang mengalir melalui dawai mengaruhkan
The current flowing through the wire induces a
medan magnet
magnetic field
3. Huraikan corak yang terbentuk oleh serbuk besi di sekeliling dawai.
Describe the pattern formed by the iron filings around the wire.
Bulatan sepusat / Concentric circles
4. Apakah kesan terhadap medan magnet apabila arah arus disongsangkan?
What effect does reversing the direction of current have on the magnetic field?
Arah
medan magnet akan berubah.
The
direction
of the magnetic field will change.
133
Sains Tingkatan 3 Bab 7 Keelektrikan
5. Apakah elektromagnet? / What is an electromagnet?
Elektromagnet ialah magnet sementara. Elektromagnet hanya mempunyai kesan magnet
mengalir melaluinya.
apabila
arus
An electromagnet is a temporary magnet. It only has magnetic effects when a
current
flows
through it.
6. Apakah keelektromagnetan? / What is electromagnetism?
Keelektromagnetan ialah kajian tentang hubung kait antara
kemagnetan
keelektrikan
dengan
Electromagnetism is the study of the relationship between
and
electricity
magnetism
7. Adakah dawai yang digunakan dalam aktiviti ini suatu elektromagnet?
Is the wire used in this activity an electromagnet?
Ya / Yes
Kesimpulan
1. Apabila arus mengalir melalui dawai lurus,
When current flows through a straight wire, a
magnetic field
2. Arah medan magnet bergantung kepada arah
Kelas:
Masteri PBS
Elektrostatik ialah kajian cas elektrik statik.
Resistance is the characteristic of a material that opposes
Band 2
(a) tenaga elektrik / electrical energy
Tenaga elektrik ialah tenaga yang dihasilkan
apabila arus elektrik mengalir.
Electrical energy is the energy produced when electric
current flows.
(b) voltan / voltage
Voltan ialah tenaga yang diperlukan untuk
menggerakkan cas elektrik atau elektron dari satu
the flow of electrical charges through it.
3. (a) Apakah alat pengukur untuk mengukur
or electrons from one point to another.
134
What is the instrument used to measure
(i) arus elektrik? / current?
Ammeter / Ammeter
(ii) voltan? / voltage?
Voltmeter / Voltmeter
(b) Nyatakan unit bagi
State the unit for
(i)
(ii) voltan / voltage
volt / volt
titik ke titik yang lain.
Voltage is the energy required to move electrical charges
Tarikh:
pengaliran cas elektrik melaluinya.
Electrostatic is the study of static electrical charges.
State the definition for:
(c) rintangan / resistance
Rintangan ialah sifat suatu bahan yang menentang
What is electrostatics?
current
1. Apakah elektrostatik?
2. Nyatakan definisi bagi:
Tandatangan Guru: _______________________________
Belum Menguasai
Nama:
is induced.
arus
The direction of the magnetic field depends on the direction of the
Menguasai
diaruhkan.
medan magnet
Band 1
arus elektrik / current
ampere / ammeter
Band 1
Sains Tingkatan 3 Bab 7 Keelektrikan
4. Rajah yang berikut menunjukkan litar elektrik X dan Y dengan komponen yang sama.
The diagram below shows electric circuits X and Y with the same components.
(a) Namakan jenis litar elektrik X dan Y.
Name the type of electric circuits X and Y.
(i)
X:
Litar selari / Parallel circuit
(ii) Y:
Litar bersiri / Series circuit
(b) Lukis rajah litar X dan Y.
Draw the circuit diagram for X and Y.
X
5. Bandingkan litar bersiri dengan litar selari dengan menggunakan rumus yang diberikan.
Compare the series circuit and the parallel circuit with the formula given.
V = V1 + V2
I = I1 + I2
Litar bersiri
Series circuit
(a) V = V1 + V2
(b) I = I1 = I2
(c) R = R1 + R2
V = V1 = V2
R = R1 + R2
I = I1 = I2
1
1
1
= +
R2
R
R1
Perbezaan
Litar selari
Difference
Jumlah voltan
Total voltage
Jumlah arus
Total current
Rintangan
Resistance
Parallel circuit
(d) V = V1 = V2
(e) I = I1 + I2
1
1
1
(f) = +
R
R1
R2
6. Gariskan jawapan yang betul untuk menghubungkaitkan garis daya magnet dengan kekuatan medan magnet.
Underline the correct answer to relate the magnetic field lines and the strength to magnetic field.
(a) Medan magnet paling kuat di (bahagian tengah, bahagian hujung)
The magnetic field is the strongest at the (middle, end).
(b) Semakin rapat garis daya magnet, (semakin kuat, semakin lemah) magnet itu.
The closer the magnetic field lines, the (stronger, weaker) the magnet.
(c) Medan magnet sentiasa mengarah dari kutub (utara, selatan) ke kutub (utara, selatan).
The magnetic field always point from the (north, south) pole to the (north, south) pole.
(d) Arah medan magnet dapat dikesan dengan menggunakan (kompas, jam randik).
The direction of a magnetic field can be detected by using a (compass, stopwatch).
135
Sains Tingkatan 3 Bab 7 Keelektrikan
Nama:
Kelas:
Tarikh:
Latihan Sumatif
Soalan Struktur
1. Rajah 1.1 menunjukkan tiga mentol yang serupa, X, Y, dan
Z disambung secara selari.
Diagram 1.1 shows three identical bulbs, X, Y and Z connected
in parallel.
(b) Rajah 1.2 menunjukkan susunan radas bagi satu litar
elektrik.
Diagram 1.2 shows the apparatus set-up for an electrical
circuit.
Z
Klip kertas logam
Metal paper clip
A
Rajah 1.1 / Diagram 1.1
(a) (i) Bandingkan kecerahan mentol X, Y, dan Z jika
suis dalam litar ini dihidupkan?
Compare the brightness of bulbs X, Y and Z if the
switch in this circuit is turned on?
Ketiga-tiga mentol mempunyai kecerahan yang
sama.
Rajah 1.2 / Diagram 1.2
(i)
Apakah yang dapat diperhatikan tentang bacaan
ammeter apabila klip itu digerakkan di sepanjang
dawai dari X ke Y?
What can be observed on the ammeter reading as
the clip moves along the wire from X to Y?
Bacaan ammeter berkurang.
The three bulbs have the same brightness.
(ii)
Nyatakan sebab bagi jawapan di 1(a)(i).
State the reason for the answer in 1(a)(i).
Ketiga-tiga mentol menerima jumlah voltan yang
sama.
The three bulbs get the same amount of voltage
The ammeter reading decreases.
(ii)
Nyatakan sebab bagi jawapan di 1(b)(i).
KBAT
State the reason for the answer in 1(b)(i).
Rintangan bertambah apabila panjang dawai
bertambah.
The resistance has increased when the length of
wire is increased.
(iii)
Jika Y dialihkan, apakah yang akan berlaku
kepada X?
KBAT
If Y is removed, what will happen to X?
Mentol X masih menyala.
Bulb X still lights up.
2. Rajah 2 menunjukkan satu eksperimen yang dijalankan
untuk mengkaji hubung kait antara dua dawai, P dan Q,
dengan panjang masing-masing ialah 10 cm.
Diagram 2 shows an experiment carried out to investigate the
relationship between two wires, P and Q with length of 10 cm
respectively.
Sel kering
Dry cells
(iv)
Jika ketiga-tiga mentol itu disambung secara
bersiri, apakah yang berlaku kepada mentolmentol lain jika salah satu mentol itu terbakar?
If these three bulbs are connected in series, what will
happen to the other bulbs if one of the bulbs burns
out?
KBAT
Mentol lain tidak akan menyala.
The other bulbs will not light up.
136
Dawai P
yang nipis
Thin wire P
Ammeter
Ammeter
Suis
Switch
Mentol
Bulb
Voltmeter
Voltmeter
Sains Tingkatan 3 Bab 7 Keelektrikan
(c) Lakarkan suatu graf arus melawan tebal dawai.
Sel kering
Dry cells
Sketch a graph of current versus thickness of wire.
Dawai Q
yang tebal
Thick wire Q
Ammeter
Ammeter
Arus (A)
Current (A)
Suis
Switch
Mentol
Bulb
Voltmeter
Voltmeter
Rajah 2 / Diagram 2
(a) Rekodkan bacaan ammeter di ruang yang disediakan.
Record the ammeter reading in the spaces provided.
(d) Apakah hubung kait antara tebal dawai dengan arus?
Semakin tebal dawai, semakin besar arus yang
Bacaan ammeter / Ammeter reading =
3
What is the relationship between the thickness of the wire
and the current?
KBAT
Dawai P / Wire P
Tebal dawai (mm)
Thickness of wire (mm)
0.8
mengalir melalui dawai.
The thicker the wire, the larger the current that flows
through the wire.
Dawai Q / Wire Q
Bacaan ammeter / Ammeter reading =
1.2
(b) Ramalkan bacaan ammeter jika dawai R yang
digunakan lebih tebal daripada P tetapi lebih nipis
daripada Q.
KBAT
Predict the ammeter reading if wire R with thickness more
than P but less than Q is used.
Kira-kira 1.0 A (mana-mana jawapan antara
0.8 A 1.2 A)
(e) Huraikan kecerahan mentol dalam litar dengan
KBAT
Describe the brightness of the bulbs in the circuits with
(i) dawai P / wire P
Mentol adalah malap. / The bulb is dim.
(ii) dawai Q / wire Q
Mentol adalah cerah. / The bulb is bright.
About 1.0 A (any answer between 0.8 A 1.2 A)
137
Potrebbero piacerti anche
- Electrics Pyhsics Form 5Documento60 pagineElectrics Pyhsics Form 5aiman48Nessuna valutazione finora
- 03-Physic F5 2018-ElectricityDocumento32 pagine03-Physic F5 2018-ElectricitySreedrannNessuna valutazione finora
- Physics Definition Form 5Documento8 paginePhysics Definition Form 5Hello KittyNessuna valutazione finora
- BELONGS TO: .. : Chemistry SPM - Quick Review F4Documento8 pagineBELONGS TO: .. : Chemistry SPM - Quick Review F4Amalina Kasmunee100% (1)
- Essay Waves Esei Gelombang 2018Documento35 pagineEssay Waves Esei Gelombang 2018S.NeroshineNessuna valutazione finora
- Analysis of PEKA 1-Chem f4Documento2 pagineAnalysis of PEKA 1-Chem f4Zalilahismail IsmailNessuna valutazione finora
- SPM Percubaan 2008 SBP Chemistry AnswersDocumento19 pagineSPM Percubaan 2008 SBP Chemistry AnswersChinWynn.com94% (16)
- An Ecstatic Environment WeekDocumento3 pagineAn Ecstatic Environment WeekRin Shamsul75% (8)
- SPM 4531 2007 Physics p2 BerjawapanDocumento26 pagineSPM 4531 2007 Physics p2 Berjawapanpss smk selandar75% (4)
- JawapanBab3 PDFDocumento32 pagineJawapanBab3 PDFMashithoh RosliNessuna valutazione finora
- p2 Trial SPM Perlis 2018 - SKEMADocumento8 paginep2 Trial SPM Perlis 2018 - SKEMAIzzati NorNessuna valutazione finora
- Form 5 Chapter 2 Electricity: Van de Graaff Generator & Electric FieldsDocumento7 pagineForm 5 Chapter 2 Electricity: Van de Graaff Generator & Electric Fieldskhangsiean890% (1)
- Riang Belajar KSSM Fizik TKT 5 (English Answers) PG 1-9Documento9 pagineRiang Belajar KSSM Fizik TKT 5 (English Answers) PG 1-9汤思慧100% (1)
- Paper 2 Form 4 2020Documento28 paginePaper 2 Form 4 2020Yusfalina Mohd YusoffNessuna valutazione finora
- Science Form 3 Chapter 10Documento8 pagineScience Form 3 Chapter 10Eric ChewNessuna valutazione finora
- Experiment Physics Form 5 5.3 Emf and RDocumento13 pagineExperiment Physics Form 5 5.3 Emf and RCheah Soon Tike0% (1)
- Haba Ting 4Documento19 pagineHaba Ting 4Azura OsmanNessuna valutazione finora
- Biology Practical Reports For Form 4 Experiment 9.2 (Practical Textbook Page 128)Documento2 pagineBiology Practical Reports For Form 4 Experiment 9.2 (Practical Textbook Page 128)ke20% (1)
- Skema Fizik Percubaan K1 F5 Kedah 2016Documento5 pagineSkema Fizik Percubaan K1 F5 Kedah 2016Cheah Soon Tike25% (4)
- Tg4 Praktis 3 PDFDocumento23 pagineTg4 Praktis 3 PDFMarhamah Kamaludin100% (1)
- Soalan Sains PMRDocumento121 pagineSoalan Sains PMRFazil Jay100% (2)
- Physics Johor SPM Trial 2008 (Edu - Joshuatly.com)Documento0 paginePhysics Johor SPM Trial 2008 (Edu - Joshuatly.com)Carolyn Chang Boon ChuiNessuna valutazione finora
- 02 - Physics Module Chapter 2.1Documento9 pagine02 - Physics Module Chapter 2.1ZazaNessuna valutazione finora
- Latih Tubi 4 AkasiaDocumento24 pagineLatih Tubi 4 Akasiatumirah86Nessuna valutazione finora
- Chemical Bonds ExplainedDocumento29 pagineChemical Bonds Explainedmastor1969Nessuna valutazione finora
- Atomic structure and states of matter in Chemistry moduleDocumento30 pagineAtomic structure and states of matter in Chemistry moduleNur Irdina HaniNessuna valutazione finora
- KBSM t4 Skema Kimia k2Documento9 pagineKBSM t4 Skema Kimia k2kancil416670Nessuna valutazione finora
- Trial Negeri Sembilan Biology Pra SPM 2013 SET 1 K1 - K2 - K3 - Question - SchemeDocumento0 pagineTrial Negeri Sembilan Biology Pra SPM 2013 SET 1 K1 - K2 - K3 - Question - SchemeCikgu Faizal100% (5)
- Paper 2Documento44 paginePaper 2ayydenNessuna valutazione finora
- Answer Trial SBP Physics SPM 2013 Paper 2Documento9 pagineAnswer Trial SBP Physics SPM 2013 Paper 2Cikgu FaizalNessuna valutazione finora
- (Bahagian C)Documento22 pagine(Bahagian C)Siti Arbaiyah AhmadNessuna valutazione finora
- Biology Paper 2 SPM 2010Documento46 pagineBiology Paper 2 SPM 2010azianiNessuna valutazione finora
- ITEM BERFOKUS Fizik SPM 2022 JawapanDocumento7 pagineITEM BERFOKUS Fizik SPM 2022 JawapanNur Ain Fitriah Mohamad KholibNessuna valutazione finora
- Paper 3 Physics PendulumDocumento2 paginePaper 3 Physics Pendulumnik mohamad solehinNessuna valutazione finora
- Marking Scheme Paper 1 2 3 SBP Trial SPM 2009Documento21 pagineMarking Scheme Paper 1 2 3 SBP Trial SPM 2009Mohd Khairul AnuarNessuna valutazione finora
- Kedah-Answer Physics P1 P2 P3-Trial SPM 2009Documento16 pagineKedah-Answer Physics P1 P2 P3-Trial SPM 2009kamalharmozaNessuna valutazione finora
- Spring Constant and Hooke's LawDocumento11 pagineSpring Constant and Hooke's LawMUHAMAD ZANDAR BIN ZAKARIA KPM-GuruNessuna valutazione finora
- Ujian1 PHYSICS Form 4Documento11 pagineUjian1 PHYSICS Form 4Pauling ChiaNessuna valutazione finora
- Skema Pppa Kimia k2 SPM 2011 Selangor Kertas 2Documento14 pagineSkema Pppa Kimia k2 SPM 2011 Selangor Kertas 2Siraf IldaNessuna valutazione finora
- Modul Fizik X A PLUS 2015Documento79 pagineModul Fizik X A PLUS 2015Toral Bhatt100% (3)
- Sample Questions and Answers For Paper 3 Section B1Documento10 pagineSample Questions and Answers For Paper 3 Section B1Adsham100% (3)
- Selangor Skema Kimia Kertas 2 (Set 1)Documento17 pagineSelangor Skema Kimia Kertas 2 (Set 1)SITI RAIHANI BINTI KAMSO MoeNessuna valutazione finora
- SPM 2015 Paper 2Documento47 pagineSPM 2015 Paper 2Srikanth SagardevanNessuna valutazione finora
- Nota Padat Fizik F5 ElectricDocumento32 pagineNota Padat Fizik F5 Electricslokkro97% (38)
- Lab Experiment 3 - Charging and ElectroscopeDocumento6 pagineLab Experiment 3 - Charging and ElectroscopeMLOOK SAEEDNessuna valutazione finora
- Physics Project Report On Frictional ElectricityDocumento20 paginePhysics Project Report On Frictional Electricityvazhkaia oru trollNessuna valutazione finora
- Activity #2 - ElectroscopeDocumento4 pagineActivity #2 - ElectroscopeTUSHAR DASH0% (1)
- St12a1 Condino, Samanthalouise PT2 ElectroscopeDocumento5 pagineSt12a1 Condino, Samanthalouise PT2 ElectroscopeSamantha Louise CondinoNessuna valutazione finora
- Electrolysis: Time Key QuestionDocumento3 pagineElectrolysis: Time Key QuestionPradeep YallankiNessuna valutazione finora
- Physics 1 - Class XIIDocumento311 paginePhysics 1 - Class XIISunil Nahata100% (1)
- Physics Electroscope Practical ReportDocumento4 paginePhysics Electroscope Practical ReportNATHAN0% (2)
- Electroscope Lab ActivityDocumento5 pagineElectroscope Lab ActivityReysel MonteroNessuna valutazione finora
- 8.6 Copper Plating and ElectrolysisDocumento12 pagine8.6 Copper Plating and ElectrolysisADITYA RAHMANNessuna valutazione finora
- NCERT Physics STD 12 Part 1Documento311 pagineNCERT Physics STD 12 Part 1Yash MaheshwariNessuna valutazione finora
- Electric Charges and Fields ExplainedDocumento291 pagineElectric Charges and Fields Explainedshaileshgadbail100% (1)
- Mine Electrical Study GuideDocumento314 pagineMine Electrical Study GuideAnand AgrawalNessuna valutazione finora
- ElectricityDocumento16 pagineElectricitypatrick omonyNessuna valutazione finora
- 6-lab-making-an-electroscopeDocumento8 pagine6-lab-making-an-electroscopechrystlerestrada14Nessuna valutazione finora
- Electrochemistry Lab ExperienceDocumento15 pagineElectrochemistry Lab ExperienceA HNessuna valutazione finora
- Physics Investigatory DraftDocumento15 paginePhysics Investigatory DraftRavanNessuna valutazione finora
- Chapter 7 Fourier Series: 1 Learning OutcomesDocumento12 pagineChapter 7 Fourier Series: 1 Learning OutcomesMorsaleen ChowdhuryNessuna valutazione finora
- Laboratory Stress-Strain Tests For Developments in Geotechnical Engineering Research and PracticeDocumento61 pagineLaboratory Stress-Strain Tests For Developments in Geotechnical Engineering Research and PracticeRami Mahmoud BakrNessuna valutazione finora
- PRELIM EXAM SOLUTIONSDocumento8 paginePRELIM EXAM SOLUTIONSamielynNessuna valutazione finora
- Ruta Al Caos PDFDocumento33 pagineRuta Al Caos PDFDiego VilchesNessuna valutazione finora
- Module6 - Ideal Gas ProcessesApplicationDocumento20 pagineModule6 - Ideal Gas ProcessesApplicationJohn Dalton ValenciaNessuna valutazione finora
- Dokumen - Tips - Chap 23 64 Regular Physics PDFDocumento394 pagineDokumen - Tips - Chap 23 64 Regular Physics PDFNadiaNessuna valutazione finora
- Fluid Phase Equilib. 2007, 261, 104-110Documento7 pagineFluid Phase Equilib. 2007, 261, 104-110GióngManAymorickNessuna valutazione finora
- PG - M.sc. - Physics - 345 21 - Quantum Mechanics-IDocumento304 paginePG - M.sc. - Physics - 345 21 - Quantum Mechanics-I17 CSE Lokesh VNessuna valutazione finora
- Mga Sagot Ni Ashe Montage (Gen. Physics)Documento4 pagineMga Sagot Ni Ashe Montage (Gen. Physics)John Michael Cañero MaonNessuna valutazione finora
- smts-2 Theory of Structures by B.C. Punmia Text PDFDocumento497 paginesmts-2 Theory of Structures by B.C. Punmia Text PDFAman Dubey100% (1)
- XRY-1A Oxygen Bomb CalorimeterDocumento16 pagineXRY-1A Oxygen Bomb CalorimeterFrank.J83% (6)
- Fundamentals of PFC CorrectionDocumento24 pagineFundamentals of PFC Correctionsuji100% (1)
- Vector Algebra: Unit IvDocumento95 pagineVector Algebra: Unit IvTharindu PrabhathNessuna valutazione finora
- Salinity and Water Effect On Electrical Properties of Fragile Clayey SandstoneDocumento9 pagineSalinity and Water Effect On Electrical Properties of Fragile Clayey Sandstoneandrea.cipagautaNessuna valutazione finora
- Problem Sheet 3Documento2 pagineProblem Sheet 3balochfrahan.2003Nessuna valutazione finora
- Moody Chart Solver, HDocumento3 pagineMoody Chart Solver, HAnonymous LrKeCiUNessuna valutazione finora
- Creep Testing Kappa SSDocumento2 pagineCreep Testing Kappa SSGustavo LealNessuna valutazione finora
- IEEE-A Primer On Capacitor Bank Protection PDFDocumento6 pagineIEEE-A Primer On Capacitor Bank Protection PDFGustavo AguayoNessuna valutazione finora
- NMR Spectroscopy Integrals and MultiplicityDocumento6 pagineNMR Spectroscopy Integrals and MultiplicitysupriyoNessuna valutazione finora
- QM16 SHOQuestionsDocumento10 pagineQM16 SHOQuestionsGaurav YadavNessuna valutazione finora
- Ic Engines Quiz - 1Documento1 paginaIc Engines Quiz - 1ratchagarajaNessuna valutazione finora
- Physics Mechanics Help BookletDocumento88 paginePhysics Mechanics Help Bookletdj7597100% (1)
- CFD With Opensource Software: Non-Newtonian Models in Openfoam Implementation of A Non-Newtonian ModelDocumento19 pagineCFD With Opensource Software: Non-Newtonian Models in Openfoam Implementation of A Non-Newtonian ModelDino DinoNessuna valutazione finora
- Oppenheimer TranscriptDocumento54 pagineOppenheimer TranscriptRatkoMRNessuna valutazione finora
- Cam Clay and Modified Cam Clay Material Models ExplainedDocumento11 pagineCam Clay and Modified Cam Clay Material Models ExplainedJonathan TeixeiraNessuna valutazione finora
- Rectilinear and rotational kinematics problemsDocumento5 pagineRectilinear and rotational kinematics problemsAljay Dungao40% (5)
- Theory of PlasticityDocumento110 pagineTheory of Plasticitytayyeb803Nessuna valutazione finora
- 3.A - The First Law of Thermodynamics (Answer) - Physics LibreTextsDocumento5 pagine3.A - The First Law of Thermodynamics (Answer) - Physics LibreTextsFASIKAW GASHAWNessuna valutazione finora
- Pump Calc ExampleDocumento21 paginePump Calc ExampleMohammad Usman HabibNessuna valutazione finora
- Ce 6306 Som Part A AnswersDocumento21 pagineCe 6306 Som Part A Answersommech2020Nessuna valutazione finora