Documenti di Didattica
Documenti di Professioni
Documenti di Cultura
Cellular Structures
Caricato da
Cheryl Bautista De GuzmanTitolo originale
Copyright
Formati disponibili
Condividi questo documento
Condividi o incorpora il documento
Hai trovato utile questo documento?
Questo contenuto è inappropriato?
Segnala questo documentoCopyright:
Formati disponibili
Cellular Structures
Caricato da
Cheryl Bautista De GuzmanCopyright:
Formati disponibili
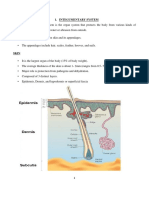
CELLULAR STRUCTURES
THREE DIFFERENT ELEMENTS IN THE
BODY
o CELLS
o INTERCELLULAR SUBSTANCES
o BODY FLUIDS
CELL
Smallest functional and structural units of
the body
Basic unit of life
TWO BASIC CELL TYPES:
EUKARYOTIC CELL
PROKARYOTIC CELL
o EUKARYOTIC CELL
Cell which has a true nucleus
o
o
o
o
o
o
o
nucleus
Lacking of nuclear envelope
Nuclear substance is mixed or in
direct contact with the rest of
the cytoplasm
PHYSIOLOGIC PROPERTIES OF
PROTOPLASM
IRRITABILITY
CONTRACTILITY
CONDUCTIVITY
ABSORPTION AND SECRETION
EXCRETION
RESPIRATION
GROWTH AND REPRODUCTION
PRINCIPAL PARTS OF THE CELL
o CELL MEMBRANE
o CYTOPLASM
o NUCLEUS
1. CELL MEMBRANE
Trilaminar Layer
Membrane Lipids, Mostly Phospholipids
have a hydrophilic phosphate which is polar
in nature and a hydrophobic which ia a nonpolar end
FUNCTIONS:
o Gives shape to the cell
o Delimits or separate the cell from
the Environment
in and out of the cell
Serves as the recognition site acting as
antigenic determinants
Serves as the selective barriers providing for
a selection of what enters and leaves the cell.
o Selective Permeability
MODIFICATION OR SPECIALIZATION OF
and surrounded by a nuclear
membrane or nuclear envelope
PROKARYOTIC CELL
Cell which has no presence of
Regulates the passage of materials
THE CELL MEMBRANE
JUNCTIONAL COMPLEX
INVAGINATIONS
MICROVILLI
CILIA
JUNCTIONAL COMPLEXES
Structures that provide for
cell
attachments
TYPES:
DESMOSOMES
INTERMEDIATE JUNCTION
NEXUS / GAP JUNCTION
TIGHT JUNCTION
DESMOSOMES
Macula Adherens
Points of firm intercullar adhesions
Abundant in stratified epithelia of the
Mouth, Esophagus, Skin and Vagina
SIGNIFICANCE:
Site of Attachment of the
Cytoskeleton to the cell surface
Sites of cell to cell adhesions
INTERMEDIATE JUNCTION
Zonula Adherens
Fascia Adherens
The intercellular space is filled with
electron dense amorphous materials.
It is quiete extensive in the intercalated
discs of cardiac muscle.
GAP JUNCTION
Concerned with the
communication
Usually seen in epithelial, muscular and
nervous tissue
ZONULA OCCLUDENS
Important in the formation of a barrier
prevents the free passage of the
substances across the epithelium
Commonly found in the git and inter-
cell
to
cell
endothelial contacts of brain tissue as
well as capillary.
TYPES OF ORGANELLES
Membrane Bound Organelles- Mitochondria,
INVAGINATIONS
VESICULAR PITS
INFOLDINGS
VESICULAR PITS
Occur as a phagocytic and pinocytic
vesicles.
INFOLDINGS
Greatly increase the cell surface because
Centrioles, microtubules and microfilaments.
I.
of their inward projections
MICROVILLI
Non-motile cellular extensions which
serves to increase the absorptive surface
of cells
Facilitate movements and passage of
substances in between other cells and
interstitial components
FORMS OF MICROVILLI:
STRIATED BORDERS FD. in the
absorptive cells of the intestinal
epithelium
BRUSH BORDERS FD. in the cells of
the proximal convoluted tubules of the
kidney
STEREOCILIA FD. in the cells of some
testicular ducts as in the ductus
epididymis and ductus deferens.
CILIA
Motile projections and characterized by a
rapid forward stroke and slow backward
stroke
Found in the cells lining the upper
respiratory tract
2.
CYTOPLASM
Protoplasm outside the nucleus which contains
organelles and inclusions.
Contains the biochemical components of the
cytoplasm
Contains CHONS, Lipids and CHO
A. ORGANELLESLiving
substances
performing define or specific functions.
B. INCLUSIONSInert
or
non-living
substances that do not perform definite
function
EXAMPLES: Vacuoles, Crystals, Droplets,
Lipids, Glycogen, Secretory granules
ER, Golgi complex, lysosomes and micro-bodies
Non-membrane Bound Organelles- Ribosomes,
MITOCHONDRIA
Powerhouse of the cell
Concerned primarily with the production of
energy and are abundant with high metabolic
rates
Synthesize ATP- Energy source of the cell
Accumulation of calcium
Synthesize of nucleic acids and CHONS
Oxidation of fatty acids
ENDOPLASMIC RETICULUM
CHON synthesis
Complex network of paired
II.
membranes,
saccules, vacuoles and tubules with flattened
cisternae
TYPES:
o ROUGH ER- Granular endoplasmic
reticulum because it contains attached
ribosomes and concerned with CHON
synthesis
SMOOTH ER- Non-granular ER and
doesnt contain ribosome
SEVERAL FUNCTIONS OF ROUGH ER
o In striated muscles, it is concerned with
the release and recapture of calcium ions
during contraction and relaxation of
muscles.
Synthesis of steroid hormones in some
endocrine glands
Detoxification of
especially in the liver
Lipids and cholesterol metabolism in the
liver
Formation of HCL in the parietal cells of
toxic
substances
stomach
GOLGI COMPLEX
o Dictyosomes
o Packaging area of the cell
o Accumulate
and
concentrate
o
secretory products of the cell
Site of sulfation
the
CONSISTS OF GOLGI APPARATUS
o SACCULES
o VESICLES
o VACUOLES
LYSOSOMES
o Suicide bag of the cell
o Contain hydrolyctic enzymes called as
acid hydrolases which is responsible for
the intracellular digestion
TYPES:
PRIMARY LYSOSOMES
Not engaged in enzymatic activities
SECONDARY LYSOSOMES
Involved in enzymatic activities
FUNCTIONS OF LYSOSOME:
1. Defense mechanism- being the site of
destruction of foreign bodies
2. Participate in the normal replacement
of cell components and organelles
3. Its
deficiency
can
cause
Metachromatic Leukodystrophy
CENTRIOLES
o Center of activity associated with cell
o
o
division
Self-duplicating
organelles
and
are
prominent in mitotic cell division
FUNCTIONS OF CENTRIOLES:
1. Serves as basal bodies and sites of
epithelial cilia
2.
Determine the polarity of the cells
PEROXISOMES
o Microbodies
o Producing hydrogen peroxide abundant in the
liver, kidneys, bronchioles and odonthoblast
FILAMENTS
o MICROFILAMENTS- Contractile filaments
-Actin and myosin filament in skeletal
muscles
o INTERMEDIATE FILAMENTS- Cytoskeleton
in epithelial tissue
- Known as TONOFILAMENT
- In nervous tissue, Neurofilaments are
seen in axons and dendrites
MICROTUBULES
FUNCTIONS:
o
Functional elements of the spindle apparatus in
dividing cells
Form the mitotic spindles along which the
chromosomes move
Play an important role in maintaining different
cell shape
Potrebbero piacerti anche
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeDa EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeValutazione: 4 su 5 stelle4/5 (5783)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Da EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Valutazione: 4 su 5 stelle4/5 (98)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItDa EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItValutazione: 4.5 su 5 stelle4.5/5 (838)
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeDa EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeValutazione: 4.5 su 5 stelle4.5/5 (537)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerDa EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerValutazione: 4.5 su 5 stelle4.5/5 (271)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceDa EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceValutazione: 4 su 5 stelle4/5 (890)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingDa EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingValutazione: 3.5 su 5 stelle3.5/5 (399)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnDa EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnValutazione: 4.5 su 5 stelle4.5/5 (234)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceDa EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceValutazione: 4 su 5 stelle4/5 (587)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaDa EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaValutazione: 4.5 su 5 stelle4.5/5 (265)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryDa EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryValutazione: 3.5 su 5 stelle3.5/5 (231)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealDa EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealValutazione: 4 su 5 stelle4/5 (72)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureDa EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureValutazione: 4.5 su 5 stelle4.5/5 (474)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersDa EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersValutazione: 4.5 su 5 stelle4.5/5 (344)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaDa EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaValutazione: 4 su 5 stelle4/5 (45)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyDa EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyValutazione: 3.5 su 5 stelle3.5/5 (2219)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreDa EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreValutazione: 4 su 5 stelle4/5 (1090)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Da EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Valutazione: 4.5 su 5 stelle4.5/5 (119)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesDa EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesValutazione: 4 su 5 stelle4/5 (821)
- Structure of BacteriaDocumento13 pagineStructure of BacteriaRirin UtariNessuna valutazione finora
- Newborn Hypothermia and Hyperthermia (Final Copy)Documento30 pagineNewborn Hypothermia and Hyperthermia (Final Copy)Shizuka Marycris Amane67% (3)
- Understanding 1st, 2nd and 3rd Degree Heart BlocksDocumento3 pagineUnderstanding 1st, 2nd and 3rd Degree Heart BlockslhenNessuna valutazione finora
- Neurology Crossword Puzzle Answer KeyDocumento1 paginaNeurology Crossword Puzzle Answer KeyRavinaAhujaNessuna valutazione finora
- Cerebral EdemaDocumento5 pagineCerebral EdemaAdilah AdeebNessuna valutazione finora
- Assessment of HearingDocumento51 pagineAssessment of HearingSwetha PasupuletiNessuna valutazione finora
- Benign Diseases of ThyroidDocumento70 pagineBenign Diseases of ThyroidMounica MekalaNessuna valutazione finora
- Acute and Chronic PyelonephritisDocumento7 pagineAcute and Chronic PyelonephritisMatthew Ryan100% (1)
- 英文TG900series 8885 lowDocumento4 pagine英文TG900series 8885 lowJose L GuzCamNessuna valutazione finora
- The Integumentary System: Layers and Functions of SkinDocumento8 pagineThe Integumentary System: Layers and Functions of SkinAmanuel MaruNessuna valutazione finora
- Pedia2 Sepsis (Dr. Seng)Documento3 paginePedia2 Sepsis (Dr. Seng)Tony DawaNessuna valutazione finora
- Genetika PopulasiDocumento48 pagineGenetika PopulasiRoy SinagaNessuna valutazione finora
- Digestive ExamDocumento13 pagineDigestive Examapi-294622133Nessuna valutazione finora
- How Ketone Bodies Fuel Brain and HeartDocumento3 pagineHow Ketone Bodies Fuel Brain and Heartdaef32Nessuna valutazione finora
- Peripheral Testosterone MetabolismDocumento8 paginePeripheral Testosterone MetabolismAgung SentosaNessuna valutazione finora
- Nptel: Biomechanics - Web CourseDocumento2 pagineNptel: Biomechanics - Web CourseErin BarryNessuna valutazione finora
- Test Bank TNCC Full Solution Pack All TNCC Exams and Study Questions Are Here All Answered CorrecDocumento109 pagineTest Bank TNCC Full Solution Pack All TNCC Exams and Study Questions Are Here All Answered Correcmary011danielNessuna valutazione finora
- Bio 320 Practical 7Documento12 pagineBio 320 Practical 7MuhammadAsyraf50% (2)
- Lesson Plan On RhinitisDocumento15 pagineLesson Plan On Rhinitiskiran mahal100% (4)
- RECONSTRUCTION MAndibula 2Documento62 pagineRECONSTRUCTION MAndibula 2RadianNasution100% (1)
- The Circulatory SystemDocumento8 pagineThe Circulatory Systemrosario marcelaNessuna valutazione finora
- Guillain Barre SyndromeDocumento2 pagineGuillain Barre SyndromeTheresia Avila KurniaNessuna valutazione finora
- NPTEL Stress Management MCQ AssignmentDocumento5 pagineNPTEL Stress Management MCQ AssignmentSnehaNessuna valutazione finora
- Pedia Pulmo 2 10.18.16Documento73 paginePedia Pulmo 2 10.18.16Medisina101Nessuna valutazione finora
- India Ink Staining of Proteins On Nitrocellulose PaperDocumento6 pagineIndia Ink Staining of Proteins On Nitrocellulose PaperMaggieNessuna valutazione finora
- Amphibian Graphs?Documento9 pagineAmphibian Graphs?Anshumaan PatraNessuna valutazione finora
- Maxillomandibular Advancement As The Initial Treatment of Obstructive Sleep Apnoea: Is The Mandibular Occlusal Plane The Key?Documento9 pagineMaxillomandibular Advancement As The Initial Treatment of Obstructive Sleep Apnoea: Is The Mandibular Occlusal Plane The Key?Jorge Antonio Espinoza YañezNessuna valutazione finora
- Brewing Technology (2017)Documento190 pagineBrewing Technology (2017)Јован АдамовNessuna valutazione finora
- BioPsych - Reviewer (MIdterm Exam) - Chapter 1Documento6 pagineBioPsych - Reviewer (MIdterm Exam) - Chapter 1Francis Xavier AlcazarNessuna valutazione finora
- Liver Cirrhosis NCP 1Documento6 pagineLiver Cirrhosis NCP 1Paolo Rafael D EsguerraNessuna valutazione finora